
HackBot
AI-powered cybersecurity chatbot designed to provide helpful and accurate answers to your cybersecurity-related queries and also do code analysis and scan analysis.
Stars: 232

HackBot is an AI-powered cybersecurity chatbot designed to provide accurate answers to cybersecurity-related queries, conduct code analysis, and scan analysis. It utilizes the Meta-LLama2 AI model through the 'LlamaCpp' library to respond coherently. The chatbot offers features like local AI/Runpod deployment support, cybersecurity chat assistance, interactive interface, clear output presentation, static code analysis, and vulnerability analysis. Users can interact with HackBot through a command-line interface and utilize it for various cybersecurity tasks.
README:
_ _ _ ____ _
| | | | __ _ ___| | _| __ ) ___ | |_
| |_| |/ _` |/ __| |/ / _ \ / _ \| __| By: Morpheuslord
| _ | (_| | (__| <| |_) | (_) | |_ AI used: Meta-LLama2
|_| |_|\__,_|\___|_|\_\____/ \___/ \__|
Welcome to HackBot, an AI-powered cybersecurity chatbot designed to provide helpful and accurate answers to your cybersecurity-related queries and also do code analysis and scan analysis. Whether you are a security researcher, an ethical hacker, or just curious about cybersecurity, HackBot is here to assist you in finding the information you need.
HackBot utilizes the powerful language model Meta-LLama2 through the "LlamaCpp" library. This allows HackBot to respond to your questions in a coherent and relevant manner. Please make sure to keep your queries in English and adhere to the guidelines provided to get the best results from HackBot.
- Local AI/ Runpod Deployment Support: I have added an option using which you can easily deploy the Hackbot chat interface and use llama in 2 ways:
-
Using RunPod: You can use runpod serverless endpoint deployment of llama and connect them to the chatbot by changing the
AI_OPTIONsection of the .env file forRunpod you need to use RUNPODand forLocal Llama deployment LOCALLLAMA.RUNPOD&LOCALLLAMA -
Key Notes: For the runpod version of the llama to work you need to make sure the
RUNPOD IDand yourRUNPOD API KEYare set. - AI Cybersecurity Chat: HackBot can answer various cybersecurity-related queries, helping you with penetration testing, security analysis, and more.
- Interactive Interface: The chatbot provides an interactive command-line interface, making it easy to have conversations with HackBot.
- Clear Output: HackBot presents its responses in a well-formatted markdown, providing easily readable and organized answers.
- Static Code Analysis: Utilizes the provided scan data or log file for conducting static code analysis. It thoroughly examines the source code without executing it, identifying potential vulnerabilities, coding errors, and security issues.
- Vulnerability Analysis: Performs a comprehensive vulnerability analysis using the provided scan data or log file. It identifies and assesses security weaknesses, misconfigurations, and potential exploits present in the target system or network.
Using LLama2 is one of the best offline and free options out there. It is currently under improvement I am working on a prompt that will better incorporate cybersecurity perspective into the AI. I have to thank @thisserand and his llama2_local repo and also his YT video YT_Video. They were great resources. To be frank the llama2 code is 95% his, I just yanked the code and added a Flask API functionality to it.
The Accuracy of the AI offline and outside the codes test was great and had equal accuracy to openai or bard but while in code it was facing a few issues may be because of the prompting and all. I will try and fix it.
The speed depends on your system and the GPU and CPU configs you have. currently, it is using the TheBloke/Llama-2-7B-Chat-GGML model and can be changed via the portscanner and dnsrecon files.
For now, the llama code and scans are handled differently. After a few tests, I found out llama needs to be trained a little to operate like how I intended it to work so it needs some time. Any suggestions on how I can do that can be added to the discussions of this repo Discussions Link. For now, the output won't be a divided list of all the data instead will be an explanation of the vulnerability or issues discovered by the AI.
The prompt for the model usage looks like this:
[INST] <<SYS>> {user_instruction}<</SYS>> NMAP Data to be analyzed: {user_message} [/INST]
The instructions looks like this:
Do a NMAP scan analysis on the provided NMAP scan information. The NMAP output must return in a asked format accorging to the provided output format. The data must be accurate in regards towards a pentest report.
The data must follow the following rules:
1) The NMAP scans must be done from a pentester point of view
2) The final output must be minimal according to the format given.
