
nobodywho
NobodyWho is an inference engine that lets you run LLMs locally and efficiently on any device.
Stars: 700
NobodyWho is a plugin for the Godot game engine that enables interaction with local LLMs for interactive storytelling. Users can install it from Godot editor or GitHub releases page, providing their own LLM in GGUF format. The plugin consists of `NobodyWhoModel` node for model file, `NobodyWhoChat` node for chat interaction, and `NobodyWhoEmbedding` node for generating embeddings. It offers a programming interface for sending text to LLM, receiving responses, and starting the LLM worker.
README:
NobodyWho is a library that lets you run LLMs locally and efficiently on any device.
We currently support Python and Godot, with more integrations on the way.
- 🏃 Run any LLM locally, offline, for free
- ⚒️ Fast, simple tool calling - just pass a normal function
- 👌 Guaranteed perfect tool calling every time, automatically derives a grammar from your function signature
- 🗨️ Conversation-aware preemptive context shifting, for lobotomy-free conversations of infinite length
- 💻 Ship optimized native code for multiple platforms: Windows, Linux, macOS, Android
- ⚡ Super fast inference on GPU powered by Vulkan or Metal
- 🤖 Compatible with thousands of pre-trained LLMs - use any LLM in the GGUF format
- 🦙 Powered by the wonderful llama.cpp
Start by installing NobodyWho. This is simply
pip install nobodywhoNext download a model. For a quick start we recommend this one. It is quite small, but will get the job done.
Then you start generating a response from the model with the following code snippet:
from nobodywho import Chat
chat = Chat("./path/to/your/model.gguf")
response = chat.ask("Is water wet?")
for token in response:
print(token, end="", flush=True)If you want to block and wait for the complete response as a string, you can use .completed():
full_response = chat.ask("Is water wet?").completed()You can also setup a basic interactive chatbot very quickly with the code snippet below:
from nobodywho import Chat, TokenStream
chat = Chat("./path/to/your/model.gguf")
while True:
prompt = input("Enter your prompt: ")
response: TokenStream = chat.ask(prompt)
for token in response:
print(token, end="", flush=True)
print()Once you have a chat up and running you will likely want to give it access to tools. This is very easy in NobodyWho:
import math
from nobodywho import tool, Chat
@tool(description="Calculates the area of a circle given its radius")
def circle_area(radius: float) -> str:
area = math.pi * radius ** 2
return f"Circle with radius {radius} has area {area:.2f}"
chat = Chat("./path/to/your/model.gguf", tools=[circle_area])Adding tools to your chat like above will automatically make these available to the model. There plenty of things you can do with tools and many of these are coverend in our docs.
You can install it from inside the Godot editor: In Godot 4.5+, go to AssetLib and search for "NobodyWho".
...or you can grab a specific version from our github releases page. You can install these zip files by going to the "AssetLib" tab in Godot and selecting "Import".
Make sure that the ignore asset root option is set in the import dialogue.
For further instructions on how to setup NobodyWho in Godot please refer to our docs.
The documentation has everything you might want to know: https://docs.nobodywho.ooo/
- ⭐ Star the repo and spread the word about NobodyWho!
- Join our Discord or Matrix communities
- Found a bug? Open an issue!
- Submit your own PR - contributions welcome
- Help improve docs or write tutorials
Currently only Linux, MacOS, Android and Windows are supported platforms.
iOS exports seem very feasible. See issue #114
Web exports will be a bit trickier to get right. See issue #111.
There has been some confusion about the licensing terms of NobodyWho. To clarify:
Linking two programs or linking an existing software with your own work does not – at least under European law – produce a derivative or extend the coverage of the linked software licence to your own work. [1]
You are allowed to use this plugin in proprietary and commercial projects, free of charge.
If you distribute modified versions of the code in this repo, you must open source those changes.
Feel free to make proprietary projects using NobodyWho, but don't make a proprietary fork of NobodyWho.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for nobodywho
Similar Open Source Tools

nobodywho
NobodyWho is a plugin for the Godot game engine that enables interaction with local LLMs for interactive storytelling. Users can install it from Godot editor or GitHub releases page, providing their own LLM in GGUF format. The plugin consists of `NobodyWhoModel` node for model file, `NobodyWhoChat` node for chat interaction, and `NobodyWhoEmbedding` node for generating embeddings. It offers a programming interface for sending text to LLM, receiving responses, and starting the LLM worker.
