
OpenMusic
OpenMusic: SOTA Text-to-music (TTM) Generation
Stars: 507
OpenMusic is a repository providing an implementation of QA-MDT, a Quality-Aware Masked Diffusion Transformer for music generation. The code integrates state-of-the-art models and offers training strategies for music generation. The repository includes implementations of AudioLDM, PixArt-alpha, MDT, AudioMAE, and Open-Sora. Users can train or fine-tune the model using different strategies and datasets. The model is well-pretrained and can be used for music generation tasks. The repository also includes instructions for preparing datasets, training the model, and performing inference. Contact information is provided for any questions or suggestions regarding the project.
README:
(Trying to support audio-to-audio generation is in my todo list, such that you can input music tracks and the LDM will help merge them~)
We have succeeded in extending our model to inf-long music generation in a zero-shot manner
Thanks for advertisement on locally test in YouTube! - by @Fahd Mirza
Diffusers Implementation 🧨 - by @jadechoghari - Hugging Face 🤗.
Setting up is super easy! Just follow the instructions below:
pip install -r gradio/requirements.txt
python gradio/gradio_app.py
We have to admit that the Unet architecture still has some probability advantage in subjective musicality, but this is not measured in the metric. And, we did have some models that were better on the metric, or trained for longer, but we observed that the models generally became less musicality after training too long, so we picked a model that was moderate on the metric as an open source sample. If you need more models (extreme metric pursuit or extreme musically pursuit, please contact me)
without any fancy design, just a quality injection, and enjoy your beautiful music
Down the main checkpoint of our QA-MDT model from https://huggingface.co/lichang0928/QA-MDT
For chinese users, you can also download your checkpoint through following link:
https://pan.baidu.com/s/1N0XqVxtF_x9I7fWb07LPqw?pwd=9nkt
This repository provides an implementation of QA-MDT, integrating state-of-the-art models for music generation. The code and methods are based on the following repositories:
Python 3.10
qamdt.yamlBefore training, you need to download extra ckpts needed in ./audioldm_train/config/mos_as_token/qa_mdt.yaml and offset_pretrained_checkpoints.json
Noted that: All above checkpoints can be downloaded from:
sh run.shOur model is already well-pretrained. If you wish to retrain or fine-tune it, you can choose to use or not use our QA strategy. We offer several training strategies:
-
MDT w.o quality token:
PixArt_MDT -
MDT with quality token:
Pixart_MDT_MOS_AS_TOKEN -
DiT:
PixArt_Slow -
U-net w / w.o quality prefix:
you can just follow AudioLDM and make your dataset as illustrated in our paper (method part)
To train or fine-tune, simply change "Your_Class" in audioldm_train.modules.diffusionmodules.PixArt.Your_Class in our config file.
you can also try modifying the patch size, overlap size for your best performance and computing resources trade off (see our Appendix in arXiv paper)
We use the LMDB dataset format for training. You can modify the dataloader according to your own training needs.
If you'd like to follow our process (though we don't recommend it, as it can be complex), here's how you can create a toy LMDB dataset:
-
Create a Proto File
First, create a file named
datum_all.protowith the following content:syntax = "proto2"; message Datum_all { repeated float wav_file = 1; required string caption_original = 2; repeated string caption_generated = 3; required float mos = 4; }
-
Generate Python Bindings
(Your protoc version should be 3.4, and you can download it here)
Run the following command in your terminal to generate Python bindings:
protoc --python_out=./ datum_all.protoThis will create a file called datum_all_pb2.py. We have also provided this file in our datasets folder, and you can check if it matches the one you generated. Never attempt to modify this file, as doing so could cause errors.
- Code for Preparing a toy LMDB Dataset
The following Python script demonstrates how to prepare your dataset in the LMDB format:
import torch
import os
import lmdb
import time
import numpy as np
import librosa
import os
import soundfile as sf
import io
from datum_all_pb2 import Datum_all as Datum_out
device = 'cpu'
count = 0
total_hours = 0
# Define paths
lmdb_file = '/disk1/changli/toy_lmdb'
toy_path = '/disk1/changli/audioset'
lmdb_key = os.path.join(lmdb_file, 'data_key.key')
# Open LMDB environment
env = lmdb.open(lmdb_file, map_size=1e12)
txn = env.begin(write=True)
final_keys = []
def _resample_load_librosa(path: str, sample_rate: int, downmix_to_mono: bool, **kwargs):
"""Load and resample audio using librosa."""
