
AppAgent
AppAgent: Multimodal Agents as Smartphone Users, an LLM-based multimodal agent framework designed to operate smartphone apps.
Stars: 4688
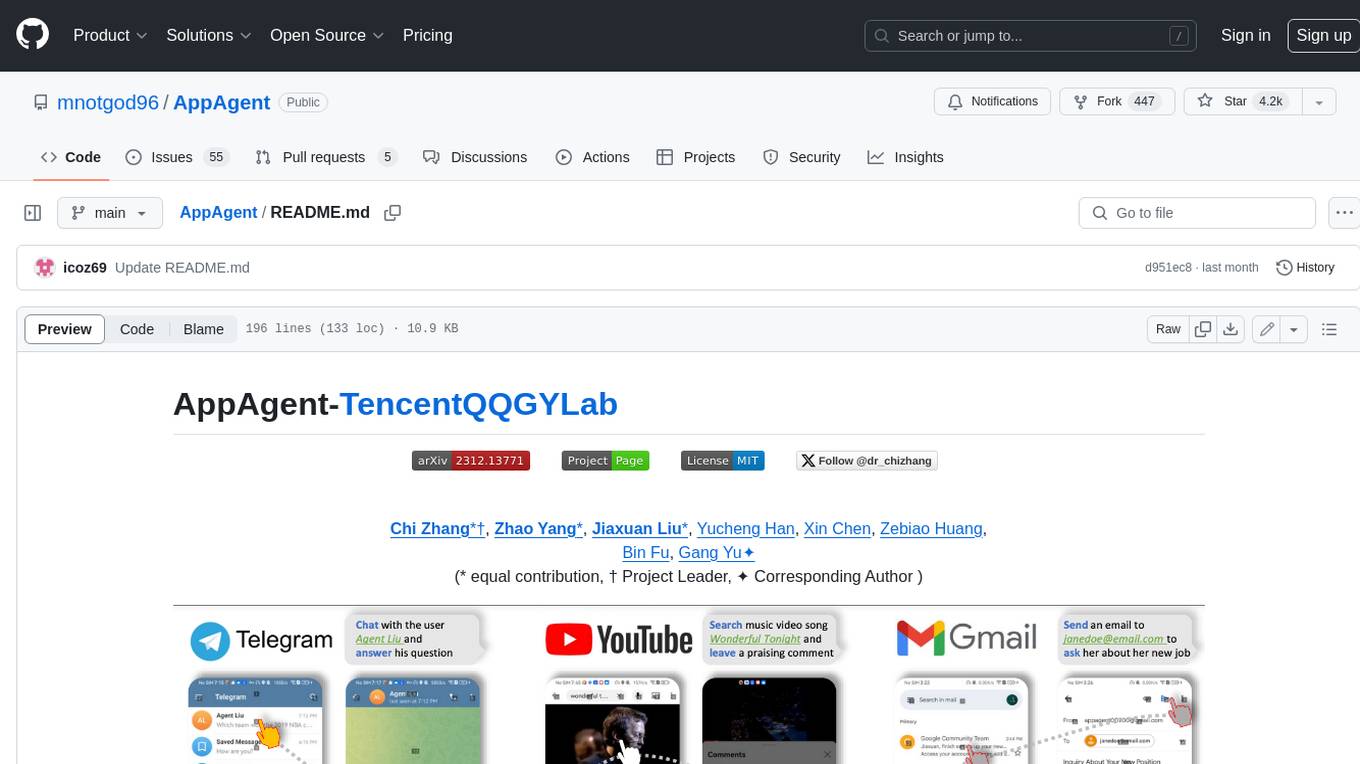
AppAgent is a novel LLM-based multimodal agent framework designed to operate smartphone applications. Our framework enables the agent to operate smartphone applications through a simplified action space, mimicking human-like interactions such as tapping and swiping. This novel approach bypasses the need for system back-end access, thereby broadening its applicability across diverse apps. Central to our agent's functionality is its innovative learning method. The agent learns to navigate and use new apps either through autonomous exploration or by observing human demonstrations. This process generates a knowledge base that the agent refers to for executing complex tasks across different applications.
README:
AppAgent-TencentQQGYLab
Chi Zhang*†, Zhao Yang*, Jiaxuan Liu*, Yucheng Han, Xin Chen, Zebiao Huang,
Bin Fu, Gang Yu✦
(* equal contribution, † Project Leader, ✦ Corresponding Author )
ℹ️Should you encounter any issues
ℹ️This project will be synchronously updated on the official TencentQQGYLab Github Page.
