doris
Apache Doris is an easy-to-use, high performance and unified analytics database.
Stars: 15022
Doris is a lightweight and user-friendly data visualization tool designed for quick and easy exploration of datasets. It provides a simple interface for users to upload their data and generate interactive visualizations without the need for coding. With Doris, users can easily create charts, graphs, and dashboards to analyze and present their data in a visually appealing way. The tool supports various data formats and offers customization options to tailor visualizations to specific needs. Whether you are a data analyst, researcher, or student, Doris simplifies the process of data exploration and presentation.
README:
English • العربية • বাংলা • Deutsch • Español • فارسی • Français • हिन्दी • Bahasa Indonesia • Italiano • 日本語 • 한국어 • Polski • Português • Română • Русский • Slovenščina • ไทย • Türkçe • Українська • Tiếng Việt • 简体中文 • 繁體中文
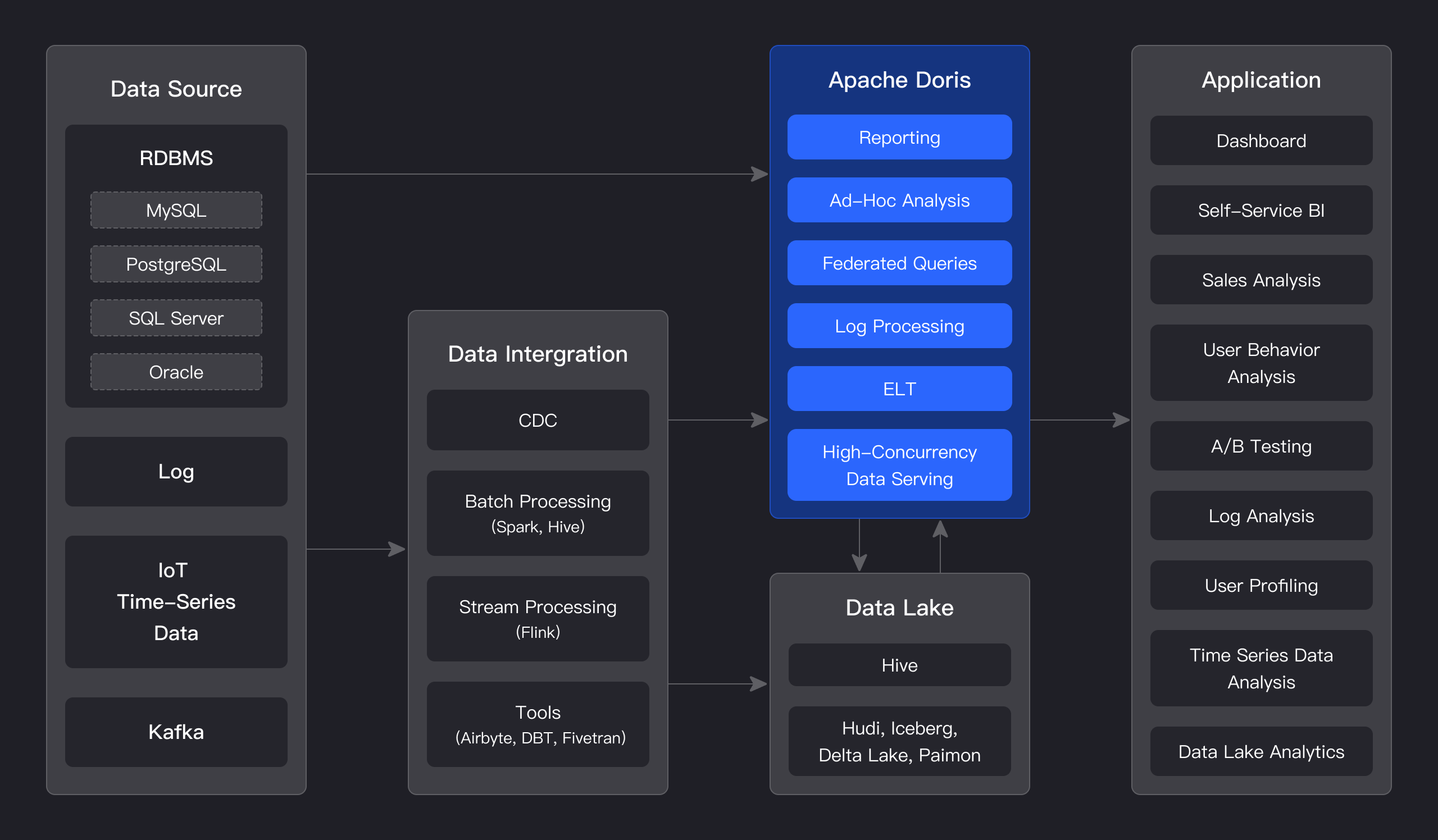
Apache Doris is an easy-to-use, high-performance and real-time analytical database based on MPP architecture, known for its extreme speed and ease of use. It only requires a sub-second response time to return query results under massive data and can support not only high-concurrency point query scenarios but also high-throughput complex analysis scenarios.
All this makes Apache Doris an ideal tool for scenarios including report analysis, ad-hoc query, unified data warehouse, and data lake query acceleration. On Apache Doris, users can build various applications, such as user behavior analysis, AB test platform, log retrieval analysis, user portrait analysis, and order analysis.
🎉 Check out the 🔗All releases, where you'll find a chronological summary of Apache Doris versions released over the past year.
👀 Explore the 🔗Official Website to discover Apache Doris's core features, blogs, and user cases in detail.