src, sr = librosa.load(path, sr=sample_rate, mono=downmix_to_mono, **kwargs)
return src
start_time = time.time()
# Walk through the dataset directory
for root, _, files in os.walk(toy_path):
for file in files:
audio_path = os.path.join(root, file)
key_tmp = audio_path.replace('/', '_')
audio = _resample_load_librosa(audio_path, 16000, True)
# Create a new Datum object
datum = Datum_out()
datum.wav_file.extend(audio)
datum.caption_original = 'audio'.encode()
datum.caption_generated.append('audio'.encode())
datum.mos = -1
# Write to LMDB
txn.put(key_tmp.encode(), datum.SerializeToString())
final_keys.append(key_tmp)
count += 1
total_hours += 1.00 / 60 / 10
if count % 1 == 0:
elapsed_time = time.time() - start_time
print(f'{count} files written, time: {elapsed_time:.2f}s')
txn.commit()
txn = env.begin(write=True)
# Finalize transaction
try:
total_time = time.time() - start_time
print(f'Packing completed: {count} files written, total_hours: {total_hours:.2f}, time: {total_time:.2f}s')
txn.commit()
except:
pass
env.close()
# Save the LMDB keys
with open(lmdb_key, 'w') as f:
for key in final_keys:
f.write(key + '\n')otherwise, you can just use the dataloader in AudioLDM
-
Input your generated lmdb path and its corresponding key file path into the config
-
Start your training
sh infer/infer.sh
# you may change the infer.sh for witch quality level you want to infer
# defaultly, it should be set to 5 which represent highest quality
# Additionally, it may be useful to change the prompt with text prefix "high quality",
# which match the training process and may further improve performanceThis is the first time I open source such a project, the code, the organization, the open source may not be perfect. If you have any questions about our model, code and datasets, feel free to contact me via below links, and I'm looking forward to any suggestions:
- Email: [email protected]
- WeChat: 19524292801
I will try my best to provide more projects on music and audio in the future ~
If you find this project useful, please consider citing:
@article{li2024quality,
title={Quality-aware Masked Diffusion Transformer for Enhanced Music Generation},
author={Li, Chang and Wang, Ruoyu and Liu, Lijuan and Du, Jun and Sun, Yixuan and Guo, Zilu and Zhang, Zhenrong and Jiang, Yuan},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.15863},
year={2024}
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for OpenMusic
Similar Open Source Tools

OpenMusic
OpenMusic is a repository providing an implementation of QA-MDT, a Quality-Aware Masked Diffusion Transformer for music generation. The code integrates state-of-the-art models and offers training strategies for music generation. The repository includes implementations of AudioLDM, PixArt-alpha, MDT, AudioMAE, and Open-Sora. Users can train or fine-tune the model using different strategies and datasets. The model is well-pretrained and can be used for music generation tasks. The repository also includes instructions for preparing datasets, training the model, and performing inference. Contact information is provided for any questions or suggestions regarding the project.
qa-mdt
This repository provides an implementation of QA-MDT, integrating state-of-the-art models for music generation. It offers a Quality-Aware Masked Diffusion Transformer for enhanced music generation. The code is based on various repositories like AudioLDM, PixArt-alpha, MDT, AudioMAE, and Open-Sora. The implementation allows for training and fine-tuning the model with different strategies and datasets. The repository also includes instructions for preparing datasets in LMDB format and provides a script for creating a toy LMDB dataset. The model can be used for music generation tasks, with a focus on quality injection to enhance the musicality of generated music.
chromem-go
chromem-go is an embeddable vector database for Go with a Chroma-like interface and zero third-party dependencies. It enables retrieval augmented generation (RAG) and similar embeddings-based features in Go apps without the need for a separate database. The focus is on simplicity and performance for common use cases, allowing querying of documents with minimal memory allocations. The project is in beta and may introduce breaking changes before v1.0.0.
