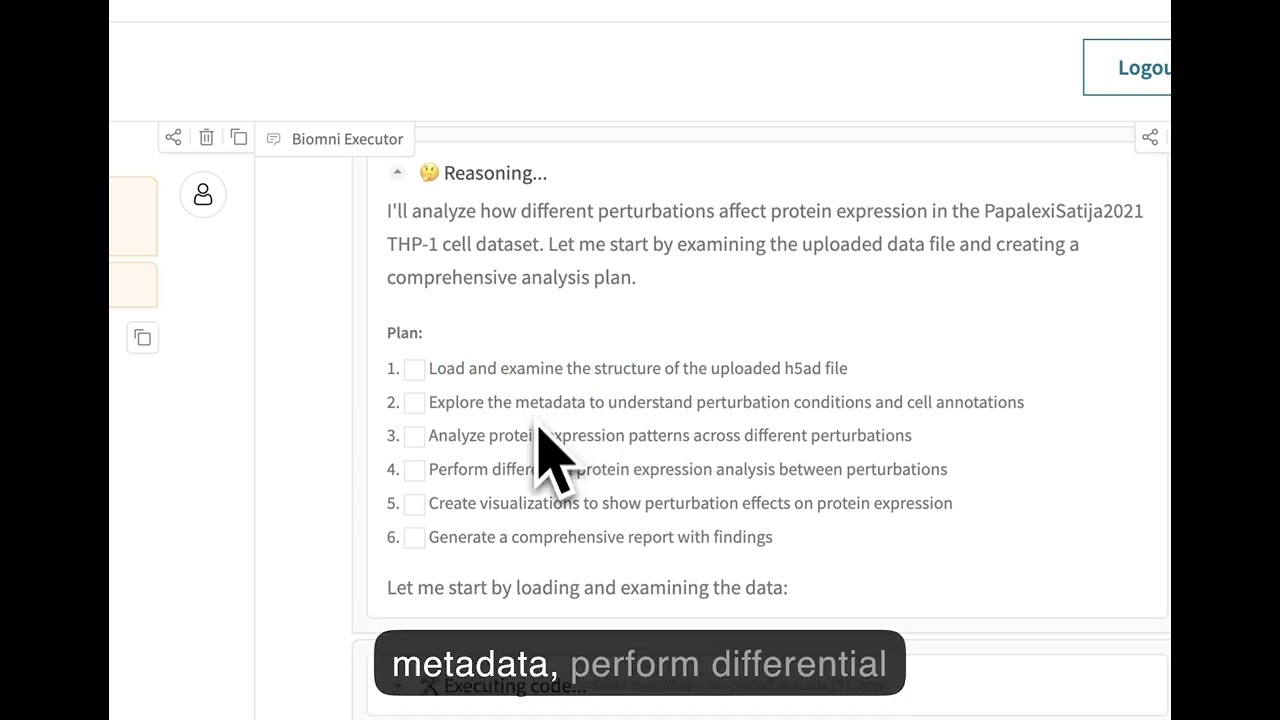
Biomni
Biomni: a general-purpose biomedical AI agent
Stars: 2135

Biomni is a general-purpose biomedical AI agent designed to autonomously execute a wide range of research tasks across diverse biomedical subfields. By integrating cutting-edge large language model (LLM) reasoning with retrieval-augmented planning and code-based execution, Biomni helps scientists dramatically enhance research productivity and generate testable hypotheses.
README:
Biomni is a general-purpose biomedical AI agent designed to autonomously execute a wide range of research tasks across diverse biomedical subfields. By integrating cutting-edge large language model (LLM) reasoning with retrieval-augmented planning and code-based execution, Biomni helps scientists dramatically enhance research productivity and generate testable hypotheses.
Our software environment is massive and we provide a single setup.sh script to setup. Follow this file to setup the env first.