MaiBot
MaiBot is an intelligent QQ group chat bot based on a large language model. It is developed using the nonebot2 framework, with LLM providing conversation abilities, MongoDB for data persistence support, and NapCat as the QQ protocol endpoint support. The project is in active development stage, with features like chat functionality, emoji functionality, schedule management, memory function, knowledge base function, and relationship function planned for future updates. The project aims to create a 'life form' active in QQ group chats, focusing on companionship and creating a more human-like presence rather than a perfect assistant. The application generates content from AI models, so users are advised to discern carefully and not use it for illegal purposes.
lite.koboldai.net
KoboldAI Lite is a standalone Web UI that serves as a text editor designed for use with generative LLMs. It is compatible with KoboldAI United and KoboldAI Client, bundled with KoboldCPP, and integrates with the AI Horde for text and image generation. The UI offers multiple modes for different writing styles, supports various file formats, includes premade scenarios, and allows easy sharing of stories. Users can enjoy features such as memory, undo/redo, text-to-speech, and a range of samplers and configurations. The tool is mobile-friendly and can be used directly from a browser without any setup or installation.
OllamaSharp
OllamaSharp is a .NET binding for the Ollama API, providing an intuitive API client to interact with Ollama. It offers support for all Ollama API endpoints, real-time streaming, progress reporting, and an API console for remote management. Users can easily set up the client, list models, pull models with progress feedback, stream completions, and build interactive chats. The project includes a demo console for exploring and managing the Ollama host.
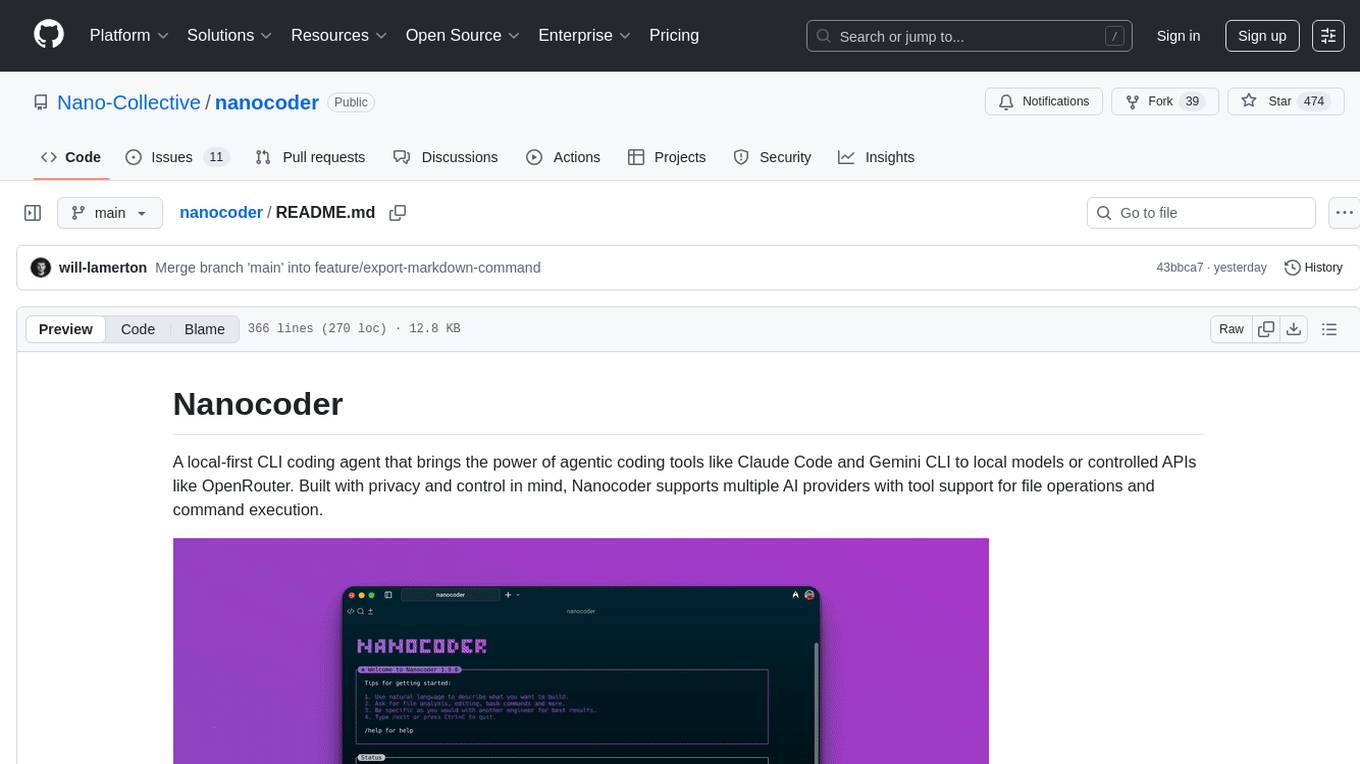
nanocoder
Nanocoder is a versatile code editor designed for beginners and experienced programmers alike. It provides a user-friendly interface with features such as syntax highlighting, code completion, and error checking. With Nanocoder, you can easily write and debug code in various programming languages, making it an ideal tool for learning, practicing, and developing software projects. Whether you are a student, hobbyist, or professional developer, Nanocoder offers a seamless coding experience to boost your productivity and creativity.
