
dLLM-RL
TraceRL: Revolutionizing Reinforcement Learning Framework for Diffusion Large Language Models
Stars: 222
dLLM-RL is a revolutionary reinforcement learning framework designed for Diffusion Large Language Models. It supports various models with diverse structures, offers inference acceleration, RL training capabilities, and SFT functionalities. The tool introduces TraceRL for trajectory-aware RL and diffusion-based value models for optimization stability. Users can download and try models like TraDo-4B-Instruct and TraDo-8B-Instruct. The tool also provides support for multi-node setups and easy building of reinforcement learning methods. Additionally, it offers supervised fine-tuning strategies for different models and tasks.
README:
- Model Support: TraDo, SDAR, Dream, LLaDA, MMaDA, Diffu-Coder We support models with diverse structures, including full attention models, adapted models, and block attention models.
- Inference Acceleration: improved KV-cache, jetengine (based on nano-vllm), different sampling strategies, support multi-nodes, easy to build your own accelerated inference methods
- RL Training: TraceRL (support diffusion value model), coupled RL, random masking RL, accelerated sampling, including Math, coding, and general RL tasks, support multi-nodes, easy to build your reinforcement learning methods across diverse settings
- SFT: Block SFT, semi-AR SFT, random masking SFT, support multi-nodes and long-CoT finetune
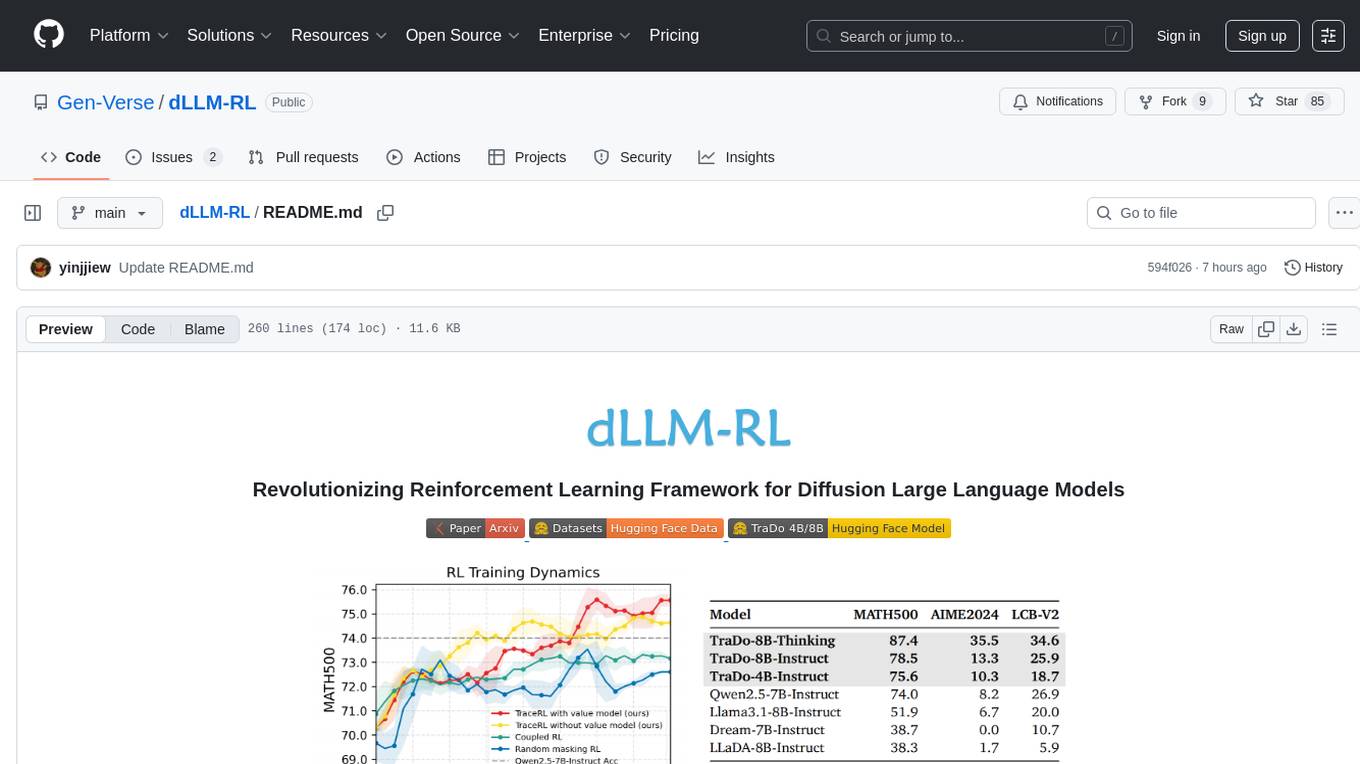
We propose TraceRL, a trajectory-aware reinforcement learning method for diffusion language models, which demonstrates the best performance among RL approaches for DLMs. We also introduce a diffusion-based value model that reduces variance and improves stability during optimization.
