
bionemo-framework
BioNeMo Framework: For building and adapting AI models in drug discovery at scale
Stars: 661
NVIDIA BioNeMo Framework is a collection of programming tools, libraries, and models for computational drug discovery. It accelerates building and adapting biomolecular AI models by providing domain-specific, optimized models and tooling for GPU-based computational resources. The framework offers comprehensive documentation and support for both community and enterprise users.
README:
NVIDIA BioNeMo Framework is a comprehensive suite of programming tools, libraries, and models designed for digital biology. It accelerates the most time-consuming and costly stages of building and adapting biomolecular AI models by providing domain-specific, optimized model recipes and tooling that are easily integrated into GPU-based computational resources with state-of-the-art performance.

Training benchmarks for ESM-2, a well known protein sequence model using the BERT architecture.
# Try BioNeMo Recipes in Google Colab (Recommend A100, may be too slow or run out of memory on T4)
# Copy paste into Google Colab cells
!git clone https://github.com/NVIDIA/bionemo-framework.git
cd bionemo-framework/bionemo-recipes/recipes/esm2_native_te/
# Install transformer_engine[pytorch] from source, it takes a long time to install from PYPI
!curl -L -o transformer_engine_torch-2.8.0-cp312-cp312-linux_x86_64.whl "https://drive.google.com/uc?export=download&id=1Oz6dkkIMahv3LN_fQhhQRolZ3m-sr9SF"
!pip install --no-build-isolation transformer-engine transformer_engine_torch-2.8.0-cp312-cp312-linux_x86_64.whl
# Install dependencies
!pip install -r requirements.txt
# Run ESM2 Native Recipes with TE
!python train_ddp.py- 10/27/2025 CodonFM recipe released! This is an accelerated version of the original research codebase with scientific preprint.
- 09/30/2025 Megatron/NeMo 5D parallel BioNeMo Framework image v2.7 released on NGC for both x86 and ARM CPUs.
- 09/01/2025 bionemo-recipes goes live! Lightweight and portable examples with state-of-the-art training performance you can riff on to meet your needs.
A core use-case of the BioNeMo Framework is to help digital biology scientists accelerate and scale their model training onto a compute cluster. This repository contains 3 categories of modules for this use-case:
1. Models using fully-sharded-data-parallel (FSDP), which is possible with a number of different implementations including PyTorch’s FSDP2/FSDP1 and NVIDIA megatron-FSDP. Sharding a model with FSDP typically requires only a few lines of code changes. You can find models and ready-to-run recipes parallelized with megatron-FSDP and accelerated with NVIDIA TransformerEngine (TE) in bionemo-recipes.
(Click to expand) bionemo-recipes support matrix
| Directory | Description | Support Status | 5D Parallel | Megatron-FSDP | TE | Sequence Packing | FP8 | Context Parallelism |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
models/amplify
|
TE accelerated protein BERT, pushed to HuggingFace | ✅ Active | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | 🚧 WIP | ✅ | 🚧 WIP |
models/esm2
|
TE accelerated protein BERT, pushed to HuggingFace | ✅ Active | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
models/llama3
|
TE accelerated Llama 3 | ✅ Active | ❌ | 🚧 WIP | ✅ | ✅ | 🚧 WIP | 🚧 WIP |
models/geneformer
|
TE accelerated single-cell BERT | 🚧 WIP | ❌ | ✅ | 🚧 WIP | 🚧 WIP | 🚧 WIP | 🚧 WIP |
recipes/codonfm_ptl_te
|
Recipe for CodonFM's Encodon using TE | ✅ Active | ❌ | 🚧 WIP | ✅ | ✅ | 🚧 WIP | 🚧 WIP |
recipes/esm2_accelerate_te
|
Recipe for ESM2 TE + HF Accelerate | ✅ Active | ❌ | 🚧 WIP | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | 🚧 WIP |
recipes/esm2_native_te
|
Recipe for ESM2 TE + native PyTorch | ✅ Active | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | 🚧 WIP |
recipes/geneformer_native_te_mfsdp_fp8
|
Recipe for Geneformer HF model | 🚧 WIP | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | 🚧 WIP |
recipes/llama3_native_te
|
Recipe for Llama 3 TE + native PyTorch | ✅ Active | ❌ | 🚧 WIP | ✅ | ✅ | 🚧 WIP | 🚧 WIP |
recipes/vit
|
Recipe for Vision Transformer | 🚧 WIP | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | 🚧 WIP |
2. Models using explicit 5D parallelism (tensor parallel, pipeline parallel, context parallel, etc.), for which NVIDIA provides accelerated support with NeMo and Megatron-Core. 5D parallelism requires explicit modification of the model code to make it shardable along different dimensions. The models for this style of acceleration and parallelism can be found in the sub-packages directory. While it is possible to pip install the models, we strongly suggest using our Docker image that comes with NeMo and Megatron-Core pre-installed.
