
paddler
Stateful load balancer custom-tailored for llama.cpp 🏓🦙
Stars: 715
Paddler is an open-source load balancer and reverse proxy designed specifically for optimizing servers running llama.cpp. It overcomes typical load balancing challenges by maintaining a stateful load balancer that is aware of each server's available slots, ensuring efficient request distribution. Paddler also supports dynamic addition or removal of servers, enabling integration with autoscaling tools.
README:
[!IMPORTANT]
Big chances! Paddler is rewritten into Rust (from Golang) and uses Pingora framework for the networking stack.Version
1.0.0brings some minor API changes and reporting improvements.The next plan is to introduce a supervisor who does not just monitor llamas.cpp instances, but to also manage them (replace models without dropping requests, etc.).
Paddler is an open-source, production-ready, stateful load balancer and reverse proxy designed to optimize servers running llama.cpp.
Typical load balancing strategies like round robin and least connections are ineffective for llama.cpp servers, which utilize continuous batching algorithms and allow to configure slots to handle multiple requests concurrently.
Paddler is designed to support llama.cpp-specific features like slots. It works by maintaining a stateful load balancer aware of each server's available slots, ensuring efficient request distribution.
[!NOTE] In simple terms, the
slotsin llama.cpp refer to predefined memory slices within the server that handle individual requests. When a request comes in, it is assigned to an available slot for processing. They are predictable and highly configurable.You can learn more about them in llama.cpp server documentation.
- Uses agents to monitor the slots of individual llama.cpp instances.
- Supports the dynamic addition or removal of llama.cpp servers, enabling integration with autoscaling tools.
- Buffers requests, allowing to scale from zero hosts.
- Integrates with StatsD protocol but also comes with a built-in dashboard.
- AWS integration.
Paddler's aware of each server's available slots, ensuring efficient request ("R") distribution
llama.cpp instances need to be registered in Paddler. Paddler’s agents should be installed alongside llama.cpp instances so that they can report their slots status to the load balancer.
The sequence repeats for each agent:
sequenceDiagram
participant loadbalancer as Paddler Load Balancer
participant agent as Paddler Agent
participant llamacpp as llama.cpp
agent->>llamacpp: Hey, are you alive?
llamacpp-->>agent: Yes, this is my slots status
agent-->>loadbalancer: llama.cpp is still working
loadbalancer->>llamacpp: I have a request for you to handleDownload the latest release for Linux, Mac, or Windows from the releases page.
On Linux, if you want Paddler to be accessible system-wide, rename the downloaded executable to /usr/bin/paddler (or /usr/local/bin/paddler).
Slots endpoint is required to be enabled in llama.cpp. To do so, run llama.cpp with the --slots flag.
The next step is to run Paddler’s agents. Agents register your llama.cpp instances in Paddler and monitor the slots of llama.cpp instances. They should be installed on the same host as your server that runs llama.cpp.
An agent needs a few pieces of information:
-
external-llamacpp-addrtells how the load balancer can connect to the llama.cpp instance -
local-llamacpp-addrtells how the agent can connect to the llama.cpp instance -
management-addrtell where the agent should report the slots status
Run the following to start a Paddler’s agent (replace the hosts and ports with your own server addresses when deploying):
./paddler agent \
--external-llamacpp-addr 127.0.0.1:8088 \
--local-llamacpp-addr 127.0.0.1:8088 \
--management-addr 127.0.0.1:8085With the --name flag, you can assign each agent a custom name. This name will be displayed in the management dashboard and not used for any other purpose.
If your llama.cpp instance requires an API key, you can provide it with the --local-llamacpp-api-key flag.
Load balancer collects data from agents and exposes reverse proxy to the outside world.
It requires two sets of flags:
-
management-addrtells where the load balancer should listen for updates from agents -
reverseproxy-addrtells how load balancer can be reached from the outside hosts
To start the load balancer, run:
./paddler balancer \
--management-addr 127.0.0.1:8085 \
--reverseproxy-addr 196.168.2.10:8080management-host and management-port in agents should be the same as in the load balancer.
You can enable dashboard to see the status of the agents with
--management-dashboard-enable flag. If enabled, it is available at the
management server address under /dashboard path.