Based on TraceRL, we derive a series of diffusion language models, TraDo, which achieve state-of-the-art performance on math and coding reasoning tasks. TraDo-4B-Instruct and TraDo-8B-Instruct are trained solely with TraceRL, while the first long-CoT diffusion language model, TraDo-8B-Thinking, is obtained through a combination of TraceRL and long-CoT data SFT. TraDo models challenge AR models with strong empirical results, as shown in the following table.
We can download and try our model:
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
from generate import block_diffusion_generate
model_name = "Gen-Verse/TraDo-8B-Instruct"
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_name, trust_remote_code=True, torch_dtype="float16", device_map="cuda"
)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name, trust_remote_code=True)
prompt = "What's the solution of x^2 - 2x + 1 = 0\nPlease reason step by step, and put your final answer within \\boxed{}.\n"
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": prompt}]
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=True)
tokens = tokenizer.batch_encode_plus([text], return_tensors='pt', padding=True, truncation=True, max_length=200)
tokens = {k: v.to(model.device) for k, v in tokens.items()}
output_ids = block_diffusion_generate(
model,
prompt=tokens,
mask_id=151669,
gen_length=200,
block_length=4, denoising_steps=4,
temperature=1.0, top_k=0, top_p=1.0,
remasking_strategy="low_confidence_dynamic",
confidence_threshold=0.9
)
output_text = tokenizer.decode(output_ids[0], skip_special_tokens=False)
cleaned_text = output_text.replace('<|MASK|>', '').replace('<|endoftext|>', '')
print(cleaned_text)
- [2025-09-08] 🔥 We release our models, TraDo-4B-Instruct and TraDo-8B-Instruct, and the long-CoT diffusion language model TraDo-8B-Thinking.
- [2025-09-08] 🔥 We release inference and training (SFT and RL) code compatible with a wide range of diffusion language models, including TraDo, SDAR, Dream, LLaDA, MMaDA, and Diffu-Coder.
conda create --name dllm-rl python=3.10
source activate dllm-rl
pip install torch==2.6.0
pip install --no-cache-dir \
https://github.com/Dao-AILab/flash-attention/releases/download/v2.7.4.post1/\
flash_attn-2.7.4.post1+cu12torch2.6cxx11abiFALSE-cp310-cp310-linux_x86_64.whl
pip install -r requirements.txtYou can navigate to ./data to download datasets for evaluation and training, for example as follows. In that directory, you will also find detailed instructions on how to modify your own dataset.
cd data
python download_data.py --dataset MATH500
python download_data.py --dataset MATH_train
cd ..After downloading the data, you are almost ready to evaluate or train diffusion language models. The only remaining step is to select (or create) a config file in ./configs that corresponds to your project, and then use the following commands. Details on how to select and modify (or create) a config file are provided in ./configs.
After downloading the data, take TraDo models as an example. You can set the configurations in configs/trado_eval.yaml (see instructions and details in ./configs) and run the following commands to perform inference with different sampling strategies.
python eval.py config=configs/trado_eval.yaml
# python eval.py config=configs/trado_longcot_eval.yaml
# python eval.py config=configs/sdar_eval.yaml
# python eval.py config=configs/dream_eval.yaml
# python eval.py config=configs/llada_eval.yaml
# see details in ./configsUse trado_eval.yaml for TraDo models' inference, sdar_eval.yaml for SDAR, dream_eval.yaml for Dream and Diffu-Coder, and llada_eval.yaml for LLaDA and MMaDA. Instructions on how to set the configurations are provided in the corresponding configuration files.
We support both general tasks and coding tasks (including automated execution of code) in evaluation.
There are two main sampling methods you can choose:
Static Sampling: unmask fixed number of tokens each time
Dynamic Sampling: unmask tokens based on a chosen threshold, faster than static
To have a look how diffusion language models sample, open ./sample/trace.viewer.html in your browser, or generate trajectory by your self with ./sample/get_trace_viewer.py.
