
ChatAFL
Large Language Model guided Protocol Fuzzing (NDSS'24)
Stars: 257
ChatAFL is a protocol fuzzer guided by large language models (LLMs) that extracts machine-readable grammar for protocol mutation, increases message diversity, and breaks coverage plateaus. It integrates with ProfuzzBench for stateful fuzzing of network protocols, providing smooth integration. The artifact includes modified versions of AFLNet and ProfuzzBench, source code for ChatAFL with proposed strategies, and scripts for setup, execution, analysis, and cleanup. Users can analyze data, construct plots, examine LLM-generated grammars, enriched seeds, and state-stall responses, and reproduce results with downsized experiments. Customization options include modifying fuzzers, tuning parameters, adding new subjects, troubleshooting, and working on GPT-4. Limitations include interaction with OpenAI's Large Language Models and a hard limit of 150,000 tokens per minute.
README:
ChatAFL is a protocol fuzzer guided by large language models (LLMs). It is built on top of AFLNet but integrates with three concrete components. Firstly, the fuzzer uses the LLM to extract a machine-readable grammar for a protocol that is used for structure-aware mutation. Secondly, the fuzzer uses the LLM to increase the diversity of messages in the recorded message sequences that are used as initial seeds. Lastly, the fuzzer uses the LLM to break out of a coverage plateau, where the LLM is prompted to generate messages to reach new states.
The ChatAFL artifact is configured within ProfuzzBench, a widely-used benchmark for stateful fuzzing of network protocols. This allows for smooth integration with an already established format.
ChatAFL-Artifact
├── aflnet: a modified version of AFLNet which outputs states and state transitions
├── analyse.sh: analysis script
├── benchmark: a modified version of ProfuzzBench, containing only text-based protocols with the addition of Lighttpd 1.4
├── clean.sh: clean script
├── ChatAFL: the source code of ChatAFL, with all strategies proposed in the paper
├── ChatAFL-CL1: ChatAFL, which only uses the structure-aware mutations (c.f. Ablation study)
├── ChatAFL-CL2: ChatAFL, which only uses the structure-aware and initial seed enrichment (c.f. Ablation study)
├── deps.sh: the script to install dependencies, asks for the password when executed
├── README: this file
├── run.sh: the execution script to run fuzzers on subjects and collect data
└── setup.sh: the preparation script to set up docker images
ChatAFL has been accepted for publication at the 31st Annual Network and Distributed System Security Symposium (NDSS) 2024. The paper is also available here. If you use this code in your scientific work, please cite the paper as follows:
@inproceedings{chatafl,
author={Ruijie Meng and Martin Mirchev and Marcel B\"{o}hme and Abhik Roychoudhury},
title={Large Language Model guided Protocol Fuzzing},
booktitle={Proceedings of the 31st Annual Network and Distributed System Security Symposium (NDSS)},
year={2024},}
Docker, Bash, Python3 with pandas and matplotlib libraries. We provide a helper script deps.sh which runs the required steps to ensure that all dependencies are provided:
./deps.shRun the following command to set up all docker images, including the subjects with all fuzzers:
KEY=<OPENAI_API_KEY> ./setup.shThe process is estimated to take about 40 minutes. OPENAI_API_KEY is your OpenAI key and please refer to this about how to obtain a key.
Utilize the run.sh script to run experiments. The command is as follows:
./run.sh <container_number> <fuzzed_time> <subjects> <fuzzers>Where container_number specifies how many containers are created to run a single fuzzer on a particular subject (each container runs one fuzzer on one subject). fuzzed_time indicates the fuzzing time in minutes. subjects is the list of subjects under test, and fuzzers is the list of fuzzers that are utilized to fuzz subjects. For example, the command (run.sh 1 5 pure-ftpd chatafl) would create 1 container for the fuzzer ChatAFL to fuzz the subject pure-ftpd for 5 minutes. In a short cut, one can execute all fuzzers and all subjects by using the writing all in place of the subject and fuzzer list.
When the script completes, in the benchmark directory a folder result-<name of subject> will be created, containing fuzzing results for each run.