As shown in the figure below, after various data integration and processing, the data sources are usually stored in the real-time data warehouse Apache Doris and the offline data lake or data warehouse (in Apache Hive, Apache Iceberg or Apache Hudi).
Apache Doris is widely used in the following scenarios:
-
Real-time Data Analysis:
-
Real-time Reporting and Decision-making: Doris provides real-time updated reports and dashboards for both internal and external enterprise use, supporting real-time decision-making in automated processes.
-
Ad Hoc Analysis: Doris offers multidimensional data analysis capabilities, enabling rapid business intelligence analysis and ad hoc queries to help users quickly uncover insights from complex data.
-
User Profiling and Behavior Analysis: Doris can analyze user behaviors such as participation, retention, and conversion, while also supporting scenarios like population insights and crowd selection for behavior analysis.
-
-
Lakehouse Analytics:
-
Lakehouse Query Acceleration: Doris accelerates lakehouse data queries with its efficient query engine.
-
Federated Analytics: Doris supports federated queries across multiple data sources, simplifying architecture and eliminating data silos.
-
Real-time Data Processing: Doris combines real-time data streams and batch data processing capabilities to meet the needs of high concurrency and low-latency complex business requirements.
-
-
SQL-based Observability:
- Log and Event Analysis: Doris enables real-time or batch analysis of logs and events in distributed systems, helping to identify issues and optimize performance.
Apache Doris uses the MySQL protocol, is highly compatible with MySQL syntax, and supports standard SQL. Users can access Apache Doris through various client tools, and it seamlessly integrates with BI tools.
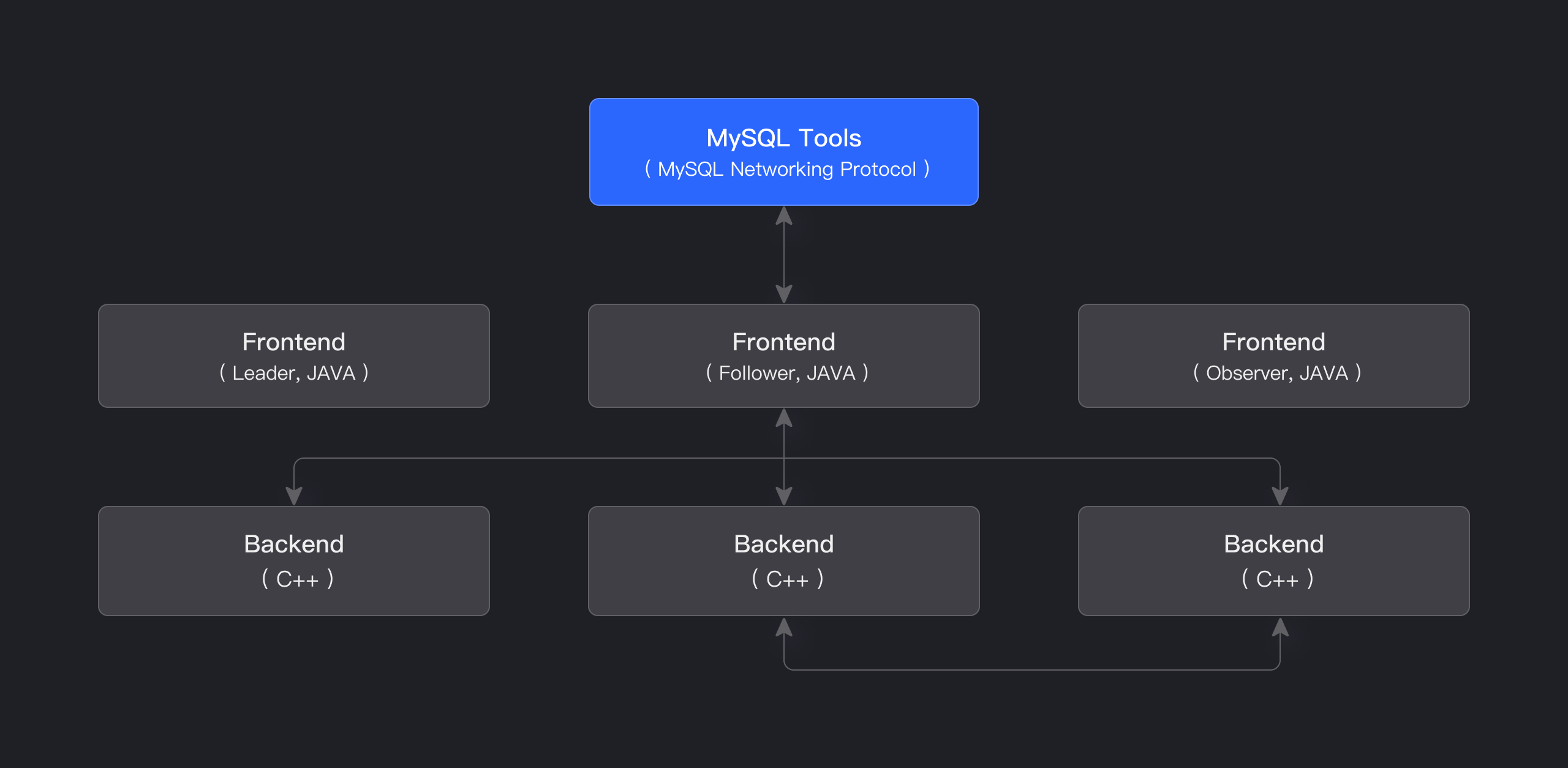
The storage-compute integrated architecture of Apache Doris is streamlined and easy to maintain. As shown in the figure below, it consists of only two types of processes:
-
Frontend (FE): Primarily responsible for handling user requests, query parsing and planning, metadata management, and node management tasks.