-
[2024.2.8]: Added
qwen-vl-max(通义千问-VL) as an alternative multi-modal model. The model is currently free to use but has a relatively poorer performance compared with GPT-4V. - [2024.1.31]: Released the evaluation benchmark used during our testing of AppAgent
- [2024.1.2]: 🔥Added an optional method for the agent to bring up a grid overlay on the screen to tap/swipe anywhere on the screen.
- [2023.12.26]: Added Tips section for better use experience; added instruction for using the Android Studio emulator for users who do not have Android devices.
- [2023.12.21]: 🔥🔥 Open-sourced the git repository, including the detailed configuration steps to implement our AppAgent!
We introduce a novel LLM-based multimodal agent framework designed to operate smartphone applications.
Our framework enables the agent to operate smartphone applications through a simplified action space, mimicking human-like interactions such as tapping and swiping. This novel approach bypasses the need for system back-end access, thereby broadening its applicability across diverse apps.
Central to our agent's functionality is its innovative learning method. The agent learns to navigate and use new apps either through autonomous exploration or by observing human demonstrations. This process generates a knowledge base that the agent refers to for executing complex tasks across different applications.
The demo video shows the process of using AppAgent to follow a user on X (Twitter) in the deployment phase.
https://github.com/mnotgod96/AppAgent/assets/40715314/db99d650-dec1-4531-b4b2-e085bfcadfb7
An interesting experiment showing AppAgent's ability to pass CAPTCHA.
https://github.com/mnotgod96/AppAgent/assets/27103154/5cc7ba50-dbab-42a0-a411-a9a862482548
An example of using the grid overlay to locate a UI element that is not labeled with a numeric tag.
https://github.com/mnotgod96/AppAgent/assets/27103154/71603333-274c-46ed-8381-2f9a34cdfc53
This section will guide you on how to quickly use gpt-4-vision-preview (or qwen-vl-max) as an agent to complete specific tasks for you on
your Android app.
-
On your PC, download and install Android Debug Bridge (adb) which is a command-line tool that lets you communicate with your Android device from the PC.
-
Get an Android device and enable the USB debugging that can be found in Developer Options in Settings.
-
Connect your device to your PC using a USB cable.
-
(Optional) If you do not have an Android device but still want to try AppAgent. We recommend you download Android Studio and use the emulator that comes with it. The emulator can be found in the device manager of Android Studio. You can install apps on an emulator by downloading APK files from the internet and dragging them to the emulator. AppAgent can detect the emulated device and operate apps on it just like operating a real device.
-
Clone this repo and install the dependencies. All scripts in this project are written in Python 3 so make sure you have installed it.
cd AppAgent
pip install -r requirements.txtAppAgent needs to be powered by a multi-modal model which can receive both text and visual inputs. During our experiment
, we used gpt-4-vision-preview as the model to make decisions on how to take actions to complete a task on the smartphone.
To configure your requests to GPT-4V, you should modify config.yaml in the root directory.
There are two key parameters that must be configured to try AppAgent:
- OpenAI API key: you must purchase an eligible API key from OpenAI so that you can have access to GPT-4V.
- Request interval: this is the time interval in seconds between consecutive GPT-4V requests to control the frequency of your requests to GPT-4V. Adjust this value according to the status of your account.
Other parameters in config.yaml are well commented. Modify them as you need.
Be aware that GPT-4V is not free. Each request/response pair involved in this project costs around $0.03. Use it wisely.
You can also try qwen-vl-max (通义千问-VL) as the alternative multi-modal model to power the AppAgent. The model is currently
free to use but its performance in the context of AppAgent is poorer compared with GPT-4V.
To use it, you should create an Alibaba Cloud account and create a Dashscope API key to fill in the DASHSCOPE_API_KEY field
in the config.yaml file. Change the MODEL field from OpenAI to Qwen as well.
If you want to test AppAgent using your own models, you should write a new model class in scripts/model.py accordingly.
Our paper proposed a novel solution that involves two phases, exploration, and deployment, to turn GPT-4V into a capable agent that can help users operate their Android phones when a task is given. The exploration phase starts with a task given by you, and you can choose to let the agent either explore the app on its own or learn from your demonstration. In both cases, the agent generates documentation for elements interacted during the exploration/demonstration and saves them for use in the deployment phase.
This solution features a fully autonomous exploration which allows the agent to explore the use of the app by attempting the given task without any intervention from humans.