3) The final output must be kept to a minimal.
4) If a value not found in the scan just mention an empty string.
5) Analyze everything even the smallest of data.
6) Completely analyze the data provided and give a confirm answer using the output format.
7) mention all the data you found in the output format provided so that regex can be used on it.
8) avoid unnecessary explaination.
9) the critical score must be calculated based on the CVE if present or by the nature of the services open
10) the os information must contain the OS used my the target.
11) the open ports must include all the open ports listed in the data[tcp] and varifying if it by checking its states value. you should not negect even one open port.
12) the vulnerable services can be determined via speculation of the service nature or by analyzing the CVE's found.
The output format:
critical score:
- Give info on the criticality
"os information":
- List out the OS information
"open ports and services":
- List open ports
- List open ports services
"vulnerable service":
- Based on CVEs or nature of the ports opened list the vulnerable services
"found cve":
- List the CVE's found and list the main issues.
Using the instruction set and the data provided via the prompt the llama AI generates its output.
For the most usage I suggest you create an runpod serverless endpoit deployment of llama you can refer this tutorial for that tutorial. Follow the tutorial for better use.
Before you proceed with the installation, ensure you have the following prerequisites:
- Python (3.11 or later)
-
pip3package manager -
Visual studio Code- Follow the steps in this link llama-cpp-prereq-install-instructions cmake
git clone https://github.com/morpheuslord/hackbot.git
cd hackbotpip3 install -r requirements.txtpython3 hackbot.pyThe first time you run HackBot, it will check for the AI model required for the chatbot. If the model is not present, it will be automatically downloaded and saved as "llama-2-7b-chat.ggmlv3.q4_0.bin" in the project directory.
To start a conversation with HackBot, run the following command:
The .env file must look like this:
RUNPOD_ENDPOINT_ID = ""
RUNPOD_API_KEY = ""
AI_OPTION = "LLAMALOCAL"After that is done run this.
python hackbot.pyThe .env file must look like this:
RUNPOD_ENDPOINT_ID = "<<SERVERLESS ENDPOINT ID>>"
RUNPOD_API_KEY = "<<RUNPOD API KEY>>"
AI_OPTION = "RUNPOD"After that is done run this.
python3 hackbot.pyHackBot will display a banner and wait for your input. You can ask cybersecurity-related questions, and HackBot will respond with informative answers. To exit the chat, simply type "quit_bot" in the input prompt.
Here are some additional commands you can use:
-
clear_screen: Clears the console screen for better readability. -
quit_bot: This is used to quit the chat application -
bot_banner: Prints the default bots banner. -
contact_dev: Provides my contact information. -
save_chat: Saves the current session interactions. -
vuln_analysis: Does a Vuln analysis using the scan data or log file. -
static_code_analysis: Does a Static code analysis using the scan data or log file.
Note: I am working on more addons and more such commands to give a more chatGPT experience
Please Note: HackBot's responses are based on the Meta-LLama2 AI model, and its accuracy depends on the quality of the queries and data provided to it.
I am also working on AI training by which I can teach it how to be more accurately tuned to work for hackers on a much more professional level.
We welcome contributions to improve HackBot's functionality and accuracy. If you encounter any issues or have suggestions for enhancements, please feel free to open an issue or submit a pull request. Follow these steps to contribute:
- Fork the repository.
- Create a new branch with a descriptive name.
- Make your changes and commit them.
- Push your changes to your forked repository.
- Open a pull request to the
mainbranch of this repository.
Please maintain a clean commit history and adhere to the project's coding guidelines.
If anyone with the know-how of training text generation models can help improve the code. For the AI training part, I have prepared a dataset and a working code for the training but I am facing issues with the training part and collaboration on that will be appreciated. You can view the dataset on :
The Github version of the dataset is for the OpenAI training and the other is for Llama2-7b from meta. The AIM of the dataset is to try and possibly generate an AI model capable enough to better work with CVE data. If you feel the dataset is lacking then feel free to modify and share your views.
