
skyvern
Automate browser based workflows with AI
Stars: 20466

Skyvern automates browser-based workflows using LLMs and computer vision. It provides a simple API endpoint to fully automate manual workflows, replacing brittle or unreliable automation solutions. Traditional approaches to browser automations required writing custom scripts for websites, often relying on DOM parsing and XPath-based interactions which would break whenever the website layouts changed. Instead of only relying on code-defined XPath interactions, Skyvern adds computer vision and LLMs to the mix to parse items in the viewport in real-time, create a plan for interaction and interact with them. This approach gives us a few advantages: 1. Skyvern can operate on websites it’s never seen before, as it’s able to map visual elements to actions necessary to complete a workflow, without any customized code 2. Skyvern is resistant to website layout changes, as there are no pre-determined XPaths or other selectors our system is looking for while trying to navigate 3. Skyvern leverages LLMs to reason through interactions to ensure we can cover complex situations. Examples include: 1. If you wanted to get an auto insurance quote from Geico, the answer to a common question “Were you eligible to drive at 18?” could be inferred from the driver receiving their license at age 16 2. If you were doing competitor analysis, it’s understanding that an Arnold Palmer 22 oz can at 7/11 is almost definitely the same product as a 23 oz can at Gopuff (even though the sizes are slightly different, which could be a rounding error!) Want to see examples of Skyvern in action? Jump to #real-world-examples-of- skyvern
README:
🐉 Automate Browser-based workflows using LLMs and Computer Vision 🐉
Skyvern automates browser-based workflows using LLMs and computer vision. It provides a Playwright-compatible SDK that adds AI functionality on top of playwright, as well as a no-code workflow builder to help both technical and non-technical users automate manual workflows on any website, replacing brittle or unreliable automation solutions.
Traditional approaches to browser automations required writing custom scripts for websites, often relying on DOM parsing and XPath-based interactions which would break whenever the website layouts changed.
Instead of only relying on code-defined XPath interactions, Skyvern relies on Vision LLMs to learn and interact with the websites.
Skyvern was inspired by the Task-Driven autonomous agent design popularized by BabyAGI and AutoGPT -- with one major bonus: we give Skyvern the ability to interact with websites using browser automation libraries like Playwright.
Skyvern uses a swarm of agents to comprehend a website, and plan and execute its actions:

This approach has a few advantages:
- Skyvern can operate on websites it's never seen before, as it's able to map visual elements to actions necessary to complete a workflow, without any customized code
- Skyvern is resistant to website layout changes, as there are no pre-determined XPaths or other selectors our system is looking for while trying to navigate
- Skyvern is able to take a single workflow and apply it to a large number of websites, as it's able to reason through the interactions necessary to complete the workflow A detailed technical report can be found here.
https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/5cab4668-e8e2-4982-8551-aab05ff73a7f
Skyvern Cloud is a managed cloud version of Skyvern that allows you to run Skyvern without worrying about the infrastructure. It allows you to run multiple Skyvern instances in parallel and comes bundled with anti-bot detection mechanisms, proxy network, and CAPTCHA solvers.
If you'd like to try it out, navigate to app.skyvern.com and create an account.
Choose your preferred setup method:
Dependencies needed:
- Python 3.11.x, works with 3.12, not ready yet for 3.13
- NodeJS & NPM
Additionally, for Windows:
- Rust
- VS Code with C++ dev tools and Windows SDK
pip install skyvernskyvern quickstartIf you already have a database you want to use, pass a custom connection string to skip the local Docker PostgreSQL setup:
skyvern quickstart --database-string "postgresql+psycopg://user:password@localhost:5432/skyvern"- Install Docker Desktop
- Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/skyvern-ai/skyvern.git && cd skyvern
- Run quickstart with Docker Compose:
When prompted, choose "Docker Compose" for the full containerized setup.
pip install skyvern && skyvern quickstart - Navigate to http://localhost:8080
Skyvern is a Playwright extension that adds AI-powered browser automation. It gives you the full power of Playwright with additional AI capabilities—use natural language prompts to interact with elements, extract data, and automate complex multi-step workflows.
Installation:
- Python:
pip install skyvernthen runskyvern quickstartfor local setup - TypeScript:
npm install @skyvern/client
Skyvern adds four core AI commands directly on the page object:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
page.act(prompt) |
Perform actions using natural language (e.g., "Click the login button") |
page.extract(prompt, schema) |
Extract structured data from the page with optional JSON schema |
page.validate(prompt) |
Validate page state, returns bool (e.g., "Check if user is logged in") |
page.prompt(prompt, schema) |
Send arbitrary prompts to the LLM with optional response schema |
Additionally, page.agent provides higher-level workflow commands:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
page.agent.run_task(prompt) |
Execute complex multi-step tasks |
page.agent.login(credential_type, credential_id) |
Authenticate with stored credentials (Skyvern, Bitwarden, 1Password) |
page.agent.download_files(prompt) |
Navigate and download files |
page.agent.run_workflow(workflow_id) |
Execute pre-built workflows |
All standard Playwright actions support an optional prompt parameter for AI-powered element location:
| Action | Playwright | AI-Augmented |
|---|---|---|
| Click | page.click("#btn") |
page.click(prompt="Click login button") |
| Fill | page.fill("#email", "[email protected]") |
page.fill(prompt="Email field", value="[email protected]") |
| Select | page.select_option("#country", "US") |
page.select_option(prompt="Country dropdown", value="US") |
| Upload | page.upload_file("#file", "doc.pdf") |
page.upload_file(prompt="Upload area", files="doc.pdf") |
Three interaction modes:
# 1. Traditional Playwright - CSS/XPath selectors
await page.click("#submit-button")
# 2. AI-powered - natural language
await page.click(prompt="Click the green Submit button")
# 3. AI fallback - tries selector first, falls back to AI if it fails
await page.click("#submit-btn", prompt="Click the Submit button")# act - Perform actions using natural language
await page.act("Click the login button and wait for the dashboard to load")
# extract - Extract structured data with optional JSON schema
result = await page.extract("Get the product name and price")
result = await page.extract(
prompt="Extract order details",
schema={"order_id": "string", "total": "number", "items": "array"}
)
# validate - Check page state (returns bool)
is_logged_in = await page.validate("Check if the user is logged in")
# prompt - Send arbitrary prompts to the LLM
summary = await page.prompt("Summarize what's on this page")Run via UI:
skyvern run allNavigate to http://localhost:8080 to run tasks through the web interface.
