
WildBench
Benchmarking LLMs with Challenging Tasks from Real Users
Stars: 144
WildBench is a tool designed for benchmarking Large Language Models (LLMs) with challenging tasks sourced from real users in the wild. It provides a platform for evaluating the performance of various models on a range of tasks. Users can easily add new models to the benchmark by following the provided guidelines. The tool supports models from Hugging Face and other APIs, allowing for comprehensive evaluation and comparison. WildBench facilitates running inference and evaluation scripts, enabling users to contribute to the benchmark and collaborate on improving model performance.
README:
📑 Paper | 🤗 Leaderboard & 🤗 Dataset
HF_MODEL_ID="Magpie-Align/Llama-3-8B-Magpie-Align-v0.1" # example model id
MODEL_PRETTY_NAME="Llama-3-8B-Magpie-Align-v0.1" # example model name
NUM_GPUS=4 # depending on your hardwares;
# do inference on WildBench
bash scripts/_common_vllm.sh $HF_MODEL_ID $MODEL_PRETTY_NAME $NUM_GPUS
# submit to OpenAI for eval (WB-Score)
bash evaluation/run_score_eval_batch.sh ${MODEL_PRETTY_NAME}
# check the batch job status
python src/openai_batch_eval/check_batch_status_with_model_name.py ${MODEL_PRETTY_NAME}
# show the table
bash leaderboard/show_eval.sh score_only [!NOTE] If your model is on HuggingFace and/or it is supported by vLLM, please add the chat template to the tokenizer config and follow the Shortcut below. If your model is not supported by vLLM, you can still create an Issue and let us know how to run your model.
Click to expand
conda create -n zeroeval python=3.10
conda activate zeroeval
# pip install vllm -U # pip install -e vllm
pip install vllm==0.5.1
pip install -r requirements.txtbash scripts/_common_vllm.sh [hf_model_id] [model_pretty_name] [num_gpus]
# bash scripts/_common_vllm.sh m-a-p/neo_7b_instruct_v0.1 neo_7b_instruct_v0.1 4 # example
# 1st arg is hf_name; 2nd is the pretty name; 3rd is the number of shards (gpus)Case 1: Models supported by vLLM
You can take the files under scripts as a reference to add a new model to the benchmark, for example, to add Yi-1.5-9B-Chat.sh to the benchmark, you can follow the following steps:
- Create a script named "Yi-1.5-9B-Chat.sh.py" under
scriptsfolder. - Copy and paste the most similar existing script file to it, rename the file to the
[model_pretty_name].sh. - Change the
model_nameandmodel_pretty_nameto01-ai/Yi-1.5-9B-ChatandYi-1.5-9B-Chat.shrespectively. Make sure thatmodel_nameis the same as the model name in the Hugging Face model hub, and themodel_pretty_nameis the same as the script name without the.pyextension. - Specify the conversation template for this model by modifying the code in
src/fastchat_conversation.pyor setting the--use_hf_conv_templateargument if your hugingface model contains a conversation template in tokenizer config. - Run your script to make sure it works. You can run the script by running
bash scripts/Yi-1.5-9B-Chat.shin the root folder. - Create a PR to add your script to the benchmark.
For Step 3-5, you can also use the above shortcut common command to run the model if your model is supported by vLLM and has a conversation template on hf's tokenizer config.
Case 2: Models that are only supported by native HuggingFace API
Some new models may not be supported by vLLM for now. You can do the same thing as above but use --engine hf in the script instead, and test your script. Note that some models may need more specific configurations, and you will need to read the code and modify them accordingly. In these cases, you should add name-checking conditions to ensure that the model-specific changes are only applied to the specific model.
Case 3: Private API-based Models
You should change the code to add these APIs, for example, gemini, cohere, claude, and reka. You can refer to the --engine openai logic in the existing scripts to add your own API-based models. Please make sure that you do not expose your API keys in the code. If your model is on Together.AI platform, you can use the --engine together option to run your model, see scripts/[email protected] for an example.
