
GhostOS
A framework offers an OS simulator within a Python Code Interface for AI Agents
Stars: 58
GhostOS is an AI Agent framework designed to replace JSON Schema with a Turing-complete code interaction interface (Moss Protocol). It aims to create intelligent entities capable of continuous learning and growth through code generation and project management. The framework supports various capabilities such as turning Python files into web agents, real-time voice conversation, body movements control, and emotion expression. GhostOS is still in early experimental development and focuses on out-of-the-box capabilities for AI agents.
README:
The AI
Ghostswander in theShells.
(This document is translated from zh-cn to english by Moonshot)
Using Python code SpheroBoltGPT,
an intelligent robot with a SpheroBolt as its body is defined.
If you have a SpheroBolt, running ghostos web ghostos.demo.sphero.bolt_gpt can start this robot.
The demo initially implements the following features:
- Real-time voice conversation.
- Control of body movements and drawing graphics on an 8x8 LED matrix.
- Learning skills that include actions and animations through natural language dialogue.
- Expressing emotions through movements during conversation.
GhostOS is an AI Agent framework designed to replace JSON Schema
with a Turing-complete code interaction interface (Moss Protocol),
becoming the core method for interaction between LLM and Agent system capabilities. For more details:
MOSS: Enabling Code-Driven Evolution and Context Management for AI Agents
The expected objects called through code
include tools, personality, agent swarm, workflows, thinking, planning, knowledge, and memory.
This allows a Meta-Agent to become an intelligent entity capable of continuous learning and growth through code
generation and project management.
And such an intelligent agent implemented with a code repository can also be shared and installed in the form of a repository.
GhostOS Still in the early experimental developing, the current version mainly implements out-of-the-box capabilities,
including:
- [x] Turn a python file into a web agent
- [x] Agent web UI built by Streamlit Web
- [x] Support llms like
OpenAI,Moonshot - [x] Support OpenAI vision
- [x] Support OpenAI Realtime Beta
GhostOSremains a beta AI project, strongly recommending installation in containers such as Docker rather than running locally.
Install GhostOS package:
pip install ghostosInitialize workspace (directory app as default), The runtime files of the current version will be stored in the
directory.
ghostos initConfigure the model. Default to use OpenAI gpt-4o, requiring the environment variable OPENAI_API_KEY.
export OPENAI_API_KEY="your openai api key"
# Optionals:
export OPENAI_PROXY="sock5://localhost:[your-port]" # setup openai proxy
export DEEPSEEK_API_KEY="your deepseek api key"
epoxrt MOONSHOT_API_KEY="your moonshot api key"Or you can use configuration ui by streamlit:
ghostos configThen test the default agent:
# run an agent with python filename or modulename
ghostos web ghostos.demo.agents.jojoOr turn a local Python file into an Agent, that can be instructed to call functions or methods within the file through natural language conversations.
ghostos web [my_path_file_path]some demo agents
ghostos web ghostos.demo.agents.jojo
ghostos web ghostos.demo.test_agents.moonshot # moonshot-v1-32k model
ghostos web ghostos.demo.test_agents.deepseek_chat # deepseek chat model
ghostos web ghostos.demo.test_agents.openai_o1_mini # openai o1 mini modelYou can create a local Python file and define your own Agents. For more details
GhostOS support OpenAI Realtime,
using pyaudio to handle realtime audio i/o.
Need to install the dependencies first:
pip install 'ghostos[realtime]'You may face some difficulties while install pyaudio on your device, I'm sure gpt-4o, google or stackoverflow will offer you solutions.
from ghostos.bootstrap import make_app_container, get_ghostos
from ghostos.ghosts.chatbot import Chatbot
# create your own root ioc container.
# register or replace the dependencies by IoC service providers.
container = make_app_container(...)
# fetch the GhostOS instance.
ghostos = get_ghostos(container)