Python SDK:
from skyvern import Skyvern
# Local mode
skyvern = Skyvern.local()
# Or connect to Skyvern Cloud
skyvern = Skyvern(api_key="your-api-key")
# Launch browser and get page
browser = await skyvern.launch_cloud_browser()
page = await browser.get_working_page()
# Mix Playwright with AI-powered actions
await page.goto("https://example.com")
await page.click("#login-button") # Traditional Playwright
await page.agent.login(credential_type="skyvern", credential_id="cred_123") # AI login
await page.click(prompt="Add first item to cart") # AI-augmented click
await page.agent.run_task("Complete checkout with: John Snow, 12345") # AI taskTypeScript SDK:
import { Skyvern } from "@skyvern/client";
const skyvern = new Skyvern({ apiKey: "your-api-key" });
const browser = await skyvern.launchCloudBrowser();
const page = await browser.getWorkingPage();
// Mix Playwright with AI-powered actions
await page.goto("https://example.com");
await page.click("#login-button"); // Traditional Playwright
await page.agent.login("skyvern", { credentialId: "cred_123" }); // AI login
await page.click({ prompt: "Add first item to cart" }); // AI-augmented click
await page.agent.runTask("Complete checkout with: John Snow, 12345"); // AI task
await browser.close();Simple task execution:
from skyvern import Skyvern
skyvern = Skyvern()
task = await skyvern.run_task(prompt="Find the top post on hackernews today")
print(task)[!WARNING] Since Chrome 136, Chrome refuses any CDP connect to the browser using the default user_data_dir. In order to use your browser data, Skyvern copies your default user_data_dir to
./tmp/user_data_dirthe first time connecting to your local browser.
- Just With Python Code
from skyvern import Skyvern
# The path to your Chrome browser. This example path is for Mac.
browser_path = "/Applications/Google Chrome.app/Contents/MacOS/Google Chrome"
skyvern = Skyvern(
base_url="http://localhost:8000",
api_key="YOUR_API_KEY",
browser_path=browser_path,
)
task = await skyvern.run_task(
prompt="Find the top post on hackernews today",
)- With Skyvern Service
Add two variables to your .env file:
# The path to your Chrome browser. This example path is for Mac.
CHROME_EXECUTABLE_PATH="/Applications/Google Chrome.app/Contents/MacOS/Google Chrome"
BROWSER_TYPE=cdp-connectRestart Skyvern service skyvern run all and run the task through UI or code
Grab the cdp connection url and pass it to Skyvern
from skyvern import Skyvern
skyvern = Skyvern(cdp_url="your cdp connection url")
task = await skyvern.run_task(
prompt="Find the top post on hackernews today",
)You can do this by adding the data_extraction_schema parameter:
from skyvern import Skyvern
skyvern = Skyvern()
task = await skyvern.run_task(
prompt="Find the top post on hackernews today",
data_extraction_schema={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The title of the top post"
},
"url": {
"type": "string",
"description": "The URL of the top post"
},
"points": {
"type": "integer",
"description": "Number of points the post has received"
}
}
}
)# Launch the Skyvern Server Separately*
skyvern run server
# Launch the Skyvern UI
skyvern run ui
# Check status of the Skyvern service
skyvern status
# Stop the Skyvern service
skyvern stop all
# Stop the Skyvern UI
skyvern stop ui
# Stop the Skyvern Server Separately
skyvern stop serverSkyvern has SOTA performance on the WebBench benchmark with a 64.4% accuracy. The technical report + evaluation can be found here
Skyvern is the best performing agent on WRITE tasks (eg filling out forms, logging in, downloading files, etc), which is primarily used for RPA (Robotic Process Automation) adjacent tasks.
Tasks are the fundamental building block inside Skyvern. Each task is a single request to Skyvern, instructing it to navigate through a website and accomplish a specific goal.
Tasks require you to specify a url, prompt, and can optionally include a data schema (if you want the output to conform to a specific schema) and error codes (if you want Skyvern to stop running in specific situations).
Workflows are a way to chain multiple tasks together to form a cohesive unit of work.
For example, if you wanted to download all invoices newer than January 1st, you could create a workflow that first navigated to the invoices page, then filtered down to only show invoices newer than January 1st, extracted a list of all eligible invoices, and iterated through each invoice to download it.
Another example is if you wanted to automate purchasing products from an e-commerce store, you could create a workflow that first navigated to the desired product, then added it to a cart. Second, it would navigate to the cart and validate the cart state. Finally, it would go through the checkout process to purchase the items.