The analyze.sh script is used to analyze data and construct plots illustrating the average code and state coverage over time for fuzzers on each subject. The script is executed using the following command:
./analyze.sh <subjects> <fuzzed_time> The script takes in 2 arguments - subjects is the list of subjects under test and fuzzed_time is the duration of the run to be analyzed. Note that, the second argument is optional and the script by default will assume that the execution time is 1440 minutes, which is equal to 1 day. For example, the command (analyze.sh exim 240) will analyze the first 4 hours of the execution results of the exim subject.
Upon completion of execution, the script will process the archives by construcing csv files, containing the covered number of branches, states, and state transitions over time. Furthermore, these csv files will be processed into PNG files which are plots, illustrating the average code and state coverage over time for fuzzers on each subject (cov_over_time... for the code and branch coverage, state_over_time... for the state and state transition coverage). All of this information is moved to a res_<subject name> folder in the root directory with a timestamp.
When the evaluation of the artifact is completed, running the clean.sh script will ensure that the only leftover files are in this directory:
./clean.shThe source code for the grammar generation is located in the function setup_llm_grammars in afl-fuzz.c with helper functions in chat-llm.c.
The responses of the LLM for the grammar generation can be found in the protocol-grammars directory in the resulting archive of a run.
The source code for the seed enrichment is located in the function get_seeds_with_messsage_types in afl-fuzz.c with helper functions in chat-llm.c.
The enriched seeds can be found in the seed queue directory in the resulting archive of a run. These files have the name id:...,orig:enriched_.
The source code for the state stall processing is located in the function fuzz_one and starts at line 6846 (if (uninteresting_times >= UNINTERESTING_THRESHOLD && chat_times < CHATTING_THRESHOLD){).
The state stall prompts and their corresponding responses can be found in the stall-interactions directory in the resulting archive of a run. The files are of the form request-<id> and response-<id>, containing the request we have constructed and the response from the LLM.
To conduct the experiments outlined in the paper, we utilized a vast amount of resources. It is impractical to replicate all the experiments within a single day using a standard desktop machine. To facilitate the evaluation of the artifact, we downsized our experiments, employing fewer fuzzers, subjects, and iterations.
ChatAFL can cover more states and code, and achieve the same state and code coverage faster than the baseline tool AFLNet. We run the following commands to support these claims:
./run.sh 5 240 kamailio,pure-ftpd,live555 chatafl,aflnet
./analyze.sh kamailio,pure-ftpd,live555 240Upon completion of the commands, a folder prefixed with res_ will be generated. This folder contains PNG files illustrating the state and code covered by two fuzzers over time as well as the output archives from all the runs. It will be placed in the root directory of the artifact.
Each strategy proposed in ChatAFL contributes to varying degrees of improvement in code coverage. We run the following commands to support this claim:
./run.sh 5 240 proftpd,exim chatafl,chatafl-cl1,chatafl-cl2
./analyze.sh proftpd,exim 240Upon completion of the commands, a folder prefixed with res_ will be generated. This folder contains PNG files illustrating the code covered by three fuzzers over time as well as the output archives from all the runs. It will be placed in the root directory of the artifact.
If a modification is done to any of the fuzzers, re-executing setup.sh will rebuild all the images with the modified version. All provided versions of ChatAFL contain a Dockerfile, allowing for the checking of build failures in the same environment as the one for the subjects and having a clean image, where one can setup different subjects.
All parameters, used in the experiments are located in config.h and chat-llm.h. The parameters, specific to ChatAFL are:
In config.h:
- EPSILON_CHOICE
- UNINTERESTING_THRESHOLD
- CHATTING_THRESHOLD
In chat-llm.h:
- STALL_RETRIES
- GRAMMAR_RETRIES
- MESSAGE_TYPE_RETRIES
- ENRICHMENT_RETRIES
- MAX_ENRICHMENT_MESSAGE_TYPES
- MAX_ENRICHMENT_CORPUS_SIZE
To add an extra subject, we refer to the instructions, provied by ProfuzzBench for adding a new benchmark subject. As an example, we have added Lighttpd 1.4 as a new subject to the benchmark.