[!NOTE] Available since v1.0.0
By default, Paddler blocks access to /slots endpoint, even if it is enabled in llama.cpp, because it exposes a lot of sensistive information about the server, and should only be used internally. If you want to expose it anyway, you can use the --slots-endpoint-enable flag.
.
[!NOTE] Available since v0.8.0
In some cases (see: #20), you might want to rewrite the Host header.
In such cases, you can use the --rewrite-host-header flag. If used, Paddler will use the external host provided by agents instead of the balancer host when forwarding the requests.
Paddler balancer endpoint aggregates the slots of all llama.cpp instances and reports the total number of available and processing slots.
Aggregated health status is available at the /api/v1/agents endpoint of the management server.
[!NOTE] Available since v0.3.0
Load balancer's buffered requests allow your infrastructure to scale from zero hosts by providing an additional metric (unhandled requests).
It also gives your infrastructure some additional time to add additional hosts. For example, if your autoscaler is setting up an additional server, putting an incoming request on hold for 60 seconds might give it a chance to be handled even though there might be no available llama.cpp instances at the moment of issuing it.
Scaling from zero hosts is especially suitable for low-traffic projects because it allows you to cut costs on your infrastructure—you won't be paying your cloud provider anything if you are not using your service at the moment.
https://github.com/distantmagic/paddler/assets/1286785/34b93e4c-0746-4eed-8be3-cd698e15cbf9
Although Paddler integrates with the StatsD protocol, you can preview the cluster's state using a built-in dashboard.
Paddler needs to be compiled with the web_dashboard feature flag enabled (enabled by default in GitHub releases).
To start the dashboard, run paddler balancer with the --management-dashboard-enable flag.
[!NOTE] Available since v1.2.0
You can connect to any running Paddler instance with paddler dashboard --management-addr [HOST]:[PORT].
Thank you @Propfend for contributing the TUI Dashboard!
[!NOTE] Available since v0.3.0
[!TIP] If you keep your stack self-hosted you can use Prometheus with StatsD exporter to handle the incoming metrics.
[!TIP] This feature works with AWS CloudWatch Agent as well.
Paddler supports the following StatsD metrics:
-
requests_bufferednumber of buffered requests since the last report (resets after each report) -
slots_idletotal idle slots -
slots_processingtotal slots processing requests
All of them use gauge internally.
StatsD metrics need to be enabled with the following flags:
./paddler balancer \
# .. put all the other flags here ...
--statsd-addr=127.0.0.1:8125If you do not provide the --statsd-addr flag, the StatsD metrics will not be collected.
- Add TUI dashboard (
paddler dashboard --management-addr [HOST]:[PORT]) to be able to easily observe balancer instances from the terminal level
- More meaningful error messages when the agent can't connect to the llama.cpp slot endpoint, or when slot endpoint is not enabled in llama.cpp
- Set default logging level to
infofor agents and balancer to increase the amount of information in the logs (it wasn't clean if the agent was running or not) - Enable LTO optimization for the release builds (see #28)
The first stable release! Paddler is now rewritten in Rust and uses the Pingora framework for the networking stack. A few minor API changes and reporting improvements are introduced (documented in the README). API and configuration are now stable, and won't be changed until version 2.0.0.
This is a stability/quality release. The next plan is to introduce a supervisor who does not just monitor llama.cpp instances, but to also manage them.
Requires llama.cpp version b4027 or above.
This update is a minor release to make Paddler compatible with /slots endpoint changes introduced in llama.cpp b4027.
Requires llama.cpp version b4027 or above.
Latest supported llama.cpp release: b4026
- Add
--local-llamacpp-api-keyflag to balancer to support llama.cpp API keys (see: #23)
- Add
--rewrite-host-headerflag to balancer to rewrite theHostheader in forwarded requests (see: #20)
- Incorrect preemptive counting of remaining slots in some scenarios
Requires at least b3606 llama.cpp release.
-
Adjusted to handle breaking changes in llama.cpp
/healthendpoint: https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/pull/9056Instead of using the
/healthendpoint to monitor slot statuses, starting from this version, Paddler uses the/slotsendpoint to monitor llama.cpp instances. Paddler's/healthendpoint remains unchanged.