Supported workflow features include:
- Browser Task
- Browser Action
- Data Extraction
- Validation
- For Loops
- File parsing
- Sending emails
- Text Prompts
- HTTP Request Block
- Custom Code Block
- Uploading files to block storage
- (Coming soon) Conditionals
Skyvern allows you to livestream the viewport of the browser to your local machine so that you can see exactly what Skyvern is doing on the web. This is useful for debugging and understanding how Skyvern is interacting with a website, and intervening when necessary
Skyvern is natively capable of filling out form inputs on websites. Passing in information via the navigation_goal will allow Skyvern to comprehend the information and fill out the form accordingly.
Skyvern is also capable of extracting data from a website.
You can also specify a data_extraction_schema directly within the main prompt to tell Skyvern exactly what data you'd like to extract from the website, in jsonc format. Skyvern's output will be structured in accordance to the supplied schema.
Skyvern is also capable of downloading files from a website. All downloaded files are automatically uploaded to block storage (if configured), and you can access them via the UI.
Skyvern supports a number of different authentication methods to make it easier to automate tasks behind a login. If you'd like to try it out, please reach out to us via email or discord.
Skyvern supports a number of different 2FA methods to allow you to automate workflows that require 2FA.
Examples include:
- QR-based 2FA (e.g. Google Authenticator, Authy)
- Email based 2FA
- SMS based 2FA
🔐 Learn more about 2FA support here.
Skyvern currently supports the following password manager integrations:
- [x] Bitwarden
- [x] Custom Credential Service (HTTP API)
- [ ] 1Password
- [ ] LastPass
Skyvern supports the Model Context Protocol (MCP) to allow you to use any LLM that supports MCP.
See the MCP documentation here
Skyvern supports Zapier, Make.com, and N8N to allow you to connect your Skyvern workflows to other apps.
🔐 Learn more about 2FA support here.
We love to see how Skyvern is being used in the wild. Here are some examples of how Skyvern is being used to automate workflows in the real world. Please open PRs to add your own examples!
Make sure to have uv installed.
- Run this to create your virtual environment (
.venv)uv sync --group dev
- Perform initial server configuration
uv run skyvern quickstart
- Navigate to
http://localhost:8080in your browser to start using the UI The Skyvern CLI supports Windows, WSL, macOS, and Linux environments.
More extensive documentation can be found on our 📕 docs page. Please let us know if something is unclear or missing by opening an issue or reaching out to us via email or discord.
| Provider | Supported Models |
|---|---|
| OpenAI | GPT-5, GPT-5.2, GPT-4.1, o3, o4-mini |
| Anthropic | Claude 4 (Sonnet, Opus), Claude 4.5 (Haiku, Sonnet, Opus) |
| Azure OpenAI | Any GPT models. Better performance with a multimodal llm (azure/gpt4-o) |
| AWS Bedrock | Claude 3.5, Claude 3.7, Claude 4 (Sonnet, Opus), Claude 4.5 (Sonnet, Opus) |
| Gemini | Gemini 3 Pro/Flash, Gemini 2.5 Pro/Flash |
| Ollama | Run any locally hosted model via Ollama |
| OpenRouter | Access models through OpenRouter |
| OpenAI-compatible | Any custom API endpoint that follows OpenAI's API format (via liteLLM) |
| Variable | Description | Type | Sample Value |
|---|---|---|---|
ENABLE_OPENAI |
Register OpenAI models | Boolean |
true, false
|
OPENAI_API_KEY |
OpenAI API Key | String | sk-1234567890 |
OPENAI_API_BASE |
OpenAI API Base, optional | String | https://openai.api.base |
OPENAI_ORGANIZATION |
OpenAI Organization ID, optional | String | your-org-id |
Recommended LLM_KEY: OPENAI_GPT5, OPENAI_GPT5_2, OPENAI_GPT4_1, OPENAI_O3, OPENAI_O4_MINI
| Variable | Description | Type | Sample Value |
|---|---|---|---|
ENABLE_ANTHROPIC |
Register Anthropic models | Boolean |
true, false
|
ANTHROPIC_API_KEY |
Anthropic API key | String | sk-1234567890 |
Recommended LLM_KEY: ANTHROPIC_CLAUDE4.5_OPUS, ANTHROPIC_CLAUDE4.5_SONNET, ANTHROPIC_CLAUDE4_OPUS, ANTHROPIC_CLAUDE4_SONNET
| Variable | Description | Type | Sample Value |
|---|---|---|---|
ENABLE_AZURE |
Register Azure OpenAI models | Boolean |
true, false
|
AZURE_API_KEY |
Azure deployment API key | String | sk-1234567890 |
AZURE_DEPLOYMENT |
Azure OpenAI Deployment Name | String | skyvern-deployment |
AZURE_API_BASE |
Azure deployment api base url | String | https://skyvern-deployment.openai.azure.com/ |
AZURE_API_VERSION |
Azure API Version | String | 2024-02-01 |
Recommended LLM_KEY: AZURE_OPENAI
| Variable | Description | Type | Sample Value |
|---|---|---|---|
ENABLE_BEDROCK |
Register AWS Bedrock models. To use AWS Bedrock, you need to make sure your AWS configurations are set up correctly first. | Boolean |
true, false
|
Recommended LLM_KEY: BEDROCK_ANTHROPIC_CLAUDE4.5_OPUS_INFERENCE_PROFILE, BEDROCK_ANTHROPIC_CLAUDE4.5_SONNET_INFERENCE_PROFILE, BEDROCK_ANTHROPIC_CLAUDE4_OPUS_INFERENCE_PROFILE
| Variable | Description | Type | Sample Value |
|---|---|---|---|
ENABLE_GEMINI |
Register Gemini models | Boolean |
true, false
|
GEMINI_API_KEY |
Gemini API Key | String | your_google_gemini_api_key |
Recommended LLM_KEY: GEMINI_3.0_FLASH, GEMINI_2.5_PRO, GEMINI_2.5_FLASH, GEMINI_2.5_PRO_PREVIEW, GEMINI_2.5_FLASH_PREVIEW
| Variable | Description | Type | Sample Value |
|---|---|---|---|
ENABLE_OLLAMA |
Register local models via Ollama | Boolean |
true, false
|
OLLAMA_SERVER_URL |
URL for your Ollama server | String | http://host.docker.internal:11434 |
OLLAMA_MODEL |
Ollama model name to load | String | qwen2.5:7b-instruct |
OLLAMA_SUPPORTS_VISION |
Enable vision support | Boolean |
true, false
|
Recommended LLM_KEY: OLLAMA
Note: Set OLLAMA_SUPPORTS_VISION=true for vision models like qwen3-vl, llava, etc.