# Create a shell instance, which managing sessions that keep AI Ghost inside it.
# and initialize the shell level dependency providers.
shell = ghostos.create_shell("your robot shell")
# Shell can handle parallel ghosts running, and communicate them through an EventBus.
# So the Multi-Agent swarm in GhostOS is asynchronous.
shell.background_run() # Optional
# need an instance implements `ghostos.abcd.Ghost` interface.
my_chatbot: Chatbot = ...
# use Shell to create a synchronous conversation channel with the Ghost.
conversation = shell.sync(my_chatbot)
# use the conversation channel to talk
event, receiver = conversation.talk("hello?")
with receiver:
for chunk in receiver.recv():
print(chunk.content)- [ ] Out-of-the-box Agent capability libraries.
- [ ] Variable type messaging and Streamlit rendering.
- [ ] Asynchronous Multi-Agent.
- [ ] Long-term task planning and execution.
- [ ] Atomic thinking capabilities.
- [ ] Automated execution and management of tree-based projects.
- [ ] Configurable components of the framework.
- [ ] Experiments with toy-level embodied intelligence.
GhostOS, as a personal project, currently lacks the energy to focus on improving documentation, storage modules, stability, or security issues.
The project's iteration will be centered on validating three directions for a long time: code-driven embodied intelligence, code-based thinking capabilities, and code-based learning. I will also aim to optimize out-of-the-box agent abilities.
The GhostOS project is developed by the author for exploring AI applications. The basic idea is as follows:
AI Agent technology has two parallel evolutionary paths: one is the perfection of the model's own capabilities, and the other is the evolution of the Agent engineering framework. The productivity level of the Agent framework determines the feasibility of AI models in practical application scenarios.
GhostOS reflects the capabilities of an Agent from code into prompts, providing them to AI models, and the code generated by the models runs directly in the environment. Expecting the large language model do everything through a Turing-complete programming language interface, including computation, tool invocation, body control, personality switching, thinking paradigms, state scheduling, Multi-Agent, memory and recall, and other actions.
This will have stronger interaction capabilities and lower overhead than methods based on JSON schema. The conversation data generated in this process can be used for post-training or reinforcement learning of the model, thereby continuously optimizing the code generation.
The AI Agent itself is also defined by code. Therefore, a Meta-Agent can develop other Agents just like a normal programming task.
Ideally, the Meta-Agent can write code, write its own tools, define memories and chain of thoughts with data structures, and develop other Agents for itself.
Furthermore, most complex tasks with rigorous steps can be described using tree or graph data structures. Constructing a nested graph or tree using methods like JSON is very difficult, while using programming languages is the most efficient.
models can consolidate the results learned from conversations into nodes in the code, and then plan them into trees or graphs, thereby executing sufficiently complex tasks.
In this way, an AI Agent can store the knowledge and capabilities learned from natural language in the form of files and code, thereby evolving itself. This is a path of evolution beyond model iteration.
Based on this idea, GhostOS aims to turn an Agent swarm into a project constructed through code. The Agents continuously precipitate new knowledge and capabilities in the form of code, enriching the project. The Agent project can be copied, shared, or deployed in the form of repositories,
In this new form of productivity, interacting purely through code is the most critical step.
The author's ultimate goal is not GhostOS itself,
but to verify and promote the code interaction design and applications.
The hope is that one day, agents, paradigms, bodies, and tools for AI Agents can all be designed based on the same
programming language protocols,
achieving cross-project universality.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for GhostOS
Similar Open Source Tools

