
TapeAgents
TapeAgents is a framework that facilitates all stages of the LLM Agent development lifecycle
Stars: 248
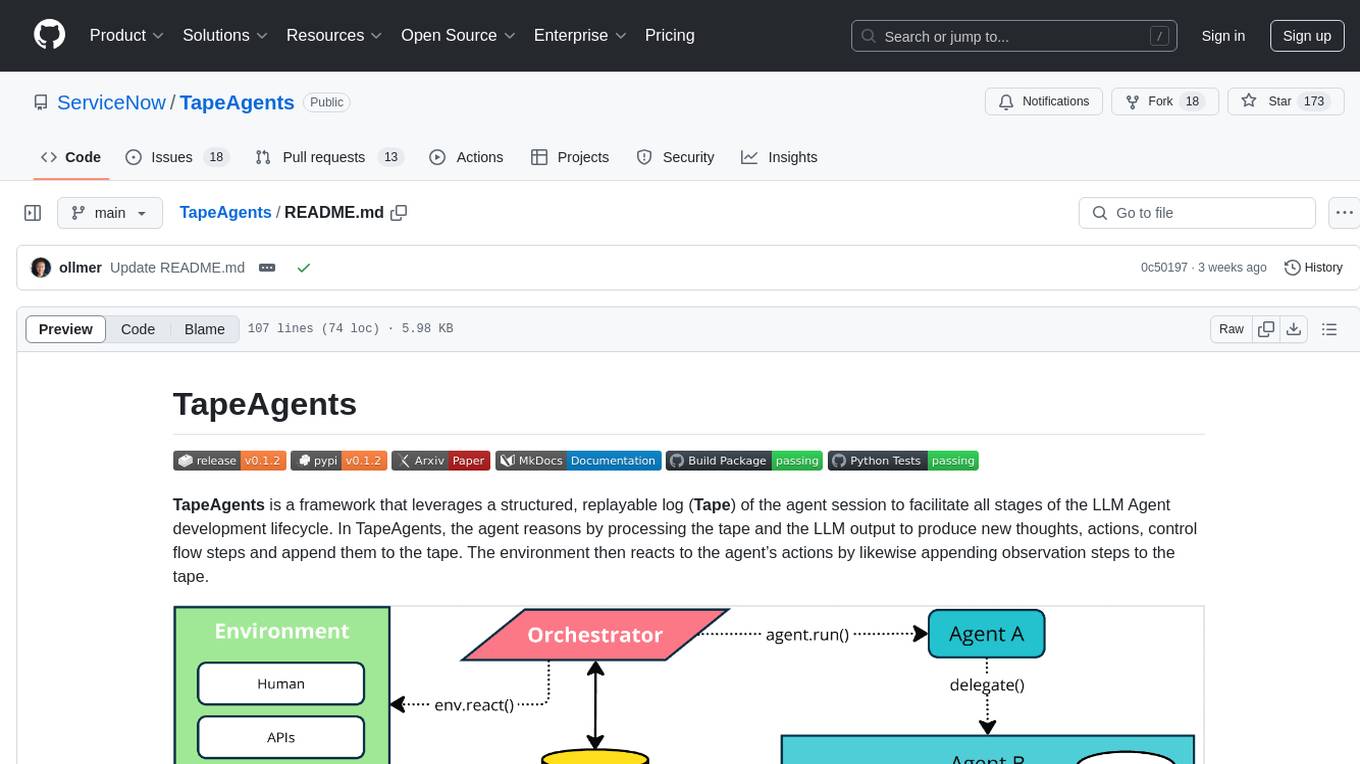
TapeAgents is a framework that leverages a structured, replayable log of the agent session to facilitate all stages of the LLM Agent development lifecycle. The agent reasons by processing the tape and the LLM output to produce new thoughts, actions, control flow steps, and append them to the tape. Key features include building agents as low-level state machines or high-level multi-agent team configurations, debugging agents with TapeAgent studio or TapeBrowser apps, serving agents with response streaming, and optimizing agent configurations using successful tapes. The Tape-centric design of TapeAgents provides ultimate flexibility in project development, allowing access to tapes for making prompts, generating next steps, and controlling agent behavior.
README:
TapeAgents is a framework that leverages a structured, replayable log (Tape) of the agent session to facilitate all stages of the LLM Agent development lifecycle. In TapeAgents, the agent reasons by processing the tape and the LLM output to produce new thoughts, actions, control flow steps and append them to the tape. The environment then reacts to the agent’s actions by likewise appending observation steps to the tape.