| Variable | Description | Type | Sample Value |
|---|---|---|---|
ENABLE_OPENROUTER |
Register OpenRouter models | Boolean |
true, false
|
OPENROUTER_API_KEY |
OpenRouter API key | String | sk-1234567890 |
OPENROUTER_MODEL |
OpenRouter model name | String | mistralai/mistral-small-3.1-24b-instruct |
OPENROUTER_API_BASE |
OpenRouter API base URL | String | https://api.openrouter.ai/v1 |
Recommended LLM_KEY: OPENROUTER
| Variable | Description | Type | Sample Value |
|---|---|---|---|
ENABLE_OPENAI_COMPATIBLE |
Register a custom OpenAI-compatible API endpoint | Boolean |
true, false
|
OPENAI_COMPATIBLE_MODEL_NAME |
Model name for OpenAI-compatible endpoint | String |
yi-34b, gpt-3.5-turbo, mistral-large, etc. |
OPENAI_COMPATIBLE_API_KEY |
API key for OpenAI-compatible endpoint | String | sk-1234567890 |
OPENAI_COMPATIBLE_API_BASE |
Base URL for OpenAI-compatible endpoint | String |
https://api.together.xyz/v1, http://localhost:8000/v1, etc. |
OPENAI_COMPATIBLE_API_VERSION |
API version for OpenAI-compatible endpoint, optional | String | 2023-05-15 |
OPENAI_COMPATIBLE_MAX_TOKENS |
Maximum tokens for completion, optional | Integer |
4096, 8192, etc. |
OPENAI_COMPATIBLE_TEMPERATURE |
Temperature setting, optional | Float |
0.0, 0.5, 0.7, etc. |
OPENAI_COMPATIBLE_SUPPORTS_VISION |
Whether model supports vision, optional | Boolean |
true, false
|
Supported LLM Key: OPENAI_COMPATIBLE
| Variable | Description | Type | Sample Value |
|---|---|---|---|
LLM_KEY |
The name of the model you want to use | String | See supported LLM keys above |
SECONDARY_LLM_KEY |
The name of the model for mini agents skyvern runs with | String | See supported LLM keys above |
LLM_CONFIG_MAX_TOKENS |
Override the max tokens used by the LLM | Integer | 128000 |
This is our planned roadmap for the next few months. If you have any suggestions or would like to see a feature added, please don't hesitate to reach out to us via email or discord.
- [x] Open Source - Open Source Skyvern's core codebase
- [x] Workflow support - Allow support to chain multiple Skyvern calls together
- [x] Improved context - Improve Skyvern's ability to understand content around interactable elements by introducing feeding relevant label context through the text prompt
- [x] Cost Savings - Improve Skyvern's stability and reduce the cost of running Skyvern by optimizing the context tree passed into Skyvern
- [x] Self-serve UI - Deprecate the Streamlit UI in favour of a React-based UI component that allows users to kick off new jobs in Skyvern
- [x] Workflow UI Builder - Introduce a UI to allow users to build and analyze workflows visually
- [x] Chrome Viewport streaming - Introduce a way to live-stream the Chrome viewport to the user's browser (as a part of the self-serve UI)
- [x] Past Runs UI - Deprecate the Streamlit UI in favour of a React-based UI that allows you to visualize past runs and their results
- [X] Auto workflow builder ("Observer") mode - Allow Skyvern to auto-generate workflows as it's navigating the web to make it easier to build new workflows
- [x] Prompt Caching - Introduce a caching layer to the LLM calls to dramatically reduce the cost of running Skyvern (memorize past actions and repeat them!)
- [x] Web Evaluation Dataset - Integrate Skyvern with public benchmark tests to track the quality of our models over time
- [ ] Improved Debug mode - Allow Skyvern to plan its actions and get "approval" before running them, allowing you to debug what it's doing and more easily iterate on the prompt
- [ ] Chrome Extension - Allow users to interact with Skyvern through a Chrome extension (incl voice mode, saving tasks, etc.)
- [ ] Skyvern Action Recorder - Allow Skyvern to watch a user complete a task and then automatically generate a workflow for it
- [ ] Interactable Livestream - Allow users to interact with the livestream in real-time to intervene when necessary (such as manually submitting sensitive forms)
- [ ] Integrate LLM Observability tools - Integrate LLM Observability tools to allow back-testing prompt changes with specific data sets + visualize the performance of Skyvern over time
- [x] Langchain Integration - Create langchain integration in langchain_community to use Skyvern as a "tool".
We welcome PRs and suggestions! Don't hesitate to open a PR/issue or to reach out to us via email or discord. Please have a look at our contribution guide and "Help Wanted" issues to get started!