Then activate the environment E1:
conda activate biomni_e1then install the biomni official pip package:
pip install biomni --upgradeFor the latest update, install from the github source version, or do:
pip install git+https://github.com/snap-stanford/Biomni.git@mainLastly, configure your API keys using one of the following methods:
Click to expand
Create a .env file in your project directory:
# Copy the example file
cp .env.example .env
# Edit the .env file with your actual API keysYour .env file should look like:
# Required: Anthropic API Key for Claude models
ANTHROPIC_API_KEY=your_anthropic_api_key_here
# Optional: OpenAI API Key (if using OpenAI models)
OPENAI_API_KEY=your_openai_api_key_here
# Optional: Azure OpenAI API Key (if using Azure OpenAI models)
OPENAI_API_KEY=your_azure_openai_api_key
OPENAI_ENDPOINT=https://your-resource-name.openai.azure.com/
# Optional: AI Studio Gemini API Key (if using Gemini models)
GEMINI_API_KEY=your_gemini_api_key_here
# Optional: groq API Key (if using groq as model provider)
GROQ_API_KEY=your_groq_api_key_here
# Optional: Set the source of your LLM for example:
#"OpenAI", "AzureOpenAI", "Anthropic", "Ollama", "Gemini", "Bedrock", "Groq", "Custom"
LLM_SOURCE=your_LLM_source_here
# Optional: AWS Bedrock Configuration (if using AWS Bedrock models)
AWS_BEARER_TOKEN_BEDROCK=your_bedrock_api_key_here
AWS_REGION=us-east-1
# Optional: Custom model serving configuration
# CUSTOM_MODEL_BASE_URL=http://localhost:8000/v1
# CUSTOM_MODEL_API_KEY=your_custom_api_key_here
# Optional: Biomni data path (defaults to ./data)
# BIOMNI_DATA_PATH=/path/to/your/data
# Optional: Timeout settings (defaults to 600 seconds)
# BIOMNI_TIMEOUT_SECONDS=600Alternatively, configure your API keys in bash profile ~/.bashrc:
export ANTHROPIC_API_KEY="YOUR_API_KEY"
export OPENAI_API_KEY="YOUR_API_KEY" # optional if you just use Claude
export OPENAI_ENDPOINT="https://your-resource-name.openai.azure.com/" # optional unless you are using Azure
export AWS_BEARER_TOKEN_BEDROCK="YOUR_BEDROCK_API_KEY" # optional for AWS Bedrock models
export AWS_REGION="us-east-1" # optional, defaults to us-east-1 for Bedrock
export GEMINI_API_KEY="YOUR_GEMINI_API_KEY" #optional if you want to use a gemini model
export GROQ_API_KEY="YOUR_GROQ_API_KEY" # Optional: set this to use models served by Groq
export LLM_SOURCE="Groq" # Optional: set this to use models served by Groq
Some Python packages are not installed by default in the Biomni environment due to dependency conflicts. If you need these features, you must install the packages manually and may need to uncomment relevant code in the codebase. See the up-to-date list and details in docs/known_conflicts.md.
Once inside the environment, you can start using Biomni:
from biomni.agent import A1
# Initialize the agent with data path, Data lake will be automatically downloaded on first run (~11GB)
agent = A1(path='./data', llm='claude-sonnet-4-20250514')
# Execute biomedical tasks using natural language
agent.go("Plan a CRISPR screen to identify genes that regulate T cell exhaustion, generate 32 genes that maximize the perturbation effect.")
agent.go("Perform scRNA-seq annotation at [PATH] and generate meaningful hypothesis")
agent.go("Predict ADMET properties for this compound: CC(C)CC1=CC=C(C=C1)C(C)C(=O)O")If you plan on using Azure for your model, always prefix the model name with azure- (e.g. llm='azure-gpt-4o').
Biomni includes a centralized configuration system that provides flexible ways to manage settings. You can configure Biomni through environment variables, runtime modifications, or direct parameters.
from biomni.config import default_config
from biomni.agent import A1
# RECOMMENDED: Modify global defaults for consistency
default_config.llm = "gpt-4"
default_config.timeout_seconds = 1200
# All agents AND database queries use these defaults
agent = A1() # Everything uses gpt-4, 1200s timeoutNote: Direct parameters to A1() only affect that agent's reasoning, not database queries. For consistent configuration across all operations, use default_config or environment variables.
For detailed configuration options, see the Configuration Guide.