Key features:
- Build your agent as a low-level state machine, as a high-level multi-agent team configuration, or as a mono-agent guided by multiple prompts
- Debug your agent with TapeAgent studio or TapeBrowser apps
- Serve your agent with response streaming
- Optimize your agent's configuration using successful tapes; finetune the LLM using revised tapes.
The Tape-centric design of TapeAgents will help you at all stages of your project:
- Build with ultimate flexibility of having access to tape for making prompts and generating next steps
- Change your prompts or team structure and resume the debug session as long as the new agent can continue from the older tape
- Fully control the Agent's tape and the Agent's acting when you use a TapeAgent in an app
- Optimize tapes and agents using the carefully crafted metadata structure that links together tapes, steps, llm calls and agent configurations
Start with the introductory Jupyter notebook to quickly learn the core concepts of the framework.
The simplest agent just to show the basic structure of the agent:
from tapeagents.agent import Agent, Node
from tapeagents.core import Prompt
from tapeagents.dialog_tape import AssistantStep, UserStep, DialogTape
from tapeagents.llms import LLMStream, LiteLLM
from tapeagents.prompting import tape_to_messages
llm = LiteLLM(model_name="gpt-4o-mini")
class MainNode(Node):
def make_prompt(self, agent: Agent, tape: DialogTape) -> Prompt:
# Render the whole tape into the prompt, each step is converted to message
return Prompt(messages=tape_to_messages(tape))
def generate_steps(self, agent: Agent, tape: DialogTape, llm_stream: LLMStream):
# Generate single tape step from the LLM output messages stream.
yield AssistantStep(content=llm_stream.get_text())
agent = Agent[DialogTape].create(llm, nodes=[MainNode()])
start_tape = DialogTape(steps=[UserStep(content="Tell me about Montreal in 3 sentences")])
final_tape = agent.run(start_tape).get_final_tape() # agent will start executing the first node
print(f"Final tape: {final_tape.model_dump_json(indent=2)}")The examples/ directory contains examples of how to use the TapeAgents framework for building, debugging, serving and improving agents. Each example is a self-contained Python script (or module) that demonstrates how to use the framework to build an agent for a specific task:
- How to build a single agent that does planning, searches the web and uses code interpreter to answer knowledge-grounded questions, solving the tasks from the GAIA benchmark.
- How to build a team of TapeAgents with AutoGen-style low-code programming paradigm
- How to finetune a TapeAgent with a small LLM to be better at math problem solving on GSM-8k dataset.
Other notable examples that demonstrate the main aspects of the framework:
- workarena - custom agent that solves WorkArena benchmark using BrowserGym environment.
- tape_improver.py - the agent that revisit and improves the tapes produced by another agent.
To run these examples, simply use:
uv run -m examples.<MODULE> <ARGS>Install the latest release with its minimal dependencies:
pip install tapeagentsYou can also install converters and finetune optional dependencies
pip install 'tapeagents[converters,finetune]'- Install uv to manage package:
Official documentation here
- Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/ServiceNow/TapeAgents.git
cd TapeAgents- Create
venvenvironment and install dependencies:
make setup
# equivalent to `uv sync --all-extras`See our full TapeAgents documentation.
For an in-depth understanding of the design principles, architecture, and research behind TapeAgents, see our technical report.
Feel free to reach out to the team:
- Dzmitry Bahdanau, [email protected]
- Oleh Shliazhko, [email protected]
- Jordan Prince Tremblay, [email protected]
- Alexandre Piché, [email protected]
We acknowledge the inspiration we took from prior frameworks, in particular LangGraph, AutoGen, AIWaves Agents and DSPy.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for TapeAgents
Similar Open Source Tools

TapeAgents
TapeAgents is a framework that leverages a structured, replayable log of the agent session to facilitate all stages of the LLM Agent development lifecycle. The agent reasons by processing the tape and the LLM output to produce new thoughts, actions, control flow steps, and append them to the tape. Key features include building agents as low-level state machines or high-level multi-agent team configurations, debugging agents with TapeAgent studio or TapeBrowser apps, serving agents with response streaming, and optimizing agent configurations using successful tapes. The Tape-centric design of TapeAgents provides ultimate flexibility in project development, allowing access to tapes for making prompts, generating next steps, and controlling agent behavior.
crewAI
crewAI is a cutting-edge framework for orchestrating role-playing, autonomous AI agents. By fostering collaborative intelligence, CrewAI empowers agents to work together seamlessly, tackling complex tasks. It provides a flexible and structured approach to AI collaboration, enabling users to define agents with specific roles, goals, and tools, and assign them tasks within a customizable process. crewAI supports integration with various LLMs, including OpenAI, and offers features such as autonomous task delegation, flexible task management, and output parsing. It is open-source and welcomes contributions, with a focus on improving the library based on usage data collected through anonymous telemetry.