GhostOS
GhostOS is an AI Agent framework designed to replace JSON Schema with a Turing-complete code interaction interface (Moss Protocol). It aims to create intelligent entities capable of continuous learning and growth through code generation and project management. The framework supports various capabilities such as turning Python files into web agents, real-time voice conversation, body movements control, and emotion expression. GhostOS is still in early experimental development and focuses on out-of-the-box capabilities for AI agents.
blades
Blades is a multimodal AI Agent framework in Go, supporting custom models, tools, memory, middleware, and more. It is well-suited for multi-turn conversations, chain reasoning, and structured output. The framework provides core components like Agent, Prompt, Chain, ModelProvider, Tool, Memory, and Middleware, enabling developers to build intelligent applications with flexible configuration and high extensibility. Blades leverages the characteristics of Go to achieve high decoupling and efficiency, making it easy to integrate different language model services and external tools. The project is in its early stages, inviting Go developers and AI enthusiasts to contribute and explore the possibilities of building AI applications in Go.
council
Council is an open-source platform designed for the rapid development and deployment of customized generative AI applications using teams of agents. It extends the LLM tool ecosystem by providing advanced control flow and scalable oversight for AI agents. Users can create sophisticated agents with predictable behavior by leveraging Council's powerful approach to control flow using Controllers, Filters, Evaluators, and Budgets. The framework allows for automated routing between agents, comparing, evaluating, and selecting the best results for a task. Council aims to facilitate packaging and deploying agents at scale on multiple platforms while enabling enterprise-grade monitoring and quality control.
agency
Agency is a python library that provides an Actor model framework for creating agent-integrated systems. It offers an easy-to-use API for connecting agents with traditional software systems, enabling flexible and scalable architectures. Agency aims to empower developers in creating custom agent-based applications by providing a foundation for experimentation and development. Key features include an intuitive API, performance and scalability through multiprocessing and AMQP support, observability and control with action and lifecycle callbacks, access policies, and detailed logging. The library also includes a demo application with multiple agent examples, OpenAI agent examples, HuggingFace transformers agent example, operating system access, Gradio UI, and Docker configuration for reference and development.
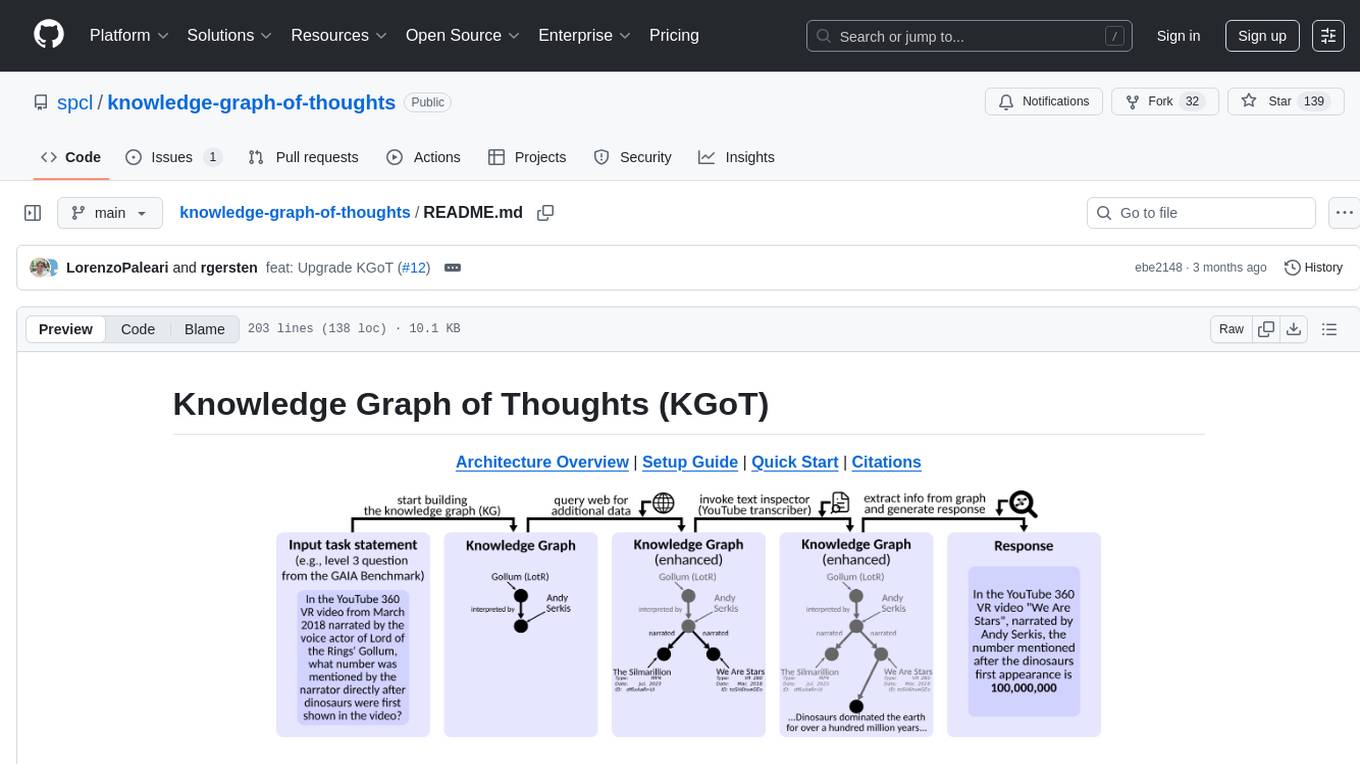
knowledge-graph-of-thoughts
Knowledge Graph of Thoughts (KGoT) is an innovative AI assistant architecture that integrates LLM reasoning with dynamically constructed knowledge graphs (KGs). KGoT extracts and structures task-relevant knowledge into a dynamic KG representation, iteratively enhanced through external tools such as math solvers, web crawlers, and Python scripts. Such structured representation of task-relevant knowledge enables low-cost models to solve complex tasks effectively. The KGoT system consists of three main components: the Controller, the Graph Store, and the Integrated Tools, each playing a critical role in the task-solving process.
aici
The Artificial Intelligence Controller Interface (AICI) lets you build Controllers that constrain and direct output of a Large Language Model (LLM) in real time. Controllers are flexible programs capable of implementing constrained decoding, dynamic editing of prompts and generated text, and coordinating execution across multiple, parallel generations. Controllers incorporate custom logic during the token-by-token decoding and maintain state during an LLM request. This allows diverse Controller strategies, from programmatic or query-based decoding to multi-agent conversations to execute efficiently in tight integration with the LLM itself.
BTGenBot
BTGenBot is a tool that generates behavior trees for robots using lightweight large language models (LLMs) with a maximum of 7 billion parameters. It fine-tunes on a specific dataset, compares multiple LLMs, and evaluates generated behavior trees using various methods. The tool demonstrates the potential of LLMs with a limited number of parameters in creating effective and efficient robot behaviors.
