
fraim
A flexible framework for security teams to build and deploy AI-powered workflows that complement their existing security operations.
Stars: 120
Fraim is an AI-powered toolkit designed for security engineers to enhance their workflows by leveraging AI capabilities. It offers solutions to find, detect, fix, and flag vulnerabilities throughout the development lifecycle. The toolkit includes features like Risk Flagger for identifying risks in code changes, Code Security Analysis for context-aware vulnerability detection, and Infrastructure as Code Analysis for spotting misconfigurations in cloud environments. Fraim can be run as a CLI tool or integrated into Github Actions, making it a versatile solution for security teams and organizations looking to enhance their security practices with AI technology.
README:
Fraim gives security engineers AI-powered workflows to help them leverage the power of AI to solve REAL business needs. The workflows in this project are companions to a security engineer to help them find, detect, fix, and flag vulnerabilities across the development lifecycle. You can run Fraim as a CLI or inside Github Actions.
Most security teams do not have visibility into the code changes happening on a day-to-day basis, and it is unrealistic to review every change. Risk Flagger solves this by requesting review on a Pull Request only if a "risk" is identified. These "risks" can be defined to match your specific use cases (ie "Flag any changes that make changes to authentication").
Perfect for:
- Security teams with no visibility into code changes
- Teams needing to focus limited security resources on the highest-priority risks
- Organizations wanting to implement "security left" practices
# Basic risk flagger with built-in risks
fraim run risk_flagger --model anthropic/claude-sonnet-4-20250514 --diff --base <base_sha> --head <head_sha> --approver security
# Custom risk considerations inline
fraim run risk_flagger --model anthropic/claude-sonnet-4-20250514 --diff --base <base_sha> --head <head_sha> --custom-risk-list-json '{"Database Changes": "All changes to a database should be flagged, similarly any networking changes that might affect the database should be flagged."}' --custom-risk-list-action replace --approver security
# Custom risk considerations
fraim run risk_flagger --model anthropic/claude-sonnet-4-20250514 --diff --base <base_sha> --head <head_sha> --custom-risk-list-filepath ./custom-risks.yaml --approver securityNOTE: we recommend using the Anthropic or OpenAI latest models for this workflow.
Most security teams rely on signature-based scanners and scattered linters that miss context and overwhelm engineers with noise. Code Security Analysis applies LLM-powered, context-aware review to surface real vulnerabilities across languages (e.g. injection, authentication/authorization flaws, insecure cryptography, secret exposure, and unsafe configurations), explaining impact and suggesting fixes. It integrates cleanly into CI via SARIF output and can run on full repos or just diffs to keep PRs secure without slowing delivery.
Perfect for:
- Security teams needing comprehensive vulnerability coverage
- Organizations requiring compliance with secure coding standards
- Teams wanting to catch vulnerabilities before they reach production
# Comprehensive code analysis
fraim run code --location https://github.com/username/repo-name
# Focus on recent changes
fraim run code --location . --diff --base main --head HEADCloud misconfigurations often slip through because policy-as-code checks and scattered linters miss context across modules, environments, and providers. Infrastructure as Code Analysis uses LLM-powered, context-aware review of Terraform, CloudFormation, and Kubernetes manifests to spot risky defaults, excessive permissions, insecure networking and storage, and compliance gaps—explaining impact and proposing safer configurations. It integrates cleanly into CI via SARIF and can run on full repos or just diffs to prevent drift without slowing delivery.
Perfect for:
- DevOps teams managing cloud infrastructure
- Organizations with strict compliance requirements
- Teams implementing Infrastructure as Code practices
- Security teams overseeing cloud security posture
# Analyze infrastructure configurations
fraim run iac --location https://github.com/username/repo-nameNOTE: This example assumes you are using an Anthropic based model.
Set your API key as a Secret in your repo. - Settings -> Secrets and Variables -> New Repository Secret -> ANTHROPIC_API_KEY Define your workflow inside your repo at .github/workflows/<action_name>.yml
name: AI Security Scan
on:
pull_request:
branches: [main]
jobs:
security-scan:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
permissions:
contents: read
actions: read
security-events: write # Required for uploading SARIF
pull-requests: write # Required for PR comments and annotations
steps:
- name: Run Fraim Security Scan
uses: fraim-dev/fraim-action@v0
with:
anthropic-api-key: ${{ secrets.ANTHROPIC_API_KEY }}
workflows: "code"- Python 3.12+
- pipx installation tool
- API Key for your chosen AI provider (Google Gemini, OpenAI, etc.)