mdream
Mdream is a lightweight and user-friendly markdown editor designed for developers and writers. It provides a simple and intuitive interface for creating and editing markdown files with real-time preview. The tool offers syntax highlighting, markdown formatting options, and the ability to export files in various formats. Mdream aims to streamline the writing process and enhance productivity for individuals working with markdown documents.
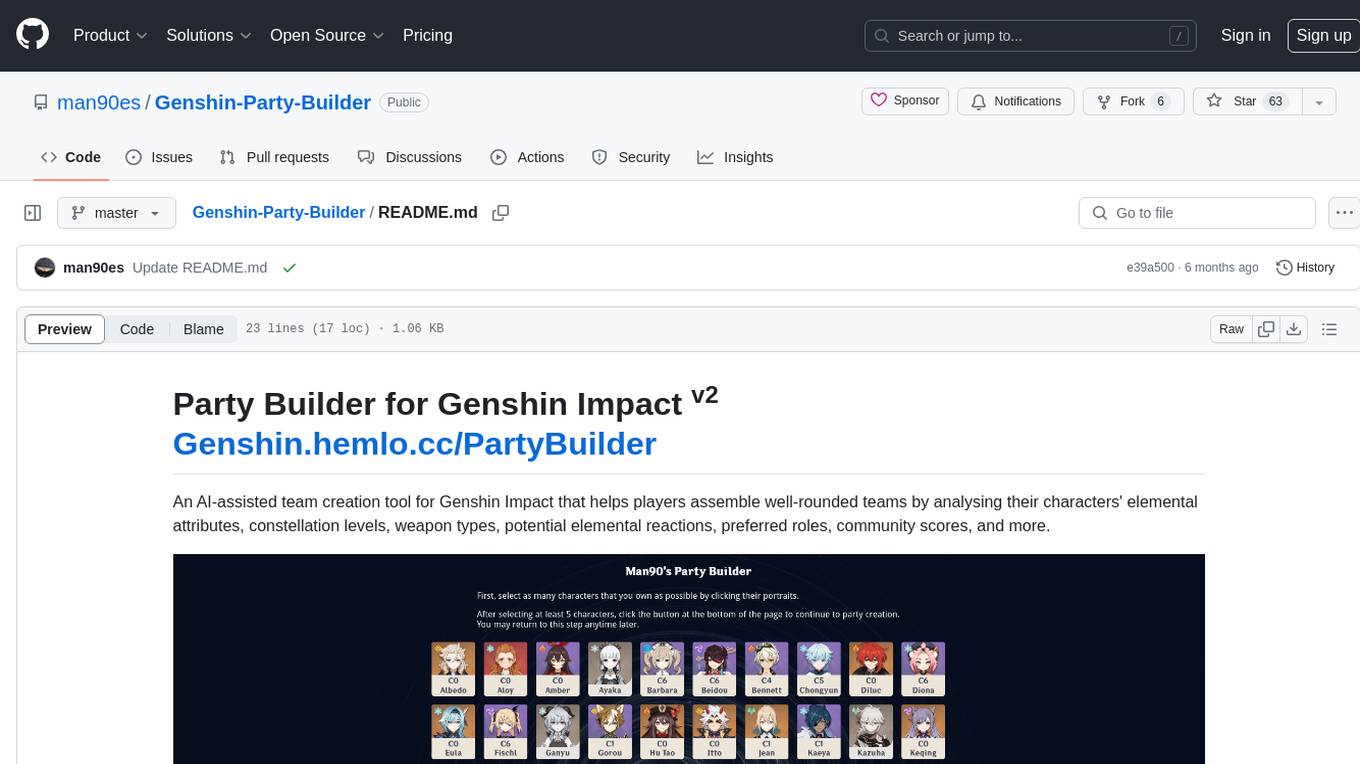
Genshin-Party-Builder
Party Builder for Genshin Impact is an AI-assisted team creation tool that helps players assemble well-rounded teams by analyzing characters' attributes, constellation levels, weapon types, elemental reactions, roles, and community scores. It allows users to optimize their team compositions for better gameplay experiences. The tool provides a user-friendly interface for easy team customization and strategy planning, enhancing the overall gaming experience for Genshin Impact players.
