nixtla
TimeGPT-1: production ready pre-trained Time Series Foundation Model for forecasting and anomaly detection. Generative pretrained transformer for time series trained on over 100B data points. It's capable of accurately predicting various domains such as retail, electricity, finance, and IoT with just a few lines of code 🚀.
Stars: 2646
Nixtla is a production-ready generative pretrained transformer for time series forecasting and anomaly detection. It can accurately predict various domains such as retail, electricity, finance, and IoT with just a few lines of code. TimeGPT introduces a paradigm shift with its standout performance, efficiency, and simplicity, making it accessible even to users with minimal coding experience. The model is based on self-attention and is independently trained on a vast time series dataset to minimize forecasting error. It offers features like zero-shot inference, fine-tuning, API access, adding exogenous variables, multiple series forecasting, custom loss function, cross-validation, prediction intervals, and handling irregular timestamps.
README:

TimeGPT is a production ready, generative pretrained transformer for time series. It's capable of accurately predicting various domains such as retail, electricity, finance, and IoT with just a few lines of code 🚀.
- Quick Start
- Installation
- Forecasting with TimeGPT
- Anomaly Detection
- Zero-shot Results
- How to Cite
- Features and Mentions
- License
- Get in Touch
https://github.com/Nixtla/nixtla/assets/4086186/163ad9e6-7a16-44e1-b2e9-dab8a0b7b6b6
pip install nixtla>=0.5.1import pandas as pd
from nixtla import NixtlaClient# Get your API Key at dashboard.nixtla.io
# 1. Instantiate the NixtlaClient
nixtla_client = NixtlaClient(api_key = 'YOUR API KEY HERE')
# 2. Read historic electricity demand data
df = pd.read_csv('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Nixtla/transfer-learning-time-series/main/datasets/electricity-short.csv')
# 3. Forecast the next 24 hours
fcst_df = nixtla_client.forecast(df, h=24, level=[80, 90])
# 4. Plot your results (optional)
nixtla_client.plot(df, fcst_df, level=[80, 90])# Get your API Key at dashboard.nixtla.io
# 1. Instantiate the NixtlaClient
nixtla_client = NixtlaClient(api_key = 'YOUR API KEY HERE')
# 2. Read Data # Wikipedia visits of NFL Star (
df = pd.read_csv('https://datasets-nixtla.s3.amazonaws.com/peyton-manning.csv')
# 3. Detect Anomalies
anomalies_df = nixtla_client.detect_anomalies(df, time_col='timestamp', target_col='value', freq='D')
# 4. Plot your results (optional)
nixtla_client.plot(df, anomalies_df,time_col='timestamp', target_col='value')Explore our API Reference to discover how to leverage TimeGPT across various programming languages including JavaScript, Go, and more.
-
Zero-shot Inference: TimeGPT can generate forecasts and detect anomalies straight out of the box, requiring no prior training data. This allows for immediate deployment and quick insights from any time series data.
-
Fine-tuning: Enhance TimeGPT's capabilities by fine-tuning the model on your specific datasets, enabling the model to adapt to the nuances of your unique time series data and improving performance on tailored tasks.
-
API Access: Integrate TimeGPT seamlessly into your applications via our robust API. Upcoming support for Azure Studio will provide even more flexible integration options. Alternatively, deploy TimeGPT on your own infrastructure to maintain full control over your data and workflows.
-
Add Exogenous Variables: Incorporate additional variables that might influence your predictions to enhance forecast accuracy. (E.g. Special Dates, events or prices)
-
Multiple Series Forecasting: Simultaneously forecast multiple time series data, optimizing workflows and resources.
-
Custom Loss Function: Tailor the fine-tuning process with a custom loss function to meet specific performance metrics.
-
Cross Validation: Implement out of the box cross-validation techniques to ensure model robustness and generalizability.
-
Prediction Intervals: Provide intervals in your predictions to quantify uncertainty effectively.
-
Irregular Timestamps: Handle data with irregular timestamps, accommodating non-uniform interval series without preprocessing.
Dive into our comprehensive documentation to discover examples and practical use cases for TimeGPT. Our documentation covers a wide range of topics, including:
-
Getting Started: Begin with our user-friendly Quickstart Guide and learn how to set up your API key effortlessly.