NOTE: These instructions are for Linux based systems, see docs for Windows installation instructions
- Install Fraim:
pipx install fraim-
Configure your AI provider:
- Get an API key from Google AI Studio
- Export it in your environment:
export GEMINI_API_KEY=your_api_key_here
- Get an API key from OpenAI Platform
- Export it in your environment:
export OPENAI_API_KEY=your_api_key_here
-
--debug: Enable debug logging for troubleshooting -
--show-logs SHOW_LOGS: Print logs to standard error output -
--log-output LOG_OUTPUT: Specify directory for log files -
--observability langfuse: Enable LLM observability and analytics
-
--location LOCATION: Repository URL or local path to analyze -
--model MODEL: AI model to use (default varies by workflow, e.g.,gemini/gemini-2.5-flash) -
--temperature TEMPERATURE: Model temperature setting (0.0-1.0, default: 0) -
--chunk-size CHUNK_SIZE: Number of lines per processing chunk -
--limit LIMIT: Maximum number of files to scan -
--globs GLOBS: File patterns to include in analysis -
--max-concurrent-chunks MAX_CONCURRENT_CHUNKS: Control parallelism
-
--diff: Analyze only git diff instead of full repository -
--head HEAD: Git head commit for diff (default: HEAD) -
--base BASE: Git base commit for diff (default: empty tree)
-
--pr-url PR_URL: URL of pull request to analyze -
--approver APPROVER: GitHub username/group to notify
Fraim supports optional observability and tracing through Langfuse, which helps track workflow performance, debug issues, and analyze AI model usage.
To enable observability:
- Install with observability support:
pipx install 'fraim[langfuse]'- Enable observability during execution:
fraim --observability langfuse run code --location /codeThis will trace your workflow execution, LLM calls, and performance metrics in Langfuse for analysis and debugging.
Join our growing community of security professionals using Fraim:
- Documentation: Visit docs.fraim.dev for comprehensive guides and tutorials
- Schedule a Demo: Book time with our team - We'd love to help! Schedule a call for anything related to Fraim (debugging, new integrations, customizing workflows, or even just to chat)
- Slack Community: Join our Slack - Get help, share ideas, and connect with other security minded people looking to use AI to help their team succeed
- Issues: Report bugs and request features via GitHub Issues
- Contributing: See the contributing guide for more information.
Fraim makes it easy to create custom security workflows tailored to your organization's specific needs:
- Workflow Engine: Orchestrates AI agents and tools in flexible, composable patterns
- LLM Integrations: Support for multiple AI providers with seamless switching
- Tool System: Extensible security analysis tools that can be combined and customized
- Input Connectors: Git repositories, file systems, APIs, and custom data sources
- Output Formatters: JSON, SARIF, HTML reports, and custom output formats
Fraim uses a flexible configuration system that allows you to:
- Customize AI model parameters for optimal performance
- Configure workflow-specific settings and thresholds
- Set up custom data sources and input methods
- Define custom output formats and destinations
- Manage API keys and authentication
See the fraim/config/ directory for configuration options.
# workflows/<name>/workflow.py
@dataclass
class MyWorkflowInput:
"""Input for the custom workflow."""
code: Contextual[str]
config: Config
type MyWorkflowOutput = List[sarif.Result]# workflows/<name>/workflow.py
# Define file patterns for your workflow
FILE_PATTERNS = [
'*.config', '*.ini', '*.yaml', '*.yml', '*.json'
]
# Load prompts from YAML files
PROMPTS = PromptTemplate.from_yaml(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), "my_prompts.yaml"))
@workflow('my_custom_workflow')
class MyCustomWorkflow(Workflow[MyWorkflowInput, MyWorkflowOutput]):
"""Analyzes custom configuration files for security issues"""
def __init__(self, config: Config, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(config, *args, **kwargs)
# Construct an LLM instance
llm = LiteLLM.from_config(config)
# Construct the analysis step
parser = PydanticOutputParser(sarif.RunResults)
self.analysis_step = LLMStep(llm, PROMPTS["system"], PROMPTS["user"], parser)
async def workflow(self, input: MyWorkflowInput) -> MyWorkflowOutput:
"""Main workflow execution"""
# 1. Analyze the configuration file
analysis_results = await self.analysis_step.run({"code": input.code})
# 2. Filter results by confidence threshold
filtered_results = self.filter_results_by_confidence(
analysis_results.results, input.config.confidence
)
return filtered_results
def filter_results_by_confidence(self, results: List[sarif.Result], confidence_threshold: int) -> List[sarif.Result]:
"""Filter results by confidence."""
return [result for result in results if result.properties.confidence > confidence_threshold]Create my_prompts.yaml in the same directory:
system: |
You are a configuration security analyzer.
