
examor
For students, scholars, interviewees and lifelong learners. Let LLMs assist you in learning 🎓
Stars: 1016
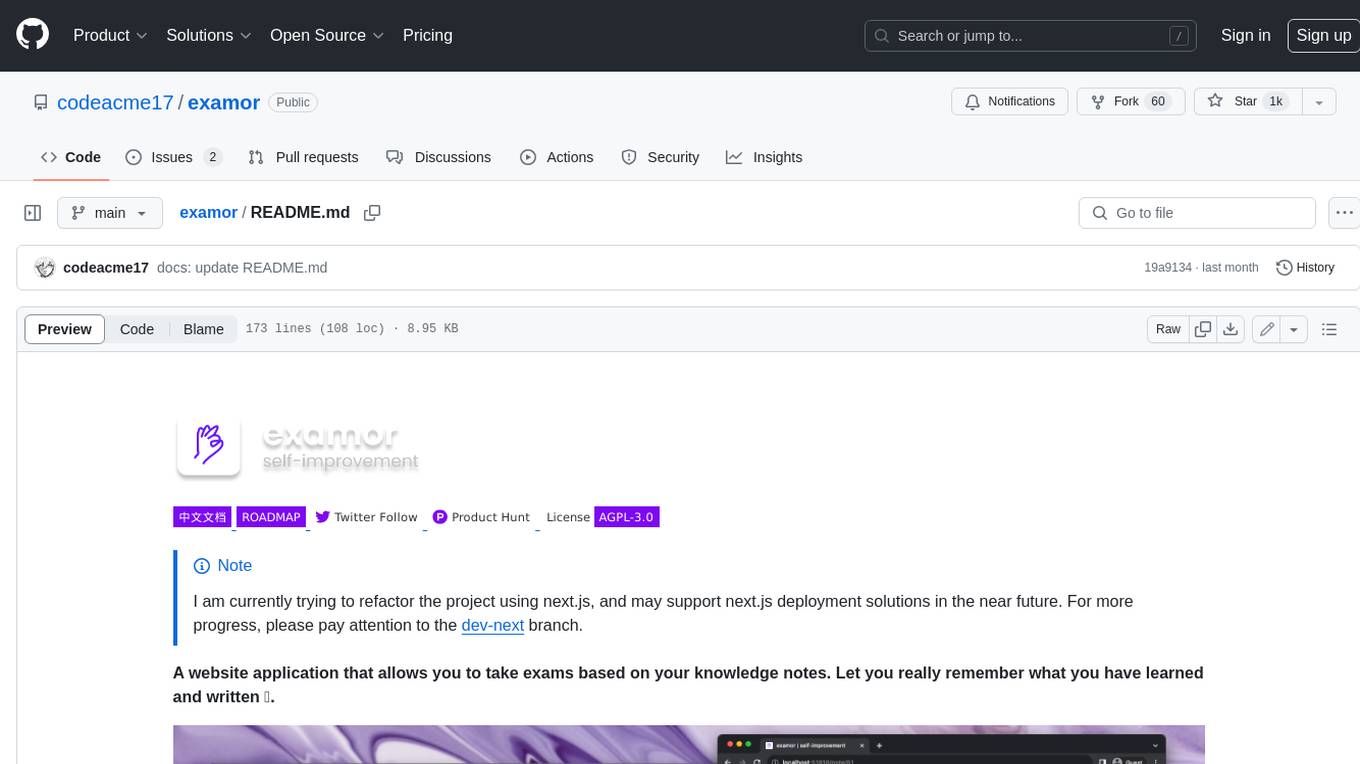
Examor is a website application that allows you to take exams based on your knowledge notes. It helps you to remember what you have learned and written. The application generates a set of questions from the documents you upload, and you can answer them to test your knowledge. Examor also uses GPT to score and validate your answers, and provides you with feedback. The application is still in its early stages of development, but it has the potential to be a valuable tool for learners.
README:
[!NOTE] I am currently trying to refactor the project using next.js, and may support next.js deployment solutions in the near future. For more progress, please pay attention to the dev-next branch.
A website application that allows you to take exams based on your knowledge notes. Let you really remember what you have learned and written 🧠.