If the fuzzer terminates with an error, a premature "I am done" message will be displayed. To examine this issue, running docker logs <containerID> will display the logs of the failing container.
We have released a new version of ChatAFL utilizing GPT-4: gpt4-version. However, it hasn't been extensively tested yet. Please feel free to reach out if you encounter any issues during use.
The current artifact interacts with OpenAI's Large Language Models (gpt-3.5-turbo-instruct and gpt-3.5-turbo). This puts a third-party limit to the degree of parallelization. The models used in this artifact have a hard limit of 150,000 tokens per minute.
We would like to thank the creators of AFLNet and ProFuzzBench for the tooling and infrastructure they have provided to the community.
This artifact is licensed under the Apache License 2.0 - see the LICENSE file for details.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for ChatAFL
Similar Open Source Tools

ChatAFL
ChatAFL is a protocol fuzzer guided by large language models (LLMs) that extracts machine-readable grammar for protocol mutation, increases message diversity, and breaks coverage plateaus. It integrates with ProfuzzBench for stateful fuzzing of network protocols, providing smooth integration. The artifact includes modified versions of AFLNet and ProfuzzBench, source code for ChatAFL with proposed strategies, and scripts for setup, execution, analysis, and cleanup. Users can analyze data, construct plots, examine LLM-generated grammars, enriched seeds, and state-stall responses, and reproduce results with downsized experiments. Customization options include modifying fuzzers, tuning parameters, adding new subjects, troubleshooting, and working on GPT-4. Limitations include interaction with OpenAI's Large Language Models and a hard limit of 150,000 tokens per minute.
monitors4codegen
This repository hosts the official code and data artifact for the paper 'Monitor-Guided Decoding of Code LMs with Static Analysis of Repository Context'. It introduces Monitor-Guided Decoding (MGD) for code generation using Language Models, where a monitor uses static analysis to guide the decoding. The repository contains datasets, evaluation scripts, inference results, a language server client 'multilspy' for static analyses, and implementation of various monitors monitoring for different properties in 3 programming languages. The monitors guide Language Models to adhere to properties like valid identifier dereferences, correct number of arguments to method calls, typestate validity of method call sequences, and more.

MegatronApp
MegatronApp is a toolchain built around the Megatron-LM training framework, offering performance tuning, slow-node detection, and training-process visualization. It includes modules like MegaScan for anomaly detection, MegaFBD for forward-backward decoupling, MegaDPP for dynamic pipeline planning, and MegaScope for visualization. The tool aims to enhance large-scale distributed training by providing valuable capabilities and insights.
BTGenBot
BTGenBot is a tool that generates behavior trees for robots using lightweight large language models (LLMs) with a maximum of 7 billion parameters. It fine-tunes on a specific dataset, compares multiple LLMs, and evaluates generated behavior trees using various methods. The tool demonstrates the potential of LLMs with a limited number of parameters in creating effective and efficient robot behaviors.
chronon
Chronon is a platform that simplifies and improves ML workflows by providing a central place to define features, ensuring point-in-time correctness for backfills, simplifying orchestration for batch and streaming pipelines, offering easy endpoints for feature fetching, and guaranteeing and measuring consistency. It offers benefits over other approaches by enabling the use of a broad set of data for training, handling large aggregations and other computationally intensive transformations, and abstracting away the infrastructure complexity of data plumbing.
ezkl
EZKL is a library and command-line tool for doing inference for deep learning models and other computational graphs in a zk-snark (ZKML). It enables the following workflow: 1. Define a computational graph, for instance a neural network (but really any arbitrary set of operations), as you would normally in pytorch or tensorflow. 2. Export the final graph of operations as an .onnx file and some sample inputs to a .json file. 3. Point ezkl to the .onnx and .json files to generate a ZK-SNARK circuit with which you can prove statements such as: > "I ran this publicly available neural network on some private data and it produced this output" > "I ran my private neural network on some public data and it produced this output" > "I correctly ran this publicly available neural network on some public data and it produced this output" In the backend we use the collaboratively-developed Halo2 as a proof system. The generated proofs can then be verified with much less computational resources, including on-chain (with the Ethereum Virtual Machine), in a browser, or on a device.
gpt-subtrans
GPT-Subtrans is an open-source subtitle translator that utilizes large language models (LLMs) as translation services. It supports translation between any language pairs that the language model supports. Note that GPT-Subtrans requires an active internet connection, as subtitles are sent to the provider's servers for translation, and their privacy policy applies.
