
nesa
Run AI models end-to-end encrypted.
Stars: 860

Nesa is a tool that allows users to run on-prem AI for a fraction of the cost through a blind API. It provides blind privacy, zero latency on protected inference, wide model coverage, cost savings compared to cloud and on-prem AI, RAG support, and ChatGPT compatibility. Nesa achieves blind AI through Equivariant Encryption (EE), a new security technology that provides complete inference encryption with no additional latency. EE allows users to perform inference on neural networks without exposing the underlying data, preserving data privacy and security.
README:
Forget multi-million dollar on-prem infrastructure for AI, get the same privacy guarantees in an API: run AI like the biggest enterprises do.
Latest: Nesa now supports image and video models and RAG with end-to-end encryption.
nesa serves AI requests with zero visibility on underlying data and full blindness on query.
nesa delivers zero latency on encrypted inference (<1% original execution time).
nesa supports encryption on many models including Llama, Mistral, Stable Diffusion and thousands of others.
nesa can deliver significant cost savings as an API vs. on-prem AI infrastructure.
nesa supports encryption of RAG for full end-to-end privacy in-cloud.
nesa provides a ChatGPT-compatible API for running encrypted AI with a one line change.
nesa is one click to install and go. See documentation.
At Nesa, privacy is a critical objective. On our path toward universal private AI, we confronted a key challenge: how can we perform inference on neural networks without exposing the underlying input and output data to external parties, while returning requests without high latency? Traditional approaches, such as differential privacy, ZKML or homomorphic encryption (HE), while conceptually strong, fall short in practical deployments for complex neural architectures. These methods struggle to handle non-linear operations efficiently, often imposing substantial computational overhead that makes them infeasible to integrate into real-time or large-scale systems.
Equivariant Encryption (EE) is a new security technology by Nesa, similar to Homomorphic Encryption (HE) in arithmetic-based privacy-preserving structure, but executed inside unique discrete architectures designed to provide complete inference encryption without additional latency.
The result is the first portable on-prem AI infrastructure solution inside of an API. Your cloud provider cannot see your data and queries with Nesa.
A snapshot of Equivariant Encryption's properties versus homomorphic encryption:
| Feature | Equivariant Encryption (EE) | Homomorphic Encryption (HE) |
|---|---|---|
| Latency Overhead | Zero | Very High |
| Non-Linear Operations | Exact | Approximation Needed |
| User Key Control | Direct & Custom | Schema-Defined |
| Cryptographic Hardness | Massive Combinatorial Complexity | Standard Hardness Assumptions |
Zero overhead: Nesa's EE provides the same latency as plaintext inference, with no slowdowns.
100k+ factorial: Nesa's EE has a massive combinatorial complexity, contributing to the strongest security guarantees.
We have implemented and investigated numerous methodologies that promise end-to-end data privacy. We began with deep orchestration work in Trusted Execution Environments (TEE) which is a hardware solution that decrypts, transforms, and re-encrypts data in secure memory. The issue with TEEs, besides cost and access, is that they still provide full back-door administrator access to your data, which for many enterprises and use cases is insufficient. Differential privacy seeks to obscure sensitive details by adding statistical noise, but it cannot fully prevent inference on raw data once it is processed by a model. Homomorphic encryption, on the other hand, is mathematically elegant: it permits computations directly on encrypted data. This is achieved through operations that are homomorphic to addition and multiplication, enabling algebraic manipulation of ciphertexts that, once decrypted, yield the correct plaintext results. Such a property is exceptionally appealing in scenarios like outsourced cloud computations, where one can perform inference off-site without revealing the sensitive inputs.
However, standard HE schemes are tailored around arithmetic operations. Neural networks, especially those with layers like attention mechanisms, activation functions, or normalization steps, do not map cleanly onto ring or field operations alone. Adapting HE to these complex transformations typically incurs prohibitive computational costs, slowing inference to impractical speeds.
Despite this, the conceptual promise of HE—running inference on encrypted data without decryption—prompted us to seek an alternative. We aimed to preserve the protective qualities of encrypted computation while working around the bottlenecks introduced by non-linear neural functions.
Our solution is Equivariant Encryption (EE). The term equivariance signifies a change in representation that preserves the operational structure from the model’s perspective. In other words, we transform the input data into an encrypted domain where the neural network’s computations can be carried out as though it were processing plaintext, all while maintaining the secrecy of the underlying information.