(Click to expand) sub-packages models support matrix
| Directory | Description | Support | 5D Parallel | Megatron-FSDP | TE | Sequence Packing | FP8 | Context Parallel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
bionemo-core |
Model Config/test data utils | ✅ Active | ✅ | N/A | ✅ | ❌ | N/A | N/A |
bionemo-evo2 |
5D parallel model | ✅ Active | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
bionemo-example_model |
Example 5D parallel model | 🔧 Maintenance | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ |
bionemo-llm |
5D parallel base model (BioBert) | ✅ Active | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
bionemo-testing |
Testing Utilities | ✅ Active | ✅ | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
3. Tooling for dataloading and in-the-training-loop processing, which are lightweight and individually pip installable. These are also in the sub-packages directory adjacent to the 5D parallel models.
(Click to expand) sub-packages tooling support matrix
| Directory | Description | Support | 5D Parallel | Megatron-FSDP | TE | Sequence Packing | FP8 | Context Parallel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
bionemo-moco |
Molecular Co-design tools | ✅ Active | ❌ | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
bionemo-noodles |
Python API to fast FASTA file I/O | 🔧 Maintenance | ❌ | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
bionemo-scspeedtest |
Single Cell Dataloading benchmark tests | ✅ Active | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
bionemo-size-aware-batching |
Memory consumption aware batching | 🔧 Maintenance | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
bionemo-scdl |
Modular Single Cell Data Loader | ✅ Active | ✅ Compatible | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
bionemo-webdatamodule |
PyTorch Lightning module to use WebDataset | 🔧 Maintenance | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A |
BioNeMo Framework is part of a larger ecosystem of NVIDIA Biopharma products. Get notified of new releases, bug fixes, critical security updates, and more for biopharma. Subscribe.
-
Official Documentation: Contents of
sub-packagesincluding user guides, API references, and troubleshooting, are documented on our official documentation. Nightly builds of this documentation is available on BioNeMo Framework GitHub Pages -
🚧 In-Progress Documentation 🚧:
bionemo-recipesdocumentation is currently work in progress, however the recipes are meant to be self-documented and easy to understand—we suggest you throw them into your favorite genai code assistant!
Full documentation on using the BioNeMo Framework is provided in our documentation:
https://docs.nvidia.com/bionemo-framework/latest/user-guide/. To simplify the integration of optimized third-party dependencies, BioNeMo is primarily distributed as a containerized library. You can download the latest released container for the BioNeMo Framework from
NGC. To launch a pre-built container, you can use the brev.dev launchable or execute the following command:
docker run --rm -it \
--gpus=all --ipc=host --ulimit memlock=-1 --ulimit stack=67108864 \
nvcr.io/nvidia/clara/bionemo-framework:nightly \
/bin/bashThe NeMo and Megatron-LM dependencies are included as git submodules in bionemo2. The pinned commits for these submodules represent the "last-known-good" versions of these packages that are confirmed to be working with bionemo2 (and those that are tested in CI).