Easy-Translate
Easy-Translate is a script designed for translating large text files with a single command. It supports various models like M2M100, NLLB200, SeamlessM4T, LLaMA, and Bloom. The tool is beginner-friendly and offers seamless and customizable features for advanced users. It allows acceleration on CPU, multi-CPU, GPU, multi-GPU, and TPU, with support for different precisions and decoding strategies. Easy-Translate also provides an evaluation script for translations. Built on HuggingFace's Transformers and Accelerate library, it supports prompt usage and loading huge models efficiently.

rl
TorchRL is an open-source Reinforcement Learning (RL) library for PyTorch. It provides pytorch and **python-first** , low and high level abstractions for RL that are intended to be **efficient** , **modular** , **documented** and properly **tested**. The code is aimed at supporting research in RL. Most of it is written in python in a highly modular way, such that researchers can easily swap components, transform them or write new ones with little effort.
LLM-Pruner
LLM-Pruner is a tool for structural pruning of large language models, allowing task-agnostic compression while retaining multi-task solving ability. It supports automatic structural pruning of various LLMs with minimal human effort. The tool is efficient, requiring only 3 minutes for pruning and 3 hours for post-training. Supported LLMs include Llama-3.1, Llama-3, Llama-2, LLaMA, BLOOM, Vicuna, and Baichuan. Updates include support for new LLMs like GQA and BLOOM, as well as fine-tuning results achieving high accuracy. The tool provides step-by-step instructions for pruning, post-training, and evaluation, along with a Gradio interface for text generation. Limitations include issues with generating repetitive or nonsensical tokens in compressed models and manual operations for certain models.
WildBench
WildBench is a tool designed for benchmarking Large Language Models (LLMs) with challenging tasks sourced from real users in the wild. It provides a platform for evaluating the performance of various models on a range of tasks. Users can easily add new models to the benchmark by following the provided guidelines. The tool supports models from Hugging Face and other APIs, allowing for comprehensive evaluation and comparison. WildBench facilitates running inference and evaluation scripts, enabling users to contribute to the benchmark and collaborate on improving model performance.
MemoryLLM
MemoryLLM is a large language model designed for self-updating capabilities. It offers pretrained models with different memory capacities and features, such as chat models. The repository provides training code, evaluation scripts, and datasets for custom experiments. MemoryLLM aims to enhance knowledge retention and performance on various natural language processing tasks.

memobase
Memobase is a user profile-based memory system designed to enhance Generative AI applications by enabling them to remember, understand, and evolve with users. It provides structured user profiles, scalable profiling, easy integration with existing LLM stacks, batch processing for speed, and is production-ready. Users can manage users, insert data, get memory profiles, and track user preferences and behaviors. Memobase is ideal for applications that require user analysis, tracking, and personalized interactions.
hugging-chat-api
Unofficial HuggingChat Python API for creating chatbots, supporting features like image generation, web search, memorizing context, and changing LLMs. Users can log in, chat with the ChatBot, perform web searches, create new conversations, manage conversations, switch models, get conversation info, use assistants, and delete conversations. The API also includes a CLI mode with various commands for interacting with the tool. Users are advised not to use the application for high-stakes decisions or advice and to avoid high-frequency requests to preserve server resources.
ALMA
ALMA (Advanced Language Model-based Translator) is a many-to-many LLM-based translation model that utilizes a two-step fine-tuning process on monolingual and parallel data to achieve strong translation performance. ALMA-R builds upon ALMA models with LoRA fine-tuning and Contrastive Preference Optimization (CPO) for even better performance, surpassing GPT-4 and WMT winners. The repository provides ALMA and ALMA-R models, datasets, environment setup, evaluation scripts, training guides, and data information for users to leverage these models for translation tasks.

supallm
Supallm is a Python library for super resolution of images using deep learning techniques. It provides pre-trained models for enhancing image quality by increasing resolution. The library is easy to use and allows users to upscale images with high fidelity and detail. Supallm is suitable for tasks such as enhancing image quality, improving visual appearance, and increasing the resolution of low-quality images. It is a valuable tool for researchers, photographers, graphic designers, and anyone looking to enhance image quality using AI technology.
bigcodebench
BigCodeBench is an easy-to-use benchmark for code generation with practical and challenging programming tasks. It aims to evaluate the true programming capabilities of large language models (LLMs) in a more realistic setting. The benchmark is designed for HumanEval-like function-level code generation tasks, but with much more complex instructions and diverse function calls. BigCodeBench focuses on the evaluation of LLM4Code with diverse function calls and complex instructions, providing precise evaluation & ranking and pre-generated samples to accelerate code intelligence research. It inherits the design of the EvalPlus framework but differs in terms of execution environment and test evaluation.