You can also perform inference across multiple nodes using multinode_eval.py with the same configuration files, with only minor modifications as instructed in the configuration files.
In multi-node setup, the first node controls the others. You can run
python multinode_eval.py config=configs/dream_multinode_eval.yaml on the first node to eval, or submit the following as the entry command for a job:
if [[ ${MLP_ROLE_INDEX:-0} -eq 0 ]]; then
python multinode_eval.py config=configs/dream_multinode_eval.yaml
else
exec tail -f /dev/null
fi
# python multinode_eval.py config=configs/trado_longcot_multinode_eval.yaml
# python multinode_eval.py config=configs/llada_multinode_eval.yaml
# ...After downloading the data and model and setting the configuration, you can start reinforcement learning simply with:
python rl.py config=configs/rl_trado.yaml
# python rl.py config=configs/rl_sdar.yaml
# python rl.py config=configs/rl_dream.yaml
# python rl.py config=configs/rl_llada.yaml
# python rl.py config=configs/rl_mmada.yaml
# see details in ./configsWe support TraceRL (optionally with a diffusion-based value model), Coupled RL, and random masking RL across different diffusion language models. The sampling process has been accelerated in all cases by KV-cache.
TraceRL: We optimize the policy based on how it generates sequences. For block-attention models, training can be performed efficiently thanks to block attention. For full-attention models, we introduce a shrinkage parameter, s, that aggregates every s neighboring steps to accelerate training. We also provide a choice of value models for TraceRL, which we find can reduce variance and improve training stability, enabling the use of larger learning rates or fewer gradient accumulation steps more reliably than without using value model.
Random Masking RL: The sampled data are randomly masked and used as training data in RL with a PPO-like objective.
Coupled RL: For each sampled random masking setting, Coupled RL additionally introduces its complement, serving as an extra data sample for training.
We also support a multi-node RL framework; you can submit the following as the entry command:
if [[ ${MLP_ROLE_INDEX:-0} -eq 0 ]]; then
python multinode_rl.py config=configs/multinode_rl_trado.yaml
else
exec tail -f /dev/null
fi
# python multinode_rl.py config=configs/multinode_rl_sdar.yaml
# python multinode_rl.py config=configs/multinode_rl_dream.yaml
# python multinode_rl.py config=configs/multinode_rl_llada.yaml
# python multinode_rl.py config=configs/multinode_rl_mmada.yamlAfter downloading the data and setting the configurations, you can start supervised fine-tuning with:
accelerate launch \
--num_machines 1 \
--machine_rank 0 \
--main_process_ip 127.0.0.1 \
--main_process_port 8888 \
--config_file accelerate_configs/1_node_8_gpus_deepspeed_zero3.yaml \
train/sft_trado.py \
config=configs/sft_trado.yaml
# sft_sdar.py, sft_sdar.yaml
# sft_dream.py, sft_dream.yaml
# sft_llada.py, sft_llada.yaml
# sft_mmada.py, sft_mmada.yaml
# see details in ./configsWe support different SFT strategies for different models.
Block diffusion models (e.g., TraDo and SDAR): support semi-autoregressive fine-tuning or trace fine-tuning (requires setting a specific trace first).
Adapted full-attention models (e.g., Dream and DiffuCoder): support the semi-autoregressive method (using sliced data), random-masking SFT, and AR training (i.e., standard SFT for LLMs).
Pretrained full-attention models (e.g., LLaDA and MMaDA): support semi-autoregressive and random-masking SFT.
To use multi-node, simply run:
accelerate launch \
--num_machines $MLP_WORKER_NUM \
--machine_rank $MLP_ROLE_INDEX \
--main_process_ip $MLP_WORKER_0_HOST \
--main_process_port $MLP_WORKER_0_PORT \
--config_file accelerate_configs/4_node_8_gpus_deepspeed_zero3.yaml \
train/sft_dream.py \
config=configs/sft_dream.yaml
# sft_trado.py, sft_trado.yaml
# ...This work is heavily built on the following open-source models:
SDAR, Dream, LLaDA, MMaDA, and Diffu-coder.
these acceleration methods (engines):
and theoretical foundations:
MDLM, DiffuLLaMA, Block Diffusion.
