
llm_rl
llm & rl
Stars: 213
llm_rl is a repository that combines llm (language model) and rl (reinforcement learning) techniques. It likely focuses on using language models in reinforcement learning tasks, such as natural language understanding and generation. The repository may contain implementations of algorithms that leverage both llm and rl to improve performance in various tasks. Developers interested in exploring the intersection of language models and reinforcement learning may find this repository useful for research and experimentation.
README:
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for llm_rl
Similar Open Source Tools

llm_rl
llm_rl is a repository that combines llm (language model) and rl (reinforcement learning) techniques. It likely focuses on using language models in reinforcement learning tasks, such as natural language understanding and generation. The repository may contain implementations of algorithms that leverage both llm and rl to improve performance in various tasks. Developers interested in exploring the intersection of language models and reinforcement learning may find this repository useful for research and experimentation.
LLM-Workshop
This repository contains a collection of resources for learning about and using Large Language Models (LLMs). The resources include tutorials, code examples, and links to additional resources. LLMs are a type of artificial intelligence that can understand and generate human-like text. They have a wide range of potential applications, including natural language processing, machine translation, and chatbot development.
alignment-handbook
The Alignment Handbook provides robust training recipes for continuing pretraining and aligning language models with human and AI preferences. It includes techniques such as continued pretraining, supervised fine-tuning, reward modeling, rejection sampling, and direct preference optimization (DPO). The handbook aims to fill the gap in public resources on training these models, collecting data, and measuring metrics for optimal downstream performance.
enterprise-h2ogpte
Enterprise h2oGPTe - GenAI RAG is a repository containing code examples, notebooks, and benchmarks for the enterprise version of h2oGPTe, a powerful AI tool for generating text based on the RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) architecture. The repository provides resources for leveraging h2oGPTe in enterprise settings, including implementation guides, performance evaluations, and best practices. Users can explore various applications of h2oGPTe in natural language processing tasks, such as text generation, content creation, and conversational AI.
awesome-LLM-resources
This repository is a curated list of resources for learning and working with Large Language Models (LLMs). It includes a collection of articles, tutorials, tools, datasets, and research papers related to LLMs such as GPT-3, BERT, and Transformer models. Whether you are a researcher, developer, or enthusiast interested in natural language processing and artificial intelligence, this repository provides valuable resources to help you understand, implement, and experiment with LLMs.
intro-llm.github.io
Large Language Models (LLM) are language models built by deep neural networks containing hundreds of billions of weights, trained on a large amount of unlabeled text using self-supervised learning methods. Since 2018, companies and research institutions including Google, OpenAI, Meta, Baidu, and Huawei have released various models such as BERT, GPT, etc., which have performed well in almost all natural language processing tasks. Starting in 2021, large models have shown explosive growth, especially after the release of ChatGPT in November 2022, attracting worldwide attention. Users can interact with systems using natural language to achieve various tasks from understanding to generation, including question answering, classification, summarization, translation, and chat. Large language models demonstrate powerful knowledge of the world and understanding of language. This repository introduces the basic theory of large language models including language models, distributed model training, and reinforcement learning, and uses the Deepspeed-Chat framework as an example to introduce the implementation of large language models and ChatGPT-like systems.
cs-self-learning
This repository serves as an archive for computer science learning notes, codes, and materials. It covers a wide range of topics including basic knowledge, AI, backend & big data, tools, and other related areas. The content is organized into sections and subsections for easy navigation and reference. Users can find learning resources, programming practices, and tutorials on various subjects such as languages, data structures & algorithms, AI, frameworks, databases, development tools, and more. The repository aims to support self-learning and skill development in the field of computer science.
llama.rn
React Native binding of llama.cpp, which is an inference of LLaMA model in pure C/C++. This tool allows you to use the LLaMA model in your React Native applications for various tasks such as text completion, tokenization, detokenization, and embedding. It provides a convenient interface to interact with the LLaMA model and supports features like grammar sampling and mocking for testing purposes.
Awesome-LLM-Prune
This repository is dedicated to the pruning of large language models (LLMs). It aims to serve as a comprehensive resource for researchers and practitioners interested in the efficient reduction of model size while maintaining or enhancing performance. The repository contains various papers, summaries, and links related to different pruning approaches for LLMs, along with author information and publication details. It covers a wide range of topics such as structured pruning, unstructured pruning, semi-structured pruning, and benchmarking methods. Researchers and practitioners can explore different pruning techniques, understand their implications, and access relevant resources for further study and implementation.
Awesome-LLM-Psychometrics
This repository contains a collection of tools and resources for conducting psychometric analysis in the context of latent variable modeling. It includes scripts for data preprocessing, model estimation, and results interpretation. The tools provided here aim to assist researchers and practitioners in the field of psychology and related disciplines to analyze complex relationships among latent variables using advanced statistical techniques.