LLM-LieDetector
This repository contains code for reproducing experiments on lie detection in black-box LLMs by asking unrelated questions. It includes Q/A datasets, prompts, and fine-tuning datasets for generating lies with language models. The lie detectors rely on asking binary 'elicitation questions' to diagnose whether the model has lied. The code covers generating lies from language models, training and testing lie detectors, and generalization experiments. It requires access to GPUs and OpenAI API calls for running experiments with open-source models. Results are stored in the repository for reproducibility.
aici
The Artificial Intelligence Controller Interface (AICI) lets you build Controllers that constrain and direct output of a Large Language Model (LLM) in real time. Controllers are flexible programs capable of implementing constrained decoding, dynamic editing of prompts and generated text, and coordinating execution across multiple, parallel generations. Controllers incorporate custom logic during the token-by-token decoding and maintain state during an LLM request. This allows diverse Controller strategies, from programmatic or query-based decoding to multi-agent conversations to execute efficiently in tight integration with the LLM itself.
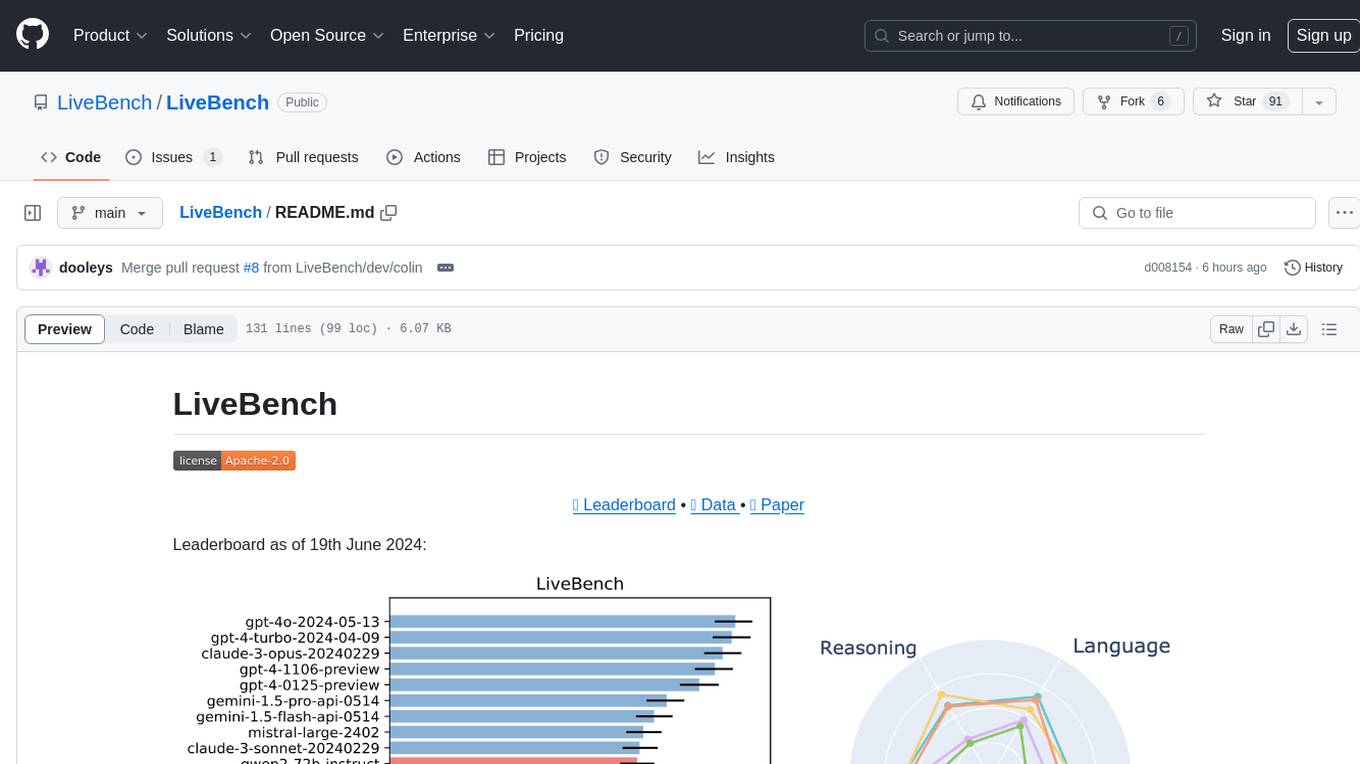
LiveBench
LiveBench is a benchmark tool designed for Language Model Models (LLMs) with a focus on limiting contamination through monthly new questions based on recent datasets, arXiv papers, news articles, and IMDb movie synopses. It provides verifiable, objective ground-truth answers for accurate scoring without an LLM judge. The tool offers 18 diverse tasks across 6 categories and promises to release more challenging tasks over time. LiveBench is built on FastChat's llm_judge module and incorporates code from LiveCodeBench and IFEval.