quivr
Quivr is a personal assistant powered by Generative AI, designed to be a second brain for users. It offers fast and efficient access to data, ensuring security and compatibility with various file formats. Quivr is open source and free to use, allowing users to share their brains publicly or keep them private. The marketplace feature enables users to share and utilize brains created by others, boosting productivity. Quivr's offline mode provides anytime, anywhere access to data. Key features include speed, security, OS compatibility, file compatibility, open source nature, public/private sharing options, a marketplace, and offline mode.

Trace
Trace is a new AutoDiff-like tool for training AI systems end-to-end with general feedback. It generalizes the back-propagation algorithm by capturing and propagating an AI system's execution trace. Implemented as a PyTorch-like Python library, users can write Python code directly and use Trace primitives to optimize certain parts, similar to training neural networks.
allms
allms is a versatile and powerful library designed to streamline the process of querying Large Language Models (LLMs). Developed by Allegro engineers, it simplifies working with LLM applications by providing a user-friendly interface, asynchronous querying, automatic retrying mechanism, error handling, and output parsing. It supports various LLM families hosted on different platforms like OpenAI, Google, Azure, and GCP. The library offers features for configuring endpoint credentials, batch querying with symbolic variables, and forcing structured output format. It also provides documentation, quickstart guides, and instructions for local development, testing, updating documentation, and making new releases.
For similar tasks

dstack
Dstack is an open-source orchestration engine for running AI workloads in any cloud. It supports a wide range of cloud providers (such as AWS, GCP, Azure, Lambda, TensorDock, Vast.ai, CUDO, RunPod, etc.) as well as on-premises infrastructure. With Dstack, you can easily set up and manage dev environments, tasks, services, and pools for your AI workloads.
one-click-llms
The one-click-llms repository provides templates for quickly setting up an API for language models. It includes advanced inferencing scripts for function calling and offers various models for text generation and fine-tuning tasks. Users can choose between Runpod and Vast.AI for different GPU configurations, with recommendations for optimal performance. The repository also supports Trelis Research and offers templates for different model sizes and types, including multi-modal APIs and chat models.

starcoder2-self-align
StarCoder2-Instruct is an open-source pipeline that introduces StarCoder2-15B-Instruct-v0.1, a self-aligned code Large Language Model (LLM) trained with a fully permissive and transparent pipeline. It generates instruction-response pairs to fine-tune StarCoder-15B without human annotations or data from proprietary LLMs. The tool is primarily finetuned for Python code generation tasks that can be verified through execution, with potential biases and limitations. Users can provide response prefixes or one-shot examples to guide the model's output. The model may have limitations with other programming languages and out-of-domain coding tasks.
enhance_llm
The enhance_llm repository contains three main parts: 1. Vector model domain fine-tuning based on llama_index and qwen fine-tuning BGE vector model. 2. Large model domain fine-tuning based on PEFT fine-tuning qwen1.5-7b-chat, with sft and dpo. 3. High-order retrieval enhanced generation (RAG) system based on the above domain work, implementing a two-stage RAG system. It includes query rewriting, recall reordering, retrieval reordering, multi-turn dialogue, and more. The repository also provides hardware and environment configurations along with star history and licensing information.
fms-fsdp
The 'fms-fsdp' repository is a companion to the Foundation Model Stack, providing a (pre)training example to efficiently train FMS models, specifically Llama2, using native PyTorch features like FSDP for training and SDPA implementation of Flash attention v2. It focuses on leveraging FSDP for training efficiently, not as an end-to-end framework. The repo benchmarks training throughput on different GPUs, shares strategies, and provides installation and training instructions. It trained a model on IBM curated data achieving high efficiency and performance metrics.