Your job is to analyze configuration files for security misconfigurations and vulnerabilities.
<vulnerability_types>
Valid vulnerability types (use EXACTLY as shown):
- Hardcoded Credentials
- Insecure Defaults
- Excessive Permissions
- Unencrypted Storage
- Weak Cryptography
- Missing Security Headers
- Debug Mode Enabled
- Exposed Secrets
- Insecure Protocols
- Missing Access Controls
</vulnerability_types>
{{ output_format }}
user: |
Analyze the following configuration file for security issues:
{{ code }}This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details.
Fraim is built by security teams, for security teams. Help us make AI-powered security accessible to everyone.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for fraim
Similar Open Source Tools

fraim
Fraim is an AI-powered toolkit designed for security engineers to enhance their workflows by leveraging AI capabilities. It offers solutions to find, detect, fix, and flag vulnerabilities throughout the development lifecycle. The toolkit includes features like Risk Flagger for identifying risks in code changes, Code Security Analysis for context-aware vulnerability detection, and Infrastructure as Code Analysis for spotting misconfigurations in cloud environments. Fraim can be run as a CLI tool or integrated into Github Actions, making it a versatile solution for security teams and organizations looking to enhance their security practices with AI technology.
action_mcp
Action MCP is a powerful tool for managing and automating your cloud infrastructure. It provides a user-friendly interface to easily create, update, and delete resources on popular cloud platforms. With Action MCP, you can streamline your deployment process, reduce manual errors, and improve overall efficiency. The tool supports various cloud providers and offers a wide range of features to meet your infrastructure management needs. Whether you are a developer, system administrator, or DevOps engineer, Action MCP can help you simplify and optimize your cloud operations.
RA.Aid
RA.Aid is an AI software development agent powered by `aider` and advanced reasoning models like `o1`. It combines `aider`'s code editing capabilities with LangChain's agent-based task execution framework to provide an intelligent assistant for research, planning, and implementation of multi-step development tasks. It handles complex programming tasks by breaking them down into manageable steps, running shell commands automatically, and leveraging expert reasoning models like OpenAI's o1. RA.Aid is designed for everyday software development, offering features such as multi-step task planning, automated command execution, and the ability to handle complex programming tasks beyond single-shot code edits.
langmanus
LangManus is a community-driven AI automation framework that combines language models with specialized tools for tasks like web search, crawling, and Python code execution. It implements a hierarchical multi-agent system with agents like Coordinator, Planner, Supervisor, Researcher, Coder, Browser, and Reporter. The framework supports LLM integration, search and retrieval tools, Python integration, workflow management, and visualization. LangManus aims to give back to the open-source community and welcomes contributions in various forms.
company-research-agent
Agentic Company Researcher is a multi-agent tool that generates comprehensive company research reports by utilizing a pipeline of AI agents to gather, curate, and synthesize information from various sources. It features multi-source research, AI-powered content filtering, real-time progress streaming, dual model architecture, modern React frontend, and modular architecture. The tool follows an agentic framework with specialized research and processing nodes, leverages separate models for content generation, uses a content curation system for relevance scoring and document processing, and implements a real-time communication system via WebSocket connections. Users can set up the tool quickly using the provided setup script or manually, and it can also be deployed using Docker and Docker Compose. The application can be used for local development and deployed to various cloud platforms like AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Docker, Heroku, and Google Cloud Run.

cosdata
Cosdata is a cutting-edge AI data platform designed to power the next generation search pipelines. It features immutability, version control, and excels in semantic search, structured knowledge graphs, hybrid search capabilities, real-time search at scale, and ML pipeline integration. The platform is customizable, scalable, efficient, enterprise-grade, easy to use, and can manage multi-modal data. It offers high performance, indexing, low latency, and high requests per second. Cosdata is designed to meet the demands of modern search applications, empowering businesses to harness the full potential of their data.