Biomni supports MCP servers for external tool integration:
from biomni.agent import A1
agent = A1()
agent.add_mcp(config_path="./mcp_config.yaml")
agent.go("Find FDA active ingredient information for ibuprofen")Built-in MCP Servers:
For usage and implementation details, see the MCP Integration Documentation and examples in tutorials/examples/add_mcp_server/ and tutorials/examples/expose_biomni_server/.
Biomni is an open-science initiative that thrives on community contributions. We welcome:
- 🔧 New Tools: Specialized analysis functions and algorithms
- 📊 Datasets: Curated biomedical data and knowledge bases
- 💻 Software: Integration of existing biomedical software packages
- 📋 Benchmarks: Evaluation datasets and performance metrics
- 📚 Misc: Tutorials, examples, and use cases
- 🔧 Update existing tools: many current tools are not optimized - fix and replacements are welcome!
Check out this Contributing Guide on how to contribute to the Biomni ecosystem.
If you have particular tool/database/software in mind that you want to add, you can also submit to this form and the biomni team will implement them.
Biomni-E1 only scratches the surface of what’s possible in the biomedical action space.
Now, we’re building Biomni-E2 — a next-generation environment developed with and for the community.
We believe that by collaboratively defining and curating a shared library of standard biomedical actions, we can accelerate science for everyone.
Join us in shaping the future of biomedical AI agent.
- Contributors with significant impact (e.g., 10+ significant & integrated tool contributions or equivalent) will be invited as co-authors on our upcoming paper in a top-tier journal or conference.
- All contributors will be acknowledged in our publications.
- More contributor perks...
Let’s build it together.
Biomni 101 - Basic concepts and first steps
More to come!
Experience Biomni through our no-code web interface at biomni.stanford.edu.
- [ ] 8 Real-world research task benchmark/leaderboard release
- [ ] A tutorial on how to contribute to Biomni
- [ ] A tutorial on baseline agents
- [x] MCP support
- [x] Biomni A1+E1 release
- Security warning: Currently, Biomni executes LLM-generated code with full system privileges. If you want to use it in production, please use in isolated/sandboxed environments. The agent can access files, network, and system commands. Be careful with sensitive data or credentials.
- This release was frozen as of April 15 2025, so it differs from the current web platform.
- Biomni itself is Apache 2.0-licensed, but certain integrated tools, databases, or software may carry more restrictive commercial licenses. Review each component carefully before any commercial use.
@article{huang2025biomni,
title={Biomni: A General-Purpose Biomedical AI Agent},
author={Huang, Kexin and Zhang, Serena and Wang, Hanchen and Qu, Yuanhao and Lu, Yingzhou and Roohani, Yusuf and Li, Ryan and Qiu, Lin and Zhang, Junze and Di, Yin and others},
journal={bioRxiv},
pages={2025--05},
year={2025},
publisher={Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory}
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Biomni
Similar Open Source Tools

Biomni
Biomni is a general-purpose biomedical AI agent designed to autonomously execute a wide range of research tasks across diverse biomedical subfields. By integrating cutting-edge large language model (LLM) reasoning with retrieval-augmented planning and code-based execution, Biomni helps scientists dramatically enhance research productivity and generate testable hypotheses.
deep-research
Deep Research is a lightning-fast tool that uses powerful AI models to generate comprehensive research reports in just a few minutes. It leverages advanced 'Thinking' and 'Task' models, combined with an internet connection, to provide fast and insightful analysis on various topics. The tool ensures privacy by processing and storing all data locally. It supports multi-platform deployment, offers support for various large language models, web search functionality, knowledge graph generation, research history preservation, local and server API support, PWA technology, multi-key payload support, multi-language support, and is built with modern technologies like Next.js and Shadcn UI. Deep Research is open-source under the MIT License.
labo
LABO is a time series forecasting and analysis framework that integrates pre-trained and fine-tuned LLMs with multi-domain agent-based systems. It allows users to create and tune agents easily for various scenarios, such as stock market trend prediction and web public opinion analysis. LABO requires a specific runtime environment setup, including system requirements, Python environment, dependency installations, and configurations. Users can fine-tune their own models using LABO's Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) for computational efficiency and continuous model updates. Additionally, LABO provides a Python library for building model training pipelines and customizing agents for specific tasks.
BentoML
BentoML is an open-source model serving library for building performant and scalable AI applications with Python. It comes with everything you need for serving optimization, model packaging, and production deployment.