To initialize these sub-modules when cloning the repo, add the --recursive flag to the git clone command:
git clone --recursive [email protected]:NVIDIA/bionemo-framework.git
cd bionemo-frameworkTo download the pinned versions of these submodules within an existing git repository, run
git submodule update --init --recursiveDifferent branches of the repo can have different pinned versions of these third-party submodules. Ensure submodules are automatically updated after switching branches or pulling updates by configuring git with:
git config submodule.recurse trueNOTE: this setting will not download new or remove old submodules with the branch's changes.
You will have to run the full git submodule update --init --recursive command in these situations.
With a locally cloned repository and initialized submodules, build the BioNeMo container using:
docker buildx build . -t my-container-tagIf you see an error message like No file descriptors available (os error 24), add the option --ulimit nofile=65535:65535 to the docker build command.
We distribute a development container configuration for vscode
(.devcontainer/devcontainer.json) that simplifies the process of local testing and development. Opening the
bionemo-framework folder with VSCode should prompt you to re-open the folder inside the devcontainer environment.
[!NOTE] The first time you launch the devcontainer, it may take a long time to build the image. Building the image locally (using the command shown above) will ensure that most of the layers are present in the local docker cache.
See the tutorials pages for example applications and getting started guides.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for bionemo-framework
Similar Open Source Tools

bionemo-framework
NVIDIA BioNeMo Framework is a collection of programming tools, libraries, and models for computational drug discovery. It accelerates building and adapting biomolecular AI models by providing domain-specific, optimized models and tooling for GPU-based computational resources. The framework offers comprehensive documentation and support for both community and enterprise users.
ms-swift
ms-swift is an official framework provided by the ModelScope community for fine-tuning and deploying large language models and multi-modal large models. It supports training, inference, evaluation, quantization, and deployment of over 400 large models and 100+ multi-modal large models. The framework includes various training technologies and accelerates inference, evaluation, and deployment modules. It offers a Gradio-based Web-UI interface and best practices for easy application of large models. ms-swift supports a wide range of model types, dataset types, hardware support, lightweight training methods, distributed training techniques, quantization training, RLHF training, multi-modal training, interface training, plugin and extension support, inference acceleration engines, model evaluation, and model quantization.
pr-agent
PR-Agent is a tool designed to assist in efficiently reviewing and handling pull requests by providing AI feedback and suggestions. It offers various tools such as Review, Describe, Improve, Ask, Update CHANGELOG, and more, with the ability to run them via different interfaces like CLI, PR Comments, or automatically triggering them when a new PR is opened. The tool supports multiple git platforms and models, emphasizing real-life practical usage and modular, customizable tools.
llumen
Llumen is a self-hosted interface optimized for modest hardware like Raspberry Pi, old laptops, and minimal VPS. It offers privacy without complexity, providing essential features with minimal resource demands. Users can enjoy sub-second cold starts, real-time token streaming, various chat modes, rich media support, and a universal API for OpenAI-compatible providers. The tool has a small footprint with a binary size of around 17MB and RAM usage under 128MB. Llumen aims to simplify the setup process and offer a user-friendly experience for individuals seeking a privacy-focused solution.
pr-agent
PR-Agent is a tool that helps to efficiently review and handle pull requests by providing AI feedbacks and suggestions. It supports various commands such as generating PR descriptions, providing code suggestions, answering questions about the PR, and updating the CHANGELOG.md file. PR-Agent can be used via CLI, GitHub Action, GitHub App, Docker, and supports multiple git providers and models. It emphasizes real-life practical usage, with each tool having a single GPT-4 call for quick and affordable responses. The PR Compression strategy enables effective handling of both short and long PRs, while the JSON prompting strategy allows for modular and customizable tools. PR-Agent Pro, the hosted version by CodiumAI, provides additional benefits such as full management, improved privacy, priority support, and extra features.