For any questions, feedback, or inquiries related to HackBot, feel free to contact the project maintainer:
- Email: [email protected]
- Twitter: @morpheuslord2
- LinkedIn: ChiranjeeviG
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for HackBot
Similar Open Source Tools

HackBot
HackBot is an AI-powered cybersecurity chatbot designed to provide accurate answers to cybersecurity-related queries, conduct code analysis, and scan analysis. It utilizes the Meta-LLama2 AI model through the 'LlamaCpp' library to respond coherently. The chatbot offers features like local AI/Runpod deployment support, cybersecurity chat assistance, interactive interface, clear output presentation, static code analysis, and vulnerability analysis. Users can interact with HackBot through a command-line interface and utilize it for various cybersecurity tasks.
gpt-subtrans
GPT-Subtrans is an open-source subtitle translator that utilizes large language models (LLMs) as translation services. It supports translation between any language pairs that the language model supports. Note that GPT-Subtrans requires an active internet connection, as subtitles are sent to the provider's servers for translation, and their privacy policy applies.
ai-rag-chat-evaluator
This repository contains scripts and tools for evaluating a chat app that uses the RAG architecture. It provides parameters to assess the quality and style of answers generated by the chat app, including system prompt, search parameters, and GPT model parameters. The tools facilitate running evaluations, with examples of evaluations on a sample chat app. The repo also offers guidance on cost estimation, setting up the project, deploying a GPT-4 model, generating ground truth data, running evaluations, and measuring the app's ability to say 'I don't know'. Users can customize evaluations, view results, and compare runs using provided tools.
ai-goat
AI Goat is a tool designed to help users learn about AI security through a series of vulnerable LLM CTF challenges. It allows users to run everything locally on their system without the need for sign-ups or cloud fees. The tool focuses on exploring security risks associated with large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT, providing practical experience for security researchers to understand vulnerabilities and exploitation techniques. AI Goat uses the Vicuna LLM, derived from Meta's LLaMA and ChatGPT's response data, to create challenges that involve prompt injections, insecure output handling, and other LLM security threats. The tool also includes a prebuilt Docker image, ai-base, containing all necessary libraries to run the LLM and challenges, along with an optional CTFd container for challenge management and flag submission.
OlympicArena
OlympicArena is a comprehensive benchmark designed to evaluate advanced AI capabilities across various disciplines. It aims to push AI towards superintelligence by tackling complex challenges in science and beyond. The repository provides detailed data for different disciplines, allows users to run inference and evaluation locally, and offers a submission platform for testing models on the test set. Additionally, it includes an annotation interface and encourages users to cite their paper if they find the code or dataset helpful.
eval-dev-quality
DevQualityEval is an evaluation benchmark and framework designed to compare and improve the quality of code generation of Language Model Models (LLMs). It provides developers with a standardized benchmark to enhance real-world usage in software development and offers users metrics and comparisons to assess the usefulness of LLMs for their tasks. The tool evaluates LLMs' performance in solving software development tasks and measures the quality of their results through a point-based system. Users can run specific tasks, such as test generation, across different programming languages to evaluate LLMs' language understanding and code generation capabilities.
ezkl
EZKL is a library and command-line tool for doing inference for deep learning models and other computational graphs in a zk-snark (ZKML). It enables the following workflow: 1. Define a computational graph, for instance a neural network (but really any arbitrary set of operations), as you would normally in pytorch or tensorflow. 2. Export the final graph of operations as an .onnx file and some sample inputs to a .json file. 3. Point ezkl to the .onnx and .json files to generate a ZK-SNARK circuit with which you can prove statements such as: > "I ran this publicly available neural network on some private data and it produced this output" > "I ran my private neural network on some public data and it produced this output" > "I correctly ran this publicly available neural network on some public data and it produced this output" In the backend we use the collaboratively-developed Halo2 as a proof system. The generated proofs can then be verified with much less computational resources, including on-chain (with the Ethereum Virtual Machine), in a browser, or on a device.
llm-subtrans
LLM-Subtrans is an open source subtitle translator that utilizes LLMs as a translation service. It supports translating subtitles between any language pairs supported by the language model. The application offers multiple subtitle formats support through a pluggable system, including .srt, .ssa/.ass, and .vtt files. Users can choose to use the packaged release for easy usage or install from source for more control over the setup. The tool requires an active internet connection as subtitles are sent to translation service providers' servers for translation.
tribe
Tribe AI is a low code tool designed to rapidly build and coordinate multi-agent teams. It leverages the langgraph framework to customize and coordinate teams of agents, allowing tasks to be split among agents with different strengths for faster and better problem-solving. The tool supports persistent conversations, observability, tool calling, human-in-the-loop functionality, easy deployment with Docker, and multi-tenancy for managing multiple users and teams.
civitai
Civitai is a platform where people can share their stable diffusion models (textual inversions, hypernetworks, aesthetic gradients, VAEs, and any other crazy stuff people do to customize their AI generations), collaborate with others to improve them, and learn from each other's work. The platform allows users to create an account, upload their models, and browse models that have been shared by others. Users can also leave comments and feedback on each other's models to facilitate collaboration and knowledge sharing.