For learners, one of the best habits should be regular self-testing - Make It Stick: The Science of Successful Learning
When I'm learning a new technology, I have the habit of taking notes and jotting down important information. It's a good habit, but I also have a bad habit of not enjoying reading the notes I've written (I'm not sure if this is the case for most people 🤔). This results in my notes becoming mere mementos without substantial use. That's why I choose to create an application that continuously prompts you with questions to review your note contents.
[!IMPORTANT] Highly recommend reading Best Documentation Practices before uploading notes to optimize your document.
git clone https://github.com/codeacme17/examor.git
cd examordocker-compose upPlease make sure Docker is installed on your local machine, and ports
51717,51818, and52020are available on your local host
Open http://localhost:51818 in your browser to access Examor. (Due to optimization scheme for modules, it may be slow when loading the program or entering a certain page for the first time)
When users create notes, they can upload associated documents. The application generates a set of questions from these documents, based on their content. These questions will be presented to the users in the future.When creating notes, users can choose the types of questions they want to generate, providing them with a richer learning experience.
After users receive daily questions, they can provide answers. GPT will score, validate, and provide the correct answers. The score is determined by evaluating the correctness of the answers and the linked document (0 ~ 10 points). This score influences the subsequent Ebbinghaus review process.
I've implemented a simplified version of Ebbinghaus memory, currently consisting of only 8 lines of code. I plan to optimize this function further in the future (v0.1).
Regarding the actual function, once GPT generates a test, the score is recorded and affects the future review date. Higher scores result in longer intervals until the next review.
[!NOTE] Recommend to use the GPT-4 model for a stable experience.
Roles can provide more possibilities for question generation and assessment. You can set roles in the configuration page. For more information about various roles, it's recommended to refer to the Role Manual.
Choose the question type when creating notes.
When practicing questions, you can answer using different methods. The image below shows an example of a single-choice question.
In the Question Bank, we've accumulated some high-quality document questions, including outstanding open-source documents and books like the default vue-component and vue-apis. Within this feature module, you can easily import these existing questions into your notes. Furthermore, we warmly welcome you to contribute more high-quality documents or books to enrich our question bank! For detailed contribution guidelines, please see Contributing to the Question Bank.
Notes Management is a module to oversee all uploaded documents. Within this module, you can delete or add new files to your uploaded notes. Note that deleting all documents under a note will clear the associated questions.
Random Question is a module that randomly selects a question from the existing question bank. Implementation of this module enables this feature.
Note is a virtual module generated in your app for each note you create. In this module, you can answer questions. Question pushing is implemented according to the Ebbinghaus memory curve. You will receive three types of question data:
-
Questions for Today's Review: As the name suggests, this data pertains to questions that need review on the current day for questions answered in the past.
-
Expired Questions: These are questions not completed within the required review timeframe on the same day, resulting in this data being collected.
-
New Questions: When the user-defined daily question count is not met from the above two data sets, this supplementary data set is pushed to the user.
Examine is a central module where users answer questions, allowing GPT to score and validate answers. The module comprises three components:
-
Answer: Users enter their answers, and test content can be displayed after submission.
-
Last Record: Records the user's previous answer to the question and the detection outcome.
-
Document Content: This component displays the actual uploaded document content, serving as the basis and final answer for the question.
When starting the project, the application checks for updates. If an update is required, the user will be notified. You can follow these steps to update:
-
Export your notes, questions, or configuration items as a backup through the Export Configuration and Notes button on the personal settings page. This will export a file named
examor-data.xlsx. You can view the file contents, but it's not recommended to modify the file content
-
Pull the latest remote code updates to refresh your local project.
-
Delete the existing Docker container and rebuild the project with the
docker-compose runcommand to incorporate the latest changes. -
Once the build is successful, navigate to the personal settings page, click the Import File button, and re-import the backed-up data into the project.
The current updating process is based on my personal usage. It might not be the best way to update. If you have better update methods, please feel free to provide assistance in the issues section ❤️
Since the project is in a very early stage, there are still many problems and bugs in the project. If you find a bug or have an idea for a new feature, please submit an issue or pull request. See more in CONTRIBUTING.