chat-your-doc
Chat Your Doc is an experimental project exploring various applications based on LLM technology. It goes beyond being just a chatbot project, focusing on researching LLM applications using tools like LangChain and LlamaIndex. The project delves into UX, computer vision, and offers a range of examples in the 'Lab Apps' section. It includes links to different apps, descriptions, launch commands, and demos, aiming to showcase the versatility and potential of LLM applications.
hcaptcha-challenger
hCaptcha Challenger is a tool designed to gracefully face hCaptcha challenges using a multimodal large language model. It does not rely on Tampermonkey scripts or third-party anti-captcha services, instead implementing interfaces for 'AI vs AI' scenarios. The tool supports various challenge types such as image labeling, drag and drop, and advanced tasks like self-supervised challenges and Agentic Workflow. Users can access documentation in multiple languages and leverage resources for tasks like model training, dataset annotation, and model upgrading. The tool aims to enhance user experience in handling hCaptcha challenges with innovative AI capabilities.

composio
Composio is a production-ready toolset for AI agents that enables users to integrate AI agents with various agentic tools effortlessly. It provides support for over 100 tools across different categories, including popular softwares like GitHub, Notion, Linear, Gmail, Slack, and more. Composio ensures managed authorization with support for six different authentication protocols, offering better agentic accuracy and ease of use. Users can easily extend Composio with additional tools, frameworks, and authorization protocols. The toolset is designed to be embeddable and pluggable, allowing for seamless integration and consistent user experience.
new-api
New API is a next-generation large model gateway and AI asset management system that provides a wide range of features, including a new UI interface, multi-language support, online recharge function, key query for usage quota, compatibility with the original One API database, model charging by usage count, channel weighted randomization, data dashboard, token grouping and model restrictions, support for various authorization login methods, support for Rerank models, OpenAI Realtime API, Claude Messages format, reasoning effort setting, content reasoning, user-specific model rate limiting, request format conversion, cache billing support, and various model support such as gpts, Midjourney-Proxy, Suno API, custom channels, Rerank models, Claude Messages format, Dify, and more.

llava-docker
This Docker image for LLaVA (Large Language and Vision Assistant) provides a convenient way to run LLaVA locally or on RunPod. LLaVA is a powerful AI tool that combines natural language processing and computer vision capabilities. With this Docker image, you can easily access LLaVA's functionalities for various tasks, including image captioning, visual question answering, text summarization, and more. The image comes pre-installed with LLaVA v1.2.0, Torch 2.1.2, xformers 0.0.23.post1, and other necessary dependencies. You can customize the model used by setting the MODEL environment variable. The image also includes a Jupyter Lab environment for interactive development and exploration. Overall, this Docker image offers a comprehensive and user-friendly platform for leveraging LLaVA's capabilities.
awsome-distributed-training
This repository contains reference architectures and test cases for distributed model training with Amazon SageMaker Hyperpod, AWS ParallelCluster, AWS Batch, and Amazon EKS. The test cases cover different types and sizes of models as well as different frameworks and parallel optimizations (Pytorch DDP/FSDP, MegatronLM, NemoMegatron...).
stm32ai-modelzoo
The STM32 AI model zoo is a collection of reference machine learning models optimized to run on STM32 microcontrollers. It provides a large collection of application-oriented models ready for re-training, scripts for easy retraining from user datasets, pre-trained models on reference datasets, and application code examples generated from user AI models. The project offers training scripts for transfer learning or training custom models from scratch. It includes performances on reference STM32 MCU and MPU for float and quantized models. The project is organized by application, providing step-by-step guides for training and deploying models.
optillm
optillm is an OpenAI API compatible optimizing inference proxy implementing state-of-the-art techniques to enhance accuracy and performance of LLMs, focusing on reasoning over coding, logical, and mathematical queries. By leveraging additional compute at inference time, it surpasses frontier models across diverse tasks.