llm
The 'llm' package for Emacs provides an interface for interacting with Large Language Models (LLMs). It abstracts functionality to a higher level, concealing API variations and ensuring compatibility with various LLMs. Users can set up providers like OpenAI, Gemini, Vertex, Claude, Ollama, GPT4All, and a fake client for testing. The package allows for chat interactions, embeddings, token counting, and function calling. It also offers advanced prompt creation and logging capabilities. Users can handle conversations, create prompts with placeholders, and contribute by creating providers.
copilot
OpenCopilot is a tool that allows users to create their own AI copilot for their products. It integrates with APIs to execute calls as needed, using LLMs to determine the appropriate endpoint and payload. Users can define API actions, validate schemas, and integrate a user-friendly chat bubble into their SaaS app. The tool is capable of calling APIs, transforming responses, and populating request fields based on context. It is not suitable for handling large APIs without JSON transformers. Users can teach the copilot via flows and embed it in their app with minimal code.

chatluna
Chatluna is a machine learning model plugin that provides chat services with large language models. It is highly extensible, supports multiple output formats, and offers features like custom conversation presets, rate limiting, and context awareness. Users can deploy Chatluna under Koishi without additional configuration. The plugin supports various models/platforms like OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, Google Gemini, and more. It also provides preset customization using YAML files and allows for easy forking and development within Koishi projects. However, the project lacks web UI, HTTP server, and project documentation, inviting contributions from the community.
ai21-python
The AI21 Labs Python SDK is a comprehensive tool for interacting with the AI21 API. It provides functionalities for chat completions, conversational RAG, token counting, error handling, and support for various cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Vertex. The SDK offers both synchronous and asynchronous usage, along with detailed examples and documentation. Users can quickly get started with the SDK to leverage AI21's powerful models for various natural language processing tasks.
laion.ai
laion.ai is a repository hosting content for the website https://laion.ai. It includes blog posts, markdown files for content editing, and credits to contributors. The content covers various topics such as about page, impressum, FAQ, team list, and blog feed.
ollama4j
Ollama4j is a Java library that serves as a wrapper or binding for the Ollama server. It allows users to communicate with the Ollama server and manage models for various deployment scenarios. The library provides APIs for interacting with Ollama, generating fake data, testing UI interactions, translating messages, and building web UIs. Users can easily integrate Ollama4j into their Java projects to leverage the functionalities offered by the Ollama server.
AlphaAvatar
AlphaAvatar is a powerful tool for creating customizable avatars with AI-generated faces. It provides a user-friendly interface to design unique characters for various purposes such as gaming, virtual reality, social media, and more. With advanced AI algorithms, users can easily generate realistic and diverse avatars to enhance their projects and engage with their audience.

PotPlayer_ChatGPT_Translate
PotPlayer_ChatGPT_Translate is a GitHub repository that provides a script to integrate ChatGPT with PotPlayer for real-time translation of chat messages during video playback. The script utilizes the power of ChatGPT's natural language processing capabilities to translate chat messages in various languages, enhancing the viewing experience for users who consume video content with subtitles or chat interactions. By seamlessly integrating ChatGPT with PotPlayer, this tool offers a convenient solution for users to enjoy multilingual content without the need for manual translation efforts. The repository includes detailed instructions on how to set up and use the script, making it accessible for both novice and experienced users interested in leveraging AI-powered translation services within the PotPlayer environment.
langfuse-docs
Langfuse Docs is a repository for langfuse.com, built on Nextra. It provides guidelines for contributing to the documentation using GitHub Codespaces and local development setup. The repository includes Python cookbooks in Jupyter notebooks format, which are converted to markdown for rendering on the site. It also covers media management for images, videos, and gifs. The stack includes Nextra, Next.js, shadcn/ui, and Tailwind CSS. Additionally, there is a bundle analysis feature to analyze the production build bundle size using @next/bundle-analyzer.