-
Advanced Techniques: Master advanced forecasting methods and learn how to enhance model accuracy with our tutorials on anomaly detection, fine-tuning models using specific loss functions, and scaling computations across distributed frameworks such as Spark, Dask, and Ray.
-
Specialized Topics: Explore specialized topics like handling exogenous variables, model validation through cross-validation, and strategies for forecasting under uncertainty.
-
Real-World Applications: Uncover how TimeGPT is applied in real-world scenarios through case studies on forecasting web traffic and predicting Bitcoin prices.
Time series data is pivotal across various sectors, including finance, healthcare, meteorology, and social sciences. Whether it's monitoring ocean tides or tracking the Dow Jones's daily closing values, time series data is crucial for forecasting and decision-making.
Traditional analysis methods such as ARIMA, ETS, MSTL, Theta, CES, machine learning models like XGBoost and LightGBM, and deep learning approaches have been standard tools for analysts. However, TimeGPT introduces a paradigm shift with its standout performance, efficiency, and simplicity. Thanks to its zero-shot inference capability, TimeGPT streamlines the analytical process, making it accessible even to users with minimal coding experience.
TimeGPT is user-friendly and low-code, enabling users to upload their time series data and either generate forecasts or detect anomalies with just a single line of code. As the only foundation model for time series analysis out of the box, TimeGPT can be integrated via our public APIs, through Azure Studio (coming soon), or deployed on your own infrastructure.
Self-attention, the revolutionary concept introduced by the paper “Attention is all you need“, is the basis of the this foundational model. The TimeGPT model is not based on any existing large language model(LLMs). It is independently trained on vast timeseries dataset as a large transformer model and is designed so as to minimize the forecasting error.
The architecture consists of an encoder-decoder structure with multiple layers, each with residual connections and layer normalization. Finally, a linear layer maps the decoder’s output to the forecasting window dimension. The general intuition is that attentionbased mechanisms are able to capture the diversity of past events and correctly extrapolate potential future distributions.
TimeGPT was trained on, to our knowledge, the largest collection of publicly available time series, collectively encompassing over 100 billion data points. This training set incorporates time series from a broad array of domains, including finance, economics, demographics, healthcare, weather, IoT sensor data, energy, web traffic, sales, transport, and banking. Due to this diverse set of domains, the training dataset contains time series with a wide range of characteristics
TimeGPT has been tested for its zero-shot inference capabilities on more than 300K unique series, which involve using the model without additional fine-tuning on the test dataset. TimeGPT outperforms a comprehensive range of well-established statistical and cutting-edge deep learning models, consistently ranking among the top three performers across various frequencies.
TimeGPT also excels by offering simple and rapid predictions using a pre-trained model. This stands in stark contrast to other models that typically require an extensive training and prediction pipeline.
For zero-shot inference, our internal tests recorded an average GPU inference speed of 0.6 milliseconds per series for TimeGPT, which nearly mirrors that of the simple Seasonal Naive.
If you find TimeGPT useful for your research, please consider citing the associated paper:
@misc{garza2023timegpt1,
title={TimeGPT-1},
author={Azul Garza and Max Mergenthaler-Canseco},
year={2023},
eprint={2310.03589},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.LG}
}
TimeGPT has been featured in many publications and has been recognized for its innovative approach to time series forecasting. Here are some of the features and mentions:
- TimeGPT Revolutionizing Time Series Forecasting
- TimeGPT: The First Foundation Model for Time Series Forecasting
- TimeGPT: Revolutionising Time Series Forecasting with Generative Models
- TimeGPT on Turing Post
- TimeGPT Presentation at AWS Events
- TimeGPT: Machine Learning for Time Series Made Accessible - Podcast
- TimeGPT on The Data Exchange
- How TimeGPT Transforms Predictive Analytics with AI
- TimeGPT: The First Foundation Model - AI Horizon Forecast
TimeGPT is closed source. However, this SDK is open source and available under the Apache 2.0 License. Feel free to contribute (check out the Contributing guide for more details).