UCAgent
UCAgent is an AI-powered automated UT verification agent for chip design. It automates chip verification workflow, supports functional and code coverage analysis, ensures consistency among documentation, code, and reports, and collaborates with mainstream Code Agents via MCP protocol. It offers three intelligent interaction modes and requires Python 3.11+, Linux/macOS OS, 4GB+ memory, and access to an AI model API. Users can clone the repository, install dependencies, configure qwen, and start verification. UCAgent supports various verification quality improvement options and basic operations through TUI shortcuts and stage color indicators. It also provides documentation build and preview using MkDocs, PDF manual build using Pandoc + XeLaTeX, and resources for further help and contribution.
DesktopCommanderMCP
Desktop Commander MCP is a server that allows the Claude desktop app to execute long-running terminal commands on your computer and manage processes through Model Context Protocol (MCP). It is built on top of MCP Filesystem Server to provide additional search and replace file editing capabilities. The tool enables users to execute terminal commands with output streaming, manage processes, perform full filesystem operations, and edit code with surgical text replacements or full file rewrites. It also supports vscode-ripgrep based recursive code or text search in folders.
UltraContextAI
UltraContextAI is a comprehensive system for managing AI interactions through memory management, lessons learned tracking, and dual-mode operation (Plan/Agent). It ensures consistent, high-quality development while maintaining detailed project documentation and knowledge retention. The system includes core components like Memory System, Lessons Learned, and Scratchpad. It operates in Plan Mode for information gathering and planning, and Agent Mode for execution. Users can create new features, fix bugs, set up projects, and update documentation using the system. Real-time updates, version control, and cross-referencing are key aspects of the system. Best practices include memory management, task tracking, and documentation standards. Tips and tricks are provided for handling AI and Cursor issues. Contributions to the system are welcome, and it is licensed under MIT License.
pipecat-flows
Pipecat Flows is a framework designed for building structured conversations in AI applications. It allows users to create both predefined conversation paths and dynamically generated flows, handling state management and LLM interactions. The framework includes a Python module for building conversation flows and a visual editor for designing and exporting flow configurations. Pipecat Flows is suitable for scenarios such as customer service scripts, intake forms, personalized experiences, and complex decision trees.
RooFlow
RooFlow is a VS Code extension that enhances AI-assisted development by providing persistent project context and optimized mode interactions. It reduces token consumption and streamlines workflow by integrating Architect, Code, Test, Debug, and Ask modes. The tool simplifies setup, offers real-time updates, and provides clearer instructions through YAML-based rule files. It includes components like Memory Bank, System Prompts, VS Code Integration, and Real-time Updates. Users can install RooFlow by downloading specific files, placing them in the project structure, and running an insert-variables script. They can then start a chat, select a mode, interact with Roo, and use the 'Update Memory Bank' command for synchronization. The Memory Bank structure includes files for active context, decision log, product context, progress tracking, and system patterns. RooFlow features persistent context, real-time updates, mode collaboration, and reduced token consumption.
llmgateway
The llmgateway repository is a tool that provides a gateway for interacting with various LLM (Large Language Model) models. It allows users to easily access and utilize pre-trained language models for tasks such as text generation, sentiment analysis, and language translation. The tool simplifies the process of integrating LLMs into applications and workflows, enabling developers to leverage the power of state-of-the-art language models for various natural language processing tasks.
model-compose
model-compose is an open-source, declarative workflow orchestrator inspired by docker-compose. It lets you define and run AI model pipelines using simple YAML files. Effortlessly connect external AI services or run local AI models within powerful, composable workflows. Features include declarative design, multi-workflow support, modular components, flexible I/O routing, streaming mode support, and more. It supports running workflows locally or serving them remotely, Docker deployment, environment variable support, and provides a CLI interface for managing AI workflows.
fastapi-langgraph-agent-production-ready-template
A production-ready FastAPI template for building AI agent applications with LangGraph integration. This template provides a robust foundation for building scalable, secure, and maintainable AI agent services. It includes features like FastAPI for high-performance async API endpoints, LangGraph integration, structured logging, rate limiting, PostgreSQL for data persistence, Docker support, security measures like JWT-based authentication and input sanitization, developer-friendly features like environment-specific configuration and type hints, a model evaluation framework with automated metric-based evaluation and detailed JSON reports, and a configuration system with environment-specific settings.