RustGPT
A complete Large Language Model implementation in pure Rust with no external ML frameworks. Demonstrates building a transformer-based language model from scratch, including pre-training, instruction tuning, interactive chat mode, full backpropagation, and modular architecture. Model learns basic world knowledge and conversational patterns. Features custom tokenization, greedy decoding, gradient clipping, modular layer system, and comprehensive test coverage. Ideal for understanding modern LLMs and key ML concepts. Dependencies include ndarray for matrix operations and rand for random number generation. Contributions welcome for model persistence, performance optimizations, better sampling, evaluation metrics, advanced architectures, training improvements, data handling, and model analysis. Follows standard Rust conventions and encourages contributions at beginner, intermediate, and advanced levels.

flashinfer
FlashInfer is a library for Language Languages Models that provides high-performance implementation of LLM GPU kernels such as FlashAttention, PageAttention and LoRA. FlashInfer focus on LLM serving and inference, and delivers state-the-art performance across diverse scenarios.
artificial-intelligence
This repository contains a collection of AI projects implemented in Python, primarily in Jupyter notebooks. The projects cover various aspects of artificial intelligence, including machine learning, deep learning, natural language processing, computer vision, and more. Each project is designed to showcase different AI techniques and algorithms, providing a hands-on learning experience for users interested in exploring the field of artificial intelligence.
bisheng
Bisheng is a leading open-source **large model application development platform** that empowers and accelerates the development and deployment of large model applications, helping users enter the next generation of application development with the best possible experience.
FLAME
FLAME is a lightweight and efficient deep learning framework designed for edge devices. It provides a simple and user-friendly interface for developing and deploying deep learning models on resource-constrained devices. With FLAME, users can easily build and optimize neural networks for tasks such as image classification, object detection, and natural language processing. The framework supports various neural network architectures and optimization techniques, making it suitable for a wide range of applications in the field of edge computing.
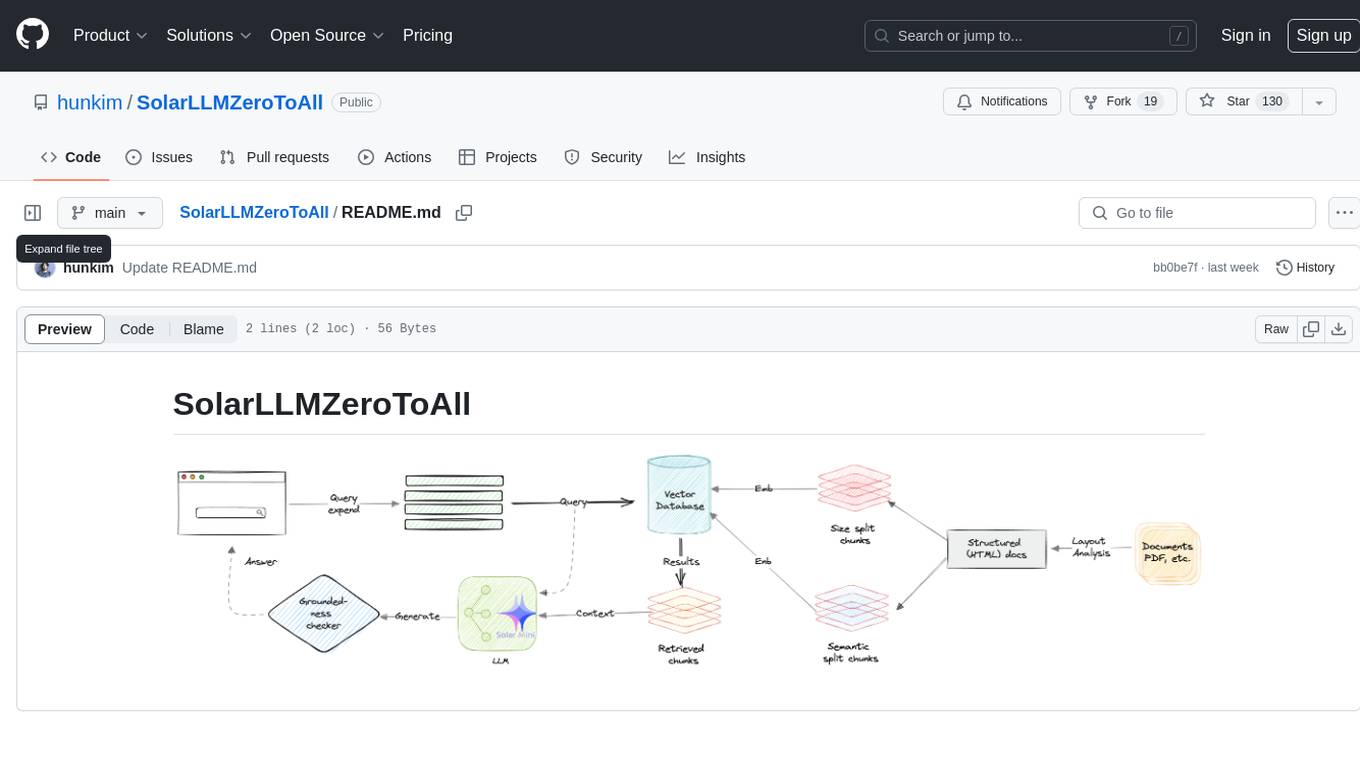
SolarLLMZeroToAll
SolarLLMZeroToAll is a comprehensive repository that provides a step-by-step guide and resources for learning and implementing Solar Longitudinal Learning Machines (SolarLLM) from scratch. The repository covers various aspects of SolarLLM, including theory, implementation, and applications, making it suitable for beginners and advanced users interested in solar energy forecasting and machine learning. The materials include detailed explanations, code examples, datasets, and visualization tools to facilitate understanding and practical implementation of SolarLLM models.