MultiPL-E
MultiPL-E is a system for translating unit test-driven neural code generation benchmarks to new languages. It is part of the BigCode Code Generation LM Harness and allows for evaluating Code LLMs using various benchmarks. The tool supports multiple versions with improvements and new language additions, providing a scalable and polyglot approach to benchmarking neural code generation. Users can access a tutorial for direct usage and explore the dataset of translated prompts on the Hugging Face Hub.

brokk
Brokk is a code assistant designed to understand code semantically, allowing LLMs to work effectively on large codebases. It offers features like agentic search, summarizing related classes, parsing stack traces, adding source for usages, and autonomously fixing errors. Users can interact with Brokk through different panels and commands, enabling them to manipulate context, ask questions, search codebase, run shell commands, and more. Brokk helps with tasks like debugging regressions, exploring codebase, AI-powered refactoring, and working with dependencies. It is particularly useful for making complex, multi-file edits with o1pro.
lovelaice
Lovelaice is an AI-powered assistant for your terminal and editor. It can run bash commands, search the Internet, answer general and technical questions, complete text files, chat casually, execute code in various languages, and more. Lovelaice is configurable with API keys and LLM models, and can be used for a wide range of tasks requiring bash commands or coding assistance. It is designed to be versatile, interactive, and helpful for daily tasks and projects.
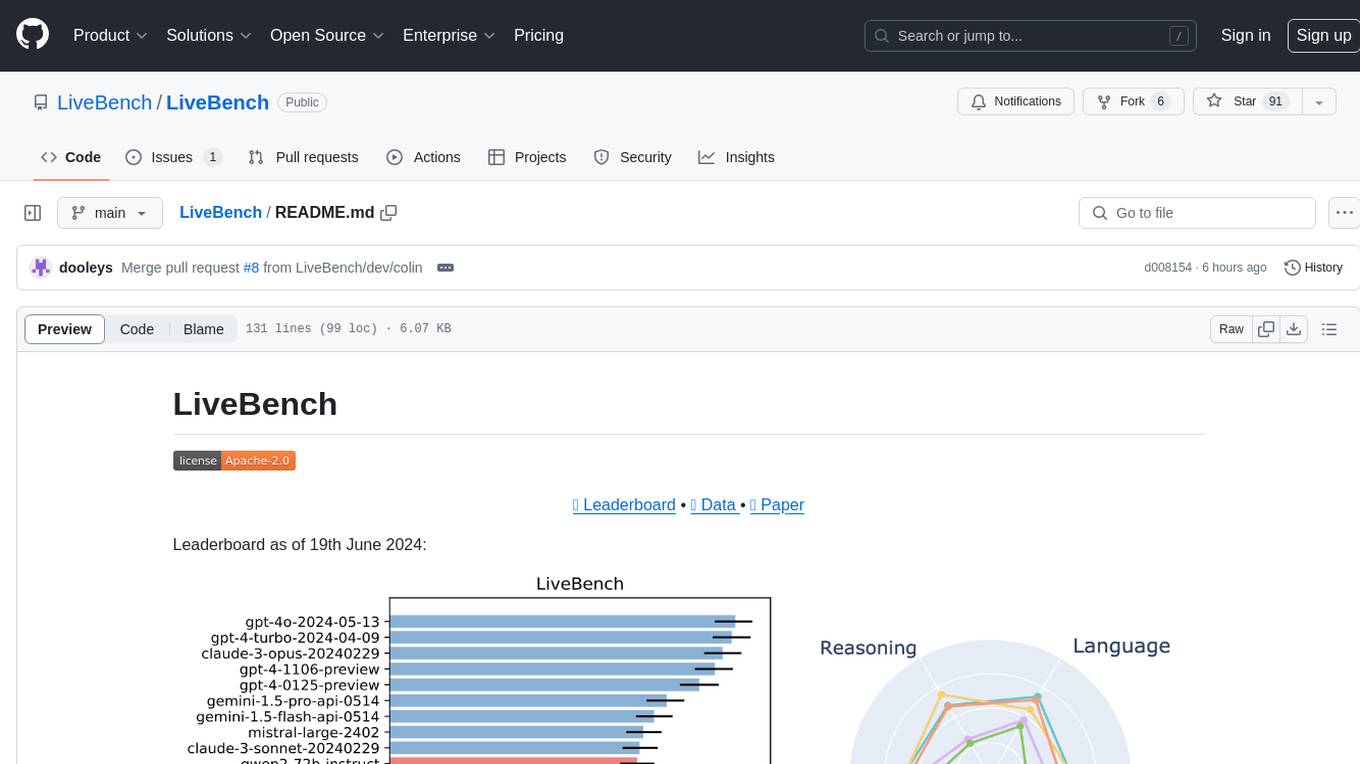
LiveBench
LiveBench is a benchmark tool designed for Language Model Models (LLMs) with a focus on limiting contamination through monthly new questions based on recent datasets, arXiv papers, news articles, and IMDb movie synopses. It provides verifiable, objective ground-truth answers for accurate scoring without an LLM judge. The tool offers 18 diverse tasks across 6 categories and promises to release more challenging tasks over time. LiveBench is built on FastChat's llm_judge module and incorporates code from LiveCodeBench and IFEval.
azure-search-openai-javascript
This sample demonstrates a few approaches for creating ChatGPT-like experiences over your own data using the Retrieval Augmented Generation pattern. It uses Azure OpenAI Service to access the ChatGPT model (gpt-35-turbo), and Azure AI Search for data indexing and retrieval.
ChatGPT-Telegram-Bot