Latest supported llama.cpp release: b3604
- Management server crashed in some scenarios due to concurrency issues
Thank you, @ScottMcNaught, for the help with debugging the issues! :)
- OpenAI compatible endpoint is now properly balanced (
/v1/chat/completions) - Balancer's reverse proxy
panicked in some scenarios when the underlyingllama.cppinstance was abruptly closed during the generation of completion tokens - Added mutex in the targets collection for better internal slots data integrity
- Requests can queue when all llama.cpp instances are busy
- AWS Metadata support for agent local IP address
- StatsD metrics support
I initially wanted to use Raft consensus algorithm (thus Paddler, because it paddles on a Raft), but eventually, I dropped that idea. The name stayed, though.
Later, people started sending me a "that's a paddlin'" clip from The Simpsons, and I just embraced it.
Discord: https://discord.gg/kysUzFqSCK
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for paddler
Similar Open Source Tools

paddler
Paddler is an open-source load balancer and reverse proxy designed specifically for optimizing servers running llama.cpp. It overcomes typical load balancing challenges by maintaining a stateful load balancer that is aware of each server's available slots, ensuring efficient request distribution. Paddler also supports dynamic addition or removal of servers, enabling integration with autoscaling tools.
0chain
Züs is a high-performance cloud on a fast blockchain offering privacy and configurable uptime. It uses erasure code to distribute data between data and parity servers, allowing flexibility for IT managers to design for security and uptime. Users can easily share encrypted data with business partners through a proxy key sharing protocol. The ecosystem includes apps like Blimp for cloud migration, Vult for personal cloud storage, and Chalk for NFT artists. Other apps include Bolt for secure wallet and staking, Atlus for blockchain explorer, and Chimney for network participation. The QoS protocol challenges providers based on response time, while the privacy protocol enables secure data sharing. Züs supports hybrid and multi-cloud architectures, allowing users to improve regulatory compliance and security requirements.
webwhiz
WebWhiz is an open-source tool that allows users to train ChatGPT on website data to build AI chatbots for customer queries. It offers easy integration, data-specific responses, regular data updates, no-code builder, chatbot customization, fine-tuning, and offline messaging. Users can create and train chatbots in a few simple steps by entering their website URL, automatically fetching and preparing training data, training ChatGPT, and embedding the chatbot on their website. WebWhiz can crawl websites monthly, collect text data and metadata, and process text data using tokens. Users can train custom data, but bringing custom open AI keys is not yet supported. The tool has no limitations on context size but may limit the number of pages based on the chosen plan. WebWhiz SDK is available on NPM, CDNs, and GitHub, and users can self-host it using Docker or manual setup involving MongoDB, Redis, Node, Python, and environment variables setup. For any issues, users can contact [email protected].
OSWorld
OSWorld is a benchmarking tool designed to evaluate multimodal agents for open-ended tasks in real computer environments. It provides a platform for running experiments, setting up virtual machines, and interacting with the environment using Python scripts. Users can install the tool on their desktop or server, manage dependencies with Conda, and run benchmark tasks. The tool supports actions like executing commands, checking for specific results, and evaluating agent performance. OSWorld aims to facilitate research in AI by providing a standardized environment for testing and comparing different agent baselines.
SeaGOAT
SeaGOAT is a local search tool that leverages vector embeddings to enable you to search your codebase semantically. It is designed to work on Linux, macOS, and Windows and can process files in various formats, including text, Markdown, Python, C, C++, TypeScript, JavaScript, HTML, Go, Java, PHP, and Ruby. SeaGOAT uses a vector database called ChromaDB and a local vector embedding engine to provide fast and accurate search results. It also supports regular expression/keyword-based matches. SeaGOAT is open-source and licensed under an open-source license, and users are welcome to examine the source code, raise concerns, or create pull requests to fix problems.
n8n-docs
n8n is an extendable workflow automation tool that enables you to connect anything to everything. It is open-source and can be self-hosted or used as a service. n8n provides a visual interface for creating workflows, which can be used to automate tasks such as data integration, data transformation, and data analysis. n8n also includes a library of pre-built nodes that can be used to connect to a variety of applications and services. This makes it easy to create complex workflows without having to write any code.

fasttrackml
FastTrackML is an experiment tracking server focused on speed and scalability, fully compatible with MLFlow. It provides a user-friendly interface to track and visualize your machine learning experiments, making it easy to compare different models and identify the best performing ones. FastTrackML is open source and can be easily installed and run with pip or Docker. It is also compatible with the MLFlow Python package, making it easy to integrate with your existing MLFlow workflows.