Mapperatorinator
Mapperatorinator is a multi-model framework that uses spectrogram inputs to generate fully featured osu! beatmaps for all gamemodes and assist modding beatmaps. The project aims to automatically generate rankable quality osu! beatmaps from any song with a high degree of customizability. The tool is built upon osuT5 and osu-diffusion, utilizing GPU compute and instances on vast.ai for development. Users can responsibly use AI in their beatmaps with this tool, ensuring disclosure of AI usage. Installation instructions include cloning the repository, creating a virtual environment, and installing dependencies. The tool offers a Web GUI for user-friendly experience and a Command-Line Inference option for advanced configurations. Additionally, an Interactive CLI script is available for terminal-based workflow with guided setup. The tool provides generation tips and features MaiMod, an AI-driven modding tool for osu! beatmaps. Mapperatorinator tokenizes beatmaps, utilizes a model architecture based on HF Transformers Whisper model, and offers multitask training format for conditional generation. The tool ensures seamless long generation, refines coordinates with diffusion, and performs post-processing for improved beatmap quality. Super timing generator enhances timing accuracy, and LoRA fine-tuning allows adaptation to specific styles or gamemodes. The project acknowledges credits and related works in the osu! community.
aisheets
Hugging Face AI Sheets is an open-source tool for building, enriching, and transforming datasets using AI models with no code. It can be deployed locally or on the Hub, providing access to thousands of open models. Users can easily generate datasets, run data generation scripts, and customize inference endpoints for text generation. The tool supports custom LLMs and offers advanced configuration options for authentication, inference, and miscellaneous settings. With AI Sheets, users can leverage the power of AI models without writing any code, making dataset management and transformation efficient and accessible.

rag-experiment-accelerator
The RAG Experiment Accelerator is a versatile tool that helps you conduct experiments and evaluations using Azure AI Search and RAG pattern. It offers a rich set of features, including experiment setup, integration with Azure AI Search, Azure Machine Learning, MLFlow, and Azure OpenAI, multiple document chunking strategies, query generation, multiple search types, sub-querying, re-ranking, metrics and evaluation, report generation, and multi-lingual support. The tool is designed to make it easier and faster to run experiments and evaluations of search queries and quality of response from OpenAI, and is useful for researchers, data scientists, and developers who want to test the performance of different search and OpenAI related hyperparameters, compare the effectiveness of various search strategies, fine-tune and optimize parameters, find the best combination of hyperparameters, and generate detailed reports and visualizations from experiment results.

eureka-ml-insights
The Eureka ML Insights Framework is a repository containing code designed to help researchers and practitioners run reproducible evaluations of generative models efficiently. Users can define custom pipelines for data processing, inference, and evaluation, as well as utilize pre-defined evaluation pipelines for key benchmarks. The framework provides a structured approach to conducting experiments and analyzing model performance across various tasks and modalities.
pgai
pgai simplifies the process of building search and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) AI applications with PostgreSQL. It brings embedding and generation AI models closer to the database, allowing users to create embeddings, retrieve LLM chat completions, reason over data for classification, summarization, and data enrichment directly from within PostgreSQL in a SQL query. The tool requires an OpenAI API key and a PostgreSQL client to enable AI functionality in the database. Users can install pgai from source, run it in a pre-built Docker container, or enable it in a Timescale Cloud service. The tool provides functions to handle API keys using psql or Python, and offers various AI functionalities like tokenizing, detokenizing, embedding, chat completion, and content moderation.

