asreview
Active learning for systematic reviews
Stars: 709

The ASReview project implements active learning for systematic reviews, utilizing AI-aided pipelines to assist in finding relevant texts for search tasks. It accelerates the screening of textual data with minimal human input, saving time and increasing output quality. The software offers three modes: Oracle for interactive screening, Exploration for teaching purposes, and Simulation for evaluating active learning models. ASReview LAB is designed to support decision-making in any discipline or industry by improving efficiency and transparency in screening large amounts of textual data.
README:
Systematically screening large amounts of textual data is time-consuming and often tiresome. The rapidly evolving field of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has allowed the development of AI-aided pipelines that assist in finding relevant texts for search tasks. A well-established approach to increasing efficiency is screening prioritization via Active Learning.
The Active learning for Systematic Reviews (ASReview) project, published in Nature Machine Intelligence implements different machine learning algorithms that interactively query the researcher. ASReview LAB is designed to accelerate the step of screening textual data with a minimum of records to be read by a human with no or very few false negatives. ASReview LAB will save time, increase the quality of output and strengthen the transparency of work when screening large amounts of textual data to retrieve relevant information. Active Learning will support decision-making in any discipline or industry.
ASReview software implements three different modes:
- Oracle Screen textual data in interaction with the active learning model. The reviewer is the 'oracle', making the labeling decisions.
- Exploration Explore or demonstrate ASReview LAB with a completely labeled dataset. This mode is suitable for teaching purposes.
- Simulation Evaluate the performance of active learning models on fully labeled data. Simulations can be run in ASReview LAB or via the command line interface with more advanced options.
The ASReview software requires Python 3.8 or later. Detailed step-by-step instructions to install Python and ASReview are available for Windows and macOS users.
pip install asreviewUpgrade ASReview with the following command:
pip install --upgrade asreviewTo install ASReview LAB with Docker, see Install with Docker.
Getting Started with ASReview LAB.
If you wish to cite the underlying methodology of the ASReview software, please use the following publication in Nature Machine Intelligence:
van de Schoot, R., de Bruin, J., Schram, R. et al. An open source machine learning framework for efficient and transparent systematic reviews. Nat Mach Intell 3, 125–133 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s42256-020-00287-7
For citing the software, please refer to the specific release of the ASReview software on Zenodo https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3345592. The menu on the right can be used to find the citation format of prevalence.
For more scientific publications on the ASReview software, go to asreview.ai/papers.
For an overview of the team working on ASReview, see ASReview Research Team. ASReview LAB is maintained by Jonathan de Bruin and Yongchao Terry Ma.
The best resources to find an answer to your question or ways to get in contact with the team are:
- Documentation - asreview.readthedocs.io
- Newsletter - asreview.ai/newsletter/subscribe
- Quick tour - ASReview LAB quick tour
- Issues or feature requests - ASReview issue tracker
- FAQ - ASReview Discussions
- Donation - asreview.ai/donate
- Contact - [email protected]
The ASReview software has an Apache 2.0 LICENSE. The ASReview team accepts no responsibility or liability for the use of the ASReview tool or any direct or indirect damages arising out of the application of the tool.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for asreview
Similar Open Source Tools

asreview
The ASReview project implements active learning for systematic reviews, utilizing AI-aided pipelines to assist in finding relevant texts for search tasks. It accelerates the screening of textual data with minimal human input, saving time and increasing output quality. The software offers three modes: Oracle for interactive screening, Exploration for teaching purposes, and Simulation for evaluating active learning models. ASReview LAB is designed to support decision-making in any discipline or industry by improving efficiency and transparency in screening large amounts of textual data.
LabelLLM
LabelLLM is an open-source data annotation platform designed to optimize the data annotation process for LLM development. It offers flexible configuration, multimodal data support, comprehensive task management, and AI-assisted annotation. Users can access a suite of annotation tools, enjoy a user-friendly experience, and enhance efficiency. The platform allows real-time monitoring of annotation progress and quality control, ensuring data integrity and timeliness.