The ChatGPT Telegram Bot is a powerful Telegram bot that utilizes various GPT models, including GPT3.5, GPT4, GPT4 Turbo, GPT4 Vision, DALL·E 3, Groq Mixtral-8x7b/LLaMA2-70b, and Claude2.1/Claude3 opus/sonnet API. It enables users to engage in efficient conversations and information searches on Telegram. The bot supports multiple AI models, online search with DuckDuckGo and Google, user-friendly interface, efficient message processing, document interaction, Markdown rendering, and convenient deployment options like Zeabur, Replit, and Docker. Users can set environment variables for configuration and deployment. The bot also provides Q&A functionality, supports model switching, and can be deployed in group chats with whitelisting. The project is open source under GPLv3 license.
For similar tasks
Academic_LLM_Sec_Papers
Academic_LLM_Sec_Papers is a curated collection of academic papers related to LLM Security Application. The repository includes papers sorted by conference name and published year, covering topics such as large language models for blockchain security, software engineering, machine learning, and more. Developers and researchers are welcome to contribute additional published papers to the list. The repository also provides information on listed conferences and journals related to security, networking, software engineering, and cryptography. The papers cover a wide range of topics including privacy risks, ethical concerns, vulnerabilities, threat modeling, code analysis, fuzzing, and more.

HackBot
HackBot is an AI-powered cybersecurity chatbot designed to provide accurate answers to cybersecurity-related queries, conduct code analysis, and scan analysis. It utilizes the Meta-LLama2 AI model through the 'LlamaCpp' library to respond coherently. The chatbot offers features like local AI/Runpod deployment support, cybersecurity chat assistance, interactive interface, clear output presentation, static code analysis, and vulnerability analysis. Users can interact with HackBot through a command-line interface and utilize it for various cybersecurity tasks.
vulnerability-analysis
The NVIDIA AI Blueprint for Vulnerability Analysis for Container Security showcases accelerated analysis on common vulnerabilities and exposures (CVE) at an enterprise scale, reducing mitigation time from days to seconds. It enables security analysts to determine software package vulnerabilities using large language models (LLMs) and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). The blueprint is designed for security analysts, IT engineers, and AI practitioners in cybersecurity. It requires NVAIE developer license and API keys for vulnerability databases, search engines, and LLM model services. Hardware requirements include L40 GPU for pipeline operation and optional LLM NIM and Embedding NIM. The workflow involves LLM pipeline for CVE impact analysis, utilizing LLM planner, agent, and summarization nodes. The blueprint uses NVIDIA NIM microservices and Morpheus Cybersecurity AI SDK for vulnerability analysis.