aikit
AIKit is a comprehensive platform for hosting, deploying, building, and fine-tuning large language models (LLMs). It offers inference using LocalAI, extensible fine-tuning interface, and OCI packaging for distributing models. AIKit supports various models, multi-modal model and image generation, Kubernetes deployment, and supply chain security. It can run on AMD64 and ARM64 CPUs, NVIDIA GPUs, and Apple Silicon (experimental). Users can quickly get started with AIKit without a GPU and access pre-made models. The platform is OpenAI API compatible and provides easy-to-use configuration for inference and fine-tuning.
crabml
Crabml is a llama.cpp compatible AI inference engine written in Rust, designed for efficient inference on various platforms with WebGPU support. It focuses on running inference tasks with SIMD acceleration and minimal memory requirements, supporting multiple models and quantization methods. The project is hackable, embeddable, and aims to provide high-performance AI inference capabilities.
agentic
Agentic is a standard AI functions/tools library optimized for TypeScript and LLM-based apps, compatible with major AI SDKs. It offers a set of thoroughly tested AI functions that can be used with favorite AI SDKs without writing glue code. The library includes various clients for services like Bing web search, calculator, Clearbit data resolution, Dexa podcast questions, and more. It also provides compound tools like SearchAndCrawl and supports multiple AI SDKs such as OpenAI, Vercel AI SDK, LangChain, LlamaIndex, Firebase Genkit, and Dexa Dexter. The goal is to create minimal clients with strongly-typed TypeScript DX, composable AIFunctions via AIFunctionSet, and compatibility with major TS AI SDKs.
For similar tasks
Generative-AI-Drug-Discovery
Generative-AI-Drug-Discovery is a public repository on GitHub focused on using tensor network machine learning approaches to accelerate GenAI for drug discovery. The repository aims to implement effective architectures and methodologies into Large Language Models (LLMs) to enhance Drug Discovery Generative AI performance.

bionemo-framework
NVIDIA BioNeMo Framework is a collection of programming tools, libraries, and models for computational drug discovery. It accelerates building and adapting biomolecular AI models by providing domain-specific, optimized models and tooling for GPU-based computational resources. The framework offers comprehensive documentation and support for both community and enterprise users.
New-AI-Drug-Discovery
New AI Drug Discovery is a repository focused on the applications of Large Language Models (LLM) in drug discovery. It provides resources, tools, and examples for leveraging LLM technology in the pharmaceutical industry. The repository aims to showcase the potential of using AI-driven approaches to accelerate the drug discovery process, improve target identification, and optimize molecular design. By exploring the intersection of artificial intelligence and drug development, this repository offers insights into the latest advancements in computational biology and cheminformatics.
Pathway-AI-Bootcamp
Welcome to the μLearn x Pathway Initiative, an exciting adventure into the world of Artificial Intelligence (AI)! This comprehensive course, developed in collaboration with Pathway, will empower you with the knowledge and skills needed to navigate the fascinating world of AI, with a special focus on Large Language Models (LLMs).