[!NOTE] If you'd like to have your model results verified and published on our leaderboard, please create an issue telling us and we'll do the inference and evaluation for you.
bash evaluation/run_score_eval_batch.sh ${MODEL_PRETTY_NAME}
bash leaderboard/show_eval.sh score_only
How do you evaluate the performance of LLMs on WildBench? (V2 Updates)
- Reward=100 if the A is much better than B.
- Reward=50 if the A is slightly better than B.
- Reward=0 if there is a Tie.
- Reward=-50 if the A is slightly worse than B.
- Reward=-100 if the A is much worse than B.
We suggest to use OpenAI's Batch Mode for evaluation, which is faster, cheaper and more reliable.
You can:
-
- Run
bash evaluation/run_all_eval_batch.sh ${MODEL_PRETTY_NAME}to submit the eval jobs.; Or if you only want to do scoring, runningbash evaluation/run_score_eval_batch.shto submit the eval jobs for only doing the WB Score. (about $5 per model)
- Run
-
- Run
python src/openai_batch_eval/check_batch_status_with_model_name.py ${MODEL_PRETTY_NAME}to track the status of the batch jobs.
- Run
-
- Step 2 will download the results when batch jobs are finished, and then you can view the results (see next section).
Remarks
-
${MODEL_PRETTY_NAME}should be the same as the script name without the.shextension. - You can also track the progress of your batch jobs here: https://platform.openai.com/batches. The maximum turnaround time is 24 hours, but it is usually much faster depending on the queue and rate limits.
- If you'd like to have more control on the evaluation methods, the detail steps are illustrated in EVAL.md.
When Step 3 in the above section is finished, you can view the results by running the following commands:
bash leaderboard/show_eval.sh # run all and show the main leaderboard
python leaderboard/show_table.py --mode main # (optional) to show the main leaderboard w/o recomputing
python leaderboard/show_table.py --mode taskwise_score # (optional) to show the taskwise scoreTo analyze the correlation between WildBench (v2) and human evaluation, we consider the correlation between different metrics and human-based Chatbot Arena Elo scores (until 2024-05-20 on Hard-English split). We find that the WB Reward-Mix has the highest correlation. Please find the pearson correlation coefficients below:

- Top Models:
['gpt-4-turbo-2024-04-09', 'claude-3-opus-20240229', 'Meta-Llama-3-70B-Instruct', 'claude-3-sonnet-20240229', 'mistral-large-2402', 'Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct'] - All Models:
['gpt-4-turbo-2024-04-09', 'claude-3-opus-20240229', 'Meta-Llama-3-70B-Instruct', 'Qwen1.5-72B-Chat', 'claude-3-sonnet-20240229', 'mistral-large-2402', 'dbrx-instruct@together', 'Mixtral-8x7B-Instruct-v0.1', 'Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct', 'tulu-2-dpo-70b', 'Llama-2-70b-chat-hf', 'Llama-2-7b-chat-hf', 'gemma-7b-it', 'gemma-2b-it']
- [ ] openchat/openchat-3.6-8b-20240522
- [ ] gemma-2
- [ ] SimPO-v0.2
- [ ] Qwen2-7B-Chat
- [x] LLM360/K2-Chat
- [x] DeepSeek-V2-Code
- [x] Yi-large-preview
- [x] THUDM/glm-4-9b-chat
- [x] chujiezheng/neo_7b_instruct_v0.1-ExPO
- [x] ZhangShenao/SELM-Llama-3-8B-Instruct-iter-3
- [x] m-a-p/neo_7b_instruct_v0.1
- [x] Reka Flash
- [x] DeepSeekV2-Chat
- [x] Reka Core
- [x] Yi-Large (via OpenAI-like APIs)
- [x] chujiezheng/Llama-3-Instruct-8B-SimPO-ExPO
- [x] chujiezheng/Starling-LM-7B-beta-ExPO
- [x] Gemini 1.5 series
- [x] Qwen2-72B-Instruct
- [x] ZhangShenao/SELM-Zephyr-7B-iter-3
- [x] NousResearch/Hermes-2-Theta-Llama-3-8B
- [x] princeton-nlp/Llama-3-Instruct-8B-SimPO
- [x] Command-R-plus
- [x] Phi-3 series
Create an Issue if you'd like to add a model that you wanna see on our leaderboard!