airbroke
Airbroke is an open-source error catcher tool designed for modern web applications. It provides a PostgreSQL-based backend with an Airbrake-compatible HTTP collector endpoint and a React-based frontend for error management. The tool focuses on simplicity, maintaining a small database footprint even under heavy data ingestion. Users can ask AI about issues, replay HTTP exceptions, and save/manage bookmarks for important occurrences. Airbroke supports multiple OAuth providers for secure user authentication and offers occurrence charts for better insights into error occurrences. The tool can be deployed in various ways, including building from source, using Docker images, deploying on Vercel, Render.com, Kubernetes with Helm, or Docker Compose. It requires Node.js, PostgreSQL, and specific system resources for deployment.
gpt-subtrans
GPT-Subtrans is an open-source subtitle translator that utilizes large language models (LLMs) as translation services. It supports translation between any language pairs that the language model supports. Note that GPT-Subtrans requires an active internet connection, as subtitles are sent to the provider's servers for translation, and their privacy policy applies.
llm-subtrans
LLM-Subtrans is an open source subtitle translator that utilizes LLMs as a translation service. It supports translating subtitles between any language pairs supported by the language model. The application offers multiple subtitle formats support through a pluggable system, including .srt, .ssa/.ass, and .vtt files. Users can choose to use the packaged release for easy usage or install from source for more control over the setup. The tool requires an active internet connection as subtitles are sent to translation service providers' servers for translation.

airbyte_serverless
AirbyteServerless is a lightweight tool designed to simplify the management of Airbyte connectors. It offers a serverless mode for running connectors, allowing users to easily move data from any source to their data warehouse. Unlike the full Airbyte-Open-Source-Platform, AirbyteServerless focuses solely on the Extract-Load process without a UI, database, or transform layer. It provides a CLI tool, 'abs', for managing connectors, creating connections, running jobs, selecting specific data streams, handling secrets securely, and scheduling remote runs. The tool is scalable, allowing independent deployment of multiple connectors. It aims to streamline the connector management process and provide a more agile alternative to the comprehensive Airbyte platform.
starter-monorepo
Starter Monorepo is a template repository for setting up a monorepo structure in your project. It provides a basic setup with configurations for managing multiple packages within a single repository. This template includes tools for package management, versioning, testing, and deployment. By using this template, you can streamline your development process, improve code sharing, and simplify dependency management across your project. Whether you are working on a small project or a large-scale application, Starter Monorepo can help you organize your codebase efficiently and enhance collaboration among team members.
CLI
Bito CLI provides a command line interface to the Bito AI chat functionality, allowing users to interact with the AI through commands. It supports complex automation and workflows, with features like long prompts and slash commands. Users can install Bito CLI on Mac, Linux, and Windows systems using various methods. The tool also offers configuration options for AI model type, access key management, and output language customization. Bito CLI is designed to enhance user experience in querying AI models and automating tasks through the command line interface.
AilyticMinds
AilyticMinds Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app designed for easy deployment and improved backend compatibility. It provides a user-friendly interface for creating and hosting chatbots, with features like mobile layout optimization and support for various providers. The tool utilizes Supabase for data storage and management, offering a secure and scalable solution for chatbot development. Users can quickly set up their own instances locally or in the cloud, with detailed instructions provided for installation and configuration.
seer
Seer is a service that provides AI capabilities to Sentry by running inference on Sentry issues and providing user insights. It is currently in early development and not yet compatible with self-hosted Sentry instances. The tool requires access to internal Sentry resources and is intended for internal Sentry employees. Users can set up the environment, download model artifacts, integrate with local Sentry, run evaluations for Autofix AI agent, and deploy to a sandbox staging environment. Development commands include applying database migrations, creating new migrations, running tests, and more. The tool also supports VCRs for recording and replaying HTTP requests.
uwazi
Uwazi is a flexible database application designed for capturing and organizing collections of information, with a focus on document management. It is developed and supported by HURIDOCS, benefiting human rights organizations globally. The tool requires NodeJs, ElasticSearch, ICU Analysis Plugin, MongoDB, Yarn, and pdftotext for installation. It offers production and development installation guides, including Docker setup. Uwazi supports hot reloading, unit and integration testing with JEST, and end-to-end testing with Nightmare or Puppeteer. The system requirements include RAM, CPU, and disk space recommendations for on-premises and development usage.