copilot-collections
Copilot Collections is an opinionated setup for GitHub Copilot tailored for delivery teams. It provides shared workflows, specialized agents, task prompts, reusable skills, and MCP integrations to streamline the software development process. The focus is on building features while letting Copilot handle the glue. The setup requires a GitHub Copilot Pro license and VS Code version 1.109 or later. It supports a standard workflow of Research, Plan, Implement, and Review, with specialized flows for UI-heavy tasks and end-to-end testing. Agents like Architect, Business Analyst, Software Engineer, UI Reviewer, Code Reviewer, and E2E Engineer assist in different stages of development. Skills like Task Analysis, Architecture Design, Codebase Analysis, Code Review, and E2E Testing provide specialized domain knowledge and workflows. The repository also includes prompts and chat commands for various tasks, along with instructions for installation and configuration in VS Code.
ControlLLM
ControlLLM is a framework that empowers large language models to leverage multi-modal tools for solving complex real-world tasks. It addresses challenges like ambiguous user prompts, inaccurate tool selection, and inefficient tool scheduling by utilizing a task decomposer, a Thoughts-on-Graph paradigm, and an execution engine with a rich toolbox. The framework excels in tasks involving image, audio, and video processing, showcasing superior accuracy, efficiency, and versatility compared to existing methods.
For similar tasks
Awesome-LLM4EDA
LLM4EDA is a repository dedicated to showcasing the emerging progress in utilizing Large Language Models for Electronic Design Automation. The repository includes resources, papers, and tools that leverage LLMs to solve problems in EDA. It covers a wide range of applications such as knowledge acquisition, code generation, code analysis, verification, and large circuit models. The goal is to provide a comprehensive understanding of how LLMs can revolutionize the EDA industry by offering innovative solutions and new interaction paradigms.
DeGPT
DeGPT is a tool designed to optimize decompiler output using Large Language Models (LLM). It requires manual installation of specific packages and setting up API key for OpenAI. The tool provides functionality to perform optimization on decompiler output by running specific scripts.
code2prompt
Code2Prompt is a powerful command-line tool that generates comprehensive prompts from codebases, designed to streamline interactions between developers and Large Language Models (LLMs) for code analysis, documentation, and improvement tasks. It bridges the gap between codebases and LLMs by converting projects into AI-friendly prompts, enabling users to leverage AI for various software development tasks. The tool offers features like holistic codebase representation, intelligent source tree generation, customizable prompt templates, smart token management, Gitignore integration, flexible file handling, clipboard-ready output, multiple output options, and enhanced code readability.
SinkFinder
SinkFinder + LLM is a closed-source semi-automatic vulnerability discovery tool that performs static code analysis on jar/war/zip files. It enhances the capability of LLM large models to verify path reachability and assess the trustworthiness score of the path based on the contextual code environment. Users can customize class and jar exclusions, depth of recursive search, and other parameters through command-line arguments. The tool generates rule.json configuration file after each run and requires configuration of the DASHSCOPE_API_KEY for LLM capabilities. The tool provides detailed logs on high-risk paths, LLM results, and other findings. Rules.json file contains sink rules for various vulnerability types with severity levels and corresponding sink methods.
open-repo-wiki
OpenRepoWiki is a tool designed to automatically generate a comprehensive wiki page for any GitHub repository. It simplifies the process of understanding the purpose, functionality, and core components of a repository by analyzing its code structure, identifying key files and functions, and providing explanations. The tool aims to assist individuals who want to learn how to build various projects by providing a summarized overview of the repository's contents. OpenRepoWiki requires certain dependencies such as Google AI Studio or Deepseek API Key, PostgreSQL for storing repository information, Github API Key for accessing repository data, and Amazon S3 for optional usage. Users can configure the tool by setting up environment variables, installing dependencies, building the server, and running the application. It is recommended to consider the token usage and opt for cost-effective options when utilizing the tool.