GhostOS
GhostOS is an AI Agent framework designed to replace JSON Schema with a Turing-complete code interaction interface (Moss Protocol). It aims to create intelligent entities capable of continuous learning and growth through code generation and project management. The framework supports various capabilities such as turning Python files into web agents, real-time voice conversation, body movements control, and emotion expression. GhostOS is still in early experimental development and focuses on out-of-the-box capabilities for AI agents.
SwiftSage
SwiftSage is a tool designed for conducting experiments in the field of machine learning and artificial intelligence. It provides a platform for researchers and developers to implement and test various algorithms and models. The tool is particularly useful for exploring new ideas and conducting experiments in a controlled environment. SwiftSage aims to streamline the process of developing and testing machine learning models, making it easier for users to iterate on their ideas and achieve better results. With its user-friendly interface and powerful features, SwiftSage is a valuable tool for anyone working in the field of AI and ML.

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.
ai2apps
AI2Apps is a visual IDE for building LLM-based AI agent applications, enabling developers to efficiently create AI agents through drag-and-drop, with features like design-to-development for rapid prototyping, direct packaging of agents into apps, powerful debugging capabilities, enhanced user interaction, efficient team collaboration, flexible deployment, multilingual support, simplified product maintenance, and extensibility through plugins.
council
Council is an open-source platform designed for the rapid development and deployment of customized generative AI applications using teams of agents. It extends the LLM tool ecosystem by providing advanced control flow and scalable oversight for AI agents. Users can create sophisticated agents with predictable behavior by leveraging Council's powerful approach to control flow using Controllers, Filters, Evaluators, and Budgets. The framework allows for automated routing between agents, comparing, evaluating, and selecting the best results for a task. Council aims to facilitate packaging and deploying agents at scale on multiple platforms while enabling enterprise-grade monitoring and quality control.
sirji
Sirji is an agentic AI framework for software development where various AI agents collaborate via a messaging protocol to solve software problems. It uses standard or user-generated recipes to list tasks and tips for problem-solving. Agents in Sirji are modular AI components that perform specific tasks based on custom pseudo code. The framework is currently implemented as a Visual Studio Code extension, providing an interactive chat interface for problem submission and feedback. Sirji sets up local or remote development environments by installing dependencies and executing generated code.

project_alice
Alice is an agentic workflow framework that integrates task execution and intelligent chat capabilities. It provides a flexible environment for creating, managing, and deploying AI agents for various purposes, leveraging a microservices architecture with MongoDB for data persistence. The framework consists of components like APIs, agents, tasks, and chats that interact to produce outputs through files, messages, task results, and URL references. Users can create, test, and deploy agentic solutions in a human-language framework, making it easy to engage with by both users and agents. The tool offers an open-source option, user management, flexible model deployment, and programmatic access to tasks and chats.
mahilo
Mahilo is a flexible framework for creating multi-agent systems that can interact with humans while sharing context internally. It allows developers to set up complex agent networks for various applications, from customer service to emergency response simulations. Agents can communicate with each other and with humans, making the system efficient by handling context from multiple agents and helping humans stay focused on specific problems. The system supports Realtime API for voice interactions, WebSocket-based communication, flexible communication patterns, session management, and easy agent definition.
AgentUp
AgentUp is an active development tool that provides a developer-first agent framework for creating AI agents with enterprise-grade infrastructure. It allows developers to define agents with configuration, ensuring consistent behavior across environments. The tool offers secure design, configuration-driven architecture, extensible ecosystem for customizations, agent-to-agent discovery, asynchronous task architecture, deterministic routing, and MCP support. It supports multiple agent types like reactive agents and iterative agents, making it suitable for chatbots, interactive applications, research tasks, and more. AgentUp is built by experienced engineers from top tech companies and is designed to make AI agents production-ready, secure, and reliable.
OpenDAN-Personal-AI-OS
OpenDAN is an open source Personal AI OS that consolidates various AI modules for personal use. It empowers users to create powerful AI agents like assistants, tutors, and companions. The OS allows agents to collaborate, integrate with services, and control smart devices. OpenDAN offers features like rapid installation, AI agent customization, connectivity via Telegram/Email, building a local knowledge base, distributed AI computing, and more. It aims to simplify life by putting AI in users' hands. The project is in early stages with ongoing development and future plans for user and kernel mode separation, home IoT device control, and an official OpenDAN SDK release.
AutoGPT
AutoGPT is a revolutionary tool that empowers everyone to harness the power of AI. With AutoGPT, you can effortlessly build, test, and delegate tasks to AI agents, unlocking a world of possibilities. Our mission is to provide the tools you need to focus on what truly matters: innovation and creativity.