CosmosAIGraph
CosmosAIGraph is an AI-powered graph and RAG implementation of OmniRAG pattern, utilizing Azure Cosmos DB and other sources. It includes presentations, reference application documentation, FAQs, and a reference dataset of Python libraries pre-vectorized. The project focuses on Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL and Apache Jena implementation for the in-memory RDF graph. It provides DockerHub images, with plans to add RBAC and Microsoft Entra ID/AAD authentication support, update AI model to gpt-4.5, and offer generic graph examples with a graph generation solution.
bocoel
BoCoEL is a tool that leverages Bayesian Optimization to efficiently evaluate large language models by selecting a subset of the corpus for evaluation. It encodes individual entries into embeddings, uses Bayesian optimization to select queries, retrieves from the corpus, and provides easily managed evaluations. The tool aims to reduce computation costs during evaluation with a dynamic budget, supporting models like GPT2, Pythia, and LLAMA through integration with Hugging Face transformers and datasets. BoCoEL offers a modular design and efficient representation of the corpus to enhance evaluation quality.
btp-cap-genai-rag
This GitHub repository provides support for developers, partners, and customers to create advanced GenAI solutions on SAP Business Technology Platform (SAP BTP) following the Reference Architecture. It includes examples on integrating Foundation Models and Large Language Models via Generative AI Hub, using LangChain in CAP, and implementing advanced techniques like Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) through embeddings and SAP HANA Cloud's Vector Engine for enhanced value in customer support scenarios.
datasets
Datasets is a repository that provides a collection of various datasets for machine learning and data analysis projects. It includes datasets in different formats such as CSV, JSON, and Excel, covering a wide range of topics including finance, healthcare, marketing, and more. The repository aims to help data scientists, researchers, and students access high-quality datasets for training models, conducting experiments, and exploring data analysis techniques.
nixtla
Nixtla is a production-ready generative pretrained transformer for time series forecasting and anomaly detection. It can accurately predict various domains such as retail, electricity, finance, and IoT with just a few lines of code. TimeGPT introduces a paradigm shift with its standout performance, efficiency, and simplicity, making it accessible even to users with minimal coding experience. The model is based on self-attention and is independently trained on a vast time series dataset to minimize forecasting error. It offers features like zero-shot inference, fine-tuning, API access, adding exogenous variables, multiple series forecasting, custom loss function, cross-validation, prediction intervals, and handling irregular timestamps.
venice
Venice is a derived data storage platform, providing the following characteristics: 1. High throughput asynchronous ingestion from batch and streaming sources (e.g. Hadoop and Samza). 2. Low latency online reads via remote queries or in-process caching. 3. Active-active replication between regions with CRDT-based conflict resolution. 4. Multi-cluster support within each region with operator-driven cluster assignment. 5. Multi-tenancy, horizontal scalability and elasticity within each cluster. The above makes Venice particularly suitable as the stateful component backing a Feature Store, such as Feathr. AI applications feed the output of their ML training jobs into Venice and then query the data for use during online inference workloads.
Geoweaver
Geoweaver is an in-browser software that enables users to easily compose and execute full-stack data processing workflows using online spatial data facilities, high-performance computation platforms, and open-source deep learning libraries. It provides server management, code repository, workflow orchestration software, and history recording capabilities. Users can run it from both local and remote machines. Geoweaver aims to make data processing workflows manageable for non-coder scientists and preserve model run history. It offers features like progress storage, organization, SSH connection to external servers, and a web UI with Python support.

llm_client
llm_client is a Rust interface designed for Local Large Language Models (LLMs) that offers automated build support for CPU, CUDA, MacOS, easy model presets, and a novel cascading prompt workflow for controlled generation. It provides a breadth of configuration options and API support for various OpenAI compatible APIs. The tool is primarily focused on deterministic signals from probabilistic LLM vibes, enabling specialized workflows for specific tasks and reproducible outcomes.