-
Backend (BE): Primarily responsible for data storage and query execution. Data is partitioned into shards and stored with multiple replicas across BE nodes.
In a production environment, multiple FE nodes can be deployed for disaster recovery. Each FE node maintains a full copy of the metadata. The FE nodes are divided into three roles:
| Role | Function |
|---|---|
| Master | The FE Master node is responsible for metadata read and write operations. When metadata changes occur in the Master, they are synchronized to Follower or Observer nodes via the BDB JE protocol. |
| Follower | The Follower node is responsible for reading metadata. If the Master node fails, a Follower node can be selected as the new Master. |
| Observer | The Observer node is responsible for reading metadata and is mainly used to increase query concurrency. It does not participate in cluster leadership elections. |
Both FE and BE processes are horizontally scalable, enabling a single cluster to support hundreds of machines and tens of petabytes of storage capacity. The FE and BE processes use a consistency protocol to ensure high availability of services and high reliability of data. The storage-compute integrated architecture is highly integrated, significantly reducing the operational complexity of distributed systems.
-
High Availability: In Apache Doris, both metadata and data are stored with multiple replicas, synchronizing data logs via the quorum protocol. Data write is considered successful once a majority of replicas have completed the write, ensuring that the cluster remains available even if a few nodes fail. Apache Doris supports both same-city and cross-region disaster recovery, enabling dual-cluster master-slave modes. When some nodes experience failures, the cluster can automatically isolate the faulty nodes, preventing the overall cluster availability from being affected.
-
High Compatibility: Apache Doris is highly compatible with the MySQL protocol and supports standard SQL syntax, covering most MySQL and Hive functions. This high compatibility allows users to seamlessly migrate and integrate existing applications and tools. Apache Doris supports the MySQL ecosystem, enabling users to connect Doris using MySQL Client tools for more convenient operations and maintenance. It also supports MySQL protocol compatibility for BI reporting tools and data transmission tools, ensuring efficiency and stability in data analysis and data transmission processes.
-
Real-Time Data Warehouse: Based on Apache Doris, a real-time data warehouse service can be built. Apache Doris offers second-level data ingestion capabilities, capturing incremental changes from upstream online transactional databases into Doris within seconds. Leveraging vectorized engines, MPP architecture, and Pipeline execution engines, Doris provides sub-second data query capabilities, thereby constructing a high-performance, low-latency real-time data warehouse platform.
-
Unified Lakehouse: Apache Doris can build a unified lakehouse architecture based on external data sources such as data lakes or relational databases. The Doris unified lakehouse solution enables seamless integration and free data flow between data lakes and data warehouses, helping users directly utilize data warehouse capabilities to solve data analysis problems in data lakes while fully leveraging data lake data management capabilities to enhance data value.
-
Flexible Modeling: Apache Doris offers various modeling approaches, such as wide table models, pre-aggregation models, star/snowflake schemas, etc. During data import, data can be flattened into wide tables and written into Doris through compute engines like Flink or Spark, or data can be directly imported into Doris, performing data modeling operations through views, materialized views, or real-time multi-table joins.
Doris provides an efficient SQL interface and is fully compatible with the MySQL protocol. Its query engine is based on an MPP (Massively Parallel Processing) architecture, capable of efficiently executing complex analytical queries and achieving low-latency real-time queries. Through columnar storage technology for data encoding and compression, it significantly optimizes query performance and storage compression ratio.
Apache Doris adopts the MySQL protocol, supports standard SQL, and is highly compatible with MySQL syntax. Users can access Apache Doris through various client tools and seamlessly integrate it with BI tools, including but not limited to Smartbi, DataEase, FineBI, Tableau, Power BI, and Apache Superset. Apache Doris can work as the data source for any BI tools that support the MySQL protocol.
Apache Doris has a columnar storage engine, which encodes, compresses, and reads data by column. This enables a very high data compression ratio and largely reduces unnecessary data scanning, thus making more efficient use of IO and CPU resources.
Apache Doris supports various index structures to minimize data scans:
-
Sorted Compound Key Index: Users can specify three columns at most to form a compound sort key. This can effectively prune data to better support highly concurrent reporting scenarios.
-
Min/Max Index: This enables effective data filtering in equivalence and range queries of numeric types.
-
BloomFilter Index: This is very effective in equivalence filtering and pruning of high-cardinality columns.
-
Inverted Index: This enables fast searching for any field.
Apache Doris supports a variety of data models and has optimized them for different scenarios:
-
Detail Model (Duplicate Key Model): A detail data model designed to meet the detailed storage requirements of fact tables.
-
Primary Key Model (Unique Key Model): Ensures unique keys; data with the same key is overwritten, enabling row-level data updates.
-
Aggregate Model (Aggregate Key Model): Merges value columns with the same key, significantly improving performance through pre-aggregation.
Apache Doris also supports strongly consistent single-table materialized views and asynchronously refreshed multi-table materialized views. Single-table materialized views are automatically refreshed and maintained by the system, requiring no manual intervention from users. Multi-table materialized views can be refreshed periodically using in-cluster scheduling or external scheduling tools, reducing the complexity of data modeling.