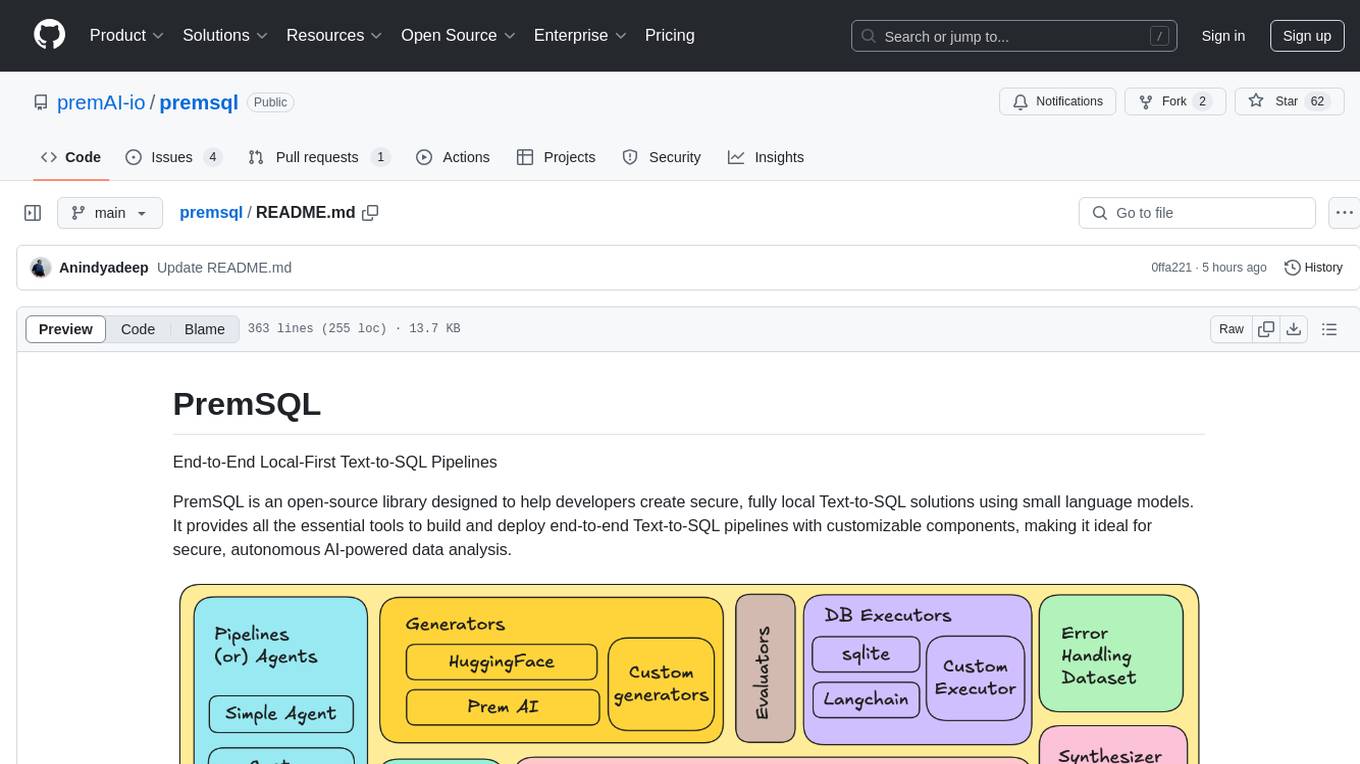
premsql
PremSQL is an open-source library designed to help developers create secure, fully local Text-to-SQL solutions using small language models. It provides essential tools for building and deploying end-to-end Text-to-SQL pipelines with customizable components, ideal for secure, autonomous AI-powered data analysis. The library offers features like Local-First approach, Customizable Datasets, Robust Executors and Evaluators, Advanced Generators, Error Handling and Self-Correction, Fine-Tuning Support, and End-to-End Pipelines. Users can fine-tune models, generate SQL queries from natural language inputs, handle errors, and evaluate model performance against predefined metrics. PremSQL is extendible for customization and private data usage.