To start, run learn.py in the root directory. Follow the prompted instructions to select autonomous exploration
as the operating mode and provide the app name and task description. Then, your agent will do the job for you. Under
this mode, AppAgent will reflect on its previous action making sure its action adheres to the given task and generate
documentation for the elements explored.
python learn.pyThis solution requires users to demonstrate a similar task first. AppAgent will learn from the demo and generate documentations for UI elements seen during the demo.
To start human demonstration, you should run learn.py in the root directory. Follow the prompted instructions to select
human demonstration as the operating mode and provide the app name and task description. A screenshot of your phone
will be captured and all interactive elements shown on the screen will be labeled with numeric tags. You need to follow
the prompts to determine your next action and the target of the action. When you believe the demonstration is finished,
type stop to end the demo.
python learn.pyAfter the exploration phase finishes, you can run run.py in the root directory. Follow the prompted instructions to enter
the name of the app, select the appropriate documentation base you want the agent to use and provide the task
description. Then, your agent will do the job for you. The agent will automatically detect if there is documentation
base generated before for the app; if there is no documentation found, you can also choose to run the agent without any
documentation (success rate not guaranteed).
python run.py- For an improved experience, you might permit AppAgent to undertake a broader range of tasks through autonomous exploration, or you can directly demonstrate more app functions to enhance the app documentation. Generally, the more extensive the documentation provided to the agent, the higher the likelihood of successful task completion.
- It is always a good practice to inspect the documentation generated by the agent. When you find some documentation not accurately describe the function of the element, manually revising the documentation is also an option.
Please refer to evaluation benchmark.
- [ ] Incorporate more LLM APIs into the project.
- [x] Open source the Benchmark.
- [x] Open source the configuration.
@misc{yang2023appagent,
title={AppAgent: Multimodal Agents as Smartphone Users},
author={Chi Zhang and Zhao Yang and Jiaxuan Liu and Yucheng Han and Xin Chen and Zebiao Huang and Bin Fu and Gang Yu},
year={2023},
eprint={2312.13771},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV}
}The MIT license.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for AppAgent
Similar Open Source Tools

AppAgent
AppAgent is a novel LLM-based multimodal agent framework designed to operate smartphone applications. Our framework enables the agent to operate smartphone applications through a simplified action space, mimicking human-like interactions such as tapping and swiping. This novel approach bypasses the need for system back-end access, thereby broadening its applicability across diverse apps. Central to our agent's functionality is its innovative learning method. The agent learns to navigate and use new apps either through autonomous exploration or by observing human demonstrations. This process generates a knowledge base that the agent refers to for executing complex tasks across different applications.
lumigator
Lumigator is an open-source platform developed by Mozilla.ai to help users select the most suitable language model for their specific needs. It supports the evaluation of summarization tasks using sequence-to-sequence models such as BART and BERT, as well as causal models like GPT and Mistral. The platform aims to make model selection transparent, efficient, and empowering by providing a framework for comparing LLMs using task-specific metrics to evaluate how well a model fits a project's needs. Lumigator is in the early stages of development and plans to expand support to additional machine learning tasks and use cases in the future.
sorcery
Sorcery is a SillyTavern extension that allows AI characters to interact with the real world by executing user-defined scripts at specific events in the chat. It is easy to use and does not require a specially trained function calling model. Sorcery can be used to control smart home appliances, interact with virtual characters, and perform various tasks in the chat environment. It works by injecting instructions into the system prompt and intercepting markers to run associated scripts, providing a seamless user experience.
reverse-engineering-assistant
ReVA (Reverse Engineering Assistant) is a project aimed at building a disassembler agnostic AI assistant for reverse engineering tasks. It utilizes a tool-driven approach, providing small tools to the user to empower them in completing complex tasks. The assistant is designed to accept various inputs, guide the user in correcting mistakes, and provide additional context to encourage exploration. Users can ask questions, perform tasks like decompilation, class diagram generation, variable renaming, and more. ReVA supports different language models for online and local inference, with easy configuration options. The workflow involves opening the RE tool and program, then starting a chat session to interact with the assistant. Installation includes setting up the Python component, running the chat tool, and configuring the Ghidra extension for seamless integration. ReVA aims to enhance the reverse engineering process by breaking down actions into small parts, including the user's thoughts in the output, and providing support for monitoring and adjusting prompts.