@article{wang2025revolutionizing,
title={Revolutionizing reinforcement learning framework for diffusion large language models},
author={Wang, Yinjie and Yang, Ling and Li, Bowen and Tian, Ye and Shen, Ke and Wang, Mengdi},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2509.06949},
year={2025}
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for dLLM-RL
Similar Open Source Tools

dLLM-RL
dLLM-RL is a revolutionary reinforcement learning framework designed for Diffusion Large Language Models. It supports various models with diverse structures, offers inference acceleration, RL training capabilities, and SFT functionalities. The tool introduces TraceRL for trajectory-aware RL and diffusion-based value models for optimization stability. Users can download and try models like TraDo-4B-Instruct and TraDo-8B-Instruct. The tool also provides support for multi-node setups and easy building of reinforcement learning methods. Additionally, it offers supervised fine-tuning strategies for different models and tasks.
labo
LABO is a time series forecasting and analysis framework that integrates pre-trained and fine-tuned LLMs with multi-domain agent-based systems. It allows users to create and tune agents easily for various scenarios, such as stock market trend prediction and web public opinion analysis. LABO requires a specific runtime environment setup, including system requirements, Python environment, dependency installations, and configurations. Users can fine-tune their own models using LABO's Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) for computational efficiency and continuous model updates. Additionally, LABO provides a Python library for building model training pipelines and customizing agents for specific tasks.

rl
TorchRL is an open-source Reinforcement Learning (RL) library for PyTorch. It provides pytorch and **python-first** , low and high level abstractions for RL that are intended to be **efficient** , **modular** , **documented** and properly **tested**. The code is aimed at supporting research in RL. Most of it is written in python in a highly modular way, such that researchers can easily swap components, transform them or write new ones with little effort.

MInference
MInference is a tool designed to accelerate pre-filling for long-context Language Models (LLMs) by leveraging dynamic sparse attention. It achieves up to a 10x speedup for pre-filling on an A100 while maintaining accuracy. The tool supports various decoding LLMs, including LLaMA-style models and Phi models, and provides custom kernels for attention computation. MInference is useful for researchers and developers working with large-scale language models who aim to improve efficiency without compromising accuracy.
lionagi
LionAGI is a robust framework for orchestrating multi-step AI operations with precise control. It allows users to bring together multiple models, advanced reasoning, tool integrations, and custom validations in a single coherent pipeline. The framework is structured, expandable, controlled, and transparent, offering features like real-time logging, message introspection, and tool usage tracking. LionAGI supports advanced multi-step reasoning with ReAct, integrates with Anthropic's Model Context Protocol, and provides observability and debugging tools. Users can seamlessly orchestrate multiple models, integrate with Claude Code CLI SDK, and leverage a fan-out fan-in pattern for orchestration. The framework also offers optional dependencies for additional functionalities like reader tools, local inference support, rich output formatting, database support, and graph visualization.

embodied-agents
Embodied Agents is a toolkit for integrating large multi-modal models into existing robot stacks with just a few lines of code. It provides consistency, reliability, scalability, and is configurable to any observation and action space. The toolkit is designed to reduce complexities involved in setting up inference endpoints, converting between different model formats, and collecting/storing datasets. It aims to facilitate data collection and sharing among roboticists by providing Python-first abstractions that are modular, extensible, and applicable to a wide range of tasks. The toolkit supports asynchronous and remote thread-safe agent execution for maximal responsiveness and scalability, and is compatible with various APIs like HuggingFace Spaces, Datasets, Gymnasium Spaces, Ollama, and OpenAI. It also offers automatic dataset recording and optional uploads to the HuggingFace hub.
ProX
ProX is a lm-based data refinement framework that automates the process of cleaning and improving data used in pre-training large language models. It offers better performance, domain flexibility, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional methods. The framework has been shown to improve model performance by over 2% and boost accuracy by up to 20% in tasks like math. ProX is designed to refine data at scale without the need for manual adjustments, making it a valuable tool for data preprocessing in natural language processing tasks.
effective_llm_alignment
This is a super customizable, concise, user-friendly, and efficient toolkit for training and aligning LLMs. It provides support for various methods such as SFT, Distillation, DPO, ORPO, CPO, SimPO, SMPO, Non-pair Reward Modeling, Special prompts basket format, Rejection Sampling, Scoring using RM, Effective FAISS Map-Reduce Deduplication, LLM scoring using RM, NER, CLIP, Classification, and STS. The toolkit offers key libraries like PyTorch, Transformers, TRL, Accelerate, FSDP, DeepSpeed, and tools for result logging with wandb or clearml. It allows mixing datasets, generation and logging in wandb/clearml, vLLM batched generation, and aligns models using the SMPO method.