- [ ] support models via openai-style apis
- [ ] Show task categorized results
@misc{lin2024wildbench,
title={WildBench: Benchmarking LLMs with Challenging Tasks from Real Users in the Wild},
author={Bill Yuchen Lin and Yuntian Deng and Khyathi Chandu and Faeze Brahman and Abhilasha Ravichander and Valentina Pyatkin and Nouha Dziri and Ronan Le Bras and Yejin Choi},
year={2024},
eprint={2406.04770},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2406.04770}
}For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for WildBench
Similar Open Source Tools

WildBench
WildBench is a tool designed for benchmarking Large Language Models (LLMs) with challenging tasks sourced from real users in the wild. It provides a platform for evaluating the performance of various models on a range of tasks. Users can easily add new models to the benchmark by following the provided guidelines. The tool supports models from Hugging Face and other APIs, allowing for comprehensive evaluation and comparison. WildBench facilitates running inference and evaluation scripts, enabling users to contribute to the benchmark and collaborate on improving model performance.
bigcodebench
BigCodeBench is an easy-to-use benchmark for code generation with practical and challenging programming tasks. It aims to evaluate the true programming capabilities of large language models (LLMs) in a more realistic setting. The benchmark is designed for HumanEval-like function-level code generation tasks, but with much more complex instructions and diverse function calls. BigCodeBench focuses on the evaluation of LLM4Code with diverse function calls and complex instructions, providing precise evaluation & ranking and pre-generated samples to accelerate code intelligence research. It inherits the design of the EvalPlus framework but differs in terms of execution environment and test evaluation.
OpenMusic
OpenMusic is a repository providing an implementation of QA-MDT, a Quality-Aware Masked Diffusion Transformer for music generation. The code integrates state-of-the-art models and offers training strategies for music generation. The repository includes implementations of AudioLDM, PixArt-alpha, MDT, AudioMAE, and Open-Sora. Users can train or fine-tune the model using different strategies and datasets. The model is well-pretrained and can be used for music generation tasks. The repository also includes instructions for preparing datasets, training the model, and performing inference. Contact information is provided for any questions or suggestions regarding the project.
LLM-Pruner
LLM-Pruner is a tool for structural pruning of large language models, allowing task-agnostic compression while retaining multi-task solving ability. It supports automatic structural pruning of various LLMs with minimal human effort. The tool is efficient, requiring only 3 minutes for pruning and 3 hours for post-training. Supported LLMs include Llama-3.1, Llama-3, Llama-2, LLaMA, BLOOM, Vicuna, and Baichuan. Updates include support for new LLMs like GQA and BLOOM, as well as fine-tuning results achieving high accuracy. The tool provides step-by-step instructions for pruning, post-training, and evaluation, along with a Gradio interface for text generation. Limitations include issues with generating repetitive or nonsensical tokens in compressed models and manual operations for certain models.
qa-mdt
This repository provides an implementation of QA-MDT, integrating state-of-the-art models for music generation. It offers a Quality-Aware Masked Diffusion Transformer for enhanced music generation. The code is based on various repositories like AudioLDM, PixArt-alpha, MDT, AudioMAE, and Open-Sora. The implementation allows for training and fine-tuning the model with different strategies and datasets. The repository also includes instructions for preparing datasets in LMDB format and provides a script for creating a toy LMDB dataset. The model can be used for music generation tasks, with a focus on quality injection to enhance the musicality of generated music.