NeMo
NeMo Framework is a generative AI framework built for researchers and pytorch developers working on large language models (LLMs), multimodal models (MM), automatic speech recognition (ASR), and text-to-speech synthesis (TTS). The primary objective of NeMo is to provide a scalable framework for researchers and developers from industry and academia to more easily implement and design new generative AI models by being able to leverage existing code and pretrained models.
OREAL
OREAL is a reinforcement learning framework designed for mathematical reasoning tasks, aiming to achieve optimal performance through outcome reward-based learning. The framework utilizes behavior cloning, reshaping rewards, and token-level reward models to address challenges in sparse rewards and partial correctness. OREAL has achieved significant results, with a 7B model reaching 94.0 pass@1 accuracy on MATH-500 and surpassing previous 32B models. The tool provides training tutorials and Hugging Face model repositories for easy access and implementation.
baal
Baal is an active learning library that supports both industrial applications and research use cases. It provides a framework for Bayesian active learning methods such as Monte-Carlo Dropout, MCDropConnect, Deep ensembles, and Semi-supervised learning. Baal helps in labeling the most uncertain items in the dataset pool to improve model performance and reduce annotation effort. The library is actively maintained by a dedicated team and has been used in various research papers for production and experimentation.

domino
Domino is an open source workflow management platform that provides an intuitive GUI for creating, editing, and monitoring workflows. It also offers a standard way of writing and publishing functional pieces that can be reused in multiple workflows. Domino is powered by Apache Airflow for top-tier workflows scheduling and monitoring.

aitlas
The AiTLAS toolbox (Artificial Intelligence Toolbox for Earth Observation) includes state-of-the-art machine learning methods for exploratory and predictive analysis of satellite imagery as well as a repository of AI-ready Earth Observation (EO) datasets. It can be easily applied for a variety of Earth Observation tasks, such as land use and cover classification, crop type prediction, localization of specific objects (semantic segmentation), etc. The main goal of AiTLAS is to facilitate better usability and adoption of novel AI methods (and models) by EO experts, while offering easy access and standardized format of EO datasets to AI experts which allows benchmarking of various existing and novel AI methods tailored for EO data.
For similar tasks
Co-LLM-Agents
This repository contains code for building cooperative embodied agents modularly with large language models. The agents are trained to perform tasks in two different environments: ThreeDWorld Multi-Agent Transport (TDW-MAT) and Communicative Watch-And-Help (C-WAH). TDW-MAT is a multi-agent environment where agents must transport objects to a goal position using containers. C-WAH is an extension of the Watch-And-Help challenge, which enables agents to send messages to each other. The code in this repository can be used to train agents to perform tasks in both of these environments.
GPT4Point
GPT4Point is a unified framework for point-language understanding and generation. It aligns 3D point clouds with language, providing a comprehensive solution for tasks such as 3D captioning and controlled 3D generation. The project includes an automated point-language dataset annotation engine, a novel object-level point cloud benchmark, and a 3D multi-modality model. Users can train and evaluate models using the provided code and datasets, with a focus on improving models' understanding capabilities and facilitating the generation of 3D objects.

asreview
The ASReview project implements active learning for systematic reviews, utilizing AI-aided pipelines to assist in finding relevant texts for search tasks. It accelerates the screening of textual data with minimal human input, saving time and increasing output quality. The software offers three modes: Oracle for interactive screening, Exploration for teaching purposes, and Simulation for evaluating active learning models. ASReview LAB is designed to support decision-making in any discipline or industry by improving efficiency and transparency in screening large amounts of textual data.