For any questions or feedback, please feel free to reach out to us at ops [at] nixtla.io.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for nixtla
Similar Open Source Tools

nixtla
Nixtla is a production-ready generative pretrained transformer for time series forecasting and anomaly detection. It can accurately predict various domains such as retail, electricity, finance, and IoT with just a few lines of code. TimeGPT introduces a paradigm shift with its standout performance, efficiency, and simplicity, making it accessible even to users with minimal coding experience. The model is based on self-attention and is independently trained on a vast time series dataset to minimize forecasting error. It offers features like zero-shot inference, fine-tuning, API access, adding exogenous variables, multiple series forecasting, custom loss function, cross-validation, prediction intervals, and handling irregular timestamps.
pytorch-forecasting
PyTorch Forecasting is a PyTorch-based package for time series forecasting with state-of-the-art network architectures. It offers a high-level API for training networks on pandas data frames and utilizes PyTorch Lightning for scalable training on GPUs and CPUs. The package aims to simplify time series forecasting with neural networks by providing a flexible API for professionals and default settings for beginners. It includes a timeseries dataset class, base model class, multiple neural network architectures, multi-horizon timeseries metrics, and hyperparameter tuning with optuna. PyTorch Forecasting is built on pytorch-lightning for easy training on various hardware configurations.
llm-course
The LLM course is divided into three parts: 1. 🧩 **LLM Fundamentals** covers essential knowledge about mathematics, Python, and neural networks. 2. 🧑🔬 **The LLM Scientist** focuses on building the best possible LLMs using the latest techniques. 3. 👷 **The LLM Engineer** focuses on creating LLM-based applications and deploying them. For an interactive version of this course, I created two **LLM assistants** that will answer questions and test your knowledge in a personalized way: * 🤗 **HuggingChat Assistant**: Free version using Mixtral-8x7B. * 🤖 **ChatGPT Assistant**: Requires a premium account. ## 📝 Notebooks A list of notebooks and articles related to large language models. ### Tools | Notebook | Description | Notebook | |----------|-------------|----------| | 🧐 LLM AutoEval | Automatically evaluate your LLMs using RunPod |  | | 🥱 LazyMergekit | Easily merge models using MergeKit in one click. |  | | 🦎 LazyAxolotl | Fine-tune models in the cloud using Axolotl in one click. |  | | ⚡ AutoQuant | Quantize LLMs in GGUF, GPTQ, EXL2, AWQ, and HQQ formats in one click. |  | | 🌳 Model Family Tree | Visualize the family tree of merged models. |  | | 🚀 ZeroSpace | Automatically create a Gradio chat interface using a free ZeroGPU. |  |
agentUniverse
agentUniverse is a framework for developing applications powered by multi-agent based on large language model. It provides essential components for building single agent and multi-agent collaboration mechanism for customizing collaboration patterns. Developers can easily construct multi-agent applications and share pattern practices from different fields. The framework includes pre-installed collaboration patterns like PEER and DOE for complex task breakdown and data-intensive tasks.
HuixiangDou2
HuixiangDou2 is a robustly optimized GraphRAG approach that integrates multiple open-source projects to improve performance in graph-based augmented generation. It conducts comparative experiments and achieves a significant score increase, leading to a GraphRAG implementation with recognized performance. The repository provides code improvements, dense retrieval for querying entities and relationships, real domain knowledge testing, and impact analysis on accuracy.
Controllable-RAG-Agent
This repository contains a sophisticated deterministic graph-based solution for answering complex questions using a controllable autonomous agent. The solution is designed to ensure that answers are solely based on the provided data, avoiding hallucinations. It involves various steps such as PDF loading, text preprocessing, summarization, database creation, encoding, and utilizing large language models. The algorithm follows a detailed workflow involving planning, retrieval, answering, replanning, content distillation, and performance evaluation. Heuristics and techniques implemented focus on content encoding, anonymizing questions, task breakdown, content distillation, chain of thought answering, verification, and model performance evaluation.

raga-llm-hub
Raga LLM Hub is a comprehensive evaluation toolkit for Language and Learning Models (LLMs) with over 100 meticulously designed metrics. It allows developers and organizations to evaluate and compare LLMs effectively, establishing guardrails for LLMs and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) applications. The platform assesses aspects like Relevance & Understanding, Content Quality, Hallucination, Safety & Bias, Context Relevance, Guardrails, and Vulnerability scanning, along with Metric-Based Tests for quantitative analysis. It helps teams identify and fix issues throughout the LLM lifecycle, revolutionizing reliability and trustworthiness.