Rather than relying exclusively on arithmetic operations compatible with HE, EE integrates specialized transformations designed around the internal properties of neural networks. We exploit the known architecture, layer composition, and input-output mappings of the model to construct a system in which each step of inference operates correctly on encrypted inputs. This approach avoids expensive retraining on encrypted datasets. Instead, by following a set of mathematical guidelines, we can generate a new variant of the model that works with our encryption schema in a matter of seconds.
Formally, given some plaintext $p_i$, and some ciphertext $c_i$, with $p_i$ = decrypt($c_i$), our EE framework ensures that decrypt(nonlinear($c_1,c_2$)) = nonlinear($p_1,p_2$), where "nonlinear" represents a specific set of non-linear neural functions.
Crucially, the complexity of inference under EE does not surpass that of the unencrypted version. Each forward pass through the network involves approximately the same computational cost. Thus, inference latency remains unchanged, a significant advantage compared to conventional HE-based techniques.
To illustrate this with a tangible example, consider transformer-based models like ChatGPT, Claude, or Llama. These models employ tokenizers to convert text into discrete tokens, each mapped to an integer token ID. Under EE, we implement a specialized tokenizer that produces a different, encrypted set of token IDs. The network, now adapted to EE, treats these encrypted token IDs as standard inputs. It processes them identically to how it would process normal tokens, ultimately returning encrypted output tokens that can be decrypted locally by the user. The following diagram outlines this workflow:
In this setup, all data traveling over the network remains encrypted, and the transformations that produce and consume these tokens are carefully chosen to deny any straightforward method for recovering the plaintext. The attacker sees only encrypted tokens and a model variant designed to operate on that encrypted space, providing no direct, low-cost avenue to extract the original information.
Below is a more detailed breakdown of how Equivariant Encryption matches or outperforms the expectations we have from traditional Homomorphic Encryption methods:
| Property | Homomorphic Encryption (HE) | Equivariant Encryption (EE) |
|---|---|---|
| Data Confidentiality (Server Blindness) | The server never sees plaintext data. | The server never sees plaintext data. |
| End-to-End Encrypted Computation | Operations should be fully on encrypted data, with no intermediate decryptions. | EE models run directly on encrypted tokens. No intermediate decryptions are required. |
| User-Controlled Encryption | Users should hold keys and control encryption/decryption. | Only the user can map plaintext to transformed tokens using the EE tokenizer as a private key. |
| Preservation of Accuracy | The decrypted output should match the result of plaintext inference. | EE ensures final results are identical to plaintext inference outputs, with no accuracy loss. |
| Support for Arbitrary Model Structures | HE struggles with non-linearities and complex NN layers. | EE is designed for modern neural architectures and preserves non-linearities. |
| Minimal Performance Overhead | HE incurs large computational overhead. | EE imposes no overhead; inference latency matches that of the underlying model on plaintext data. |
| No Approximation of Functions | HE may require approximations of complex operations. | EE avoids approximations, preserving exact neural network functions post-transformation. |
| Scalability to Large Models | Handling large models under HE is impractical. | EE scales naturally with large models without any computational penalties. |
| Compatibility with Existing Pipelines | HE often requires extensive pipeline modifications. | EE requires a one-time transformation, after which pipelines operate as normal. |
| Clear Security Model & Robustness | HE has strong theoretical foundations. | EE provides a massively complex, secure combinatorial search space, making brute-force attacks impossible. |
We have tested EE with various baseline attack vectors, which can be found here: https://github.com/nesaorg/nesa/blob/main/Attack_Paper.pdf
Using a state-of-the-art large language model such as GPT-4o to evaluate whether the output P(Oi) is a good answer to the prompt P(Ii).
Using domain knowledge to design the loss function L, so that the loss L can capture the semantic meaning in the (decrypted) input, output and between.
The most naive method is brute force, trying all possible permutations P and choosing the one with the minimal loss value. This algorithm requires time complexity of N!, which is infeasible.
Randomly sampling M permutations and choosing the one with the lowest loss value. One can also try genetic algorithms to mix and cross-over multiple tries at different permutations.
Starting with an arbitrary initial permutation P. The set of moves is the set of permutations that one can reach by transposing two elements of the permutation.