TokenFormer
TokenFormer is a fully attention-based neural network architecture that leverages tokenized model parameters to enhance architectural flexibility. It aims to maximize the flexibility of neural networks by unifying token-token and token-parameter interactions through the attention mechanism. The architecture allows for incremental model scaling and has shown promising results in language modeling and visual modeling tasks. The codebase is clean, concise, easily readable, state-of-the-art, and relies on minimal dependencies.
open-unlearning
OpenUnlearning is an easily extensible framework that unifies LLM unlearning evaluation benchmarks. It provides efficient implementations of TOFU and MUSE unlearning benchmarks, supporting 5 unlearning methods, 3+ datasets, 6+ evaluation metrics, and 7+ LLMs. Users can easily extend the framework to incorporate more variants, collaborate by adding new benchmarks, unlearning methods, datasets, and evaluation metrics, and drive progress in the field.

sieves
sieves is a library for zero- and few-shot NLP tasks with structured generation, enabling rapid prototyping of NLP applications without the need for training. It simplifies NLP prototyping by bundling capabilities into a single library, providing zero- and few-shot model support, a unified interface for structured generation, built-in tasks for common NLP operations, easy extendability, document-based pipeline architecture, caching to prevent redundant model calls, and more. The tool draws inspiration from spaCy and spacy-llm, offering features like immediate inference, observable pipelines, integrated tools for document parsing and text chunking, ready-to-use tasks such as classification, summarization, translation, and more, persistence for saving and loading pipelines, distillation for specialized model creation, and caching to optimize performance.
zo2
ZO2 (Zeroth-Order Offloading) is an innovative framework designed to enhance the fine-tuning of large language models (LLMs) using zeroth-order (ZO) optimization techniques and advanced offloading technologies. It is tailored for setups with limited GPU memory, enabling the fine-tuning of models with over 175 billion parameters on single GPUs with as little as 18GB of memory. ZO2 optimizes CPU offloading, incorporates dynamic scheduling, and has the capability to handle very large models efficiently without extra time costs or accuracy losses.
PDEBench
PDEBench provides a diverse and comprehensive set of benchmarks for scientific machine learning, including challenging and realistic physical problems. The repository consists of code for generating datasets, uploading and downloading datasets, training and evaluating machine learning models as baselines. It features a wide range of PDEs, realistic and difficult problems, ready-to-use datasets with various conditions and parameters. PDEBench aims for extensibility and invites participation from the SciML community to improve and extend the benchmark.
Pixel-Reasoner
Pixel Reasoner is a framework that introduces reasoning in the pixel-space for Vision-Language Models (VLMs), enabling them to directly inspect, interrogate, and infer from visual evidences. This enhances reasoning fidelity for visual tasks by equipping VLMs with visual reasoning operations like zoom-in and select-frame. The framework addresses challenges like model's imbalanced competence and reluctance to adopt pixel-space operations through a two-phase training approach involving instruction tuning and curiosity-driven reinforcement learning. With these visual operations, VLMs can interact with complex visual inputs such as images or videos to gather necessary information, leading to improved performance across visual reasoning benchmarks.
AgentFly
AgentFly is an extensible framework for building LLM agents with reinforcement learning. It supports multi-turn training by adapting traditional RL methods with token-level masking. It features a decorator-based interface for defining tools and reward functions, enabling seamless extension and ease of use. To support high-throughput training, it implemented asynchronous execution of tool calls and reward computations, and designed a centralized resource management system for scalable environment coordination. A suite of prebuilt tools and environments are provided.
Easy-Translate
Easy-Translate is a script designed for translating large text files with a single command. It supports various models like M2M100, NLLB200, SeamlessM4T, LLaMA, and Bloom. The tool is beginner-friendly and offers seamless and customizable features for advanced users. It allows acceleration on CPU, multi-CPU, GPU, multi-GPU, and TPU, with support for different precisions and decoding strategies. Easy-Translate also provides an evaluation script for translations. Built on HuggingFace's Transformers and Accelerate library, it supports prompt usage and loading huge models efficiently.
For similar tasks
AutoGPTQ
AutoGPTQ is an easy-to-use LLM quantization package with user-friendly APIs, based on GPTQ algorithm (weight-only quantization). It provides a simple and efficient way to quantize large language models (LLMs) to reduce their size and computational cost while maintaining their performance. AutoGPTQ supports a wide range of LLM models, including GPT-2, GPT-J, OPT, and BLOOM. It also supports various evaluation tasks, such as language modeling, sequence classification, and text summarization. With AutoGPTQ, users can easily quantize their LLM models and deploy them on resource-constrained devices, such as mobile phones and embedded systems.