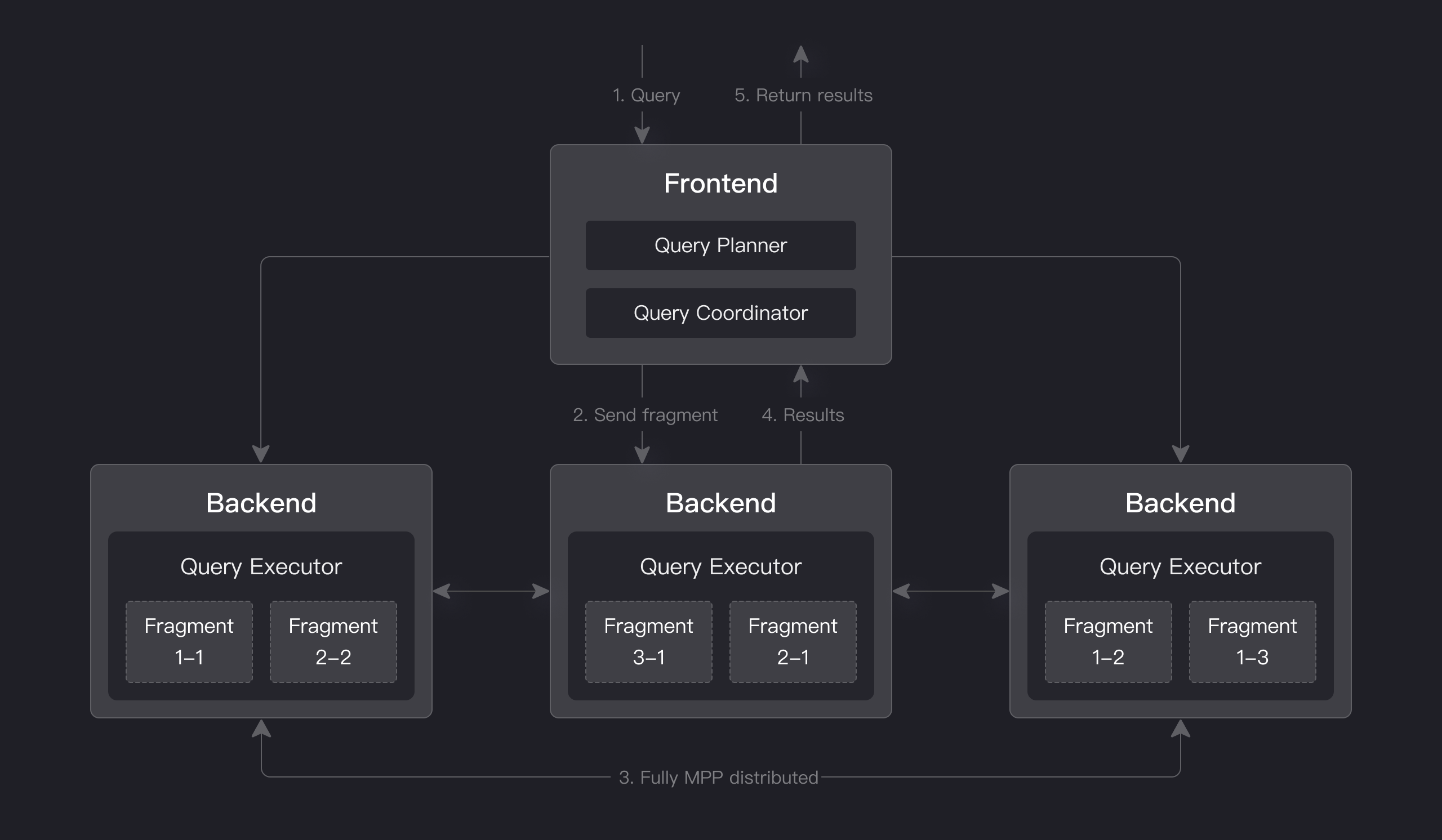
Apache Doris has an MPP-based query engine for parallel execution between and within nodes. It supports distributed shuffle join for large tables to better handle complicated queries.
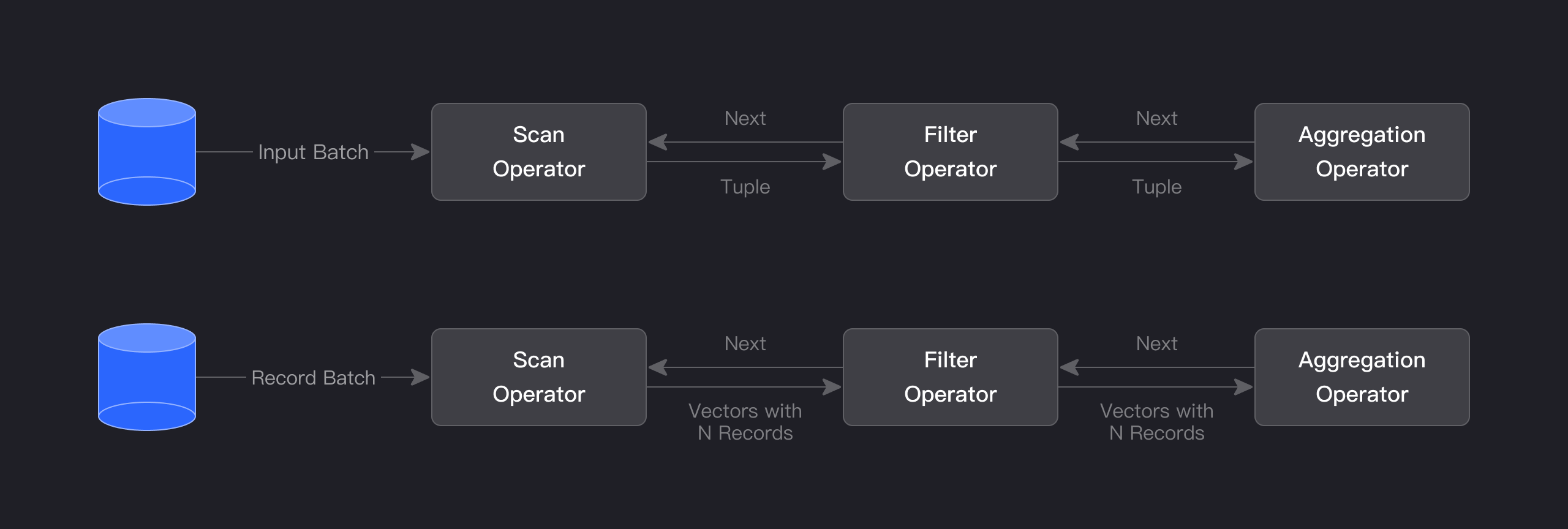
The query engine of Apache Doris is fully vectorized, with all memory structures laid out in a columnar format. This can largely reduce virtual function calls, increase cache hit rates, and make efficient use of SIMD instructions. Apache Doris delivers a 5~10 times higher performance in wide table aggregation scenarios than non-vectorized engines.