AGPL-3.0 license © 2023-Present leyoonafr
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for examor
Similar Open Source Tools

examor
Examor is a website application that allows you to take exams based on your knowledge notes. It helps you to remember what you have learned and written. The application generates a set of questions from the documents you upload, and you can answer them to test your knowledge. Examor also uses GPT to score and validate your answers, and provides you with feedback. The application is still in its early stages of development, but it has the potential to be a valuable tool for learners.

HackBot
HackBot is an AI-powered cybersecurity chatbot designed to provide accurate answers to cybersecurity-related queries, conduct code analysis, and scan analysis. It utilizes the Meta-LLama2 AI model through the 'LlamaCpp' library to respond coherently. The chatbot offers features like local AI/Runpod deployment support, cybersecurity chat assistance, interactive interface, clear output presentation, static code analysis, and vulnerability analysis. Users can interact with HackBot through a command-line interface and utilize it for various cybersecurity tasks.
aiid
The Artificial Intelligence Incident Database (AIID) is a collection of incidents involving the development and use of artificial intelligence (AI). The database is designed to help researchers, policymakers, and the public understand the potential risks and benefits of AI, and to inform the development of policies and practices to mitigate the risks and promote the benefits of AI. The AIID is a collaborative project involving researchers from the University of California, Berkeley, the University of Washington, and the University of Toronto.
gptauthor
GPT Author is a command-line tool designed to help users write long form, multi-chapter stories by providing a story prompt and generating a synopsis and subsequent chapters using ChatGPT. Users can review and make changes to the generated content before finalizing the story output in Markdown and HTML formats. The tool aims to unleash storytelling genius by combining human input with AI-generated content, offering a seamless writing experience for creating engaging narratives.
LLocalSearch
LLocalSearch is a completely locally running search aggregator using LLM Agents. The user can ask a question and the system will use a chain of LLMs to find the answer. The user can see the progress of the agents and the final answer. No OpenAI or Google API keys are needed.
ersilia
The Ersilia Model Hub is a unified platform of pre-trained AI/ML models dedicated to infectious and neglected disease research. It offers an open-source, low-code solution that provides seamless access to AI/ML models for drug discovery. Models housed in the hub come from two sources: published models from literature (with due third-party acknowledgment) and custom models developed by the Ersilia team or contributors.
ollama-ebook-summary
The 'ollama-ebook-summary' repository is a Python project that creates bulleted notes summaries of books and long texts, particularly in epub and pdf formats with ToC metadata. It automates the extraction of chapters, splits them into ~2000 token chunks, and allows for asking arbitrary questions to parts of the text for improved granularity of response. The tool aims to provide summaries for each page of a book rather than a one-page summary of the entire document, enhancing content curation and knowledge sharing capabilities.
EdgeChains
EdgeChains is an open-source chain-of-thought engineering framework tailored for Large Language Models (LLMs)- like OpenAI GPT, LLama2, Falcon, etc. - With a focus on enterprise-grade deployability and scalability. EdgeChains is specifically designed to **orchestrate** such applications. At EdgeChains, we take a unique approach to Generative AI - we think Generative AI is a deployment and configuration management challenge rather than a UI and library design pattern challenge. We build on top of a tech that has solved this problem in a different domain - Kubernetes Config Management - and bring that to Generative AI. Edgechains is built on top of jsonnet, originally built by Google based on their experience managing a vast amount of configuration code in the Borg infrastructure.
ai-rag-chat-evaluator
This repository contains scripts and tools for evaluating a chat app that uses the RAG architecture. It provides parameters to assess the quality and style of answers generated by the chat app, including system prompt, search parameters, and GPT model parameters. The tools facilitate running evaluations, with examples of evaluations on a sample chat app. The repo also offers guidance on cost estimation, setting up the project, deploying a GPT-4 model, generating ground truth data, running evaluations, and measuring the app's ability to say 'I don't know'. Users can customize evaluations, view results, and compare runs using provided tools.
tribe
Tribe AI is a low code tool designed to rapidly build and coordinate multi-agent teams. It leverages the langgraph framework to customize and coordinate teams of agents, allowing tasks to be split among agents with different strengths for faster and better problem-solving. The tool supports persistent conversations, observability, tool calling, human-in-the-loop functionality, easy deployment with Docker, and multi-tenancy for managing multiple users and teams.