Qwen-TensorRT-LLM
Qwen-TensorRT-LLM is a project developed for the NVIDIA TensorRT Hackathon 2023, focusing on accelerating inference for the Qwen-7B-Chat model using TRT-LLM. The project offers various functionalities such as FP16/BF16 support, INT8 and INT4 quantization options, Tensor Parallel for multi-GPU parallelism, web demo setup with gradio, Triton API deployment for maximum throughput/concurrency, fastapi integration for openai requests, CLI interaction, and langchain support. It supports models like qwen2, qwen, and qwen-vl for both base and chat models. The project also provides tutorials on Bilibili and blogs for adapting Qwen models in NVIDIA TensorRT-LLM, along with hardware requirements and quick start guides for different model types and quantization methods.
stable-diffusion.cpp
The stable-diffusion.cpp repository provides an implementation for inferring stable diffusion in pure C/C++. It offers features such as support for different versions of stable diffusion, lightweight and dependency-free implementation, various quantization support, memory-efficient CPU inference, GPU acceleration, and more. Users can download the built executable program or build it manually. The repository also includes instructions for downloading weights, building from scratch, using different acceleration methods, running the tool, converting weights, and utilizing various features like Flash Attention, ESRGAN upscaling, PhotoMaker support, and more. Additionally, it mentions future TODOs and provides information on memory requirements, bindings, UIs, contributors, and references.

LMOps
LMOps is a research initiative focusing on fundamental research and technology for building AI products with foundation models, particularly enabling AI capabilities with Large Language Models (LLMs) and Generative AI models. The project explores various aspects such as prompt optimization, longer context handling, LLM alignment, acceleration of LLMs, LLM customization, and understanding in-context learning. It also includes tools like Promptist for automatic prompt optimization, Structured Prompting for efficient long-sequence prompts consumption, and X-Prompt for extensible prompts beyond natural language. Additionally, LLMA accelerators are developed to speed up LLM inference by referencing and copying text spans from documents. The project aims to advance technologies that facilitate prompting language models and enhance the performance of LLMs in various scenarios.
Awesome-Efficient-LLM
Awesome-Efficient-LLM is a curated list focusing on efficient large language models. It includes topics such as knowledge distillation, network pruning, quantization, inference acceleration, efficient MOE, efficient architecture of LLM, KV cache compression, text compression, low-rank decomposition, hardware/system, tuning, and survey. The repository provides a collection of papers and projects related to improving the efficiency of large language models through various techniques like sparsity, quantization, and compression.
TensorRT-Model-Optimizer
The NVIDIA TensorRT Model Optimizer is a library designed to quantize and compress deep learning models for optimized inference on GPUs. It offers state-of-the-art model optimization techniques including quantization and sparsity to reduce inference costs for generative AI models. Users can easily stack different optimization techniques to produce quantized checkpoints from torch or ONNX models. The quantized checkpoints are ready for deployment in inference frameworks like TensorRT-LLM or TensorRT, with planned integrations for NVIDIA NeMo and Megatron-LM. The tool also supports 8-bit quantization with Stable Diffusion for enterprise users on NVIDIA NIM. Model Optimizer is available for free on NVIDIA PyPI, and this repository serves as a platform for sharing examples, GPU-optimized recipes, and collecting community feedback.
lightning-bolts
Bolts package provides a variety of components to extend PyTorch Lightning, such as callbacks & datasets, for applied research and production. Users can accelerate Lightning training with the Torch ORT Callback to optimize ONNX graph for faster training & inference. Additionally, users can introduce sparsity with the SparseMLCallback to accelerate inference by leveraging the DeepSparse engine. Specific research implementations are encouraged, with contributions that help train SSL models and integrate with Lightning Flash for state-of-the-art models in applied research.
ms-swift
ms-swift is an official framework provided by the ModelScope community for fine-tuning and deploying large language models and multi-modal large models. It supports training, inference, evaluation, quantization, and deployment of over 400 large models and 100+ multi-modal large models. The framework includes various training technologies and accelerates inference, evaluation, and deployment modules. It offers a Gradio-based Web-UI interface and best practices for easy application of large models. ms-swift supports a wide range of model types, dataset types, hardware support, lightweight training methods, distributed training techniques, quantization training, RLHF training, multi-modal training, interface training, plugin and extension support, inference acceleration engines, model evaluation, and model quantization.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.