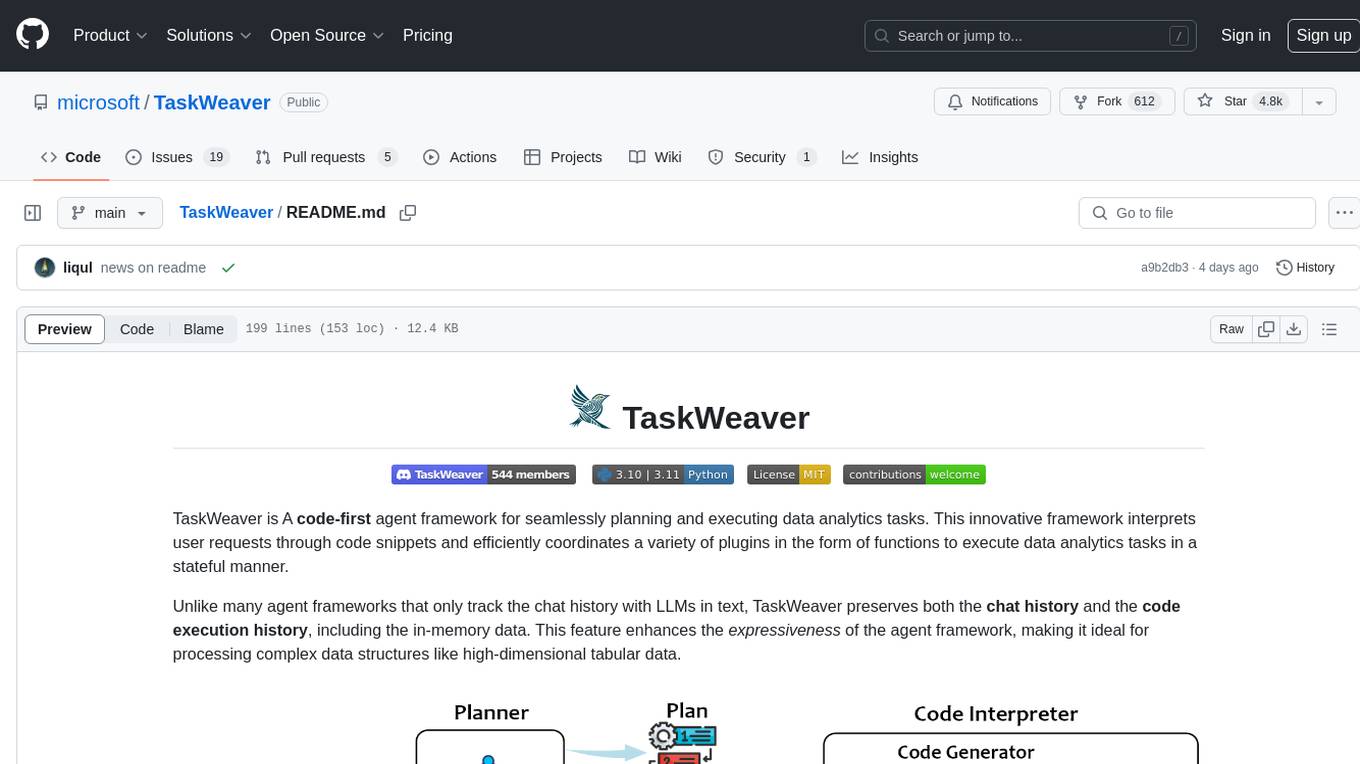
TaskWeaver
TaskWeaver is a code-first agent framework designed for planning and executing data analytics tasks. It interprets user requests through code snippets, coordinates various plugins to execute tasks in a stateful manner, and preserves both chat history and code execution history. It supports rich data structures, customized algorithms, domain-specific knowledge incorporation, stateful execution, code verification, easy debugging, security considerations, and easy extension. TaskWeaver is easy to use with CLI and WebUI support, and it can be integrated as a library. It offers detailed documentation, demo examples, and citation guidelines.