CodebaseToPrompt
CodebaseToPrompt is a simple tool that converts a local directory into a structured prompt for Large Language Models (LLMs). It allows users to select specific files for code review, analysis, or documentation by exploring and filtering through the file tree in a browser-based interface. The tool generates a formatted output that can be directly used with AI tools, provides token count estimates, and supports local storage for saving selections. Users can easily copy the selected files in the desired format for further use.
air
air is an R formatter and language server written in Rust. It is currently in alpha stage, so users should expect breaking changes in both the API and formatting results. The tool draws inspiration from various sources like roslyn, swift, rust-analyzer, prettier, biome, and ruff. It provides formatters and language servers, influenced by design decisions from these tools. Users can install air using standalone installers for macOS, Linux, and Windows, which automatically add air to the PATH. Developers can also install the dev version of the air CLI and VS Code extension for further customization and development.
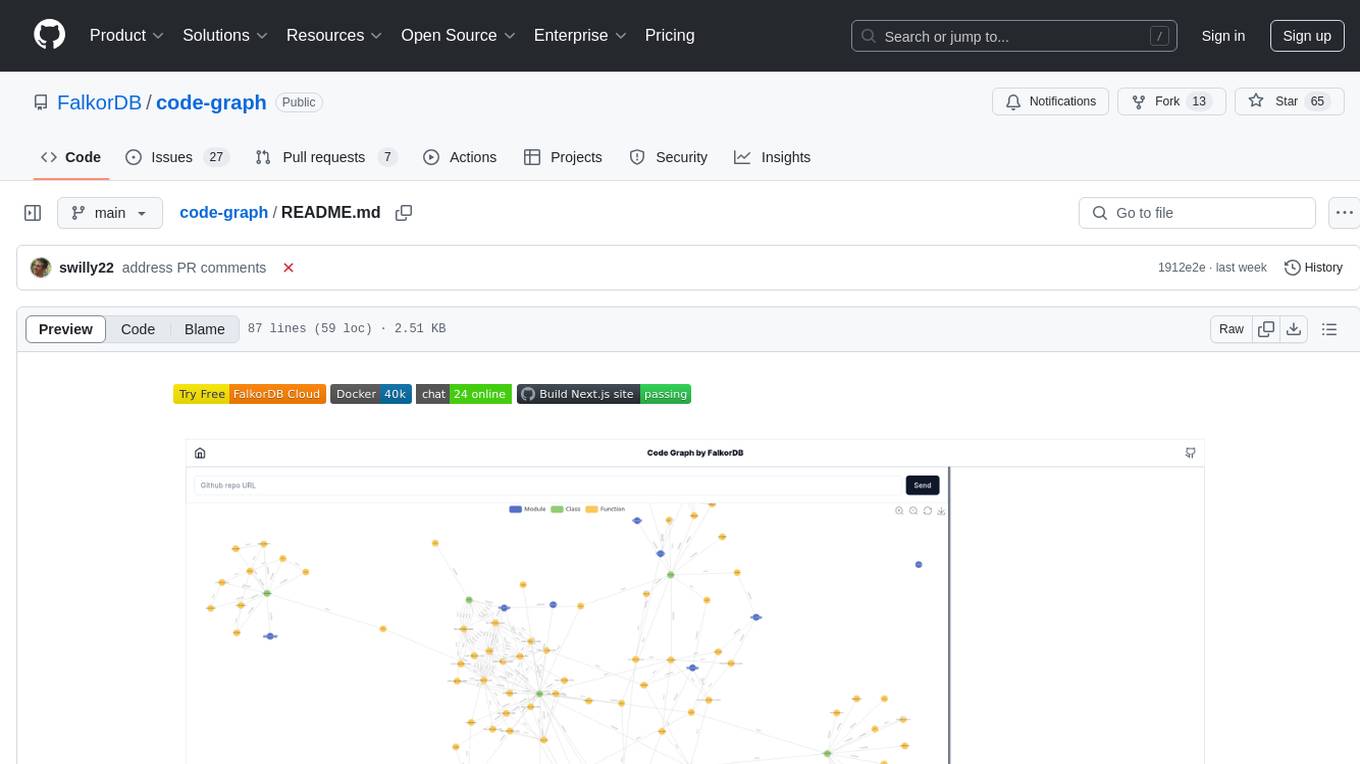
code-graph
Code-graph is a tool composed of FalkorDB Graph DB, Code-Graph-Backend, and Code-Graph-Frontend. It allows users to store and query graphs, manage backend logic, and interact with the website. Users can run the components locally by setting up environment variables and installing dependencies. The tool supports analyzing C & Python source files with plans to add support for more languages in the future. It provides a local repository analysis feature and a live demo accessible through a web browser.