We provide a community encrypted model on Hugging Face to demonstrate how Equivariant Encryption works.
import torch
from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification, AutoTokenizer
# Initialize model and tokenizer
model_name = "nesaorg/distilbert-sentiment-encrypted-community-v1"
model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(model_name, num_labels=2)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)# Prepare input and run inference
inputs = tokenizer("Hello, I love you", return_tensors="pt")
with torch.no_grad():
logits = model(**inputs).logits
# Process results
predicted_class_id = logits.argmax().item()
label = model.config.id2label[predicted_class_id]
score = torch.max(torch.nn.Softmax()(logits)).item()
print(f"The sentiment was classified as {label} with a confidence score of {score:.2f}")We invite the community to examine and test the security claims of Equivariant Encryption. As part of our commitment to transparency and continual refinement, we have organized a competition encouraging participants to probe for weaknesses and demonstrate potential exploits.
For details, please visit: https://github.com/nesaorg/Equivariant-Encryption-for-AI/blob/main/CONTEST.md
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for nesa
Similar Open Source Tools

nesa
Nesa is a tool that allows users to run on-prem AI for a fraction of the cost through a blind API. It provides blind privacy, zero latency on protected inference, wide model coverage, cost savings compared to cloud and on-prem AI, RAG support, and ChatGPT compatibility. Nesa achieves blind AI through Equivariant Encryption (EE), a new security technology that provides complete inference encryption with no additional latency. EE allows users to perform inference on neural networks without exposing the underlying data, preserving data privacy and security.

Equivariant-Encryption-for-AI
At Nesa, privacy is a critical objective. Equivariant Encryption (EE) is a solution developed to perform inference on neural networks without exposing input and output data. EE integrates specialized transformations for neural networks, maintaining data privacy while ensuring inference operates correctly on encrypted inputs. It provides the same latency as plaintext inference with no slowdowns and offers strong security guarantees. EE avoids the computational costs of traditional Homomorphic Encryption (HE) by preserving non-linear neural functions. The tool is designed for modern neural architectures, ensuring accuracy, scalability, and compatibility with existing pipelines.
MemoryBear
MemoryBear is a next-generation AI memory system developed by RedBear AI, focusing on overcoming limitations in knowledge storage and multi-agent collaboration. It empowers AI with human-like memory capabilities, enabling deep knowledge understanding and cognitive collaboration. The system addresses challenges such as knowledge forgetting, memory gaps in multi-agent collaboration, and semantic ambiguity during reasoning. MemoryBear's core features include memory extraction engine, graph storage, hybrid search, memory forgetting engine, self-reflection engine, and FastAPI services. It offers a standardized service architecture for efficient integration and invocation across applications.
gepa
GEPA (Genetic-Pareto) is a framework for optimizing arbitrary systems composed of text components like AI prompts, code snippets, or textual specs against any evaluation metric. It employs LLMs to reflect on system behavior, using feedback from execution and evaluation traces to drive targeted improvements. Through iterative mutation, reflection, and Pareto-aware candidate selection, GEPA evolves robust, high-performing variants with minimal evaluations, co-evolving multiple components in modular systems for domain-specific gains. The repository provides the official implementation of the GEPA algorithm as proposed in the paper titled 'GEPA: Reflective Prompt Evolution Can Outperform Reinforcement Learning'.

magpie
This is the official repository for 'Alignment Data Synthesis from Scratch by Prompting Aligned LLMs with Nothing'. Magpie is a tool designed to synthesize high-quality instruction data at scale by extracting it directly from an aligned Large Language Models (LLMs). It aims to democratize AI by generating large-scale alignment data and enhancing the transparency of model alignment processes. Magpie has been tested on various model families and can be used to fine-tune models for improved performance on alignment benchmarks such as AlpacaEval, ArenaHard, and WildBench.