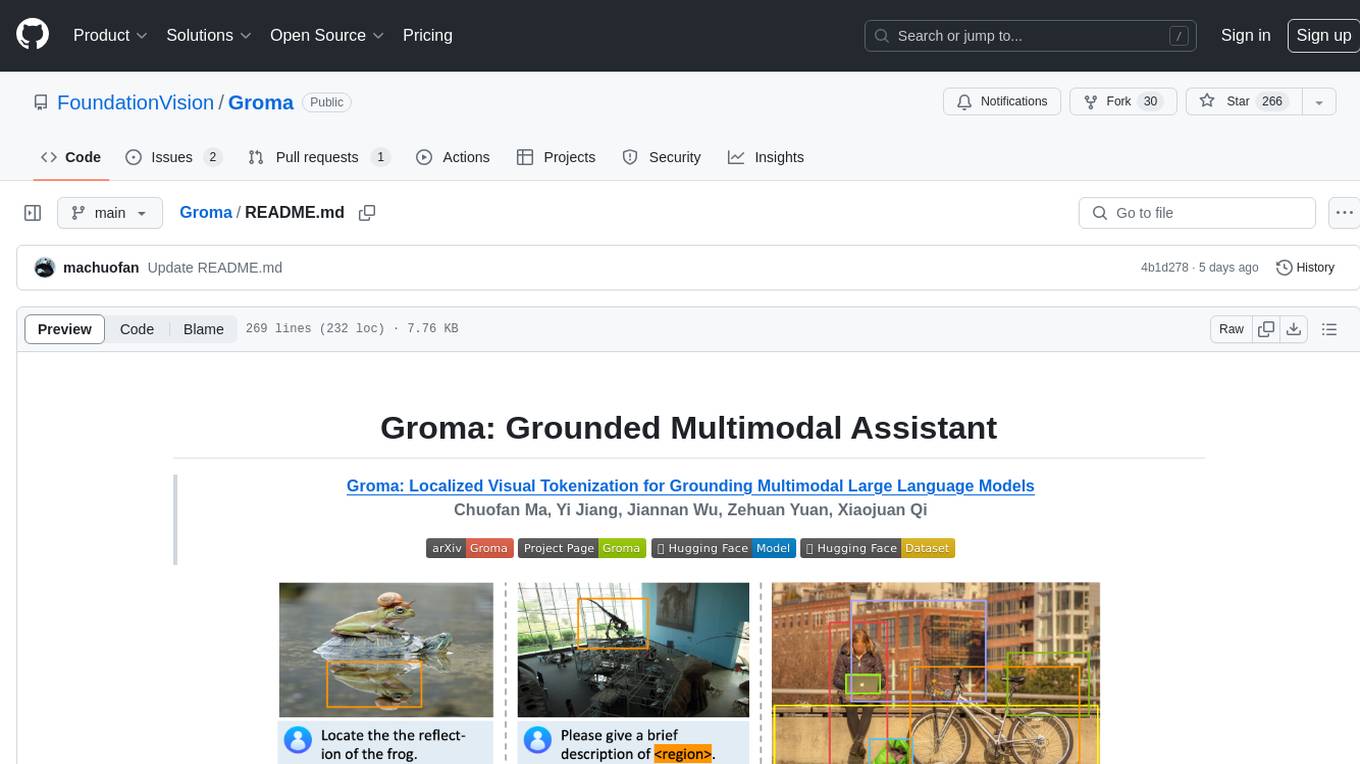
Groma
Groma is a grounded multimodal assistant that excels in region understanding and visual grounding. It can process user-defined region inputs and generate contextually grounded long-form responses. The tool presents a unique paradigm for multimodal large language models, focusing on visual tokenization for localization. Groma achieves state-of-the-art performance in referring expression comprehension benchmarks. The tool provides pretrained model weights and instructions for data preparation, training, inference, and evaluation. Users can customize training by starting from intermediate checkpoints. Groma is designed to handle tasks related to detection pretraining, alignment pretraining, instruction finetuning, instruction following, and more.
amber-train
Amber is the first model in the LLM360 family, an initiative for comprehensive and fully open-sourced LLMs. It is a 7B English language model with the LLaMA architecture. The model type is a language model with the same architecture as LLaMA-7B. It is licensed under Apache 2.0. The resources available include training code, data preparation, metrics, and fully processed Amber pretraining data. The model has been trained on various datasets like Arxiv, Book, C4, Refined-Web, StarCoder, StackExchange, and Wikipedia. The hyperparameters include a total of 6.7B parameters, hidden size of 4096, intermediate size of 11008, 32 attention heads, 32 hidden layers, RMSNorm ε of 1e^-6, max sequence length of 2048, and a vocabulary size of 32000.