LaVague
LaVague is an open-source Large Action Model framework that uses advanced AI techniques to compile natural language instructions into browser automation code. It leverages Selenium or Playwright for browser actions. Users can interact with LaVague through an interactive Gradio interface to automate web interactions. The tool requires an OpenAI API key for default examples and offers a Playwright integration guide. Contributors can help by working on outlined tasks, submitting PRs, and engaging with the community on Discord. The project roadmap is available to track progress, but users should exercise caution when executing LLM-generated code using 'exec'.
ezkl
EZKL is a library and command-line tool for doing inference for deep learning models and other computational graphs in a zk-snark (ZKML). It enables the following workflow: 1. Define a computational graph, for instance a neural network (but really any arbitrary set of operations), as you would normally in pytorch or tensorflow. 2. Export the final graph of operations as an .onnx file and some sample inputs to a .json file. 3. Point ezkl to the .onnx and .json files to generate a ZK-SNARK circuit with which you can prove statements such as: > "I ran this publicly available neural network on some private data and it produced this output" > "I ran my private neural network on some public data and it produced this output" > "I correctly ran this publicly available neural network on some public data and it produced this output" In the backend we use the collaboratively-developed Halo2 as a proof system. The generated proofs can then be verified with much less computational resources, including on-chain (with the Ethereum Virtual Machine), in a browser, or on a device.
LLMonFHIR
LLMonFHIR is an iOS application that utilizes large language models (LLMs) to interpret and provide context around patient data in the Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) format. It connects to the OpenAI GPT API to analyze FHIR resources, supports multiple languages, and allows users to interact with their health data stored in the Apple Health app. The app aims to simplify complex health records, provide insights, and facilitate deeper understanding through a conversational interface. However, it is an experimental app for informational purposes only and should not be used as a substitute for professional medical advice. Users are advised to verify information provided by AI models and consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice.
quimera
Quimera is an exploit-generator tool that utilizes large language models (LLMs) to uncover smart contract exploits in Foundry. It follows steps such as obtaining the smart contract's source code, creating a prompt for the exploit goal, generating or enhancing a Foundry test case, running the test, and analyzing the transaction trace for profitability. The tool is currently in an experimental prototype stage, focusing on optimizing settings, prompt creation, and exploring its capabilities. It has successfully rediscovered known exploits like APEMAGA, VISOR, FIRE, XAI, and Thunder-Loan using Gemini Pro 2.5 06-05.
CustomSuggestionServiceForCopilotForXcode
This repository provides a custom suggestion service for Copilot for Xcode, allowing users to enhance code suggestions using chat models. It supports different suggestion services and strategies for generating code suggestions. Users can customize prompt formats and utilize local models for code completion.
WilmerAI
WilmerAI is a middleware system designed to process prompts before sending them to Large Language Models (LLMs). It categorizes prompts, routes them to appropriate workflows, and generates manageable prompts for local models. It acts as an intermediary between the user interface and LLM APIs, supporting multiple backend LLMs simultaneously. WilmerAI provides API endpoints compatible with OpenAI API, supports prompt templates, and offers flexible connections to various LLM APIs. The project is under heavy development and may contain bugs or incomplete code.
mahilo
Mahilo is a flexible framework for creating multi-agent systems that can interact with humans while sharing context internally. It allows developers to set up complex agent networks for various applications, from customer service to emergency response simulations. Agents can communicate with each other and with humans, making the system efficient by handling context from multiple agents and helping humans stay focused on specific problems. The system supports Realtime API for voice interactions, WebSocket-based communication, flexible communication patterns, session management, and easy agent definition.
SalesGPT
SalesGPT is an open-source AI agent designed for sales, utilizing context-awareness and LLMs to work across various communication channels like voice, email, and texting. It aims to enhance sales conversations by understanding the stage of the conversation and providing tools like product knowledge base to reduce errors. The agent can autonomously generate payment links, handle objections, and close sales. It also offers features like automated email communication, meeting scheduling, and integration with various LLMs for customization. SalesGPT is optimized for low latency in voice channels and ensures human supervision where necessary. The tool provides enterprise-grade security and supports LangSmith tracing for monitoring and evaluation of intelligent agents built on LLM frameworks.
wandb
Weights & Biases (W&B) is a platform that helps users build better machine learning models faster by tracking and visualizing all components of the machine learning pipeline, from datasets to production models. It offers tools for tracking, debugging, evaluating, and monitoring machine learning applications. W&B provides integrations with popular frameworks like PyTorch, TensorFlow/Keras, Hugging Face Transformers, PyTorch Lightning, XGBoost, and Sci-Kit Learn. Users can easily log metrics, visualize performance, and compare experiments using W&B. The platform also supports hosting options in the cloud or on private infrastructure, making it versatile for various deployment needs.