For similar tasks

paddler
Paddler is an open-source load balancer and reverse proxy designed specifically for optimizing servers running llama.cpp. It overcomes typical load balancing challenges by maintaining a stateful load balancer that is aware of each server's available slots, ensuring efficient request distribution. Paddler also supports dynamic addition or removal of servers, enabling integration with autoscaling tools.
mcp-hub
MCP Hub is a centralized manager for Model Context Protocol (MCP) servers, offering dynamic server management and monitoring, REST API for tool execution and resource access, MCP Server marketplace integration, real-time server status tracking, client connection management, and process lifecycle handling. It acts as a central management server connecting to and managing multiple MCP servers, providing unified API endpoints for client access, handling server lifecycle and health monitoring, and routing requests between clients and MCP servers.
For similar jobs
flux-aio
Flux All-In-One is a lightweight distribution optimized for running the GitOps Toolkit controllers as a single deployable unit on Kubernetes clusters. It is designed for bare clusters, edge clusters, clusters with restricted communication, clusters with egress via proxies, and serverless clusters. The distribution follows semver versioning and provides documentation for specifications, installation, upgrade, OCI sync configuration, Git sync configuration, and multi-tenancy configuration. Users can deploy Flux using Timoni CLI and a Timoni Bundle file, fine-tune installation options, sync from public Git repositories, bootstrap repositories, and uninstall Flux without affecting reconciled workloads.

paddler
Paddler is an open-source load balancer and reverse proxy designed specifically for optimizing servers running llama.cpp. It overcomes typical load balancing challenges by maintaining a stateful load balancer that is aware of each server's available slots, ensuring efficient request distribution. Paddler also supports dynamic addition or removal of servers, enabling integration with autoscaling tools.
DaoCloud-docs
DaoCloud Enterprise 5.0 Documentation provides detailed information on using DaoCloud, a Certified Kubernetes Service Provider. The documentation covers current and legacy versions, workflow control using GitOps, and instructions for opening a PR and previewing changes locally. It also includes naming conventions, writing tips, references, and acknowledgments to contributors. Users can find guidelines on writing, contributing, and translating pages, along with using tools like MkDocs, Docker, and Poetry for managing the documentation.
ztncui-aio
This repository contains a Docker image with ZeroTier One and ztncui to set up a standalone ZeroTier network controller with a web user interface. It provides features like Golang auto-mkworld for generating a planet file, supports local persistent storage configuration, and includes a public file server. Users can build the Docker image, set up the container with specific environment variables, and manage the ZeroTier network controller through the web interface.
devops-gpt
DevOpsGPT is a revolutionary tool designed to streamline your workflow and empower you to build systems and automate tasks with ease. Tired of spending hours on repetitive DevOps tasks? DevOpsGPT is here to help! Whether you're setting up infrastructure, speeding up deployments, or tackling any other DevOps challenge, our app can make your life easier and more productive. With DevOpsGPT, you can expect faster task completion, simplified workflows, and increased efficiency. Ready to experience the DevOpsGPT difference? Visit our website, sign in or create an account, start exploring the features, and share your feedback to help us improve. DevOpsGPT will become an essential tool in your DevOps toolkit.