engine-core
Engine Core is a project that demonstrates a pattern for enabling Large Language Models (LLMs) to undertake tasks with a dynamic system prompt and a collection of tool functions known as chat strategies. These strategies allow for the dynamic alteration of chat history, system prompts, and available tools on every run. The project includes example strategies such as demoStrategy, backendStrategy, and shellStrategy. Additionally, LLM integrations like Anthropic or OpenAI have been extracted into adapters to enable running the same app code and strategies while switching foundation models.
BentoDiffusion
BentoDiffusion is a BentoML example project that demonstrates how to serve and deploy diffusion models in the Stable Diffusion (SD) family. These models are specialized in generating and manipulating images based on text prompts. The project provides a guide on using SDXL Turbo as an example, along with instructions on prerequisites, installing dependencies, running the BentoML service, and deploying to BentoCloud. Users can interact with the deployed service using Swagger UI or other methods. Additionally, the project offers the option to choose from various diffusion models available in the repository for deployment.
pgai
pgai simplifies the process of building search and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) AI applications with PostgreSQL. It brings embedding and generation AI models closer to the database, allowing users to create embeddings, retrieve LLM chat completions, reason over data for classification, summarization, and data enrichment directly from within PostgreSQL in a SQL query. The tool requires an OpenAI API key and a PostgreSQL client to enable AI functionality in the database. Users can install pgai from source, run it in a pre-built Docker container, or enable it in a Timescale Cloud service. The tool provides functions to handle API keys using psql or Python, and offers various AI functionalities like tokenizing, detokenizing, embedding, chat completion, and content moderation.
kork
Kork is an experimental Langchain chain that helps build natural language APIs powered by LLMs. It allows assembling a natural language API from python functions, generating a prompt for correct program writing, executing programs safely, and controlling the kind of programs LLMs can generate. The language is limited to variable declarations, function invocations, and arithmetic operations, ensuring predictability and safety in production settings.
AIlice
AIlice is a fully autonomous, general-purpose AI agent that aims to create a standalone artificial intelligence assistant, similar to JARVIS, based on the open-source LLM. AIlice achieves this goal by building a "text computer" that uses a Large Language Model (LLM) as its core processor. Currently, AIlice demonstrates proficiency in a range of tasks, including thematic research, coding, system management, literature reviews, and complex hybrid tasks that go beyond these basic capabilities. AIlice has reached near-perfect performance in everyday tasks using GPT-4 and is making strides towards practical application with the latest open-source models. We will ultimately achieve self-evolution of AI agents. That is, AI agents will autonomously build their own feature expansions and new types of agents, unleashing LLM's knowledge and reasoning capabilities into the real world seamlessly.
ezkl
EZKL is a library and command-line tool for doing inference for deep learning models and other computational graphs in a zk-snark (ZKML). It enables the following workflow: 1. Define a computational graph, for instance a neural network (but really any arbitrary set of operations), as you would normally in pytorch or tensorflow. 2. Export the final graph of operations as an .onnx file and some sample inputs to a .json file. 3. Point ezkl to the .onnx and .json files to generate a ZK-SNARK circuit with which you can prove statements such as: > "I ran this publicly available neural network on some private data and it produced this output" > "I ran my private neural network on some public data and it produced this output" > "I correctly ran this publicly available neural network on some public data and it produced this output" In the backend we use the collaboratively-developed Halo2 as a proof system. The generated proofs can then be verified with much less computational resources, including on-chain (with the Ethereum Virtual Machine), in a browser, or on a device.