If you want to chat with the skyvern repository to get a high level overview of how it is structured, how to build off it, and how to resolve usage questions, check out Code Sage.
By Default, Skyvern collects basic usage statistics to help us understand how Skyvern is being used. If you would like to opt-out of telemetry, please set the SKYVERN_TELEMETRY environment variable to false.
Skyvern's open source repository is supported via a managed cloud. All of the core logic powering Skyvern is available in this open source repository licensed under the AGPL-3.0 License, with the exception of anti-bot measures available in our managed cloud offering.
If you have any questions or concerns around licensing, please contact us and we would be happy to help.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for skyvern
Similar Open Source Tools

skyvern
Skyvern automates browser-based workflows using LLMs and computer vision. It provides a simple API endpoint to fully automate manual workflows, replacing brittle or unreliable automation solutions. Traditional approaches to browser automations required writing custom scripts for websites, often relying on DOM parsing and XPath-based interactions which would break whenever the website layouts changed. Instead of only relying on code-defined XPath interactions, Skyvern adds computer vision and LLMs to the mix to parse items in the viewport in real-time, create a plan for interaction and interact with them. This approach gives us a few advantages: 1. Skyvern can operate on websites it’s never seen before, as it’s able to map visual elements to actions necessary to complete a workflow, without any customized code 2. Skyvern is resistant to website layout changes, as there are no pre-determined XPaths or other selectors our system is looking for while trying to navigate 3. Skyvern leverages LLMs to reason through interactions to ensure we can cover complex situations. Examples include: 1. If you wanted to get an auto insurance quote from Geico, the answer to a common question “Were you eligible to drive at 18?” could be inferred from the driver receiving their license at age 16 2. If you were doing competitor analysis, it’s understanding that an Arnold Palmer 22 oz can at 7/11 is almost definitely the same product as a 23 oz can at Gopuff (even though the sizes are slightly different, which could be a rounding error!) Want to see examples of Skyvern in action? Jump to #real-world-examples-of- skyvern
pr-pilot
PR Pilot is an AI-powered tool designed to assist users in their daily workflow by delegating routine work to AI with confidence and predictability. It integrates seamlessly with popular development tools and allows users to interact with it through a Command-Line Interface, Python SDK, REST API, and Smart Workflows. Users can automate tasks such as generating PR titles and descriptions, summarizing and posting issues, and formatting README files. The tool aims to save time and enhance productivity by providing AI-powered solutions for common development tasks.
call-center-ai
Call Center AI is an AI-powered call center solution leveraging Azure and OpenAI GPT. It allows for AI agent-initiated phone calls or direct calls to the bot from a configured phone number. The bot is customizable for various industries like insurance, IT support, and customer service, with features such as accessing claim information, conversation history, language change, SMS sending, and more. The project is a proof of concept showcasing the integration of Azure Communication Services, Azure Cognitive Services, and Azure OpenAI for an automated call center solution.
runpod-worker-comfy
runpod-worker-comfy is a serverless API tool that allows users to run any ComfyUI workflow to generate an image. Users can provide input images as base64-encoded strings, and the generated image can be returned as a base64-encoded string or uploaded to AWS S3. The tool is built on Ubuntu + NVIDIA CUDA and provides features like built-in checkpoints and VAE models. Users can configure environment variables to upload images to AWS S3 and interact with the RunPod API to generate images. The tool also supports local testing and deployment to Docker hub using Github Actions.
agenticSeek
AgenticSeek is a voice-enabled AI assistant powered by DeepSeek R1 agents, offering a fully local alternative to cloud-based AI services. It allows users to interact with their filesystem, code in multiple languages, and perform various tasks autonomously. The tool is equipped with memory to remember user preferences and past conversations, and it can divide tasks among multiple agents for efficient execution. AgenticSeek prioritizes privacy by running entirely on the user's hardware without sending data to the cloud.
llm2sh
llm2sh is a command-line utility that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to translate plain-language requests into shell commands. It provides a convenient way to interact with your system using natural language. The tool supports multiple LLMs for command generation, offers a customizable configuration file, YOLO mode for running commands without confirmation, and is easily extensible with new LLMs and system prompts. Users can set up API keys for OpenAI, Claude, Groq, and Cerebras to use the tool effectively. llm2sh does not store user data or command history, and it does not record or send telemetry by itself, but the LLM APIs may collect and store requests and responses for their purposes.
moatless-tools
Moatless Tools is a hobby project focused on experimenting with using Large Language Models (LLMs) to edit code in large existing codebases. The project aims to build tools that insert the right context into prompts and handle responses effectively. It utilizes an agentic loop functioning as a finite state machine to transition between states like Search, Identify, PlanToCode, ClarifyChange, and EditCode for code editing tasks.
iloom-cli
iloom is a tool designed to streamline AI-assisted development by focusing on maintaining alignment between human developers and AI agents. It treats context as a first-class concern, persisting AI reasoning in issue comments rather than temporary chats. The tool allows users to collaborate with AI agents in an isolated environment, switch between complex features without losing context, document AI decisions publicly, and capture key insights and lessons learned from AI sessions. iloom is not just a tool for managing git worktrees, but a control plane for maintaining alignment between users and their AI assistants.
nano-graphrag
nano-GraphRAG is a simple, easy-to-hack implementation of GraphRAG that provides a smaller, faster, and cleaner version of the official implementation. It is about 800 lines of code, small yet scalable, asynchronous, and fully typed. The tool supports incremental insert, async methods, and various parameters for customization. Users can replace storage components and LLM functions as needed. It also allows for embedding function replacement and comes with pre-defined prompts for entity extraction and community reports. However, some features like covariates and global search implementation differ from the original GraphRAG. Future versions aim to address issues related to data source ID, community description truncation, and add new components.
thepipe
The Pipe is a multimodal-first tool for feeding files and web pages into vision-language models such as GPT-4V. It is best for LLM and RAG applications that require a deep understanding of tricky data sources. The Pipe is available as a hosted API at thepi.pe, or it can be set up locally.