feedgen
FeedGen is an open-source tool that uses Google Cloud's state-of-the-art Large Language Models (LLMs) to improve product titles, generate more comprehensive descriptions, and fill missing attributes in product feeds. It helps merchants and advertisers surface and fix quality issues in their feeds using Generative AI in a simple and configurable way. The tool relies on GCP's Vertex AI API to provide both zero-shot and few-shot inference capabilities on GCP's foundational LLMs. With few-shot prompting, users can customize the model's responses towards their own data, achieving higher quality and more consistent output. FeedGen is an Apps Script based application that runs as an HTML sidebar in Google Sheets, allowing users to optimize their feeds with ease.
modelbench
ModelBench is a tool for running safety benchmarks against AI models and generating detailed reports. It is part of the MLCommons project and is designed as a proof of concept to aggregate measures, relate them to specific harms, create benchmarks, and produce reports. The tool requires LlamaGuard for evaluating responses and a TogetherAI account for running benchmarks. Users can install ModelBench from GitHub or PyPI, run tests using Poetry, and create benchmarks by providing necessary API keys. The tool generates static HTML pages displaying benchmark scores and allows users to dump raw scores and manage cache for faster runs. ModelBench is aimed at enabling users to test their own models and create tests and benchmarks.
lovelaice
Lovelaice is an AI-powered assistant for your terminal and editor. It can run bash commands, search the Internet, answer general and technical questions, complete text files, chat casually, execute code in various languages, and more. Lovelaice is configurable with API keys and LLM models, and can be used for a wide range of tasks requiring bash commands or coding assistance. It is designed to be versatile, interactive, and helpful for daily tasks and projects.
hi-ml
The Microsoft Health Intelligence Machine Learning Toolbox is a repository that provides low-level and high-level building blocks for Machine Learning / AI researchers and practitioners. It simplifies and streamlines work on deep learning models for healthcare and life sciences by offering tested components such as data loaders, pre-processing tools, deep learning models, and cloud integration utilities. The repository includes two Python packages, 'hi-ml-azure' for helper functions in AzureML, 'hi-ml' for ML components, and 'hi-ml-cpath' for models and workflows related to histopathology images.
PromptAgent
PromptAgent is a repository for a novel automatic prompt optimization method that crafts expert-level prompts using language models. It provides a principled framework for prompt optimization by unifying prompt sampling and rewarding using MCTS algorithm. The tool supports different models like openai, palm, and huggingface models. Users can run PromptAgent to optimize prompts for specific tasks by strategically sampling model errors, generating error feedbacks, simulating future rewards, and searching for high-reward paths leading to expert prompts.
SwiftSage
SwiftSage is a tool designed for conducting experiments in the field of machine learning and artificial intelligence. It provides a platform for researchers and developers to implement and test various algorithms and models. The tool is particularly useful for exploring new ideas and conducting experiments in a controlled environment. SwiftSage aims to streamline the process of developing and testing machine learning models, making it easier for users to iterate on their ideas and achieve better results. With its user-friendly interface and powerful features, SwiftSage is a valuable tool for anyone working in the field of AI and ML.
For similar tasks

examor
Examor is a website application that allows you to take exams based on your knowledge notes. It helps you to remember what you have learned and written. The application generates a set of questions from the documents you upload, and you can answer them to test your knowledge. Examor also uses GPT to score and validate your answers, and provides you with feedback. The application is still in its early stages of development, but it has the potential to be a valuable tool for learners.
uxie
Uxie is a PDF reader app designed to revolutionize the learning experience. It offers features such as annotation, note-taking, collaboration tools, integration with LLM for enhanced learning, and flashcard generation with LLM feedback. Built using Nextjs, tRPC, Zod, TypeScript, Tailwind CSS, React Query, React Hook Form, Supabase, Prisma, and various other tools. Users can take notes, summarize PDFs, chat and collaborate with others, create custom blocks in the editor, and use AI-powered text autocompletion. The tool allows users to craft simple flashcards, test knowledge, answer questions, and receive instant feedback through AI evaluation.