codellm-devkit
Codellm-devkit (CLDK) is a Python library that serves as a multilingual program analysis framework bridging traditional static analysis tools and Large Language Models (LLMs) specialized for code (CodeLLMs). It simplifies the process of analyzing codebases across multiple programming languages, enabling the extraction of meaningful insights and facilitating LLM-based code analysis. The library provides a unified interface for integrating outputs from various analysis tools and preparing them for effective use by CodeLLMs. Codellm-devkit aims to enable the development and experimentation of robust analysis pipelines that combine traditional program analysis tools and CodeLLMs, reducing friction in multi-language code analysis and ensuring compatibility across different tools and LLM platforms. It is designed to seamlessly integrate with popular analysis tools like WALA, Tree-sitter, LLVM, and CodeQL, acting as a crucial intermediary layer for efficient communication between these tools and CodeLLMs. The project is continuously evolving to include new tools and frameworks, maintaining its versatility for code analysis and LLM integration.
kaito
KAITO is an operator that automates the AI/ML model inference or tuning workload in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, provides preset configurations to avoid adjusting workload parameters based on GPU hardware, supports popular open-sourced inference runtimes, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry. Using KAITO simplifies the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes.
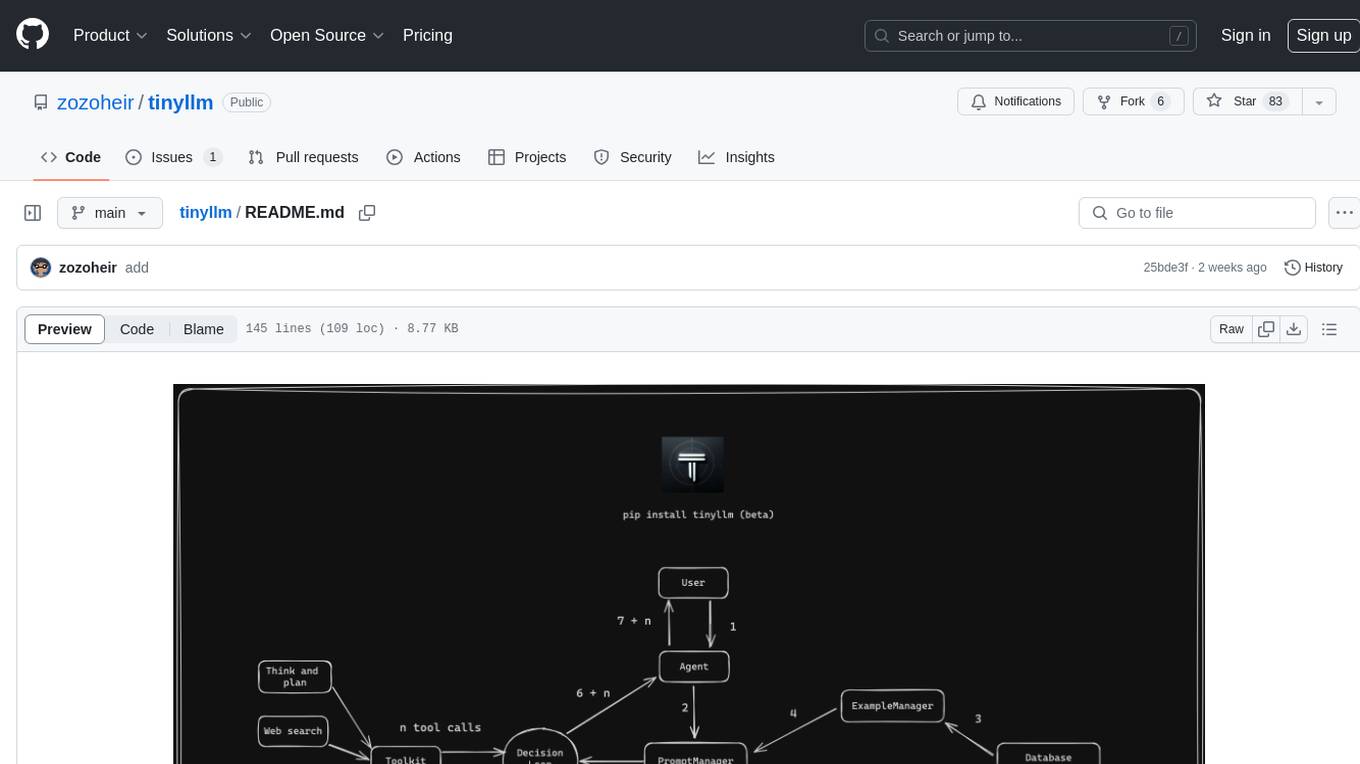
tinyllm
tinyllm is a lightweight framework designed for developing, debugging, and monitoring LLM and Agent powered applications at scale. It aims to simplify code while enabling users to create complex agents or LLM workflows in production. The core classes, Function and FunctionStream, standardize and control LLM, ToolStore, and relevant calls for scalable production use. It offers structured handling of function execution, including input/output validation, error handling, evaluation, and more, all while maintaining code readability. Users can create chains with prompts, LLM models, and evaluators in a single file without the need for extensive class definitions or spaghetti code. Additionally, tinyllm integrates with various libraries like Langfuse and provides tools for prompt engineering, observability, logging, and finite state machine design.