ontogpt
OntoGPT is a Python package for extracting structured information from text using large language models, instruction prompts, and ontology-based grounding. It provides a command line interface and a minimal web app for easy usage. The tool has been evaluated on test data and is used in related projects like TALISMAN for gene set analysis. OntoGPT enables users to extract information from text by specifying relevant terms and provides the extracted objects as output.
For similar tasks
llm-compression-intelligence
This repository presents the findings of the paper "Compression Represents Intelligence Linearly". The study reveals a strong linear correlation between the intelligence of LLMs, as measured by benchmark scores, and their ability to compress external text corpora. Compression efficiency, derived from raw text corpora, serves as a reliable evaluation metric that is linearly associated with model capabilities. The repository includes the compression corpora used in the paper, code for computing compression efficiency, and data collection and processing pipelines.
edsl
The Expected Parrot Domain-Specific Language (EDSL) package enables users to conduct computational social science and market research with AI. It facilitates designing surveys and experiments, simulating responses using large language models, and performing data labeling and other research tasks. EDSL includes built-in methods for analyzing, visualizing, and sharing research results. It is compatible with Python 3.9 - 3.11 and requires API keys for LLMs stored in a `.env` file.
fast-stable-diffusion
Fast-stable-diffusion is a project that offers notebooks for RunPod, Paperspace, and Colab Pro adaptations with AUTOMATIC1111 Webui and Dreambooth. It provides tools for running and implementing Dreambooth, a stable diffusion project. The project includes implementations by XavierXiao and is sponsored by Runpod, Paperspace, and Colab Pro.

RobustVLM
This repository contains code for the paper 'Robust CLIP: Unsupervised Adversarial Fine-Tuning of Vision Embeddings for Robust Large Vision-Language Models'. It focuses on fine-tuning CLIP in an unsupervised manner to enhance its robustness against visual adversarial attacks. By replacing the vision encoder of large vision-language models with the fine-tuned CLIP models, it achieves state-of-the-art adversarial robustness on various vision-language tasks. The repository provides adversarially fine-tuned ViT-L/14 CLIP models and offers insights into zero-shot classification settings and clean accuracy improvements.
TempCompass
TempCompass is a benchmark designed to evaluate the temporal perception ability of Video LLMs. It encompasses a diverse set of temporal aspects and task formats to comprehensively assess the capability of Video LLMs in understanding videos. The benchmark includes conflicting videos to prevent models from relying on single-frame bias and language priors. Users can clone the repository, install required packages, prepare data, run inference using examples like Video-LLaVA and Gemini, and evaluate the performance of their models across different tasks such as Multi-Choice QA, Yes/No QA, Caption Matching, and Caption Generation.

LLM-LieDetector
This repository contains code for reproducing experiments on lie detection in black-box LLMs by asking unrelated questions. It includes Q/A datasets, prompts, and fine-tuning datasets for generating lies with language models. The lie detectors rely on asking binary 'elicitation questions' to diagnose whether the model has lied. The code covers generating lies from language models, training and testing lie detectors, and generalization experiments. It requires access to GPUs and OpenAI API calls for running experiments with open-source models. Results are stored in the repository for reproducibility.
bigcodebench
BigCodeBench is an easy-to-use benchmark for code generation with practical and challenging programming tasks. It aims to evaluate the true programming capabilities of large language models (LLMs) in a more realistic setting. The benchmark is designed for HumanEval-like function-level code generation tasks, but with much more complex instructions and diverse function calls. BigCodeBench focuses on the evaluation of LLM4Code with diverse function calls and complex instructions, providing precise evaluation & ranking and pre-generated samples to accelerate code intelligence research. It inherits the design of the EvalPlus framework but differs in terms of execution environment and test evaluation.