TokenFormer
TokenFormer is a fully attention-based neural network architecture that leverages tokenized model parameters to enhance architectural flexibility. It aims to maximize the flexibility of neural networks by unifying token-token and token-parameter interactions through the attention mechanism. The architecture allows for incremental model scaling and has shown promising results in language modeling and visual modeling tasks. The codebase is clean, concise, easily readable, state-of-the-art, and relies on minimal dependencies.
ALMA
ALMA (Advanced Language Model-based Translator) is a many-to-many LLM-based translation model that utilizes a two-step fine-tuning process on monolingual and parallel data to achieve strong translation performance. ALMA-R builds upon ALMA models with LoRA fine-tuning and Contrastive Preference Optimization (CPO) for even better performance, surpassing GPT-4 and WMT winners. The repository provides ALMA and ALMA-R models, datasets, environment setup, evaluation scripts, training guides, and data information for users to leverage these models for translation tasks.
FlashRank
FlashRank is an ultra-lite and super-fast Python library designed to add re-ranking capabilities to existing search and retrieval pipelines. It is based on state-of-the-art Language Models (LLMs) and cross-encoders, offering support for pairwise/pointwise rerankers and listwise LLM-based rerankers. The library boasts the tiniest reranking model in the world (~4MB) and runs on CPU without the need for Torch or Transformers. FlashRank is cost-conscious, with a focus on low cost per invocation and smaller package size for efficient serverless deployments. It supports various models like ms-marco-TinyBERT, ms-marco-MiniLM, rank-T5-flan, ms-marco-MultiBERT, and more, with plans for future model additions. The tool is ideal for enhancing search precision and speed in scenarios where lightweight models with competitive performance are preferred.
VideoTuna
VideoTuna is a codebase for text-to-video applications that integrates multiple AI video generation models for text-to-video, image-to-video, and text-to-image generation. It provides comprehensive pipelines in video generation, including pre-training, continuous training, post-training, and fine-tuning. The models in VideoTuna include U-Net and DiT architectures for visual generation tasks, with upcoming releases of a new 3D video VAE and a controllable facial video generation model.
llm-colosseum
llm-colosseum is a tool designed to evaluate Language Model Models (LLMs) in real-time by making them fight each other in Street Fighter III. The tool assesses LLMs based on speed, strategic thinking, adaptability, out-of-the-box thinking, and resilience. It provides a benchmark for LLMs to understand their environment and take context-based actions. Users can analyze the performance of different LLMs through ELO rankings and win rate matrices. The tool allows users to run experiments, test different LLM models, and customize prompts for LLM interactions. It offers installation instructions, test mode options, logging configurations, and the ability to run the tool with local models. Users can also contribute their own LLM models for evaluation and ranking.
Easy-Translate
Easy-Translate is a script designed for translating large text files with a single command. It supports various models like M2M100, NLLB200, SeamlessM4T, LLaMA, and Bloom. The tool is beginner-friendly and offers seamless and customizable features for advanced users. It allows acceleration on CPU, multi-CPU, GPU, multi-GPU, and TPU, with support for different precisions and decoding strategies. Easy-Translate also provides an evaluation script for translations. Built on HuggingFace's Transformers and Accelerate library, it supports prompt usage and loading huge models efficiently.
evalverse
Evalverse is an open-source project designed to support Large Language Model (LLM) evaluation needs. It provides a standardized and user-friendly solution for processing and managing LLM evaluations, catering to AI research engineers and scientists. Evalverse supports various evaluation methods, insightful reports, and no-code evaluation processes. Users can access unified evaluation with submodules, request evaluations without code via Slack bot, and obtain comprehensive reports with scores, rankings, and visuals. The tool allows for easy comparison of scores across different models and swift addition of new evaluation tools.