Apache Doris uses adaptive query execution technology to dynamically adjust the execution plan based on runtime statistics. For example, it can generate a runtime filter and push it to the probe side. Specifically, it pushes the filters to the lowest-level scan node on the probe side, which largely reduces the data amount to be processed and increases join performance. The runtime filter of Apache Doris supports In/Min/Max/Bloom Filter.
Apache Doris uses a Pipeline execution engine that breaks down queries into multiple sub-tasks for parallel execution, fully leveraging multi-core CPU capabilities. It simultaneously addresses the thread explosion problem by limiting the number of query threads. The Pipeline execution engine reduces data copying and sharing, optimizes sorting and aggregation operations, thereby significantly improving query efficiency and throughput.
In terms of the optimizer, Apache Doris employs a combined optimization strategy of CBO (Cost-Based Optimizer), RBO (Rule-Based Optimizer), and HBO (History-Based Optimizer). RBO supports constant folding, subquery rewriting, predicate pushdown, and more. CBO supports join reordering and other optimizations. HBO recommends the optimal execution plan based on historical query information. These multiple optimization measures ensure that Doris can enumerate high-performance query plans across various types of queries.
-
🎯 Easy to Use: Two processes, no other dependencies; online cluster scaling, automatic replica recovery; compatible with MySQL protocol, and using standard SQL.
-
🚀 High Performance: Extremely fast performance for low-latency and high-throughput queries with columnar storage engine, modern MPP architecture, vectorized query engine, pre-aggregated materialized view and data index.
-
🖥️ Single Unified: A single system can support real-time data serving, interactive data analysis and offline data processing scenarios.
-
⚛️ Federated Querying: Supports federated querying of data lakes such as Hive, Iceberg, Hudi, and databases such as MySQL and Elasticsearch.
-
⏩ Various Data Import Methods: Supports batch import from HDFS/S3 and stream import from MySQL Binlog/Kafka; supports micro-batch writing through HTTP interface and real-time writing using Insert in JDBC.
-
🚙 Rich Ecology: Spark uses Spark-Doris-Connector to read and write Doris; Flink-Doris-Connector enables Flink CDC to implement exactly-once data writing to Doris; DBT Doris Adapter is provided to transform data in Doris with DBT.
Apache Doris has graduated from Apache incubator successfully and become a Top-Level Project in June 2022.
We deeply appreciate 🔗community contributors for their contribution to Apache Doris.
Apache Doris now has a wide user base in China and around the world, and as of today, Apache Doris is used in production environments in thousands of companies worldwide. More than 80% of the top 50 Internet companies in China in terms of market capitalization or valuation have been using Apache Doris for a long time, including Baidu, Meituan, Xiaomi, Jingdong, Bytedance, Tencent, NetEase, Kwai, Sina, 360, Mihoyo, and Ke Holdings. It is also widely used in some traditional industries such as finance, energy, manufacturing, and telecommunications.
The users of Apache Doris: 🔗Users
Add your company logo at Apache Doris Website: 🔗Add Your Company
All Documentation 🔗Docs
All release and binary version 🔗Download
See how to compile 🔗Compilation)
See how to install and deploy 🔗Installation and deployment
Doris provides support for Spark/Flink to read data stored in Doris through Connector, and also supports to write data to Doris through Connector.
Mail List is the most recognized form of communication in Apache community. See how to 🔗Subscribe Mailing Lists
If you meet any questions, feel free to file a 🔗GitHub Issue or post it in 🔗GitHub Discussion and fix it by submitting a 🔗Pull Request
We welcome your suggestions, comments (including criticisms), comments and contributions. See 🔗How to Contribute and 🔗Code Submission Guide
🔗Doris Improvement Proposal (DSIP) can be thought of as A Collection of Design Documents for all Major Feature Updates or Improvements.
🔗 Backend C++ Coding Specification should be strictly followed, which will help us achieve better code quality.
Contact us through the following mailing list.
| Name | Scope | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [email protected] | Development-related discussions | Subscribe | Unsubscribe | Archives |
- Apache Doris Official Website - Site
- Developer Mailing list - [email protected]. Mail to [email protected], follow the reply to subscribe the mail list.
- Slack channel - Join the Slack
- Twitter - Follow @doris_apache
Note Some licenses of the third-party dependencies are not compatible with Apache 2.0 License. So you need to disable some Doris features to be complied with Apache 2.0 License. For details, refer to the
thirdparty/LICENSE.txt
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for doris
Similar Open Source Tools

doris
Doris is a lightweight and user-friendly data visualization tool designed for quick and easy exploration of datasets. It provides a simple interface for users to upload their data and generate interactive visualizations without the need for coding. With Doris, users can easily create charts, graphs, and dashboards to analyze and present their data in a visually appealing way. The tool supports various data formats and offers customization options to tailor visualizations to specific needs. Whether you are a data analyst, researcher, or student, Doris simplifies the process of data exploration and presentation.