llm-course
The LLM course is divided into three parts: 1. 🧩 **LLM Fundamentals** covers essential knowledge about mathematics, Python, and neural networks. 2. 🧑🔬 **The LLM Scientist** focuses on building the best possible LLMs using the latest techniques. 3. 👷 **The LLM Engineer** focuses on creating LLM-based applications and deploying them. For an interactive version of this course, I created two **LLM assistants** that will answer questions and test your knowledge in a personalized way: * 🤗 **HuggingChat Assistant**: Free version using Mixtral-8x7B. * 🤖 **ChatGPT Assistant**: Requires a premium account. ## 📝 Notebooks A list of notebooks and articles related to large language models. ### Tools | Notebook | Description | Notebook | |----------|-------------|----------| | 🧐 LLM AutoEval | Automatically evaluate your LLMs using RunPod |  | | 🥱 LazyMergekit | Easily merge models using MergeKit in one click. |  | | 🦎 LazyAxolotl | Fine-tune models in the cloud using Axolotl in one click. |  | | ⚡ AutoQuant | Quantize LLMs in GGUF, GPTQ, EXL2, AWQ, and HQQ formats in one click. |  | | 🌳 Model Family Tree | Visualize the family tree of merged models. |  | | 🚀 ZeroSpace | Automatically create a Gradio chat interface using a free ZeroGPU. |  |
merlin
Merlin is a groundbreaking model capable of generating natural language responses intricately linked with object trajectories of multiple images. It excels in predicting and reasoning about future events based on initial observations, showcasing unprecedented capability in future prediction and reasoning. Merlin achieves state-of-the-art performance on the Future Reasoning Benchmark and multiple existing multimodal language models benchmarks, demonstrating powerful multi-modal general ability and foresight minds.
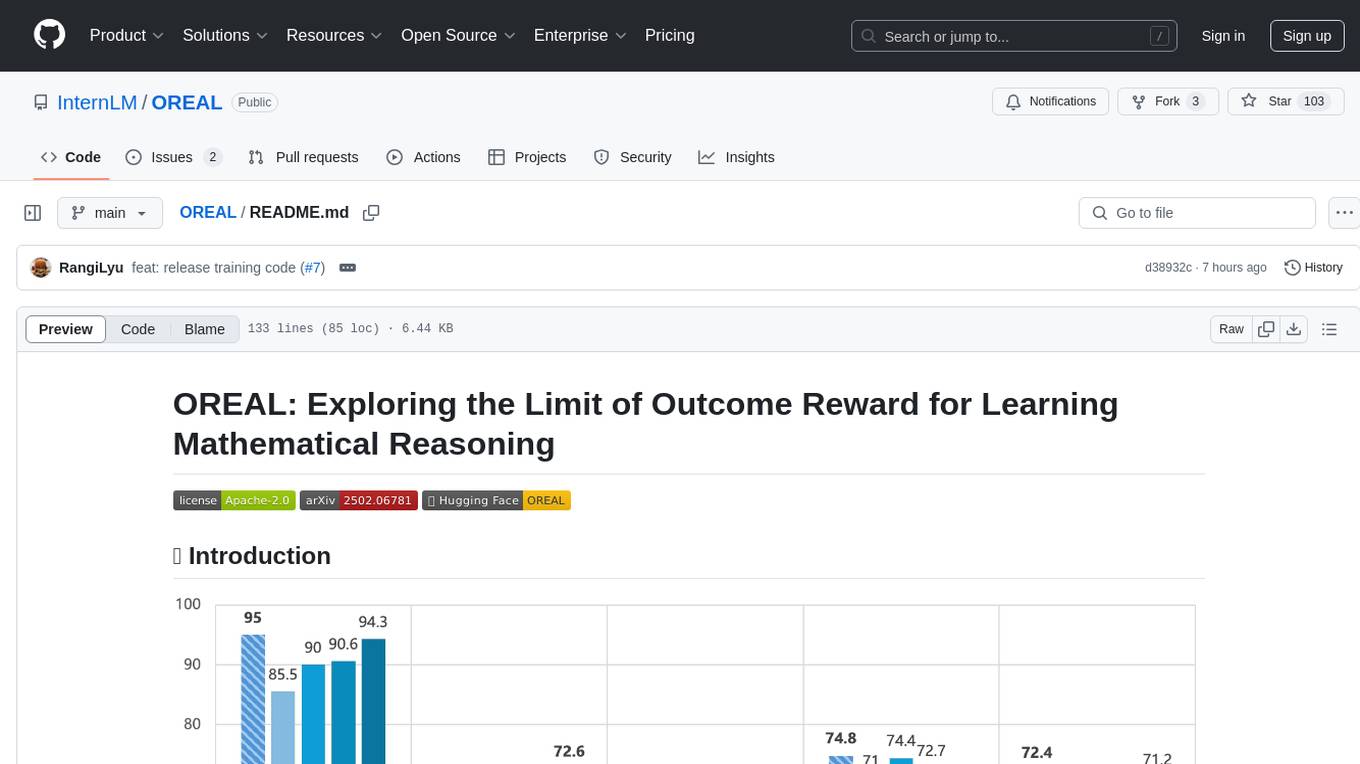
OREAL
OREAL is a reinforcement learning framework designed for mathematical reasoning tasks, aiming to achieve optimal performance through outcome reward-based learning. The framework utilizes behavior cloning, reshaping rewards, and token-level reward models to address challenges in sparse rewards and partial correctness. OREAL has achieved significant results, with a 7B model reaching 94.0 pass@1 accuracy on MATH-500 and surpassing previous 32B models. The tool provides training tutorials and Hugging Face model repositories for easy access and implementation.