Mirror-Flowers
Mirror Flowers is an out-of-the-box code security auditing tool that integrates local static scanning (line-level taint tracking + AST) with AI verification to help quickly discover and locate high-risk issues, providing repair suggestions. It supports multiple languages such as PHP, Python, JavaScript/TypeScript, and Java. The tool offers both single-file and project modes, with features like concurrent acceleration, integrated UI for visual results, and compatibility with multiple OpenAI interface providers. Users can configure the tool through environment variables or API, and can utilize it through a web UI or HTTP API for tasks like single-file auditing or project auditing.
awesome-ai-security
Awesome AI Security is a curated list of frameworks, standards, learning resources, and open source tools related to AI security. It covers a wide range of topics including general reading material, technical material & labs, podcasts, governance frameworks and standards, offensive tools and frameworks, attacking Large Language Models (LLMs), AI for offensive cyber, defensive tools and frameworks, AI for defensive cyber, data security and governance, general AI/ML safety and robustness, MCP security, LLM guardrails, safety and sandboxing for agentic AI tools, detection & scanners, OpenClaw security, privacy and confidentiality, agentic AI skills, models for cybersecurity, and more.
For similar jobs
ciso-assistant-community
CISO Assistant is a tool that helps organizations manage their cybersecurity posture and compliance. It provides a centralized platform for managing security controls, threats, and risks. CISO Assistant also includes a library of pre-built frameworks and tools to help organizations quickly and easily implement best practices.
PurpleLlama
Purple Llama is an umbrella project that aims to provide tools and evaluations to support responsible development and usage of generative AI models. It encompasses components for cybersecurity and input/output safeguards, with plans to expand in the future. The project emphasizes a collaborative approach, borrowing the concept of purple teaming from cybersecurity, to address potential risks and challenges posed by generative AI. Components within Purple Llama are licensed permissively to foster community collaboration and standardize the development of trust and safety tools for generative AI.
vpnfast.github.io
VPNFast is a lightweight and fast VPN service provider that offers secure and private internet access. With VPNFast, users can protect their online privacy, bypass geo-restrictions, and secure their internet connection from hackers and snoopers. The service provides high-speed servers in multiple locations worldwide, ensuring a reliable and seamless VPN experience for users. VPNFast is easy to use, with a user-friendly interface and simple setup process. Whether you're browsing the web, streaming content, or accessing sensitive information, VPNFast helps you stay safe and anonymous online.
taranis-ai
Taranis AI is an advanced Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT) tool that leverages Artificial Intelligence to revolutionize information gathering and situational analysis. It navigates through diverse data sources like websites to collect unstructured news articles, utilizing Natural Language Processing and Artificial Intelligence to enhance content quality. Analysts then refine these AI-augmented articles into structured reports that serve as the foundation for deliverables such as PDF files, which are ultimately published.
NightshadeAntidote
Nightshade Antidote is an image forensics tool used to analyze digital images for signs of manipulation or forgery. It implements several common techniques used in image forensics including metadata analysis, copy-move forgery detection, frequency domain analysis, and JPEG compression artifacts analysis. The tool takes an input image, performs analysis using the above techniques, and outputs a report summarizing the findings.
h4cker
This repository is a comprehensive collection of cybersecurity-related references, scripts, tools, code, and other resources. It is carefully curated and maintained by Omar Santos. The repository serves as a supplemental material provider to several books, video courses, and live training created by Omar Santos. It encompasses over 10,000 references that are instrumental for both offensive and defensive security professionals in honing their skills.
AIMr
AIMr is an AI aimbot tool written in Python that leverages modern technologies to achieve an undetected system with a pleasing appearance. It works on any game that uses human-shaped models. To optimize its performance, users should build OpenCV with CUDA. For Valorant, additional perks in the Discord and an Arduino Leonardo R3 are required.
admyral
Admyral is an open-source Cybersecurity Automation & Investigation Assistant that provides a unified console for investigations and incident handling, workflow automation creation, automatic alert investigation, and next step suggestions for analysts. It aims to tackle alert fatigue and automate security workflows effectively by offering features like workflow actions, AI actions, case management, alert handling, and more. Admyral combines security automation and case management to streamline incident response processes and improve overall security posture. The tool is open-source, transparent, and community-driven, allowing users to self-host, contribute, and collaborate on integrations and features.