For similar tasks
linesight
Linesight is a reinforcement learning project focused on advancing AI capabilities in the racing game Trackmania. It aims to push the boundaries of AI performance by utilizing deep learning algorithms to achieve human-level driving and beat world records on official campaign tracks. The project provides an interface to interact with Trackmania Nations Forever programmatically, enabling tasks such as sending inputs, retrieving car states, and capturing screenshots. With a strong emphasis on equality of input devices, Linesight serves as a benchmark for testing various reinforcement learning algorithms in a challenging and dynamic gaming environment.
BrainX
BrainX is a tool designed for AI enthusiasts to explore and experiment with various machine learning algorithms and models. It provides a user-friendly interface for building, training, and evaluating AI models. The tool aims to simplify the process of developing AI applications and enable users to quickly prototype and test their ideas.

llm_rl
llm_rl is a repository that combines llm (language model) and rl (reinforcement learning) techniques. It likely focuses on using language models in reinforcement learning tasks, such as natural language understanding and generation. The repository may contain implementations of algorithms that leverage both llm and rl to improve performance in various tasks. Developers interested in exploring the intersection of language models and reinforcement learning may find this repository useful for research and experimentation.
Automodel
Automodel is a Python library for automating the process of building and evaluating machine learning models. It provides a set of tools and utilities to streamline the model development workflow, from data preprocessing to model selection and evaluation. With Automodel, users can easily experiment with different algorithms, hyperparameters, and feature engineering techniques to find the best model for their dataset. The library is designed to be user-friendly and customizable, allowing users to define their own pipelines and workflows. Automodel is suitable for data scientists, machine learning engineers, and anyone looking to quickly build and test machine learning models without the need for manual intervention.
model-mondays
Model Mondays is a repository dedicated to providing a collection of machine learning models implemented in Python. It aims to serve as a resource for individuals looking to explore and experiment with various machine learning algorithms and techniques. The repository includes a wide range of models, from simple linear regression to complex deep learning architectures, along with detailed documentation and examples to facilitate learning and understanding. Whether you are a beginner looking to get started with machine learning or an experienced practitioner seeking reference implementations, Model Mondays offers a valuable repository of models to study and leverage in your projects.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.
LocalAI
LocalAI is a free and open-source OpenAI alternative that acts as a drop-in replacement REST API compatible with OpenAI (Elevenlabs, Anthropic, etc.) API specifications for local AI inferencing. It allows users to run LLMs, generate images, audio, and more locally or on-premises with consumer-grade hardware, supporting multiple model families and not requiring a GPU. LocalAI offers features such as text generation with GPTs, text-to-audio, audio-to-text transcription, image generation with stable diffusion, OpenAI functions, embeddings generation for vector databases, constrained grammars, downloading models directly from Huggingface, and a Vision API. It provides a detailed step-by-step introduction in its Getting Started guide and supports community integrations such as custom containers, WebUIs, model galleries, and various bots for Discord, Slack, and Telegram. LocalAI also offers resources like an LLM fine-tuning guide, instructions for local building and Kubernetes installation, projects integrating LocalAI, and a how-tos section curated by the community. It encourages users to cite the repository when utilizing it in downstream projects and acknowledges the contributions of various software from the community.

AiTreasureBox
AiTreasureBox is a versatile AI tool that provides a collection of pre-trained models and algorithms for various machine learning tasks. It simplifies the process of implementing AI solutions by offering ready-to-use components that can be easily integrated into projects. With AiTreasureBox, users can quickly prototype and deploy AI applications without the need for extensive knowledge in machine learning or deep learning. The tool covers a wide range of tasks such as image classification, text generation, sentiment analysis, object detection, and more. It is designed to be user-friendly and accessible to both beginners and experienced developers, making AI development more efficient and accessible to a wider audience.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.