mscclpp
MSCCL++ is a GPU-driven communication stack for scalable AI applications. It provides a highly efficient and customizable communication stack for distributed GPU applications. MSCCL++ redefines inter-GPU communication interfaces, delivering a highly efficient and customizable communication stack for distributed GPU applications. Its design is specifically tailored to accommodate diverse performance optimization scenarios often encountered in state-of-the-art AI applications. MSCCL++ provides communication abstractions at the lowest level close to hardware and at the highest level close to application API. The lowest level of abstraction is ultra light weight which enables a user to implement logics of data movement for a collective operation such as AllReduce inside a GPU kernel extremely efficiently without worrying about memory ordering of different ops. The modularity of MSCCL++ enables a user to construct the building blocks of MSCCL++ in a high level abstraction in Python and feed them to a CUDA kernel in order to facilitate the user's productivity. MSCCL++ provides fine-grained synchronous and asynchronous 0-copy 1-sided abstracts for communication primitives such as `put()`, `get()`, `signal()`, `flush()`, and `wait()`. The 1-sided abstractions allows a user to asynchronously `put()` their data on the remote GPU as soon as it is ready without requiring the remote side to issue any receive instruction. This enables users to easily implement flexible communication logics, such as overlapping communication with computation, or implementing customized collective communication algorithms without worrying about potential deadlocks. Additionally, the 0-copy capability enables MSCCL++ to directly transfer data between user's buffers without using intermediate internal buffers which saves GPU bandwidth and memory capacity. MSCCL++ provides consistent abstractions regardless of the location of the remote GPU (either on the local node or on a remote node) or the underlying link (either NVLink/xGMI or InfiniBand). This simplifies the code for inter-GPU communication, which is often complex due to memory ordering of GPU/CPU read/writes and therefore, is error-prone.
Nucleoid
Nucleoid is a declarative (logic) runtime environment that manages both data and logic under the same runtime. It uses a declarative programming paradigm, which allows developers to focus on the business logic of the application, while the runtime manages the technical details. This allows for faster development and reduces the amount of code that needs to be written. Additionally, the sharding feature can help to distribute the load across multiple instances, which can further improve the performance of the system.
nixtla
Nixtla is a production-ready generative pretrained transformer for time series forecasting and anomaly detection. It can accurately predict various domains such as retail, electricity, finance, and IoT with just a few lines of code. TimeGPT introduces a paradigm shift with its standout performance, efficiency, and simplicity, making it accessible even to users with minimal coding experience. The model is based on self-attention and is independently trained on a vast time series dataset to minimize forecasting error. It offers features like zero-shot inference, fine-tuning, API access, adding exogenous variables, multiple series forecasting, custom loss function, cross-validation, prediction intervals, and handling irregular timestamps.

semlib
Semlib is a Python library for building data processing and data analysis pipelines that leverage the power of large language models (LLMs). It provides functional programming primitives like map, reduce, sort, and filter, programmed with natural language descriptions. Semlib handles complexities such as prompting, parsing, concurrency control, caching, and cost tracking. The library breaks down sophisticated data processing tasks into simpler steps to improve quality, feasibility, latency, cost, security, and flexibility of data processing tasks.
db-ally
db-ally is a library for creating natural language interfaces to data sources. It allows developers to outline specific use cases for a large language model (LLM) to handle, detailing the desired data format and the possible operations to fetch this data. db-ally effectively shields the complexity of the underlying data source from the model, presenting only the essential information needed for solving the specific use cases. Instead of generating arbitrary SQL, the model is asked to generate responses in a simplified query language.
bocoel
BoCoEL is a tool that leverages Bayesian Optimization to efficiently evaluate large language models by selecting a subset of the corpus for evaluation. It encodes individual entries into embeddings, uses Bayesian optimization to select queries, retrieves from the corpus, and provides easily managed evaluations. The tool aims to reduce computation costs during evaluation with a dynamic budget, supporting models like GPT2, Pythia, and LLAMA through integration with Hugging Face transformers and datasets. BoCoEL offers a modular design and efficient representation of the corpus to enhance evaluation quality.
intelligence-toolkit
The Intelligence Toolkit is a suite of interactive workflows designed to help domain experts make sense of real-world data by identifying patterns, themes, relationships, and risks within complex datasets. It utilizes generative AI (GPT models) to create reports on findings of interest. The toolkit supports analysis of case, entity, and text data, providing various interactive workflows for different intelligence tasks. Users are expected to evaluate the quality of data insights and AI interpretations before taking action. The system is designed for moderate-sized datasets and responsible use of personal case data. It uses the GPT-4 model from OpenAI or Azure OpenAI APIs for generating reports and insights.