fuse-med-ml
FuseMedML is a Python framework designed to accelerate machine learning-based discovery in the medical field by promoting code reuse. It provides a flexible design concept where data is stored in a nested dictionary, allowing easy handling of multi-modality information. The framework includes components for creating custom models, loss functions, metrics, and data processing operators. Additionally, FuseMedML offers 'batteries included' key components such as fuse.data for data processing, fuse.eval for model evaluation, and fuse.dl for reusable deep learning components. It supports PyTorch and PyTorch Lightning libraries and encourages the creation of domain extensions for specific medical domains.
ProX
ProX is a lm-based data refinement framework that automates the process of cleaning and improving data used in pre-training large language models. It offers better performance, domain flexibility, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional methods. The framework has been shown to improve model performance by over 2% and boost accuracy by up to 20% in tasks like math. ProX is designed to refine data at scale without the need for manual adjustments, making it a valuable tool for data preprocessing in natural language processing tasks.
nous
Nous is an open-source TypeScript platform for autonomous AI agents and LLM based workflows. It aims to automate processes, support requests, review code, assist with refactorings, and more. The platform supports various integrations, multiple LLMs/services, CLI and web interface, human-in-the-loop interactions, flexible deployment options, observability with OpenTelemetry tracing, and specific agents for code editing, software engineering, and code review. It offers advanced features like reasoning/planning, memory and function call history, hierarchical task decomposition, and control-loop function calling options. Nous is designed to be a flexible platform for the TypeScript community to expand and support different use cases and integrations.
DemoGPT
DemoGPT is an all-in-one agent library that provides tools, prompts, frameworks, and LLM models for streamlined agent development. It leverages GPT-3.5-turbo to generate LangChain code, creating interactive Streamlit applications. The tool is designed for creating intelligent, interactive, and inclusive solutions in LLM-based application development. It offers model flexibility, iterative development, and a commitment to user engagement. Future enhancements include integrating Gorilla for autonomous API usage and adding a publicly available database for refining the generation process.

deepeval
DeepEval is a simple-to-use, open-source LLM evaluation framework specialized for unit testing LLM outputs. It incorporates various metrics such as G-Eval, hallucination, answer relevancy, RAGAS, etc., and runs locally on your machine for evaluation. It provides a wide range of ready-to-use evaluation metrics, allows for creating custom metrics, integrates with any CI/CD environment, and enables benchmarking LLMs on popular benchmarks. DeepEval is designed for evaluating RAG and fine-tuning applications, helping users optimize hyperparameters, prevent prompt drifting, and transition from OpenAI to hosting their own Llama2 with confidence.
atropos
Atropos is a robust and scalable framework for Reinforcement Learning Environments with Large Language Models (LLMs). It provides a flexible platform to accelerate LLM-based RL research across diverse interactive settings. Atropos supports multi-turn and asynchronous RL interactions, integrates with various inference APIs, offers a standardized training interface for experimenting with different RL algorithms, and allows for easy scalability by launching more environment instances. The framework manages diverse environment types concurrently for heterogeneous, multi-modal training.

aiscript
AIScript is a unique programming language and web framework written in Rust, designed to help developers effortlessly build AI applications. It combines the strengths of Python, JavaScript, and Rust to create an intuitive, powerful, and easy-to-use tool. The language features first-class functions, built-in AI primitives, dynamic typing with static type checking, data validation, error handling inspired by Rust, a rich standard library, and automatic garbage collection. The web framework offers an elegant route DSL, automatic parameter validation, OpenAPI schema generation, database modules, authentication capabilities, and more. AIScript excels in AI-powered APIs, prototyping, microservices, data validation, and building internal tools.