MemoryBear
MemoryBear is a next-generation AI memory system developed by RedBear AI, focusing on overcoming limitations in knowledge storage and multi-agent collaboration. It empowers AI with human-like memory capabilities, enabling deep knowledge understanding and cognitive collaboration. The system addresses challenges such as knowledge forgetting, memory gaps in multi-agent collaboration, and semantic ambiguity during reasoning. MemoryBear's core features include memory extraction engine, graph storage, hybrid search, memory forgetting engine, self-reflection engine, and FastAPI services. It offers a standardized service architecture for efficient integration and invocation across applications.
reductstore
ReductStore is a high-performance time series database designed for storing and managing large amounts of unstructured blob data. It offers features such as real-time querying, batching data, and HTTP(S) API for edge computing, computer vision, and IoT applications. The database ensures data integrity, implements retention policies, and provides efficient data access, making it a cost-effective solution for applications requiring unstructured data storage and access at specific time intervals.

unified-cache-management
Unified Cache Manager (UCM) is a tool designed to persist the LLM KVCache and replace redundant computations through various retrieval mechanisms. It supports prefix caching and offers training-free sparse attention retrieval methods, enhancing performance for long sequence inference tasks. UCM also provides a PD disaggregation solution based on a storage-compute separation architecture, enabling easier management of heterogeneous computing resources. When integrated with vLLM, UCM significantly reduces inference latency in scenarios like multi-turn dialogue and long-context reasoning tasks.
PulsarRPA
PulsarRPA is a high-performance, distributed, open-source Robotic Process Automation (RPA) framework designed to handle large-scale RPA tasks with ease. It provides a comprehensive solution for browser automation, web content understanding, and data extraction. PulsarRPA addresses challenges of browser automation and accurate web data extraction from complex and evolving websites. It incorporates innovative technologies like browser rendering, RPA, intelligent scraping, advanced DOM parsing, and distributed architecture to ensure efficient, accurate, and scalable web data extraction. The tool is open-source, customizable, and supports cutting-edge information extraction technology, making it a preferred solution for large-scale web data extraction.

vulcan-sql
VulcanSQL is an Analytical Data API Framework for AI agents and data apps. It aims to help data professionals deliver RESTful APIs from databases, data warehouses or data lakes much easier and secure. It turns your SQL into APIs in no time!
seatunnel
SeaTunnel is a high-performance, distributed data integration tool trusted by numerous companies for synchronizing vast amounts of data daily. It addresses common data integration challenges by seamlessly integrating with diverse data sources, supporting multimodal data integration, complex synchronization scenarios, resource efficiency, and quality monitoring. With over 100 connectors, SeaTunnel offers batch-stream integration, distributed snapshot algorithm, multi-engine support, JDBC multiplexing, and log parsing. It provides high throughput, low latency, real-time monitoring, and supports two job development methods. Users can configure jobs, select execution engines, and parallelize data using source connectors. SeaTunnel also supports multimodal data integration, Apache SeaTunnel tools, real-world use cases, and visual management of jobs through the SeaTunnel Web Project.
CSGHub
CSGHub is an open source, trustworthy large model asset management platform that can assist users in governing the assets involved in the lifecycle of LLM and LLM applications (datasets, model files, codes, etc). With CSGHub, users can perform operations on LLM assets, including uploading, downloading, storing, verifying, and distributing, through Web interface, Git command line, or natural language Chatbot. Meanwhile, the platform provides microservice submodules and standardized OpenAPIs, which could be easily integrated with users' own systems. CSGHub is committed to bringing users an asset management platform that is natively designed for large models and can be deployed On-Premise for fully offline operation. CSGHub offers functionalities similar to a privatized Huggingface(on-premise Huggingface), managing LLM assets in a manner akin to how OpenStack Glance manages virtual machine images, Harbor manages container images, and Sonatype Nexus manages artifacts.
Geoweaver
Geoweaver is an in-browser software that enables users to easily compose and execute full-stack data processing workflows using online spatial data facilities, high-performance computation platforms, and open-source deep learning libraries. It provides server management, code repository, workflow orchestration software, and history recording capabilities. Users can run it from both local and remote machines. Geoweaver aims to make data processing workflows manageable for non-coder scientists and preserve model run history. It offers features like progress storage, organization, SSH connection to external servers, and a web UI with Python support.
cube
Cube is a semantic layer for building data applications, helping data engineers and application developers access data from modern data stores, organize it into consistent definitions, and deliver it to every application. It works with SQL-enabled data sources, providing sub-second latency and high concurrency for API requests. Cube addresses SQL code organization, performance, and access control issues in data applications, enabling efficient data modeling, access control, and performance optimizations for various tools like embedded analytics, dashboarding, reporting, and data notebooks.

qdrant
Qdrant is a vector similarity search engine and vector database. It is written in Rust, which makes it fast and reliable even under high load. Qdrant can be used for a variety of applications, including: * Semantic search * Image search * Product recommendations * Chatbots * Anomaly detection Qdrant offers a variety of features, including: * Payload storage and filtering * Hybrid search with sparse vectors * Vector quantization and on-disk storage * Distributed deployment * Highlighted features such as query planning, payload indexes, SIMD hardware acceleration, async I/O, and write-ahead logging Qdrant is available as a fully managed cloud service or as an open-source software that can be deployed on-premises.
postgresml
PostgresML is a powerful Postgres extension that seamlessly combines data storage and machine learning inference within your database. It enables running machine learning and AI operations directly within PostgreSQL, leveraging GPU acceleration for faster computations, integrating state-of-the-art large language models, providing built-in functions for text processing, enabling efficient similarity search, offering diverse ML algorithms, ensuring high performance, scalability, and security, supporting a wide range of NLP tasks, and seamlessly integrating with existing PostgreSQL tools and client libraries.