CogVLM2
CogVLM2 is a new generation of open source models that offer significant improvements in benchmarks such as TextVQA and DocVQA. It supports 8K content length, image resolution up to 1344 * 1344, and both Chinese and English languages. The project provides basic calling methods, fine-tuning examples, and OpenAI API format calling examples to help developers quickly get started with the model.
liboai
liboai is a simple C++17 library for the OpenAI API, providing developers with access to OpenAI endpoints through a collection of methods and classes. It serves as a spiritual port of OpenAI's Python library, 'openai', with similar structure and features. The library supports various functionalities such as ChatGPT, Audio, Azure, Functions, Image DALL·E, Models, Completions, Edit, Embeddings, Files, Fine-tunes, Moderation, and Asynchronous Support. Users can easily integrate the library into their C++ projects to interact with OpenAI services.
extension-gen-ai
The Looker GenAI Extension provides code examples and resources for building a Looker Extension that integrates with Vertex AI Large Language Models (LLMs). Users can leverage the power of LLMs to enhance data exploration and analysis within Looker. The extension offers generative explore functionality to ask natural language questions about data and generative insights on dashboards to analyze data by asking questions. It leverages components like BQML Remote Models, BQML Remote UDF with Vertex AI, and Custom Fine Tune Model for different integration options. Deployment involves setting up infrastructure with Terraform and deploying the Looker Extension by creating a Looker project, copying extension files, configuring BigQuery connection, connecting to Git, and testing the extension. Users can save example prompts and configure user settings for the extension. Development of the Looker Extension environment includes installing dependencies, starting the development server, and building for production.
For similar jobs
metavoice-src
MetaVoice-1B is a 1.2B parameter base model trained on 100K hours of speech for TTS (text-to-speech). It has been built with the following priorities: * Emotional speech rhythm and tone in English. * Zero-shot cloning for American & British voices, with 30s reference audio. * Support for (cross-lingual) voice cloning with finetuning. * We have had success with as little as 1 minute training data for Indian speakers. * Synthesis of arbitrary length text
suno-api