For similar tasks

Biomni
Biomni is a general-purpose biomedical AI agent designed to autonomously execute a wide range of research tasks across diverse biomedical subfields. By integrating cutting-edge large language model (LLM) reasoning with retrieval-augmented planning and code-based execution, Biomni helps scientists dramatically enhance research productivity and generate testable hypotheses.
admet_ai
ADMET-AI is a platform for ADMET prediction using Chemprop-RDKit models trained on ADMET datasets from the Therapeutics Data Commons. It offers command line, Python API, and web server interfaces for making ADMET predictions on new molecules. The platform can be easily installed using pip and supports GPU acceleration. It also provides options for processing TDC data, plotting results, and hosting a web server. ADMET-AI is a machine learning platform for evaluating large-scale chemical libraries.
For similar jobs
AlphaFold3
AlphaFold3 is an implementation of the Alpha Fold 3 model in PyTorch for accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions. It includes modules for genetic diffusion and full model examples for forward pass computations. The tool allows users to generate random pair and single representations, operate on atomic coordinates, and perform structure predictions based on input tensors. The implementation also provides functionalities for training and evaluating the model.
biochatter
Generative AI models have shown tremendous usefulness in increasing accessibility and automation of a wide range of tasks. This repository contains the `biochatter` Python package, a generic backend library for the connection of biomedical applications to conversational AI. It aims to provide a common framework for deploying, testing, and evaluating diverse models and auxiliary technologies in the biomedical domain. BioChatter is part of the BioCypher ecosystem, connecting natively to BioCypher knowledge graphs.

admet_ai
ADMET-AI is a platform for ADMET prediction using Chemprop-RDKit models trained on ADMET datasets from the Therapeutics Data Commons. It offers command line, Python API, and web server interfaces for making ADMET predictions on new molecules. The platform can be easily installed using pip and supports GPU acceleration. It also provides options for processing TDC data, plotting results, and hosting a web server. ADMET-AI is a machine learning platform for evaluating large-scale chemical libraries.
AI-Drug-Discovery-Design
AI-Drug-Discovery-Design is a repository focused on Artificial Intelligence-assisted Drug Discovery and Design. It explores the use of AI technology to accelerate and optimize the drug development process. The advantages of AI in drug design include speeding up research cycles, improving accuracy through data-driven models, reducing costs by minimizing experimental redundancies, and enabling personalized drug design for specific patients or disease characteristics.
bionemo-framework
NVIDIA BioNeMo Framework is a collection of programming tools, libraries, and models for computational drug discovery. It accelerates building and adapting biomolecular AI models by providing domain-specific, optimized models and tooling for GPU-based computational resources. The framework offers comprehensive documentation and support for both community and enterprise users.
New-AI-Drug-Discovery
New AI Drug Discovery is a repository focused on the applications of Large Language Models (LLM) in drug discovery. It provides resources, tools, and examples for leveraging LLM technology in the pharmaceutical industry. The repository aims to showcase the potential of using AI-driven approaches to accelerate the drug discovery process, improve target identification, and optimize molecular design. By exploring the intersection of artificial intelligence and drug development, this repository offers insights into the latest advancements in computational biology and cheminformatics.
gromacs_copilot
GROMACS Copilot is an agent designed to automate molecular dynamics simulations for proteins in water using GROMACS. It handles system setup, simulation execution, and result analysis automatically, providing outputs such as RMSD, RMSF, Rg, and H-bonds. Users can interact with the agent through prompts and API keys from DeepSeek and OpenAI. The tool aims to simplify the process of running MD simulations, allowing users to focus on other tasks while it handles the technical aspects of the simulations.

Biomni
Biomni is a general-purpose biomedical AI agent designed to autonomously execute a wide range of research tasks across diverse biomedical subfields. By integrating cutting-edge large language model (LLM) reasoning with retrieval-augmented planning and code-based execution, Biomni helps scientists dramatically enhance research productivity and generate testable hypotheses.