atomic_agents
Atomic Agents is a modular and extensible framework designed for creating powerful applications. It follows the principles of Atomic Design, emphasizing small and single-purpose components. Leveraging Pydantic for data validation and serialization, the framework offers a set of tools and agents that can be combined to build AI applications. It depends on the Instructor package and supports various APIs like OpenAI, Cohere, Anthropic, and Gemini. Atomic Agents is suitable for developers looking to create AI agents with a focus on modularity and flexibility.
llama-on-lambda
This project provides a proof of concept for deploying a scalable, serverless LLM Generative AI inference engine on AWS Lambda. It leverages the llama.cpp project to enable the usage of more accessible CPU and RAM configurations instead of limited and expensive GPU capabilities. By deploying a container with the llama.cpp converted models onto AWS Lambda, this project offers the advantages of scale, minimizing cost, and maximizing compute availability. The project includes AWS CDK code to create and deploy a Lambda function leveraging your model of choice, with a FastAPI frontend accessible from a Lambda URL. It is important to note that you will need ggml quantized versions of your model and model sizes under 6GB, as your inference RAM requirements cannot exceed 9GB or your Lambda function will fail.
DistiLlama
DistiLlama is a Chrome extension that leverages a locally running Large Language Model (LLM) to perform various tasks, including text summarization, chat, and document analysis. It utilizes Ollama as the locally running LLM instance and LangChain for text summarization. DistiLlama provides a user-friendly interface for interacting with the LLM, allowing users to summarize web pages, chat with documents (including PDFs), and engage in text-based conversations. The extension is easy to install and use, requiring only the installation of Ollama and a few simple steps to set up the environment. DistiLlama offers a range of customization options, including the choice of LLM model and the ability to configure the summarization chain. It also supports multimodal capabilities, allowing users to interact with the LLM through text, voice, and images. DistiLlama is a valuable tool for researchers, students, and professionals who seek to leverage the power of LLMs for various tasks without compromising data privacy.
For similar tasks

AppAgent
AppAgent is a novel LLM-based multimodal agent framework designed to operate smartphone applications. Our framework enables the agent to operate smartphone applications through a simplified action space, mimicking human-like interactions such as tapping and swiping. This novel approach bypasses the need for system back-end access, thereby broadening its applicability across diverse apps. Central to our agent's functionality is its innovative learning method. The agent learns to navigate and use new apps either through autonomous exploration or by observing human demonstrations. This process generates a knowledge base that the agent refers to for executing complex tasks across different applications.
For similar jobs

AppAgent
AppAgent is a novel LLM-based multimodal agent framework designed to operate smartphone applications. Our framework enables the agent to operate smartphone applications through a simplified action space, mimicking human-like interactions such as tapping and swiping. This novel approach bypasses the need for system back-end access, thereby broadening its applicability across diverse apps. Central to our agent's functionality is its innovative learning method. The agent learns to navigate and use new apps either through autonomous exploration or by observing human demonstrations. This process generates a knowledge base that the agent refers to for executing complex tasks across different applications.

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.
ChatFAQ
ChatFAQ is an open-source comprehensive platform for creating a wide variety of chatbots: generic ones, business-trained, or even capable of redirecting requests to human operators. It includes a specialized NLP/NLG engine based on a RAG architecture and customized chat widgets, ensuring a tailored experience for users and avoiding vendor lock-in.

agentcloud
AgentCloud is an open-source platform that enables companies to build and deploy private LLM chat apps, empowering teams to securely interact with their data. It comprises three main components: Agent Backend, Webapp, and Vector Proxy. To run this project locally, clone the repository, install Docker, and start the services. The project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 only. Contributions and feedback are welcome from the community.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.
autogen
AutoGen is a framework that enables the development of LLM applications using multiple agents that can converse with each other to solve tasks. AutoGen agents are customizable, conversable, and seamlessly allow human participation. They can operate in various modes that employ combinations of LLMs, human inputs, and tools.
llama-recipes
The llama-recipes repository provides a scalable library for fine-tuning Llama 2, along with example scripts and notebooks to quickly get started with using the Llama 2 models in a variety of use-cases, including fine-tuning for domain adaptation and building LLM-based applications with Llama 2 and other tools in the LLM ecosystem. The examples here showcase how to run Llama 2 locally, in the cloud, and on-prem.