For similar jobs
gpt_academic
GPT Academic is a powerful tool that leverages the capabilities of large language models (LLMs) to enhance academic research and writing. It provides a user-friendly interface that allows researchers, students, and professionals to interact with LLMs and utilize their abilities for various academic tasks. With GPT Academic, users can access a wide range of features and functionalities, including: * **Summarization and Paraphrasing:** GPT Academic can summarize complex texts, articles, and research papers into concise and informative summaries. It can also paraphrase text to improve clarity and readability. * **Question Answering:** Users can ask GPT Academic questions related to their research or studies, and the tool will provide comprehensive and well-informed answers based on its knowledge and understanding of the relevant literature. * **Code Generation and Explanation:** GPT Academic can generate code snippets and provide explanations for complex coding concepts. It can also help debug code and suggest improvements. * **Translation:** GPT Academic supports translation of text between multiple languages, making it a valuable tool for researchers working with international collaborations or accessing resources in different languages. * **Citation and Reference Management:** GPT Academic can help users manage their citations and references by automatically generating citations in various formats and providing suggestions for relevant references based on the user's research topic. * **Collaboration and Note-Taking:** GPT Academic allows users to collaborate on projects and take notes within the tool. They can share their work with others and access a shared workspace for real-time collaboration. * **Customizable Interface:** GPT Academic offers a customizable interface that allows users to tailor the tool to their specific needs and preferences. They can choose from a variety of themes, adjust the layout, and add or remove features to create a personalized workspace. Overall, GPT Academic is a versatile and powerful tool that can significantly enhance the productivity and efficiency of academic research and writing. It empowers users to leverage the capabilities of LLMs and unlock new possibilities for academic exploration and knowledge creation.

examor
Examor is a website application that allows you to take exams based on your knowledge notes. It helps you to remember what you have learned and written. The application generates a set of questions from the documents you upload, and you can answer them to test your knowledge. Examor also uses GPT to score and validate your answers, and provides you with feedback. The application is still in its early stages of development, but it has the potential to be a valuable tool for learners.
nlp-phd-global-equality
This repository aims to promote global equality for individuals pursuing a PhD in NLP by providing resources and information on various aspects of the academic journey. It covers topics such as applying for a PhD, getting research opportunities, preparing for the job market, and succeeding in academia. The repository is actively updated and includes contributions from experts in the field.

wdoc
wdoc is a powerful Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system designed to summarize, search, and query documents across various file types. It aims to handle large volumes of diverse document types, making it ideal for researchers, students, and professionals dealing with extensive information sources. wdoc uses LangChain to process and analyze documents, supporting tens of thousands of documents simultaneously. The system includes features like high recall and specificity, support for various Language Model Models (LLMs), advanced RAG capabilities, advanced document summaries, and support for multiple tasks. It offers markdown-formatted answers and summaries, customizable embeddings, extensive documentation, scriptability, and runtime type checking. wdoc is suitable for power users seeking document querying capabilities and AI-powered document summaries.
open-webui
Open WebUI is an extensible, feature-rich, and user-friendly self-hosted WebUI designed to operate entirely offline. It supports various LLM runners, including Ollama and OpenAI-compatible APIs. For more information, be sure to check out our Open WebUI Documentation.

glide
Glide is a cloud-native LLM gateway that provides a unified REST API for accessing various large language models (LLMs) from different providers. It handles LLMOps tasks such as model failover, caching, key management, and more, making it easy to integrate LLMs into applications. Glide supports popular LLM providers like OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI, AWS Bedrock (Titan), Cohere, Google Gemini, OctoML, and Ollama. It offers high availability, performance, and observability, and provides SDKs for Python and NodeJS to simplify integration.
litgpt
LitGPT is a command-line tool designed to easily finetune, pretrain, evaluate, and deploy 20+ LLMs **on your own data**. It features highly-optimized training recipes for the world's most powerful open-source large-language-models (LLMs).

khoj
Khoj is an open-source, personal AI assistant that extends your capabilities by creating always-available AI agents. You can share your notes and documents to extend your digital brain, and your AI agents have access to the internet, allowing you to incorporate real-time information. Khoj is accessible on Desktop, Emacs, Obsidian, Web, and Whatsapp, and you can share PDF, markdown, org-mode, notion files, and GitHub repositories. You'll get fast, accurate semantic search on top of your docs, and your agents can create deeply personal images and understand your speech. Khoj is self-hostable and always will be.