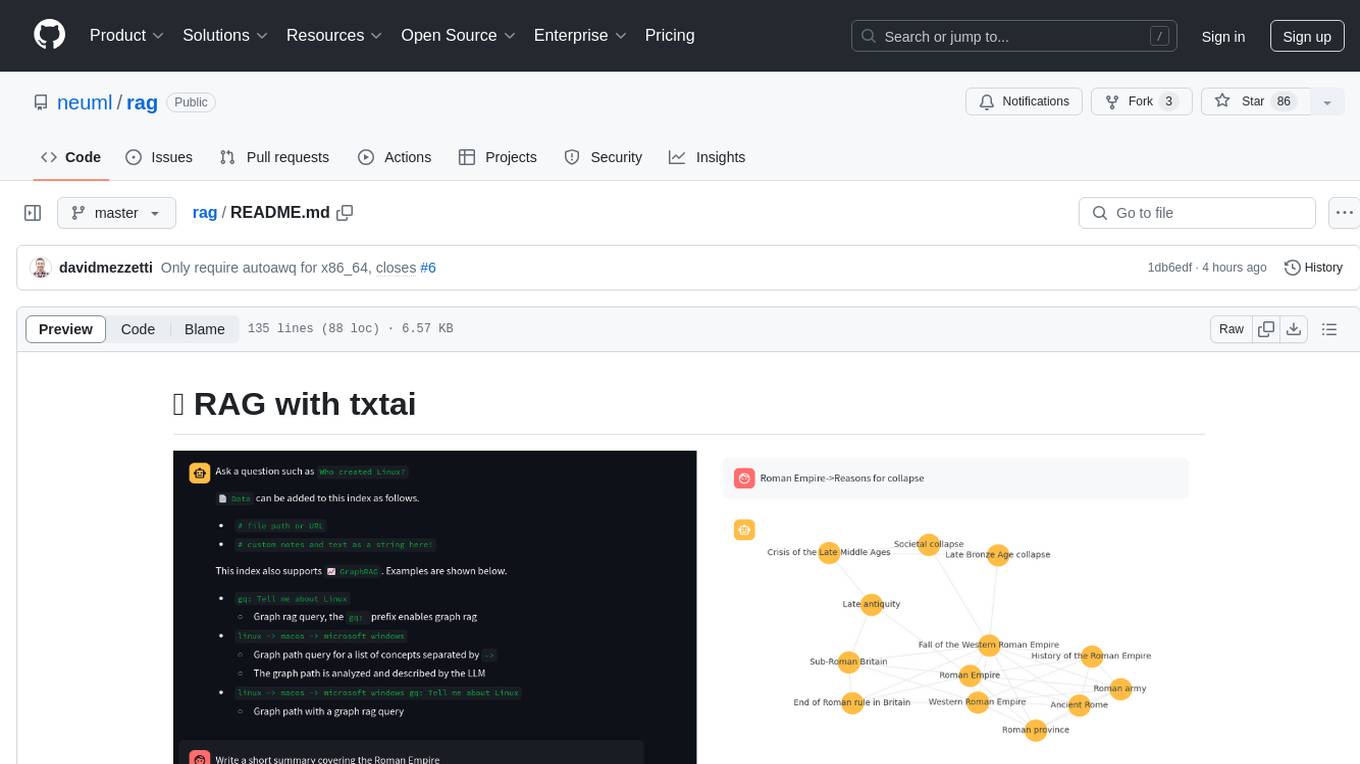
rag
RAG with txtai is a Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) Streamlit application that helps generate factually correct content by limiting the context in which a Large Language Model (LLM) can generate answers. It supports two categories of RAG: Vector RAG, where context is supplied via a vector search query, and Graph RAG, where context is supplied via a graph path traversal query. The application allows users to run queries, add data to the index, and configure various parameters to control its behavior.