LLMsKnow
LLMs Know More Than They Show is a repository containing code to reproduce the results in the paper. It includes scripts to generate model answers, extract exact answers, probe all layers and tokens, probe specific layers and tokens, conduct generalization experiments, perform resampling for error type probing and answer selection experiments, and run other baselines like logprob detection and p_true detection. The repository supports various datasets such as TriviaQA, Movies, HotpotQA, Winobias, Winogrande, NLI, IMDB, Math, and Natural questions. It also provides supported models like Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2, Mistral-7B-v0.3, Meta-Llama-3-8B, and Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct.
giskard
Giskard is an open-source Python library that automatically detects performance, bias & security issues in AI applications. The library covers LLM-based applications such as RAG agents, all the way to traditional ML models for tabular data.
SWE-bench-Live
SWE-bench-Live is a live benchmark dataset for evaluating AI systems' ability to complete real-world software engineering tasks. It is continuously updated through an automated curation pipeline, providing the community with up-to-date task instances for rigorous and contamination-free evaluation. The dataset is designed to test the performance of various AI models on software engineering tasks and supports multiple programming languages and operating systems.
EasyInstruct
EasyInstruct is a Python package proposed as an easy-to-use instruction processing framework for Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-4, LLaMA, ChatGLM in your research experiments. EasyInstruct modularizes instruction generation, selection, and prompting, while also considering their combination and interaction.
For similar tasks

WildBench
WildBench is a tool designed for benchmarking Large Language Models (LLMs) with challenging tasks sourced from real users in the wild. It provides a platform for evaluating the performance of various models on a range of tasks. Users can easily add new models to the benchmark by following the provided guidelines. The tool supports models from Hugging Face and other APIs, allowing for comprehensive evaluation and comparison. WildBench facilitates running inference and evaluation scripts, enabling users to contribute to the benchmark and collaborate on improving model performance.
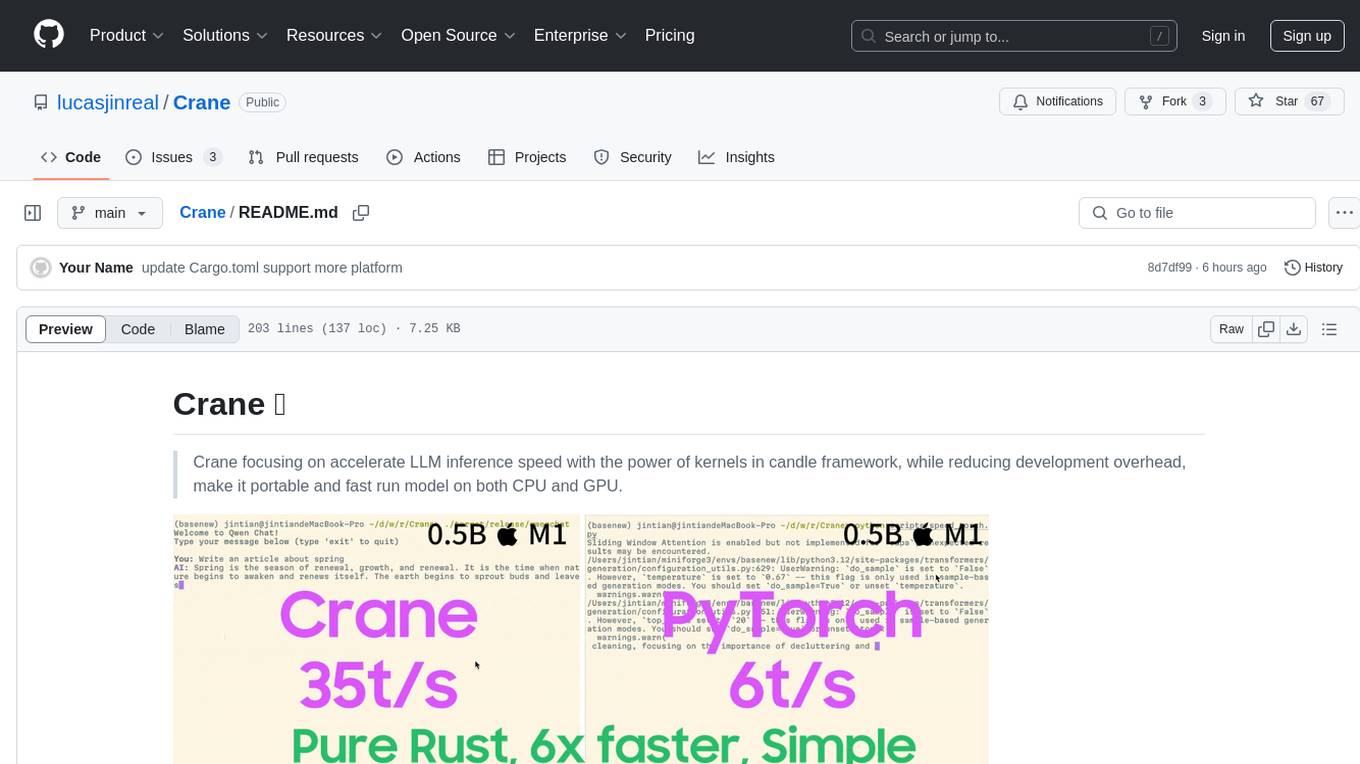
Crane
Crane is a high-performance inference framework leveraging Rust's Candle for maximum speed on CPU/GPU. It focuses on accelerating LLM inference speed with optimized kernels, reducing development overhead, and ensuring portability for running models on both CPU and GPU. Supported models include TTS systems like Spark-TTS and Orpheus-TTS, foundation models like Qwen2.5 series and basic LLMs, and multimodal models like Namo-R1 and Qwen2.5-VL. Key advantages of Crane include blazing-fast inference outperforming native PyTorch, Rust-powered to eliminate C++ complexity, Apple Silicon optimized for GPU acceleration via Metal, and hardware agnostic with a unified codebase for CPU/CUDA/Metal execution. Crane simplifies deployment with the ability to add new models with less than 100 lines of code in most cases.