LabelLLM
LabelLLM is an open-source data annotation platform designed to optimize the data annotation process for LLM development. It offers flexible configuration, multimodal data support, comprehensive task management, and AI-assisted annotation. Users can access a suite of annotation tools, enjoy a user-friendly experience, and enhance efficiency. The platform allows real-time monitoring of annotation progress and quality control, ensuring data integrity and timeliness.
apo
AutoPilot Observability (APO) is an out-of-the-box observability platform that provides one-click installation and ready-to-use capabilities. APO's OneAgent supports one-click configuration-free installation of Tracing probes, collects application fault scene logs, infrastructure metrics, network metrics of applications and downstream dependencies, and Kubernetes events. It supports collecting causality metrics based on eBPF implementation. APO integrates OpenTelemetry probes, otel-collector, Jaeger, ClickHouse, and VictoriaMetrics, reducing user configuration work. APO innovatively integrates eBPF technology with the OpenTelemetry ecosystem, significantly reducing data storage volume. It offers guided troubleshooting using eBPF technology to assist users in pinpointing fault causes on a single page.
video-search-and-summarization
The NVIDIA AI Blueprint for Video Search and Summarization is a repository showcasing video search and summarization agent with NVIDIA NIM microservices. It enables industries to make better decisions faster by providing insightful, accurate, and interactive video analytics AI agents. These agents can perform tasks like video summarization and visual question-answering, unlocking new application possibilities. The repository includes software components like NIM microservices, ingestion pipeline, and CA-RAG module, offering a comprehensive solution for analyzing and summarizing large volumes of video data. The target audience includes video analysts, IT engineers, and GenAI developers who can benefit from the blueprint's 1-click deployment steps, easy-to-manage configurations, and customization options. The repository structure overview includes directories for deployment, source code, and training notebooks, along with documentation for detailed instructions. Hardware requirements vary based on deployment topology and dependencies like VLM and LLM, with different deployment methods such as Launchable Deployment, Docker Compose Deployment, and Helm Chart Deployment provided for various use cases.
For similar tasks
awesome-mobile-robotics
The 'awesome-mobile-robotics' repository is a curated list of important content related to Mobile Robotics and AI. It includes resources such as courses, books, datasets, software and libraries, podcasts, conferences, journals, companies and jobs, laboratories and research groups, and miscellaneous resources. The repository covers a wide range of topics in the field of Mobile Robotics and AI, providing valuable information for enthusiasts, researchers, and professionals in the domain.
fiftyone-brain
FiftyOne Brain contains the open source AI/ML capabilities for the FiftyOne ecosystem, enabling users to automatically analyze and manipulate their datasets and models. Features include visual similarity search, query by text, finding unique and representative samples, finding media quality problems and annotation mistakes, and more.

mmf
MMF is a modular framework for vision and language multimodal research from Facebook AI Research. It contains reference implementations of state-of-the-art vision and language models, allowing distributed training. MMF serves as a starter codebase for challenges around vision and language datasets, such as The Hateful Memes, TextVQA, TextCaps, and VQA challenges. It is scalable, fast, and un-opinionated, providing a solid foundation for vision and language multimodal research projects.

doris
Doris is a lightweight and user-friendly data visualization tool designed for quick and easy exploration of datasets. It provides a simple interface for users to upload their data and generate interactive visualizations without the need for coding. With Doris, users can easily create charts, graphs, and dashboards to analyze and present their data in a visually appealing way. The tool supports various data formats and offers customization options to tailor visualizations to specific needs. Whether you are a data analyst, researcher, or student, Doris simplifies the process of data exploration and presentation.
EScAIP
EScAIP is an Efficiently Scaled Attention Interatomic Potential that leverages a novel multi-head self-attention formulation within graph neural networks to predict energy and forces between atoms in molecules and materials. It achieves substantial gains in efficiency, at least 10x speed up in inference time and 5x less memory usage compared to existing models. EScAIP represents a philosophy towards developing general-purpose Neural Network Interatomic Potentials that achieve better expressivity through scaling and continue to scale efficiently with increased computational resources and training data.
BioAgents
BioAgents AgentKit is an advanced AI agent framework tailored for biological and scientific research. It offers powerful conversational AI capabilities with specialized knowledge in biology, life sciences, and scientific research methodologies. The framework includes state-of-the-art analysis agents, configurable research agents, and a variety of specialized agents for tasks such as file parsing, research planning, literature search, data analysis, hypothesis generation, research reflection, and user-facing responses. BioAgents also provides support for LLM libraries, multiple search backends for literature agents, and two backends for data analysis. The project structure includes backend source code, services for chat, job queue system, real-time notifications, and JWT authentication, as well as a frontend UI built with Preact.