For similar tasks

nobodywho
NobodyWho is a plugin for the Godot game engine that enables interaction with local LLMs for interactive storytelling. Users can install it from Godot editor or GitHub releases page, providing their own LLM in GGUF format. The plugin consists of `NobodyWhoModel` node for model file, `NobodyWhoChat` node for chat interaction, and `NobodyWhoEmbedding` node for generating embeddings. It offers a programming interface for sending text to LLM, receiving responses, and starting the LLM worker.
blockoli
Blockoli is a high-performance tool for code indexing, embedding generation, and semantic search tool for use with LLMs. It is built in Rust and uses the ASTerisk crate for semantic code parsing. Blockoli allows you to efficiently index, store, and search code blocks and their embeddings using vector similarity. Key features include indexing code blocks from a codebase, generating vector embeddings for code blocks using a pre-trained model, storing code blocks and their embeddings in a SQLite database, performing efficient similarity search on code blocks using vector embeddings, providing a REST API for easy integration with other tools and platforms, and being fast and memory-efficient due to its implementation in Rust.
client-js
The Mistral JavaScript client is a library that allows you to interact with the Mistral AI API. With this client, you can perform various tasks such as listing models, chatting with streaming, chatting without streaming, and generating embeddings. To use the client, you can install it in your project using npm and then set up the client with your API key. Once the client is set up, you can use it to perform the desired tasks. For example, you can use the client to chat with a model by providing a list of messages. The client will then return the response from the model. You can also use the client to generate embeddings for a given input. The embeddings can then be used for various downstream tasks such as clustering or classification.
fastllm
A collection of LLM services you can self host via docker or modal labs to support your applications development. The goal is to provide docker containers or modal labs deployments of common patterns when using LLMs and endpoints to integrate easily with existing codebases using the openai api. It supports GPT4all's embedding api, JSONFormer api for chat completion, Cross Encoders based on sentence transformers, and provides documentation using MkDocs.
openai-kotlin
OpenAI Kotlin API client is a Kotlin client for OpenAI's API with multiplatform and coroutines capabilities. It allows users to interact with OpenAI's API using Kotlin programming language. The client supports various features such as models, chat, images, embeddings, files, fine-tuning, moderations, audio, assistants, threads, messages, and runs. It also provides guides on getting started, chat & function call, file source guide, and assistants. Sample apps are available for reference, and troubleshooting guides are provided for common issues. The project is open-source and licensed under the MIT license, allowing contributions from the community.
azure-search-vector-samples
This repository provides code samples in Python, C#, REST, and JavaScript for vector support in Azure AI Search. It includes demos for various languages showcasing vectorization of data, creating indexes, and querying vector data. Additionally, it offers tools like Azure AI Search Lab for experimenting with AI-enabled search scenarios in Azure and templates for deploying custom chat-with-your-data solutions. The repository also features documentation on vector search, hybrid search, creating and querying vector indexes, and REST API references for Azure AI Search and Azure OpenAI Service.
llm
LLM is a CLI utility and Python library for interacting with Large Language Models, both via remote APIs and models that can be installed and run on your own machine. It allows users to run prompts from the command-line, store results in SQLite, generate embeddings, and more. The tool supports self-hosted language models via plugins and provides access to remote and local models. Users can install plugins to access models by different providers, including models that can be installed and run on their own device. LLM offers various options for running Mistral models in the terminal and enables users to start chat sessions with models. Additionally, users can use a system prompt to provide instructions for processing input to the tool.
GenAI-Showcase
The Generative AI Use Cases Repository showcases a wide range of applications in generative AI, including Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), AI Agents, and industry-specific use cases. It provides practical notebooks and guidance on utilizing frameworks such as LlamaIndex and LangChain, and demonstrates how to integrate models from leading AI research companies like Anthropic and OpenAI.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.