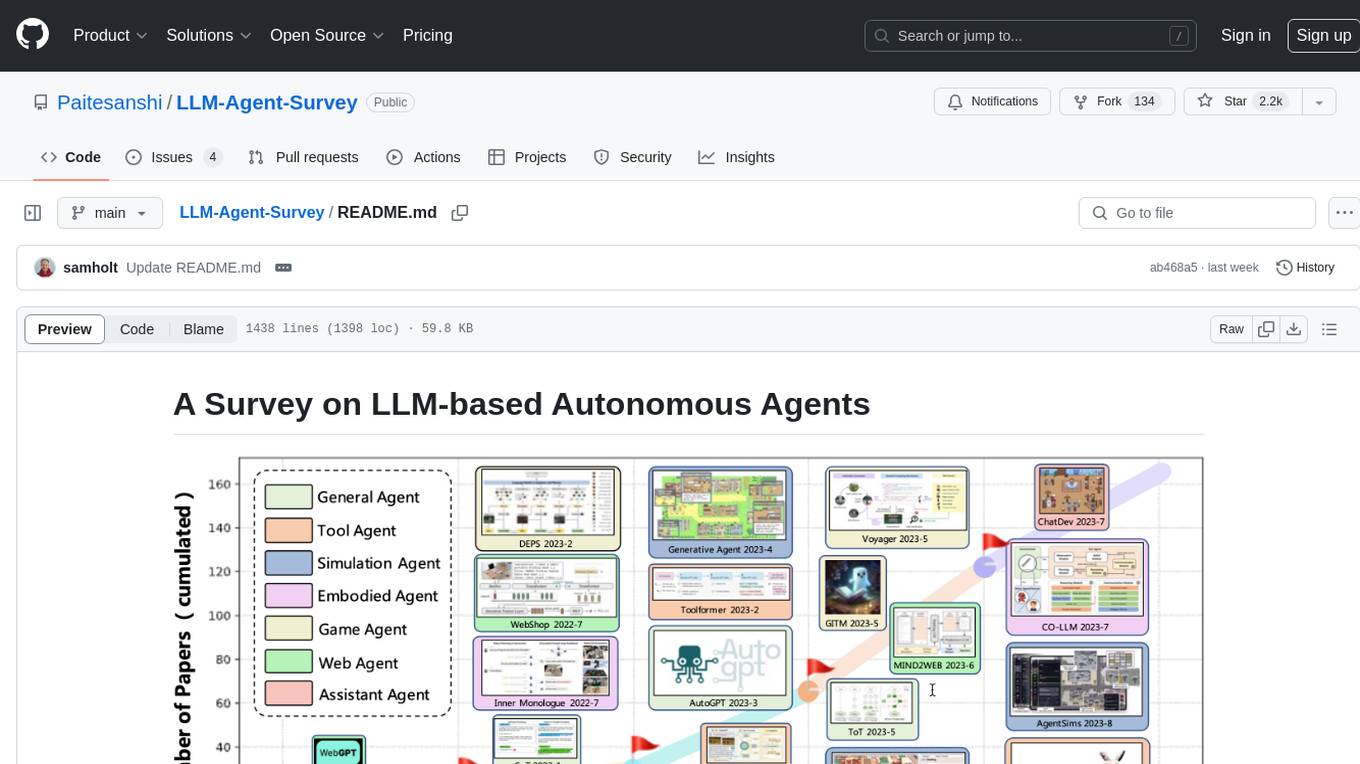
LLM-Agent-Survey
Autonomous agents are designed to achieve specific objectives through self-guided instructions. With the emergence and growth of large language models (LLMs), there is a growing trend in utilizing LLMs as fundamental controllers for these autonomous agents. This repository conducts a comprehensive survey study on the construction, application, and evaluation of LLM-based autonomous agents. It explores essential components of AI agents, application domains in natural sciences, social sciences, and engineering, and evaluation strategies. The survey aims to be a resource for researchers and practitioners in this rapidly evolving field.

genkit
Firebase Genkit (beta) is a framework with powerful tooling to help app developers build, test, deploy, and monitor AI-powered features with confidence. Genkit is cloud optimized and code-centric, integrating with many services that have free tiers to get started. It provides unified API for generation, context-aware AI features, evaluation of AI workflow, extensibility with plugins, easy deployment to Firebase or Google Cloud, observability and monitoring with OpenTelemetry, and a developer UI for prototyping and testing AI features locally. Genkit works seamlessly with Firebase or Google Cloud projects through official plugins and templates.
vector-cookbook
The Vector Cookbook is a collection of recipes and sample application starter kits for building AI applications with LLMs using PostgreSQL and Timescale Vector. Timescale Vector enhances PostgreSQL for AI applications by enabling the storage of vector, relational, and time-series data with faster search, higher recall, and more efficient time-based filtering. The repository includes resources, sample applications like TSV Time Machine, and guides for creating, storing, and querying OpenAI embeddings with PostgreSQL and pgvector. Users can learn about Timescale Vector, explore performance benchmarks, and access Python client libraries and tutorials.