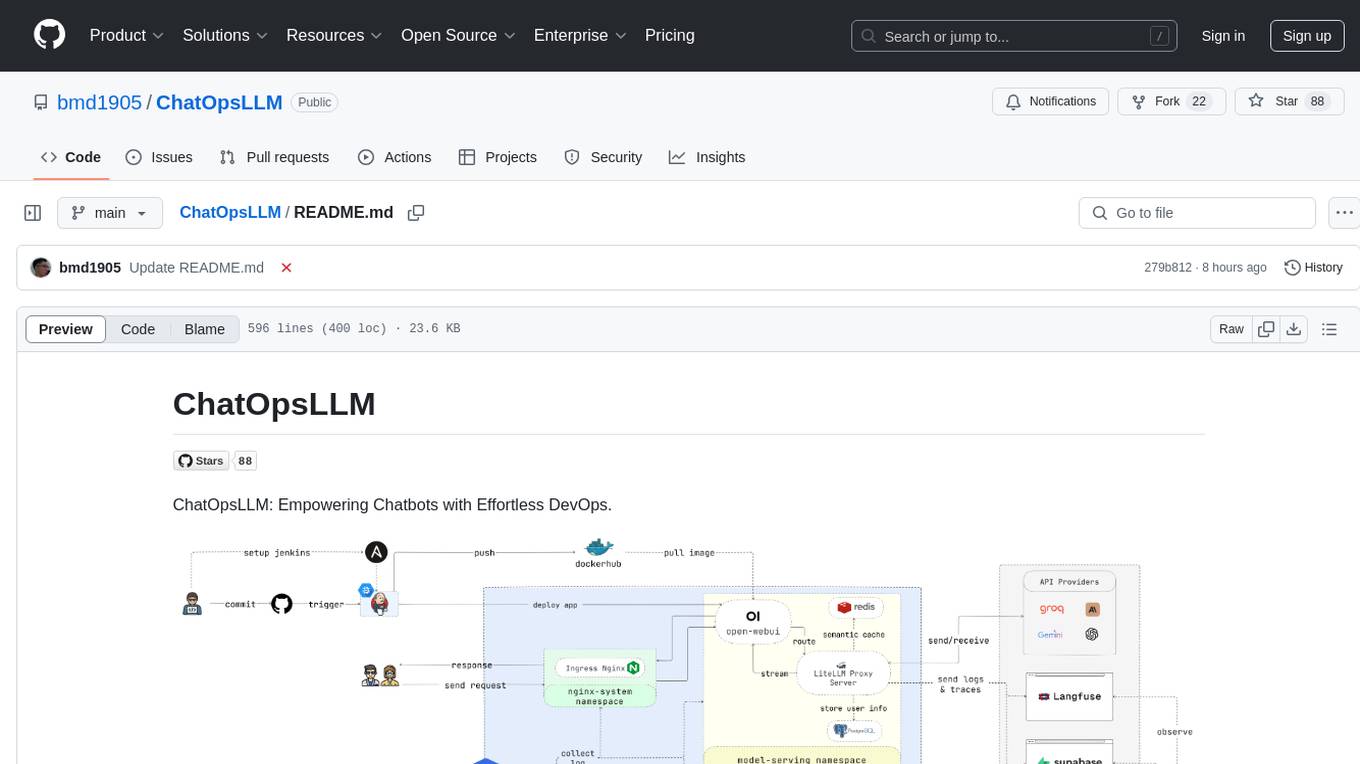
ChatOpsLLM
ChatOpsLLM is a project designed to empower chatbots with effortless DevOps capabilities. It provides an intuitive interface and streamlined workflows for managing and scaling language models. The project incorporates robust MLOps practices, including CI/CD pipelines with Jenkins and Ansible, monitoring with Prometheus and Grafana, and centralized logging with the ELK stack. Developers can find detailed documentation and instructions on the project's website.
aiops-modules
AIOps Modules is a collection of reusable Infrastructure as Code (IAC) modules that work with SeedFarmer CLI. The modules are decoupled and can be aggregated using GitOps principles to achieve desired use cases, removing heavy lifting for end users. They must be generic for reuse in Machine Learning and Foundation Model Operations domain, adhering to SeedFarmer Guide structure. The repository includes deployment steps, project manifests, and various modules for SageMaker, Mlflow, FMOps/LLMOps, MWAA, Step Functions, EKS, and example use cases. It also supports Industry Data Framework (IDF) and Autonomous Driving Data Framework (ADDF) Modules.
3FS
The Fire-Flyer File System (3FS) is a high-performance distributed file system designed for AI training and inference workloads. It leverages modern SSDs and RDMA networks to provide a shared storage layer that simplifies development of distributed applications. Key features include performance, disaggregated architecture, strong consistency, file interfaces, data preparation, dataloaders, checkpointing, and KVCache for inference. The system is well-documented with design notes, setup guide, USRBIO API reference, and P specifications. Performance metrics include peak throughput, GraySort benchmark results, and KVCache optimization. The source code is available on GitHub for cloning and installation of dependencies. Users can build 3FS and run test clusters following the provided instructions. Issues can be reported on the GitHub repository.