Docs2KG
Docs2KG is a tool designed for constructing a unified knowledge graph from heterogeneous documents. It addresses the challenges of digitizing diverse unstructured documents and constructing a high-quality knowledge graph with less effort. The tool combines bottom-up and top-down approaches, utilizing a human-LLM collaborative interface to enhance the generated knowledge graph. It organizes the knowledge graph into MetaKG, LayoutKG, and SemanticKG, providing a comprehensive view of document content. Docs2KG aims to streamline the process of knowledge graph construction and offers metrics for evaluating the quality of automatic construction.
nextpy
Nextpy is a cutting-edge software development framework optimized for AI-based code generation. It provides guardrails for defining AI system boundaries, structured outputs for prompt engineering, a powerful prompt engine for efficient processing, better AI generations with precise output control, modularity for multiplatform and extensible usage, developer-first approach for transferable knowledge, and containerized & scalable deployment options. It offers 4-10x faster performance compared to Streamlit apps, with a focus on cooperation within the open-source community and integration of key components from various projects.

latitude-llm
Latitude is an open-source prompt engineering platform that helps developers and product teams build AI features with confidence. It simplifies prompt management, aids in testing AI responses, and provides detailed analytics on request performance. Latitude offers collaborative prompt management, support for advanced features, version control, API and SDKs for integration, observability, evaluations in batch or real-time, and is community-driven. It can be deployed on Latitude Cloud for a managed solution or self-hosted for control and customization.

ReaLHF
ReaLHF is a distributed system designed for efficient RLHF training with Large Language Models (LLMs). It introduces a novel approach called parameter reallocation to dynamically redistribute LLM parameters across the cluster, optimizing allocations and parallelism for each computation workload. ReaL minimizes redundant communication while maximizing GPU utilization, achieving significantly higher Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) training throughput compared to other systems. It supports large-scale training with various parallelism strategies and enables memory-efficient training with parameter and optimizer offloading. The system seamlessly integrates with HuggingFace checkpoints and inference frameworks, allowing for easy launching of local or distributed experiments. ReaLHF offers flexibility through versatile configuration customization and supports various RLHF algorithms, including DPO, PPO, RAFT, and more, while allowing the addition of custom algorithms for high efficiency.
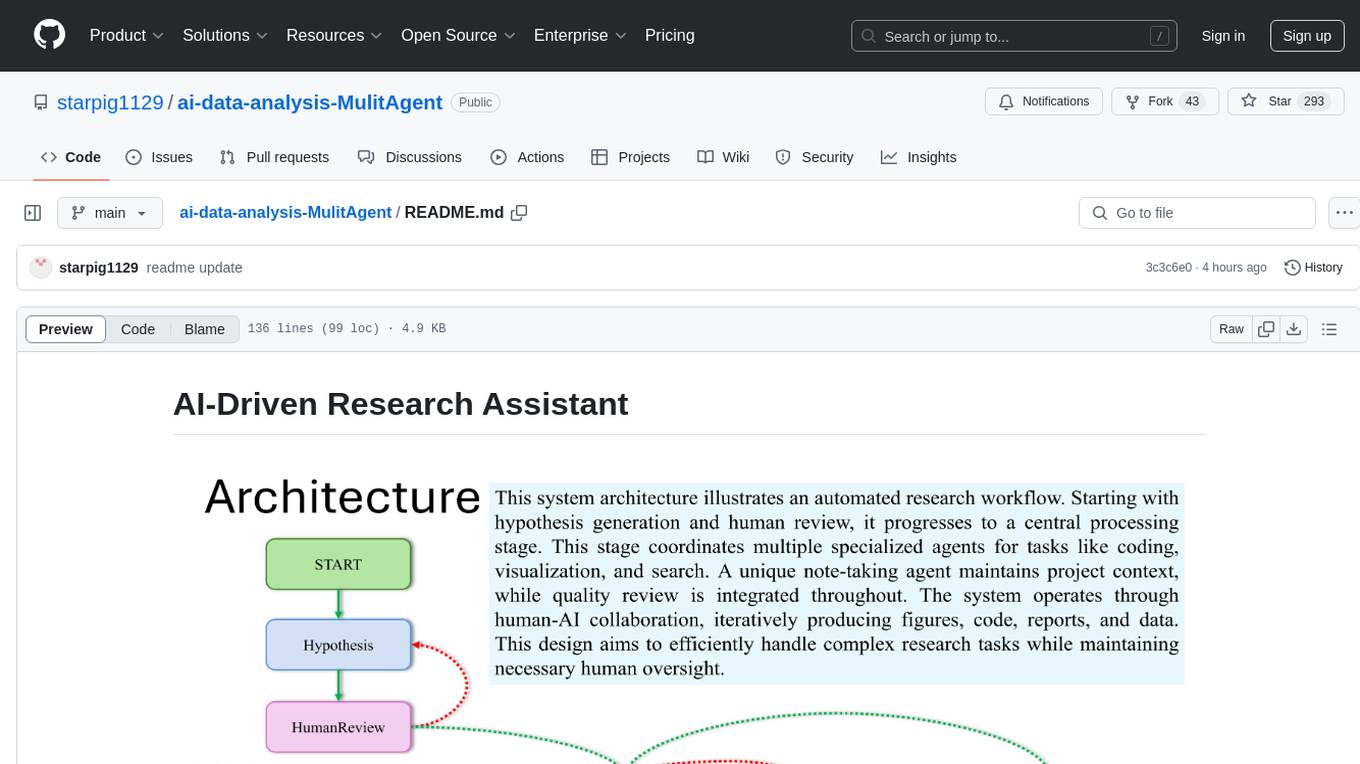
ai-data-analysis-MulitAgent