AgentPoison
AgentPoison is a repository that provides the official PyTorch implementation of the paper 'AgentPoison: Red-teaming LLM Agents via Memory or Knowledge Base Backdoor Poisoning'. It offers tools for red-teaming LLM agents by poisoning memory or knowledge bases. The repository includes trigger optimization algorithms, agent experiments, and evaluation scripts for Agent-Driver, ReAct-StrategyQA, and EHRAgent. Users can fine-tune motion planners, inject queries with triggers, and evaluate red-teaming performance. The codebase supports multiple RAG embedders and provides a unified dataset access for all three agents.
chatgpt-cli
ChatGPT CLI provides a powerful command-line interface for seamless interaction with ChatGPT models via OpenAI and Azure. It features streaming capabilities, extensive configuration options, and supports various modes like streaming, query, and interactive mode. Users can manage thread-based context, sliding window history, and provide custom context from any source. The CLI also offers model and thread listing, advanced configuration options, and supports GPT-4, GPT-3.5-turbo, and Perplexity's models. Installation is available via Homebrew or direct download, and users can configure settings through default values, a config.yaml file, or environment variables.
playword
PlayWord is a tool designed to supercharge web test automation experience with AI. It provides core features such as enabling browser operations and validations using natural language inputs, as well as monitoring interface to record and dry-run test steps. PlayWord supports multiple AI services including Anthropic, Google, and OpenAI, allowing users to select the appropriate provider based on their requirements. The tool also offers features like assertion handling, frame handling, custom variables, test recordings, and an Observer module to track user interactions on web pages. With PlayWord, users can interact with web pages using natural language commands, reducing the need to worry about element locators and providing AI-powered adaptation to UI changes.
ChatGPT-Telegram-Bot
ChatGPT Telegram Bot is a Telegram bot that provides a smooth AI experience. It supports both Azure OpenAI and native OpenAI, and offers real-time (streaming) response to AI, with a faster and smoother experience. The bot also has 15 preset bot identities that can be quickly switched, and supports custom bot identities to meet personalized needs. Additionally, it supports clearing the contents of the chat with a single click, and restarting the conversation at any time. The bot also supports native Telegram bot button support, making it easy and intuitive to implement required functions. User level division is also supported, with different levels enjoying different single session token numbers, context numbers, and session frequencies. The bot supports English and Chinese on UI, and is containerized for easy deployment.
google-cloud-gcp-openai-api
This project provides a drop-in replacement REST API for Google Cloud Vertex AI (PaLM 2, Codey, Gemini) that is compatible with the OpenAI API specifications. It aims to make Google Cloud Platform Vertex AI more accessible by translating OpenAI API calls to Vertex AI. The software is developed in Python and based on FastAPI and LangChain, designed to be simple and customizable for individual needs. It includes step-by-step guides for deployment, supports various OpenAI API services, and offers configuration through environment variables. Additionally, it provides examples for running locally and usage instructions consistent with the OpenAI API format.
binary_ninja_mcp
This repository contains a Binary Ninja plugin, MCP server, and bridge that enables seamless integration of Binary Ninja's capabilities with your favorite LLM client. It provides real-time integration, AI assistance for reverse engineering, multi-binary support, and various MCP tools for tasks like decompiling functions, getting IL code, managing comments, renaming variables, and more.
For similar tasks

skyvern
Skyvern automates browser-based workflows using LLMs and computer vision. It provides a simple API endpoint to fully automate manual workflows, replacing brittle or unreliable automation solutions. Traditional approaches to browser automations required writing custom scripts for websites, often relying on DOM parsing and XPath-based interactions which would break whenever the website layouts changed. Instead of only relying on code-defined XPath interactions, Skyvern adds computer vision and LLMs to the mix to parse items in the viewport in real-time, create a plan for interaction and interact with them. This approach gives us a few advantages: 1. Skyvern can operate on websites it’s never seen before, as it’s able to map visual elements to actions necessary to complete a workflow, without any customized code 2. Skyvern is resistant to website layout changes, as there are no pre-determined XPaths or other selectors our system is looking for while trying to navigate 3. Skyvern leverages LLMs to reason through interactions to ensure we can cover complex situations. Examples include: 1. If you wanted to get an auto insurance quote from Geico, the answer to a common question “Were you eligible to drive at 18?” could be inferred from the driver receiving their license at age 16 2. If you were doing competitor analysis, it’s understanding that an Arnold Palmer 22 oz can at 7/11 is almost definitely the same product as a 23 oz can at Gopuff (even though the sizes are slightly different, which could be a rounding error!) Want to see examples of Skyvern in action? Jump to #real-world-examples-of- skyvern

airbyte-connectors
This repository contains Airbyte connectors used in Faros and Faros Community Edition platforms as well as Airbyte Connector Development Kit (CDK) for JavaScript/TypeScript.
open-parse
Open Parse is a Python library for visually discerning document layouts and chunking them effectively. It is designed to fill the gap in open-source libraries for handling complex documents. Unlike text splitting, which converts a file to raw text and slices it up, Open Parse visually analyzes documents for superior LLM input. It also supports basic markdown for parsing headings, bold, and italics, and has high-precision table support, extracting tables into clean Markdown formats with accuracy that surpasses traditional tools. Open Parse is extensible, allowing users to easily implement their own post-processing steps. It is also intuitive, with great editor support and completion everywhere, making it easy to use and learn.
unstract
Unstract is a no-code platform that enables users to launch APIs and ETL pipelines to structure unstructured documents. With Unstract, users can go beyond co-pilots by enabling machine-to-machine automation. Unstract's Prompt Studio provides a simple, no-code approach to creating prompts for LLMs, vector databases, embedding models, and text extractors. Users can then configure Prompt Studio projects as API deployments or ETL pipelines to automate critical business processes that involve complex documents. Unstract supports a wide range of LLM providers, vector databases, embeddings, text extractors, ETL sources, and ETL destinations, providing users with the flexibility to choose the best tools for their needs.