kan-gpt
The KAN-GPT repository is a PyTorch implementation of Generative Pre-trained Transformers (GPTs) using Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs) for language modeling. It provides a model for generating text based on prompts, with a focus on improving performance compared to traditional MLP-GPT models. The repository includes scripts for training the model, downloading datasets, and evaluating model performance. Development tasks include integrating with other libraries, testing, and documentation.
LLM-SFT
LLM-SFT is a Chinese large model fine-tuning tool that supports models such as ChatGLM, LlaMA, Bloom, Baichuan-7B, and frameworks like LoRA, QLoRA, DeepSpeed, UI, and TensorboardX. It facilitates tasks like fine-tuning, inference, evaluation, and API integration. The tool provides pre-trained weights for various models and datasets for Chinese language processing. It requires specific versions of libraries like transformers and torch for different functionalities.

zshot
Zshot is a highly customizable framework for performing Zero and Few shot named entity and relationships recognition. It can be used for mentions extraction, wikification, zero and few shot named entity recognition, zero and few shot named relationship recognition, and visualization of zero-shot NER and RE extraction. The framework consists of two main components: the mentions extractor and the linker. There are multiple mentions extractors and linkers available, each serving a specific purpose. Zshot also includes a relations extractor and a knowledge extractor for extracting relations among entities and performing entity classification. The tool requires Python 3.6+ and dependencies like spacy, torch, transformers, evaluate, and datasets for evaluation over datasets like OntoNotes. Optional dependencies include flair and blink for additional functionalities. Zshot provides examples, tutorials, and evaluation methods to assess the performance of the components.
For similar jobs

asreview
The ASReview project implements active learning for systematic reviews, utilizing AI-aided pipelines to assist in finding relevant texts for search tasks. It accelerates the screening of textual data with minimal human input, saving time and increasing output quality. The software offers three modes: Oracle for interactive screening, Exploration for teaching purposes, and Simulation for evaluating active learning models. ASReview LAB is designed to support decision-making in any discipline or industry by improving efficiency and transparency in screening large amounts of textual data.
NewEraAI-Papers
The NewEraAI-Papers repository provides links to collections of influential and interesting research papers from top AI conferences, along with open-source code to promote reproducibility and provide detailed implementation insights beyond the scope of the article. Users can stay up to date with the latest advances in AI research by exploring this repository. Contributions to improve the completeness of the list are welcomed, and users can create pull requests, open issues, or contact the repository owner via email to enhance the repository further.
cltk
The Classical Language Toolkit (CLTK) is a Python library that provides natural language processing (NLP) capabilities for pre-modern languages. It offers a modular processing pipeline with pre-configured defaults and supports almost 20 languages. Users can install the latest version using pip and access detailed documentation on the official website. The toolkit is designed to meet the unique needs of researchers working with historical languages, filling a void in the NLP landscape that often neglects non-spoken languages and different research goals.