Nanoflow
NanoFlow is a throughput-oriented high-performance serving framework for Large Language Models (LLMs) that consistently delivers superior throughput compared to other frameworks by utilizing key techniques such as intra-device parallelism, asynchronous CPU scheduling, and SSD offloading. The framework proposes nano-batching to schedule compute-, memory-, and network-bound operations for simultaneous execution, leading to increased resource utilization. NanoFlow also adopts an asynchronous control flow to optimize CPU overhead and eagerly offloads KV-Cache to SSDs for multi-round conversations. The open-source codebase integrates state-of-the-art kernel libraries and provides necessary scripts for environment setup and experiment reproduction.
For similar tasks

nesa
Nesa is a tool that allows users to run on-prem AI for a fraction of the cost through a blind API. It provides blind privacy, zero latency on protected inference, wide model coverage, cost savings compared to cloud and on-prem AI, RAG support, and ChatGPT compatibility. Nesa achieves blind AI through Equivariant Encryption (EE), a new security technology that provides complete inference encryption with no additional latency. EE allows users to perform inference on neural networks without exposing the underlying data, preserving data privacy and security.

llm-app
Pathway's LLM (Large Language Model) Apps provide a platform to quickly deploy AI applications using the latest knowledge from data sources. The Python application examples in this repository are Docker-ready, exposing an HTTP API to the frontend. These apps utilize the Pathway framework for data synchronization, API serving, and low-latency data processing without the need for additional infrastructure dependencies. They connect to document data sources like S3, Google Drive, and Sharepoint, offering features like real-time data syncing, easy alert setup, scalability, monitoring, security, and unification of application logic.
kaytu
Kaytu is an AI platform that enhances cloud efficiency by analyzing historical usage data and providing intelligent recommendations for optimizing instance sizes. Users can pay for only what they need without compromising the performance of their applications. The platform is easy to use with a one-line command, allows customization for specific requirements, and ensures security by extracting metrics from the client side. Kaytu is open-source and supports AWS services, with plans to expand to GCP, Azure, GPU optimization, and observability data from Prometheus in the future.
awesome-production-llm
This repository is a curated list of open-source libraries for production large language models. It includes tools for data preprocessing, training/finetuning, evaluation/benchmarking, serving/inference, application/RAG, testing/monitoring, and guardrails/security. The repository also provides a new category called LLM Cookbook/Examples for showcasing examples and guides on using various LLM APIs.
holisticai
Holistic AI is an open-source library dedicated to assessing and improving the trustworthiness of AI systems. It focuses on measuring and mitigating bias, explainability, robustness, security, and efficacy in AI models. The tool provides comprehensive metrics, mitigation techniques, a user-friendly interface, and visualization tools to enhance AI system trustworthiness. It offers documentation, tutorials, and detailed installation instructions for easy integration into existing workflows.
langkit
LangKit is an open-source text metrics toolkit for monitoring language models. It offers methods for extracting signals from input/output text, compatible with whylogs. Features include text quality, relevance, security, sentiment, toxicity analysis. Installation via PyPI. Modules contain UDFs for whylogs. Benchmarks show throughput on AWS instances. FAQs available.
eulers-shield
Euler's Shield is a decentralized, AI-powered financial system designed to stabilize the value of Pi Coin at $314.159. It combines blockchain, machine learning, and cybersecurity to ensure the security, scalability, and decentralization of the Pi Coin ecosystem.
k8sgateway
K8sGateway is a feature-rich, fast, and flexible Kubernetes-native API gateway built on Envoy proxy and Kubernetes Gateway API. It excels in function-level routing, supports legacy apps, microservices, and serverless. It offers robust discovery capabilities, seamless integration with open-source projects, and supports hybrid applications with various technologies, architectures, protocols, and clouds.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.