Dot
Dot is a standalone, open-source application designed for seamless interaction with documents and files using local LLMs and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG). It is inspired by solutions like Nvidia's Chat with RTX, providing a user-friendly interface for those without a programming background. Pre-packaged with Mistral 7B, Dot ensures accessibility and simplicity right out of the box. Dot allows you to load multiple documents into an LLM and interact with them in a fully local environment. Supported document types include PDF, DOCX, PPTX, XLSX, and Markdown. Users can also engage with Big Dot for inquiries not directly related to their documents, similar to interacting with ChatGPT. Built with Electron JS, Dot encapsulates a comprehensive Python environment that includes all necessary libraries. The application leverages libraries such as FAISS for creating local vector stores, Langchain, llama.cpp & Huggingface for setting up conversation chains, and additional tools for document management and interaction.
instructor
Instructor is a Python library that makes it a breeze to work with structured outputs from large language models (LLMs). Built on top of Pydantic, it provides a simple, transparent, and user-friendly API to manage validation, retries, and streaming responses. Get ready to supercharge your LLM workflows!
sparrow
Sparrow is an innovative open-source solution for efficient data extraction and processing from various documents and images. It seamlessly handles forms, invoices, receipts, and other unstructured data sources. Sparrow stands out with its modular architecture, offering independent services and pipelines all optimized for robust performance. One of the critical functionalities of Sparrow - pluggable architecture. You can easily integrate and run data extraction pipelines using tools and frameworks like LlamaIndex, Haystack, or Unstructured. Sparrow enables local LLM data extraction pipelines through Ollama or Apple MLX. With Sparrow solution you get API, which helps to process and transform your data into structured output, ready to be integrated with custom workflows. Sparrow Agents - with Sparrow you can build independent LLM agents, and use API to invoke them from your system. **List of available agents:** * **llamaindex** - RAG pipeline with LlamaIndex for PDF processing * **vllamaindex** - RAG pipeline with LLamaIndex multimodal for image processing * **vprocessor** - RAG pipeline with OCR and LlamaIndex for image processing * **haystack** - RAG pipeline with Haystack for PDF processing * **fcall** - Function call pipeline * **unstructured-light** - RAG pipeline with Unstructured and LangChain, supports PDF and image processing * **unstructured** - RAG pipeline with Weaviate vector DB query, Unstructured and LangChain, supports PDF and image processing * **instructor** - RAG pipeline with Unstructured and Instructor libraries, supports PDF and image processing. Works great for JSON response generation
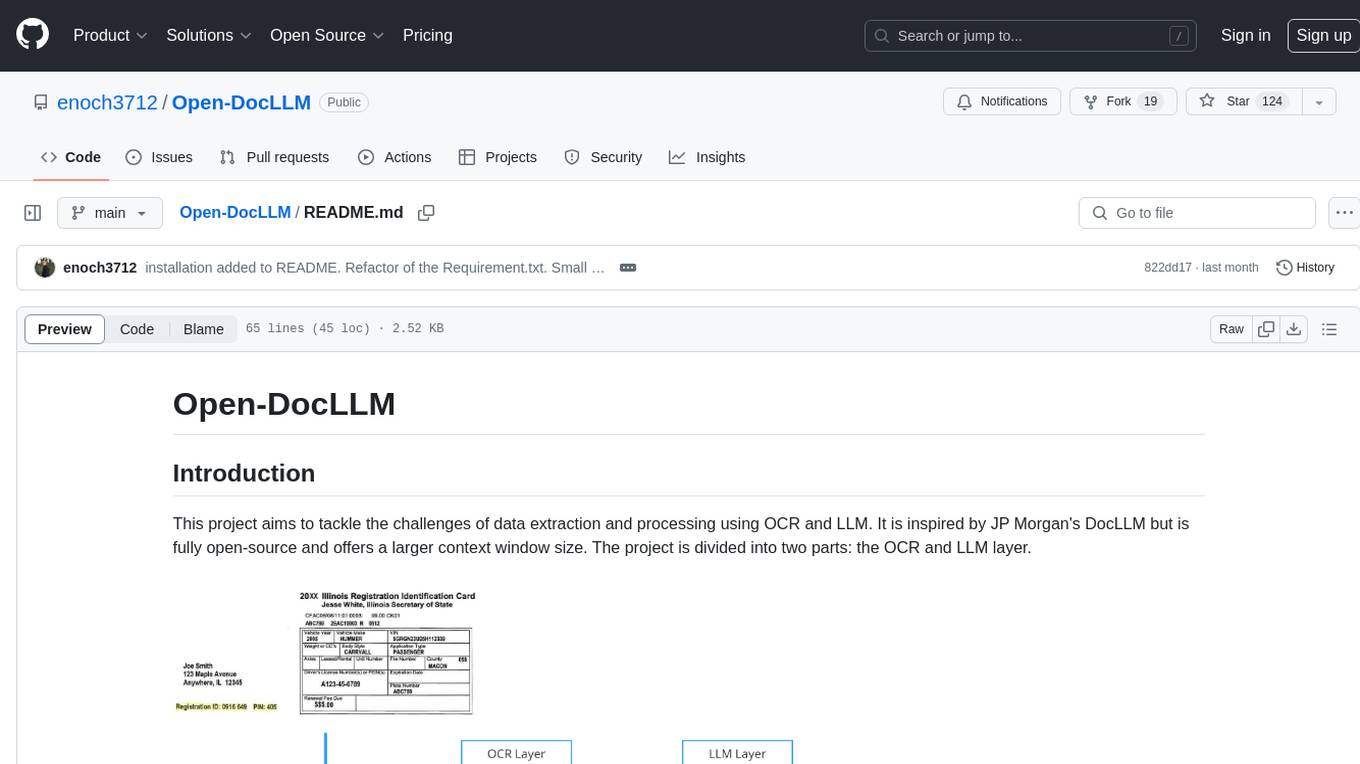
Open-DocLLM
Open-DocLLM is an open-source project that addresses data extraction and processing challenges using OCR and LLM technologies. It consists of two main layers: OCR for reading document content and LLM for extracting specific content in a structured manner. The project offers a larger context window size compared to JP Morgan's DocLLM and integrates tools like Tesseract OCR and Mistral for efficient data analysis. Users can run the models on-premises using LLM studio or Ollama, and the project includes a FastAPI app for testing purposes.