For similar jobs
aio-proxy
This script automates setting up TUIC, hysteria and other proxy-related tools in Linux. It features setting domains, getting SSL certification, setting up a simple web page, SmartSNI by Bepass, Chisel Tunnel, Hysteria V2, Tuic, Hiddify Reality Scanner, SSH, Telegram Proxy, Reverse TLS Tunnel, different panels, installing, disabling, and enabling Warp, Sing Box 4-in-1 script, showing ports in use and their corresponding processes, and an Android script to use Chisel tunnel.
aiohttp
aiohttp is an async http client/server framework that supports both client and server side of HTTP protocol. It also supports both client and server Web-Sockets out-of-the-box and avoids Callback Hell. aiohttp provides a Web-server with middleware and pluggable routing.
OpsPilot
OpsPilot is an AI-powered operations navigator developed by the WeOps team. It leverages deep learning and LLM technologies to make operations plans interactive and generalize and reason about local operations knowledge. OpsPilot can be integrated with web applications in the form of a chatbot and primarily provides the following capabilities: 1. Operations capability precipitation: By depositing operations knowledge, operations skills, and troubleshooting actions, when solving problems, it acts as a navigator and guides users to solve operations problems through dialogue. 2. Local knowledge Q&A: By indexing local knowledge and Internet knowledge and combining the capabilities of LLM, it answers users' various operations questions. 3. LLM chat: When the problem is beyond the scope of OpsPilot's ability to handle, it uses LLM's capabilities to solve various long-tail problems.
aiocoap
aiocoap is a Python library that implements the Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP) using native asyncio methods in Python 3. It supports various CoAP standards such as RFC7252, RFC7641, RFC7959, RFC8323, RFC7967, RFC8132, RFC9176, RFC8613, and draft-ietf-core-oscore-groupcomm-17. The library provides features for clients and servers, including multicast support, blockwise transfer, CoAP over TCP, TLS, and WebSockets, No-Response, PATCH/FETCH, OSCORE, and Group OSCORE. It offers an easy-to-use interface for concurrent operations and is suitable for IoT applications.
aiounifi
Aiounifi is a Python library that provides a simple interface for interacting with the Unifi Controller API. It allows users to easily manage their Unifi network devices, such as access points, switches, and gateways, through automated scripts or applications. With Aiounifi, users can retrieve device information, perform configuration changes, monitor network performance, and more, all through a convenient and efficient API wrapper. This library simplifies the process of integrating Unifi network management into custom solutions, making it ideal for network administrators, developers, and enthusiasts looking to automate and streamline their network operations.
AirConnect-Synology
AirConnect-Synology is a minimal Synology package that allows users to use AirPlay to stream to UPnP/Sonos & Chromecast devices that do not natively support AirPlay. It is compatible with DSM 7.0 and DSM 7.1, and provides detailed information on installation, configuration, supported devices, troubleshooting, and more. The package automates the installation and usage of AirConnect on Synology devices, ensuring compatibility with various architectures and firmware versions. Users can customize the configuration using the airconnect.conf file and adjust settings for specific speakers like Sonos, Bose SoundTouch, and Pioneer/Phorus/Play-Fi.

axoned
Axone is a public dPoS layer 1 designed for connecting, sharing, and monetizing resources in the AI stack. It is an open network for collaborative AI workflow management compatible with any data, model, or infrastructure, allowing sharing of data, algorithms, storage, compute, APIs, both on-chain and off-chain. The 'axoned' node of the AXONE network is built on Cosmos SDK & Tendermint consensus, enabling companies & individuals to define on-chain rules, share off-chain resources, and create new applications. Validators secure the network by maintaining uptime and staking $AXONE for rewards. The blockchain supports various platforms and follows Semantic Versioning 2.0.0. A docker image is available for quick start, with documentation on querying networks, creating wallets, starting nodes, and joining networks. Development involves Go and Cosmos SDK, with smart contracts deployed on the AXONE blockchain. The project provides a Makefile for building, installing, linting, and testing. Community involvement is encouraged through Discord, open issues, and pull requests.
paddler
Paddler is an open-source load balancer and reverse proxy designed specifically for optimizing servers running llama.cpp. It overcomes typical load balancing challenges by maintaining a stateful load balancer that is aware of each server's available slots, ensuring efficient request distribution. Paddler also supports dynamic addition or removal of servers, enabling integration with autoscaling tools.