Suno AI API is an open-source project that allows developers to integrate the music generation capabilities of Suno.ai into their own applications. The API provides a simple and convenient way to generate music, lyrics, and other audio content using Suno.ai's powerful AI models. With Suno AI API, developers can easily add music generation functionality to their apps, websites, and other projects.
bark.cpp
Bark.cpp is a C/C++ implementation of the Bark model, a real-time, multilingual text-to-speech generation model. It supports AVX, AVX2, and AVX512 for x86 architectures, and is compatible with both CPU and GPU backends. Bark.cpp also supports mixed F16/F32 precision and 4-bit, 5-bit, and 8-bit integer quantization. It can be used to generate realistic-sounding audio from text prompts.
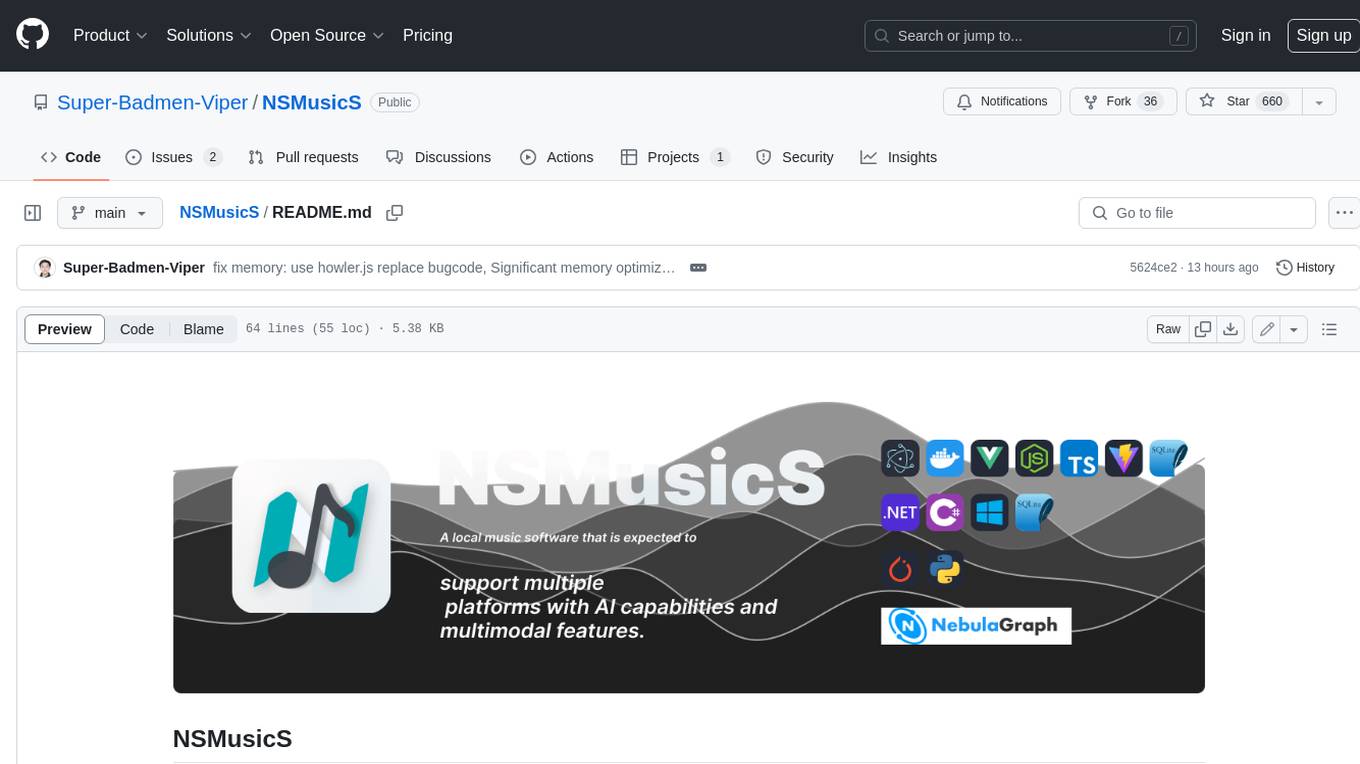
NSMusicS
NSMusicS is a local music software that is expected to support multiple platforms with AI capabilities and multimodal features. The goal of NSMusicS is to integrate various functions (such as artificial intelligence, streaming, music library management, cross platform, etc.), which can be understood as similar to Navidrome but with more features than Navidrome. It wants to become a plugin integrated application that can almost have all music functions.
ai-voice-cloning
This repository provides a tool for AI voice cloning, allowing users to generate synthetic speech that closely resembles a target speaker's voice. The tool is designed to be user-friendly and accessible, with a graphical user interface that guides users through the process of training a voice model and generating synthetic speech. The tool also includes a variety of features that allow users to customize the generated speech, such as the pitch, volume, and speaking rate. Overall, this tool is a valuable resource for anyone interested in creating realistic and engaging synthetic speech.
RVC_CLI
**RVC_CLI: Retrieval-based Voice Conversion Command Line Interface** This command-line interface (CLI) provides a comprehensive set of tools for voice conversion, enabling you to modify the pitch, timbre, and other characteristics of audio recordings. It leverages advanced machine learning models to achieve realistic and high-quality voice conversions. **Key Features:** * **Inference:** Convert the pitch and timbre of audio in real-time or process audio files in batch mode. * **TTS Inference:** Synthesize speech from text using a variety of voices and apply voice conversion