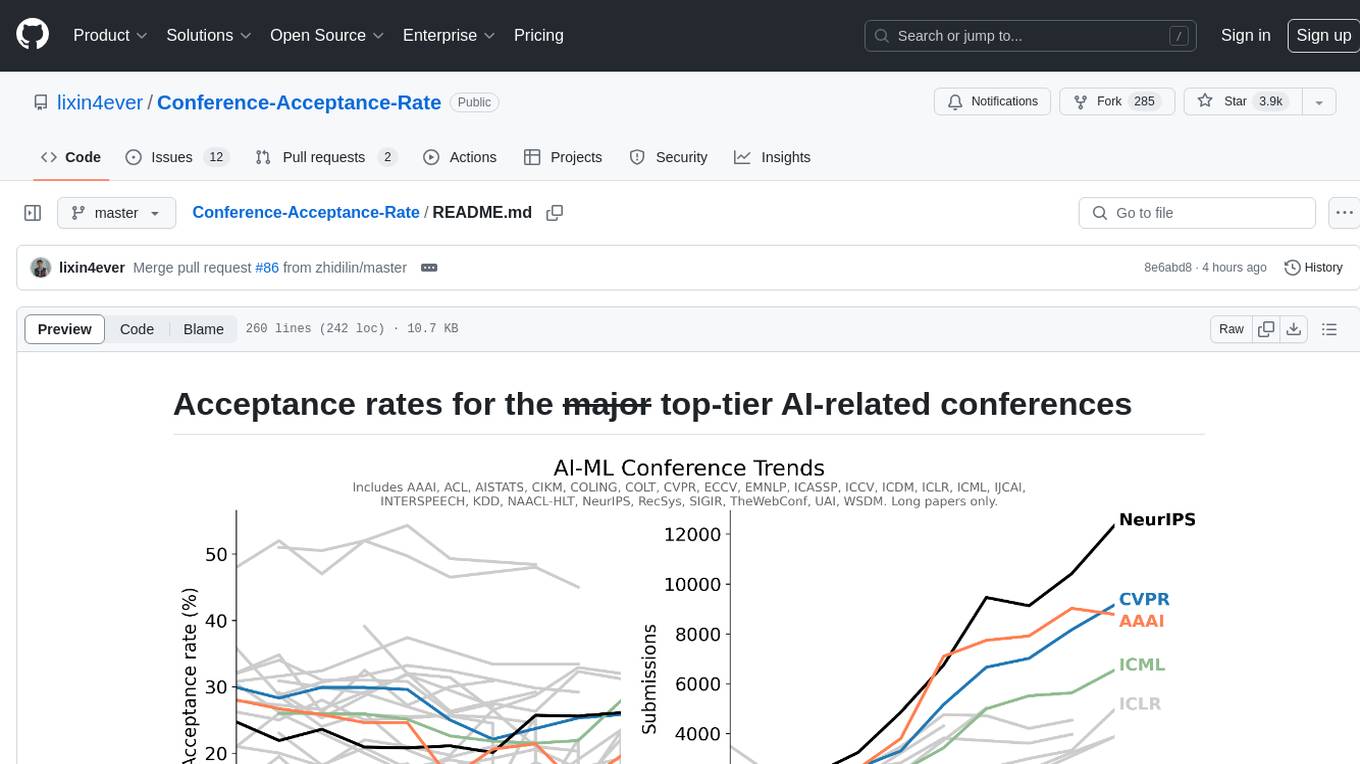
Conference-Acceptance-Rate
The 'Conference-Acceptance-Rate' repository provides acceptance rates for top-tier AI-related conferences in the fields of Natural Language Processing, Computational Linguistics, Computer Vision, Pattern Recognition, Machine Learning, Learning Theory, Artificial Intelligence, Data Mining, Information Retrieval, Speech Processing, and Signal Processing. The data includes acceptance rates for long papers and short papers over several years for each conference, allowing researchers to track trends and make informed decisions about where to submit their work.