ontogpt
OntoGPT is a Python package for extracting structured information from text using large language models, instruction prompts, and ontology-based grounding. It provides a command line interface and a minimal web app for easy usage. The tool has been evaluated on test data and is used in related projects like TALISMAN for gene set analysis. OntoGPT enables users to extract information from text by specifying relevant terms and provides the extracted objects as output.

MegatronApp
MegatronApp is a toolchain built around the Megatron-LM training framework, offering performance tuning, slow-node detection, and training-process visualization. It includes modules like MegaScan for anomaly detection, MegaFBD for forward-backward decoupling, MegaDPP for dynamic pipeline planning, and MegaScope for visualization. The tool aims to enhance large-scale distributed training by providing valuable capabilities and insights.
curategpt
CurateGPT is a prototype web application and framework designed for general purpose AI-guided curation and curation-related operations over collections of objects. It provides functionalities for loading example data, building indexes, interacting with knowledge bases, and performing tasks such as chatting with a knowledge base, querying Pubmed, interacting with a GitHub issue tracker, term autocompletion, and all-by-all comparisons. The tool is built to work best with the OpenAI gpt-4 model and OpenAI ada-text-embedding-002 for embedding, but also supports alternative models through a plugin architecture.
For similar tasks

GhostOS
GhostOS is an AI Agent framework designed to replace JSON Schema with a Turing-complete code interaction interface (Moss Protocol). It aims to create intelligent entities capable of continuous learning and growth through code generation and project management. The framework supports various capabilities such as turning Python files into web agents, real-time voice conversation, body movements control, and emotion expression. GhostOS is still in early experimental development and focuses on out-of-the-box capabilities for AI agents.
MaiBot
MaiBot is an interactive intelligent agent based on a large language model. It aims to be an 'entity' active in QQ group chats, focusing on human-like interactions. It features personification in language style, behavior planning, expression learning, plugin system for unlimited extensions, and emotion expression. The project's design philosophy emphasizes creating a 'life form' in group chats that feels real rather than perfect, with the goal of providing companionship through an AI that makes mistakes and has its own perceptions and thoughts. The code is open-source, but the runtime data of MaiBot is intended to remain closed to maintain its autonomy and conversational nature.
For similar jobs

promptflow
**Prompt flow** is a suite of development tools designed to streamline the end-to-end development cycle of LLM-based AI applications, from ideation, prototyping, testing, evaluation to production deployment and monitoring. It makes prompt engineering much easier and enables you to build LLM apps with production quality.

deepeval
DeepEval is a simple-to-use, open-source LLM evaluation framework specialized for unit testing LLM outputs. It incorporates various metrics such as G-Eval, hallucination, answer relevancy, RAGAS, etc., and runs locally on your machine for evaluation. It provides a wide range of ready-to-use evaluation metrics, allows for creating custom metrics, integrates with any CI/CD environment, and enables benchmarking LLMs on popular benchmarks. DeepEval is designed for evaluating RAG and fine-tuning applications, helping users optimize hyperparameters, prevent prompt drifting, and transition from OpenAI to hosting their own Llama2 with confidence.