For similar jobs

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.

skyvern
Skyvern automates browser-based workflows using LLMs and computer vision. It provides a simple API endpoint to fully automate manual workflows, replacing brittle or unreliable automation solutions. Traditional approaches to browser automations required writing custom scripts for websites, often relying on DOM parsing and XPath-based interactions which would break whenever the website layouts changed. Instead of only relying on code-defined XPath interactions, Skyvern adds computer vision and LLMs to the mix to parse items in the viewport in real-time, create a plan for interaction and interact with them. This approach gives us a few advantages: 1. Skyvern can operate on websites it’s never seen before, as it’s able to map visual elements to actions necessary to complete a workflow, without any customized code 2. Skyvern is resistant to website layout changes, as there are no pre-determined XPaths or other selectors our system is looking for while trying to navigate 3. Skyvern leverages LLMs to reason through interactions to ensure we can cover complex situations. Examples include: 1. If you wanted to get an auto insurance quote from Geico, the answer to a common question “Were you eligible to drive at 18?” could be inferred from the driver receiving their license at age 16 2. If you were doing competitor analysis, it’s understanding that an Arnold Palmer 22 oz can at 7/11 is almost definitely the same product as a 23 oz can at Gopuff (even though the sizes are slightly different, which could be a rounding error!) Want to see examples of Skyvern in action? Jump to #real-world-examples-of- skyvern

pandas-ai
PandasAI is a Python library that makes it easy to ask questions to your data in natural language. It helps you to explore, clean, and analyze your data using generative AI.
vanna
Vanna is an open-source Python framework for SQL generation and related functionality. It uses Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to train a model on your data, which can then be used to ask questions and get back SQL queries. Vanna is designed to be portable across different LLMs and vector databases, and it supports any SQL database. It is also secure and private, as your database contents are never sent to the LLM or the vector database.

databend
Databend is an open-source cloud data warehouse that serves as a cost-effective alternative to Snowflake. With its focus on fast query execution and data ingestion, it's designed for complex analysis of the world's largest datasets.
Avalonia-Assistant
Avalonia-Assistant is an open-source desktop intelligent assistant that aims to provide a user-friendly interactive experience based on the Avalonia UI framework and the integration of Semantic Kernel with OpenAI or other large LLM models. By utilizing Avalonia-Assistant, you can perform various desktop operations through text or voice commands, enhancing your productivity and daily office experience.
marvin
Marvin is a lightweight AI toolkit for building natural language interfaces that are reliable, scalable, and easy to trust. Each of Marvin's tools is simple and self-documenting, using AI to solve common but complex challenges like entity extraction, classification, and generating synthetic data. Each tool is independent and incrementally adoptable, so you can use them on their own or in combination with any other library. Marvin is also multi-modal, supporting both image and audio generation as well using images as inputs for extraction and classification. Marvin is for developers who care more about _using_ AI than _building_ AI, and we are focused on creating an exceptional developer experience. Marvin users should feel empowered to bring tightly-scoped "AI magic" into any traditional software project with just a few extra lines of code. Marvin aims to merge the best practices for building dependable, observable software with the best practices for building with generative AI into a single, easy-to-use library. It's a serious tool, but we hope you have fun with it. Marvin is open-source, free to use, and made with 💙 by the team at Prefect.
activepieces
Activepieces is an open source replacement for Zapier, designed to be extensible through a type-safe pieces framework written in Typescript. It features a user-friendly Workflow Builder with support for Branches, Loops, and Drag and Drop. Activepieces integrates with Google Sheets, OpenAI, Discord, and RSS, along with 80+ other integrations. The list of supported integrations continues to grow rapidly, thanks to valuable contributions from the community. Activepieces is an open ecosystem; all piece source code is available in the repository, and they are versioned and published directly to npmjs.com upon contributions. If you cannot find a specific piece on the pieces roadmap, please submit a request by visiting the following link: Request Piece Alternatively, if you are a developer, you can quickly build your own piece using our TypeScript framework. For guidance, please refer to the following guide: Contributor's Guide



