anythingllm-docs
anythingllm-docs is a documentation repository for the AnythingLLM project. It contains detailed guides, setup instructions, and information on features and legal aspects of the project. The repository structure is organized into public, pages, components, and configuration files. Users can contribute by creating issues and pull requests following specific guidelines. The project is licensed under the MIT License and has been migrated to NextJS with the help of @ShadowArcanist.

labelbox-python
Labelbox is a data-centric AI platform for enterprises to develop, optimize, and use AI to solve problems and power new products and services. Enterprises use Labelbox to curate data, generate high-quality human feedback data for computer vision and LLMs, evaluate model performance, and automate tasks by combining AI and human-centric workflows. The academic & research community uses Labelbox for cutting-edge AI research.
promptfoo
Promptfoo is a tool for testing and evaluating LLM output quality. With promptfoo, you can build reliable prompts, models, and RAGs with benchmarks specific to your use-case, speed up evaluations with caching, concurrency, and live reloading, score outputs automatically by defining metrics, use as a CLI, library, or in CI/CD, and use OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure, Google, HuggingFace, open-source models like Llama, or integrate custom API providers for any LLM API.
vespa
Vespa is a platform that performs operations such as selecting a subset of data in a large corpus, evaluating machine-learned models over the selected data, organizing and aggregating it, and returning it, typically in less than 100 milliseconds, all while the data corpus is continuously changing. It has been in development for many years and is used on a number of large internet services and apps which serve hundreds of thousands of queries from Vespa per second.
python-aiplatform
The Vertex AI SDK for Python is a library that provides a convenient way to use the Vertex AI API. It offers a high-level interface for creating and managing Vertex AI resources, such as datasets, models, and endpoints. The SDK also provides support for training and deploying custom models, as well as using AutoML models. With the Vertex AI SDK for Python, you can quickly and easily build and deploy machine learning models on Vertex AI.
ScandEval
ScandEval is a framework for evaluating pretrained language models on mono- or multilingual language tasks. It provides a unified interface for benchmarking models on a variety of tasks, including sentiment analysis, question answering, and machine translation. ScandEval is designed to be easy to use and extensible, making it a valuable tool for researchers and practitioners alike.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.