For similar jobs

fraim
Fraim is an AI-powered toolkit designed for security engineers to enhance their workflows by leveraging AI capabilities. It offers solutions to find, detect, fix, and flag vulnerabilities throughout the development lifecycle. The toolkit includes features like Risk Flagger for identifying risks in code changes, Code Security Analysis for context-aware vulnerability detection, and Infrastructure as Code Analysis for spotting misconfigurations in cloud environments. Fraim can be run as a CLI tool or integrated into Github Actions, making it a versatile solution for security teams and organizations looking to enhance their security practices with AI technology.
pup
Pup is a CLI tool designed to give AI agents access to Datadog's observability platform. It offers over 200 commands across 33 Datadog products, allowing agents to fetch metrics, identify errors, and track issues efficiently. Pup ensures that AI agents have the necessary tooling to perform tasks seamlessly, making Datadog the preferred choice for AI-native workflows. With features like self-discoverable commands, structured JSON/YAML output, OAuth2 + PKCE for secure access, and comprehensive API coverage, Pup empowers AI agents to monitor, log, analyze metrics, and enhance security effortlessly.

moonshot
Moonshot is a simple and modular tool developed by the AI Verify Foundation to evaluate Language Model Models (LLMs) and LLM applications. It brings Benchmarking and Red-Teaming together to assist AI developers, compliance teams, and AI system owners in assessing LLM performance. Moonshot can be accessed through various interfaces including User-friendly Web UI, Interactive Command Line Interface, and seamless integration into MLOps workflows via Library APIs or Web APIs. It offers features like benchmarking LLMs from popular model providers, running relevant tests, creating custom cookbooks and recipes, and automating Red Teaming to identify vulnerabilities in AI systems.

comp
Comp AI is an open-source compliance automation platform designed to assist companies in achieving compliance with standards like SOC 2, ISO 27001, and GDPR. It transforms compliance into an engineering problem solved through code, automating evidence collection, policy management, and control implementation while maintaining data and infrastructure control.
iffy
Iffy is a tool for intelligent content moderation at scale, allowing users to keep unwanted content off their platform without the need to manage a team of moderators. It provides features such as a Moderation Dashboard to view and manage all moderation activity, User Lifecycle to automatically suspend users with flagged content, Appeals Management for efficient handling of user appeals, and Powerful Rules & Presets to create custom moderation rules. Users can choose between the managed Iffy Cloud or the free self-hosted Iffy Community version, each offering different features and setup requirements.
iffy
Iffy is a tool for intelligent content moderation at scale, allowing users to keep unwanted content off their platform without the need to manage a team of moderators. It features a Moderation Dashboard to view and manage all moderation activities, User Lifecycle for automatically suspending users with flagged content, Appeals Management for efficient handling of user appeals, and Powerful Rules & Presets to create custom moderation rules based on unique business needs. Users can choose between the managed Iffy Cloud or the free self-hosted Iffy Community version, each offering different features and setups.
cli
Entire CLI is a tool that integrates into your git workflow to capture AI agent sessions on every push. It indexes sessions alongside commits, creating a searchable record of code changes in your repository. It helps you understand why code changed, recover instantly, keep Git history clean, onboard faster, and maintain traceability. Entire offers features like enabling in your project, working with your AI agent, rewinding to a previous checkpoint, resuming a previous session, and disabling Entire. It also explains key concepts like sessions and checkpoints, how it works, strategies, Git worktrees, and concurrent sessions. The tool provides commands for cleaning up data, enabling/disabling hooks, fixing stuck sessions, explaining sessions/commits, resetting state, and showing status/version. Entire uses configuration files for project and local settings, with options for enabling/disabling Entire, setting log levels, strategy, telemetry, and auto-summarization. It supports Gemini CLI in preview alongside Claude Code.
compl-ai
COMPL-AI is a compliance-centered evaluation framework for LLMs created by ETH Zurich, INSAIT, and LatticeFlow AI. It includes a technical interpretation of the EU AI Act and an open-source benchmarking suite. The framework offers tailored benchmarks covering various technical aspects of the EU AI Act, a public Hugging Face leaderboard, and support for multiple providers. Users can run evaluations using a custom CLI tool and contribute to expanding benchmark coverage. The framework is undergoing updates to enhance coverage over the EU AI Act principles and technical requirements, with a focus on risk management, data quality, and cybersecurity measures.