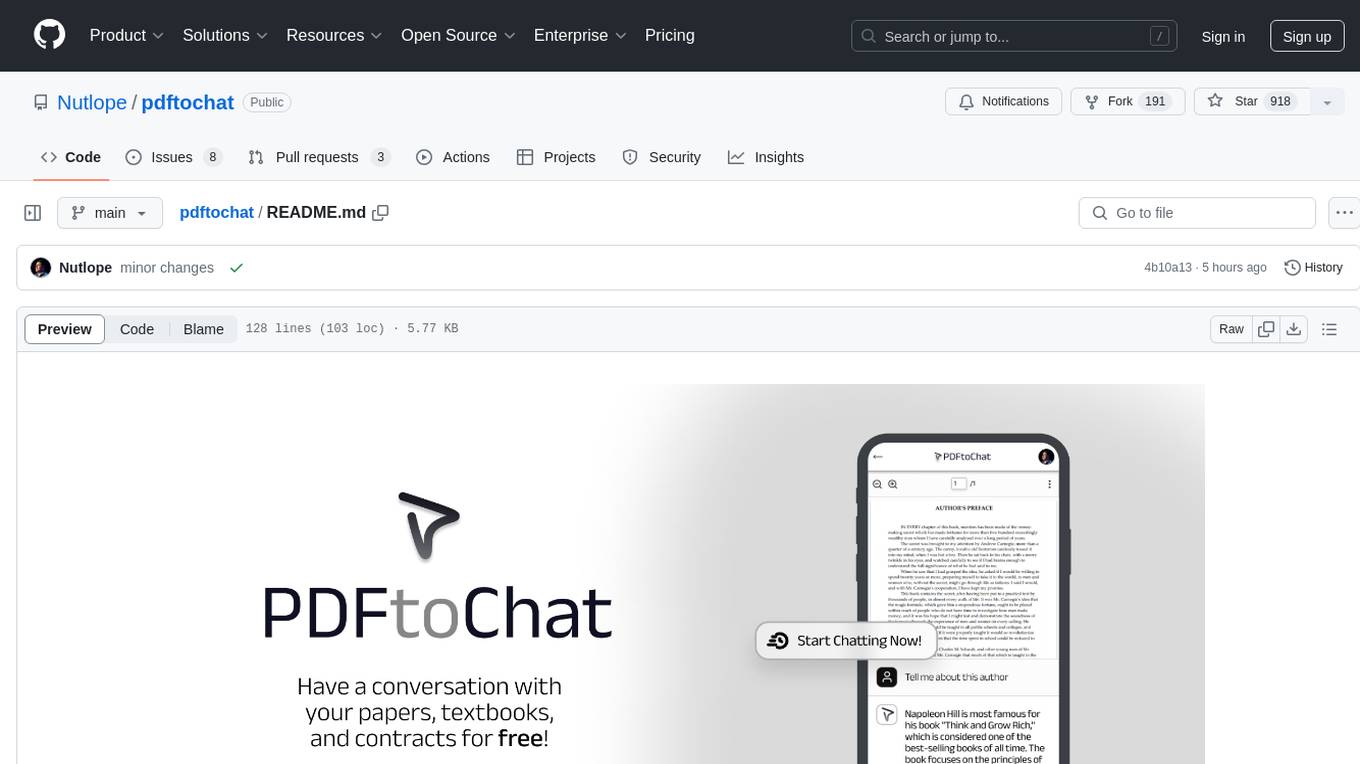
pdftochat
PDFToChat is a tool that allows users to chat with their PDF documents in seconds. It is powered by Together AI and Pinecone, utilizing a tech stack including Next.js, Mixtral, M2 Bert, LangChain.js, MongoDB Atlas, Bytescale, Vercel, Clerk, and Tailwind CSS. Users can deploy the tool to Vercel or any other host by setting up Together.ai, MongoDB Atlas database, Bytescale, Clerk, and Vercel. The tool enables users to interact with PDFs through chat, with future tasks including adding features like trash icon for deleting PDFs, exploring different embedding models, implementing auto scrolling, improving replies, benchmarking accuracy, researching chunking and retrieval best practices, adding demo video, upgrading to Next.js 14, adding analytics, customizing tailwind prose, saving chats in postgres DB, compressing large PDFs, implementing custom uploader, session tracking, error handling, and support for images in PDFs.