AI-Driven Research Assistant is an advanced AI-powered system utilizing specialized agents for data analysis, visualization, and report generation. It integrates LangChain, OpenAI's GPT models, and LangGraph for complex research processes. Key features include hypothesis generation, data processing, web search, code generation, and report writing. The system's unique Note Taker agent maintains project state, reducing overhead and improving context retention. System requirements include Python 3.10+ and Jupyter Notebook environment. Installation involves cloning the repository, setting up a Conda virtual environment, installing dependencies, and configuring environment variables. Usage instructions include setting data, running Jupyter Notebook, customizing research tasks, and viewing results. Main components include agents for hypothesis generation, process supervision, visualization, code writing, search, report writing, quality review, and note-taking. Workflow involves hypothesis generation, processing, quality review, and revision. Customization is possible by modifying agent creation and workflow definition. Current issues include OpenAI errors, NoteTaker efficiency, runtime optimization, and refiner improvement. Contributions via pull requests are welcome under the MIT License.
TurtleBenchmark
Turtle Benchmark is a novel and cheat-proof benchmark test used to evaluate large language models (LLMs). It is based on the Turtle Soup game, focusing on logical reasoning and context understanding abilities. The benchmark does not require background knowledge or model memory, providing all necessary information for judgment from stories under 200 words. The results are objective and unbiased, quantifiable as correct/incorrect/unknown, and impossible to cheat due to using real user-generated questions and dynamic data generation during online gameplay.
FrugalGPT
FrugalGPT is a framework that offers techniques for building Large Language Model (LLM) applications with budget constraints. It provides a cost-effective solution for utilizing LLMs while maintaining performance. The framework includes support for various models and offers resources for reducing costs and improving efficiency in LLM applications.
MMStar
MMStar is an elite vision-indispensable multi-modal benchmark comprising 1,500 challenge samples meticulously selected by humans. It addresses two key issues in current LLM evaluation: the unnecessary use of visual content in many samples and the existence of unintentional data leakage in LLM and LVLM training. MMStar evaluates 6 core capabilities across 18 detailed axes, ensuring a balanced distribution of samples across all dimensions.
For similar tasks

nixtla
Nixtla is a production-ready generative pretrained transformer for time series forecasting and anomaly detection. It can accurately predict various domains such as retail, electricity, finance, and IoT with just a few lines of code. TimeGPT introduces a paradigm shift with its standout performance, efficiency, and simplicity, making it accessible even to users with minimal coding experience. The model is based on self-attention and is independently trained on a vast time series dataset to minimize forecasting error. It offers features like zero-shot inference, fine-tuning, API access, adding exogenous variables, multiple series forecasting, custom loss function, cross-validation, prediction intervals, and handling irregular timestamps.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.