MegaDetector
MegaDetector is an AI model that identifies animals, people, and vehicles in camera trap images (which also makes it useful for eliminating blank images). This model is trained on several million images from a variety of ecosystems. MegaDetector is just one of many tools that aims to make conservation biologists more efficient with AI. If you want to learn about other ways to use AI to accelerate camera trap workflows, check out our of the field, affectionately titled "Everything I know about machine learning and camera traps".

leapfrogai
LeapfrogAI is a self-hosted AI platform designed to be deployed in air-gapped resource-constrained environments. It brings sophisticated AI solutions to these environments by hosting all the necessary components of an AI stack, including vector databases, model backends, API, and UI. LeapfrogAI's API closely matches that of OpenAI, allowing tools built for OpenAI/ChatGPT to function seamlessly with a LeapfrogAI backend. It provides several backends for various use cases, including llama-cpp-python, whisper, text-embeddings, and vllm. LeapfrogAI leverages Chainguard's apko to harden base python images, ensuring the latest supported Python versions are used by the other components of the stack. The LeapfrogAI SDK provides a standard set of protobuffs and python utilities for implementing backends and gRPC. LeapfrogAI offers UI options for common use-cases like chat, summarization, and transcription. It can be deployed and run locally via UDS and Kubernetes, built out using Zarf packages. LeapfrogAI is supported by a community of users and contributors, including Defense Unicorns, Beast Code, Chainguard, Exovera, Hypergiant, Pulze, SOSi, United States Navy, United States Air Force, and United States Space Force.

llava-docker
This Docker image for LLaVA (Large Language and Vision Assistant) provides a convenient way to run LLaVA locally or on RunPod. LLaVA is a powerful AI tool that combines natural language processing and computer vision capabilities. With this Docker image, you can easily access LLaVA's functionalities for various tasks, including image captioning, visual question answering, text summarization, and more. The image comes pre-installed with LLaVA v1.2.0, Torch 2.1.2, xformers 0.0.23.post1, and other necessary dependencies. You can customize the model used by setting the MODEL environment variable. The image also includes a Jupyter Lab environment for interactive development and exploration. Overall, this Docker image offers a comprehensive and user-friendly platform for leveraging LLaVA's capabilities.

carrot
The 'carrot' repository on GitHub provides a list of free and user-friendly ChatGPT mirror sites for easy access. The repository includes sponsored sites offering various GPT models and services. Users can find and share sites, report errors, and access stable and recommended sites for ChatGPT usage. The repository also includes a detailed list of ChatGPT sites, their features, and accessibility options, making it a valuable resource for ChatGPT users seeking free and unlimited GPT services.

TrustLLM
TrustLLM is a comprehensive study of trustworthiness in LLMs, including principles for different dimensions of trustworthiness, established benchmark, evaluation, and analysis of trustworthiness for mainstream LLMs, and discussion of open challenges and future directions. Specifically, we first propose a set of principles for trustworthy LLMs that span eight different dimensions. Based on these principles, we further establish a benchmark across six dimensions including truthfulness, safety, fairness, robustness, privacy, and machine ethics. We then present a study evaluating 16 mainstream LLMs in TrustLLM, consisting of over 30 datasets. The document explains how to use the trustllm python package to help you assess the performance of your LLM in trustworthiness more quickly. For more details about TrustLLM, please refer to project website.

AI-YinMei
AI-YinMei is an AI virtual anchor Vtuber development tool (N card version). It supports fastgpt knowledge base chat dialogue, a complete set of solutions for LLM large language models: [fastgpt] + [one-api] + [Xinference], supports docking bilibili live broadcast barrage reply and entering live broadcast welcome speech, supports Microsoft edge-tts speech synthesis, supports Bert-VITS2 speech synthesis, supports GPT-SoVITS speech synthesis, supports expression control Vtuber Studio, supports painting stable-diffusion-webui output OBS live broadcast room, supports painting picture pornography public-NSFW-y-distinguish, supports search and image search service duckduckgo (requires magic Internet access), supports image search service Baidu image search (no magic Internet access), supports AI reply chat box [html plug-in], supports AI singing Auto-Convert-Music, supports playlist [html plug-in], supports dancing function, supports expression video playback, supports head touching action, supports gift smashing action, supports singing automatic start dancing function, chat and singing automatic cycle swing action, supports multi scene switching, background music switching, day and night automatic switching scene, supports open singing and painting, let AI automatically judge the content.