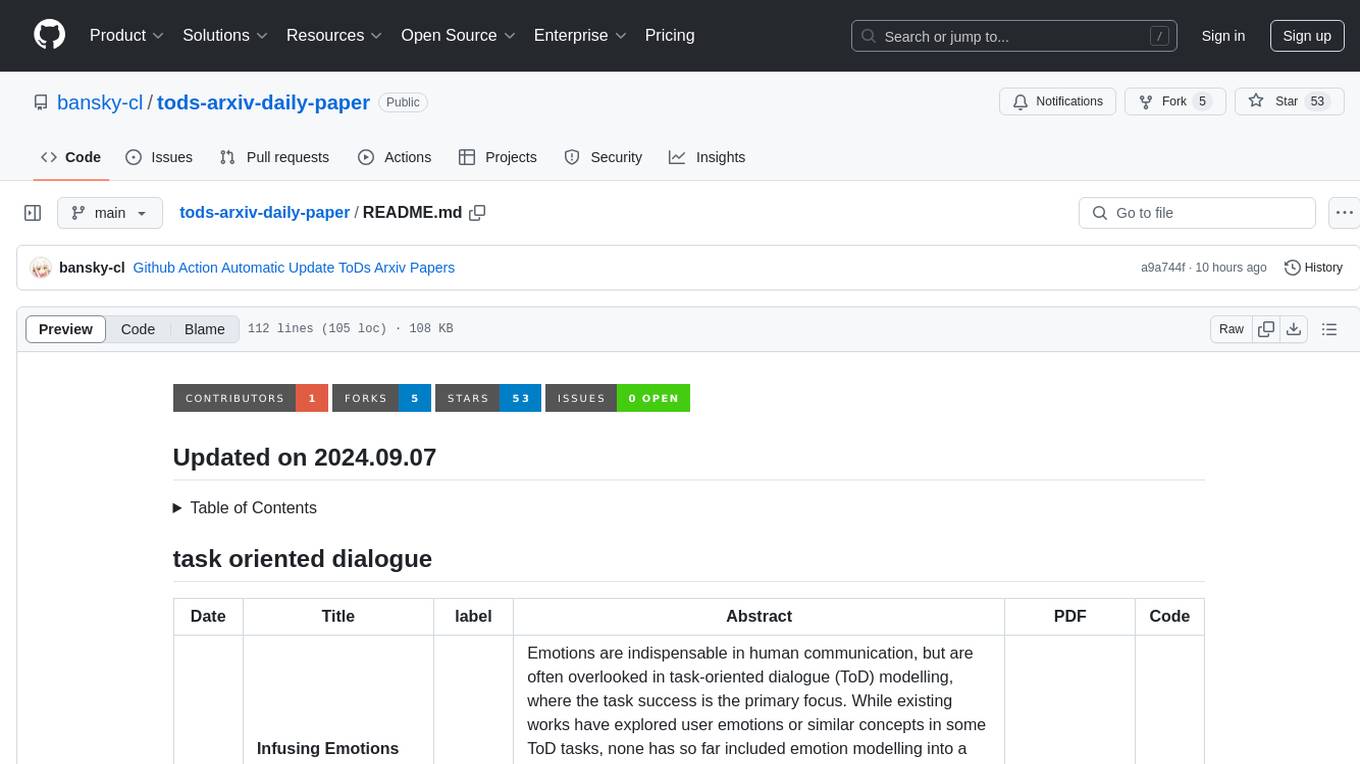
tods-arxiv-daily-paper
This repository provides a tool for fetching and summarizing daily papers from the arXiv repository. It allows users to stay updated with the latest research in various fields by automatically retrieving and summarizing papers on a daily basis. The tool simplifies the process of accessing and digesting academic papers, making it easier for researchers and enthusiasts to keep track of new developments in their areas of interest.
Awesome-LLM-Strawberry
Awesome LLM Strawberry is a collection of research papers and blogs related to OpenAI Strawberry(o1) and Reasoning. The repository is continuously updated to track the frontier of LLM Reasoning.
Call-for-Reviewers
The `Call-for-Reviewers` repository aims to collect the latest 'call for reviewers' links from various top CS/ML/AI conferences/journals. It provides an opportunity for individuals in the computer/ machine learning/ artificial intelligence fields to gain review experience for applying for NIW/H1B/EB1 or enhancing their CV. The repository helps users stay updated with the latest research trends and engage with the academic community.