cogai
The W3C Cognitive AI Community Group focuses on advancing Cognitive AI through collaboration on defining use cases, open source implementations, and application areas. The group aims to demonstrate the potential of Cognitive AI in various domains such as customer services, healthcare, cybersecurity, online learning, autonomous vehicles, manufacturing, and web search. They work on formal specifications for chunk data and rules, plausible knowledge notation, and neural networks for human-like AI. The group positions Cognitive AI as a combination of symbolic and statistical approaches inspired by human thought processes. They address research challenges including mimicry, emotional intelligence, natural language processing, and common sense reasoning. The long-term goal is to develop cognitive agents that are knowledgeable, creative, collaborative, empathic, and multilingual, capable of continual learning and self-awareness.
For similar jobs
AlphaFold3
AlphaFold3 is an implementation of the Alpha Fold 3 model in PyTorch for accurate structure prediction of biomolecular interactions. It includes modules for genetic diffusion and full model examples for forward pass computations. The tool allows users to generate random pair and single representations, operate on atomic coordinates, and perform structure predictions based on input tensors. The implementation also provides functionalities for training and evaluating the model.
biochatter
Generative AI models have shown tremendous usefulness in increasing accessibility and automation of a wide range of tasks. This repository contains the `biochatter` Python package, a generic backend library for the connection of biomedical applications to conversational AI. It aims to provide a common framework for deploying, testing, and evaluating diverse models and auxiliary technologies in the biomedical domain. BioChatter is part of the BioCypher ecosystem, connecting natively to BioCypher knowledge graphs.
admet_ai
ADMET-AI is a platform for ADMET prediction using Chemprop-RDKit models trained on ADMET datasets from the Therapeutics Data Commons. It offers command line, Python API, and web server interfaces for making ADMET predictions on new molecules. The platform can be easily installed using pip and supports GPU acceleration. It also provides options for processing TDC data, plotting results, and hosting a web server. ADMET-AI is a machine learning platform for evaluating large-scale chemical libraries.
AI-Drug-Discovery-Design
AI-Drug-Discovery-Design is a repository focused on Artificial Intelligence-assisted Drug Discovery and Design. It explores the use of AI technology to accelerate and optimize the drug development process. The advantages of AI in drug design include speeding up research cycles, improving accuracy through data-driven models, reducing costs by minimizing experimental redundancies, and enabling personalized drug design for specific patients or disease characteristics.

bionemo-framework
NVIDIA BioNeMo Framework is a collection of programming tools, libraries, and models for computational drug discovery. It accelerates building and adapting biomolecular AI models by providing domain-specific, optimized models and tooling for GPU-based computational resources. The framework offers comprehensive documentation and support for both community and enterprise users.

New-AI-Drug-Discovery
New AI Drug Discovery is a repository focused on the applications of Large Language Models (LLM) in drug discovery. It provides resources, tools, and examples for leveraging LLM technology in the pharmaceutical industry. The repository aims to showcase the potential of using AI-driven approaches to accelerate the drug discovery process, improve target identification, and optimize molecular design. By exploring the intersection of artificial intelligence and drug development, this repository offers insights into the latest advancements in computational biology and cheminformatics.
gromacs_copilot
GROMACS Copilot is an agent designed to automate molecular dynamics simulations for proteins in water using GROMACS. It handles system setup, simulation execution, and result analysis automatically, providing outputs such as RMSD, RMSF, Rg, and H-bonds. Users can interact with the agent through prompts and API keys from DeepSeek and OpenAI. The tool aims to simplify the process of running MD simulations, allowing users to focus on other tasks while it handles the technical aspects of the simulations.

Biomni
Biomni is a general-purpose biomedical AI agent designed to autonomously execute a wide range of research tasks across diverse biomedical subfields. By integrating cutting-edge large language model (LLM) reasoning with retrieval-augmented planning and code-based execution, Biomni helps scientists dramatically enhance research productivity and generate testable hypotheses.