techniques. * **Training:** Train custom voice conversion models to meet specific requirements. * **Model Management:** Extract, blend, and analyze models to fine-tune and optimize performance. * **Audio Analysis:** Inspect audio files to gain insights into their characteristics. * **API:** Integrate the CLI's functionality into your own applications or workflows. **Applications:** The RVC_CLI finds applications in various domains, including: * **Music Production:** Create unique vocal effects, harmonies, and backing vocals. * **Voiceovers:** Generate voiceovers with different accents, emotions, and styles. * **Audio Editing:** Enhance or modify audio recordings for podcasts, audiobooks, and other content. * **Research and Development:** Explore and advance the field of voice conversion technology. **For Jobs:** * Audio Engineer * Music Producer * Voiceover Artist * Audio Editor * Machine Learning Engineer **AI Keywords:** * Voice Conversion * Pitch Shifting * Timbre Modification * Machine Learning * Audio Processing **For Tasks:** * Convert Pitch * Change Timbre * Synthesize Speech * Train Model * Analyze Audio
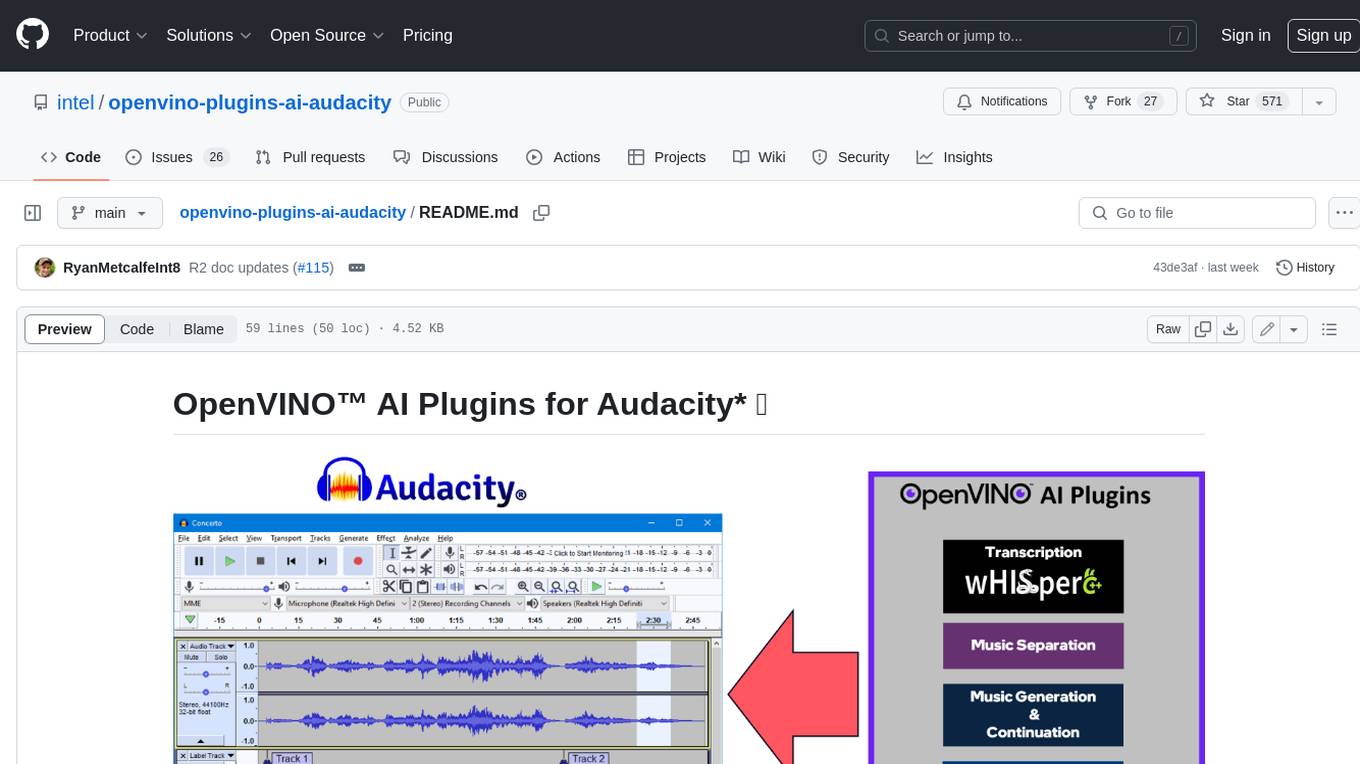
openvino-plugins-ai-audacity
OpenVINO™ AI Plugins for Audacity* are a set of AI-enabled effects, generators, and analyzers for Audacity®. These AI features run 100% locally on your PC -- no internet connection necessary! OpenVINO™ is used to run AI models on supported accelerators found on the user's system such as CPU, GPU, and NPU. * **Music Separation**: Separate a mono or stereo track into individual stems -- Drums, Bass, Vocals, & Other Instruments. * **Noise Suppression**: Removes background noise from an audio sample. * **Music Generation & Continuation**: Uses MusicGen LLM to generate snippets of music, or to generate a continuation of an existing snippet of music. * **Whisper Transcription**: Uses whisper.cpp to generate a label track containing the transcription or translation for a given selection of spoken audio or vocals.
WavCraft
WavCraft is an LLM-driven agent for audio content creation and editing. It applies LLM to connect various audio expert models and DSP function together. With WavCraft, users can edit the content of given audio clip(s) conditioned on text input, create an audio clip given text input, get more inspiration from WavCraft by prompting a script setting and let the model do the scriptwriting and create the sound, and check if your audio file is synthesized by WavCraft.