supersonic
SuperSonic is a next-generation BI platform that integrates Chat BI (powered by LLM) and Headless BI (powered by semantic layer) paradigms. This integration ensures that Chat BI has access to the same curated and governed semantic data models as traditional BI. Furthermore, the implementation of both paradigms benefits from the integration: * Chat BI's Text2SQL gets augmented with context-retrieval from semantic models. * Headless BI's query interface gets extended with natural language API. SuperSonic provides a Chat BI interface that empowers users to query data using natural language and visualize the results with suitable charts. To enable such experience, the only thing necessary is to build logical semantic models (definition of metric/dimension/tag, along with their meaning and relationships) through a Headless BI interface. Meanwhile, SuperSonic is designed to be extensible and composable, allowing custom implementations to be added and configured with Java SPI. The integration of Chat BI and Headless BI has the potential to enhance the Text2SQL generation in two dimensions: 1. Incorporate data semantics (such as business terms, column values, etc.) into the prompt, enabling LLM to better understand the semantics and reduce hallucination. 2. Offload the generation of advanced SQL syntax (such as join, formula, etc.) from LLM to the semantic layer to reduce complexity. With these ideas in mind, we develop SuperSonic as a practical reference implementation and use it to power our real-world products. Additionally, to facilitate further development we decide to open source SuperSonic as an extensible framework.
sqlcoder
Defog's SQLCoder is a family of state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs) designed for converting natural language questions into SQL queries. It outperforms popular open-source models like gpt-4 and gpt-4-turbo on SQL generation tasks. SQLCoder has been trained on more than 20,000 human-curated questions based on 10 different schemas, and the model weights are licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0. Users can interact with SQLCoder through the 'transformers' library and run queries using the 'sqlcoder launch' command in the terminal. The tool has been tested on NVIDIA GPUs with more than 16GB VRAM and Apple Silicon devices with some limitations. SQLCoder offers a demo on their website and supports quantized versions of the model for consumer GPUs with sufficient memory.
For similar jobs

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.

skyvern
Skyvern automates browser-based workflows using LLMs and computer vision. It provides a simple API endpoint to fully automate manual workflows, replacing brittle or unreliable automation solutions. Traditional approaches to browser automations required writing custom scripts for websites, often relying on DOM parsing and XPath-based interactions which would break whenever the website layouts changed. Instead of only relying on code-defined XPath interactions, Skyvern adds computer vision and LLMs to the mix to parse items in the viewport in real-time, create a plan for interaction and interact with them. This approach gives us a few advantages: 1. Skyvern can operate on websites it’s never seen before, as it’s able to map visual elements to actions necessary to complete a workflow, without any customized code 2. Skyvern is resistant to website layout changes, as there are no pre-determined XPaths or other selectors our system is looking for while trying to navigate 3. Skyvern leverages LLMs to reason through interactions to ensure we can cover complex situations. Examples include: 1. If you wanted to get an auto insurance quote from Geico, the answer to a common question “Were you eligible to drive at 18?” could be inferred from the driver receiving their license at age 16 2. If you were doing competitor analysis, it’s understanding that an Arnold Palmer 22 oz can at 7/11 is almost definitely the same product as a 23 oz can at Gopuff (even though the sizes are slightly different, which could be a rounding error!) Want to see examples of Skyvern in action? Jump to #real-world-examples-of- skyvern

pandas-ai
PandasAI is a Python library that makes it easy to ask questions to your data in natural language. It helps you to explore, clean, and analyze your data using generative AI.
vanna
Vanna is an open-source Python framework for SQL generation and related functionality. It uses Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to train a model on your data, which can then be used to ask questions and get back SQL queries. Vanna is designed to be portable across different LLMs and vector databases, and it supports any SQL database. It is also secure and private, as your database contents are never sent to the LLM or the vector database.

databend
Databend is an open-source cloud data warehouse that serves as a cost-effective alternative to Snowflake. With its focus on fast query execution and data ingestion, it's designed for complex analysis of the world's largest datasets.
Avalonia-Assistant
Avalonia-Assistant is an open-source desktop intelligent assistant that aims to provide a user-friendly interactive experience based on the Avalonia UI framework and the integration of Semantic Kernel with OpenAI or other large LLM models. By utilizing Avalonia-Assistant, you can perform various desktop operations through text or voice commands, enhancing your productivity and daily office experience.
marvin
Marvin is a lightweight AI toolkit for building natural language interfaces that are reliable, scalable, and easy to trust. Each of Marvin's tools is simple and self-documenting, using AI to solve common but complex challenges like entity extraction, classification, and generating synthetic data. Each tool is independent and incrementally adoptable, so you can use them on their own or in combination with any other library. Marvin is also multi-modal, supporting both image and audio generation as well using images as inputs for extraction and classification. Marvin is for developers who care more about _using_ AI than _building_ AI, and we are focused on creating an exceptional developer experience. Marvin users should feel empowered to bring tightly-scoped "AI magic" into any traditional software project with just a few extra lines of code. Marvin aims to merge the best practices for building dependable, observable software with the best practices for building with generative AI into a single, easy-to-use library. It's a serious tool, but we hope you have fun with it. Marvin is open-source, free to use, and made with 💙 by the team at Prefect.
activepieces
Activepieces is an open source replacement for Zapier, designed to be extensible through a type-safe pieces framework written in Typescript. It features a user-friendly Workflow Builder with support for Branches, Loops, and Drag and Drop. Activepieces integrates with Google Sheets, OpenAI, Discord, and RSS, along with 80+ other integrations. The list of supported integrations continues to grow rapidly, thanks to valuable contributions from the community. Activepieces is an open ecosystem; all piece source code is available in the repository, and they are versioned and published directly to npmjs.com upon contributions. If you cannot find a specific piece on the pieces roadmap, please submit a request by visiting the following link: Request Piece Alternatively, if you are a developer, you can quickly build your own piece using our TypeScript framework. For guidance, please refer to the following guide: Contributor's Guide





?style=for-the-badge)
?style=for-the-badge)