promptflow
**Prompt flow** is a suite of development tools designed to streamline the end-to-end development cycle of LLM-based AI applications, from ideation, prototyping, testing, evaluation to production deployment and monitoring. It makes prompt engineering much easier and enables you to build LLM apps with production quality.

agent-lightning
Agent Lightning is a lightweight and efficient tool for automating repetitive tasks in the field of data analysis and machine learning. It provides a user-friendly interface to create and manage automated workflows, allowing users to easily schedule and execute data processing, model training, and evaluation tasks. With its intuitive design and powerful features, Agent Lightning streamlines the process of building and deploying machine learning models, making it ideal for data scientists, machine learning engineers, and AI enthusiasts looking to boost their productivity and efficiency in their projects.
llama_deploy
llama_deploy is an async-first framework for deploying, scaling, and productionizing agentic multi-service systems based on workflows from llama_index. It allows building workflows in llama_index and deploying them seamlessly with minimal changes to code. The system includes services endlessly processing tasks, a control plane managing state and services, an orchestrator deciding task handling, and fault tolerance mechanisms. It is designed for high-concurrency scenarios, enabling real-time and high-throughput applications.
For similar tasks
OpenAGI
OpenAGI is an AI agent creation package designed for researchers and developers to create intelligent agents using advanced machine learning techniques. The package provides tools and resources for building and training AI models, enabling users to develop sophisticated AI applications. With a focus on collaboration and community engagement, OpenAGI aims to facilitate the integration of AI technologies into various domains, fostering innovation and knowledge sharing among experts and enthusiasts.
GPTSwarm
GPTSwarm is a graph-based framework for LLM-based agents that enables the creation of LLM-based agents from graphs and facilitates the customized and automatic self-organization of agent swarms with self-improvement capabilities. The library includes components for domain-specific operations, graph-related functions, LLM backend selection, memory management, and optimization algorithms to enhance agent performance and swarm efficiency. Users can quickly run predefined swarms or utilize tools like the file analyzer. GPTSwarm supports local LM inference via LM Studio, allowing users to run with a local LLM model. The framework has been accepted by ICML2024 and offers advanced features for experimentation and customization.
AgentForge
AgentForge is a low-code framework tailored for the rapid development, testing, and iteration of AI-powered autonomous agents and Cognitive Architectures. It is compatible with a range of LLM models and offers flexibility to run different models for different agents based on specific needs. The framework is designed for seamless extensibility and database-flexibility, making it an ideal playground for various AI projects. AgentForge is a beta-testing ground and future-proof hub for crafting intelligent, model-agnostic autonomous agents.
atomic_agents
Atomic Agents is a modular and extensible framework designed for creating powerful applications. It follows the principles of Atomic Design, emphasizing small and single-purpose components. Leveraging Pydantic for data validation and serialization, the framework offers a set of tools and agents that can be combined to build AI applications. It depends on the Instructor package and supports various APIs like OpenAI, Cohere, Anthropic, and Gemini. Atomic Agents is suitable for developers looking to create AI agents with a focus on modularity and flexibility.
LongRoPE
LongRoPE is a method to extend the context window of large language models (LLMs) beyond 2 million tokens. It identifies and exploits non-uniformities in positional embeddings to enable 8x context extension without fine-tuning. The method utilizes a progressive extension strategy with 256k fine-tuning to reach a 2048k context. It adjusts embeddings for shorter contexts to maintain performance within the original window size. LongRoPE has been shown to be effective in maintaining performance across various tasks from 4k to 2048k context lengths.
ax
Ax is a Typescript library that allows users to build intelligent agents inspired by agentic workflows and the Stanford DSP paper. It seamlessly integrates with multiple Large Language Models (LLMs) and VectorDBs to create RAG pipelines or collaborative agents capable of solving complex problems. The library offers advanced features such as streaming validation, multi-modal DSP, and automatic prompt tuning using optimizers. Users can easily convert documents of any format to text, perform smart chunking, embedding, and querying, and ensure output validation while streaming. Ax is production-ready, written in Typescript, and has zero dependencies.
Awesome-AI-Agents
Awesome-AI-Agents is a curated list of projects, frameworks, benchmarks, platforms, and related resources focused on autonomous AI agents powered by Large Language Models (LLMs). The repository showcases a wide range of applications, multi-agent task solver projects, agent society simulations, and advanced components for building and customizing AI agents. It also includes frameworks for orchestrating role-playing, evaluating LLM-as-Agent performance, and connecting LLMs with real-world applications through platforms and APIs. Additionally, the repository features surveys, paper lists, and blogs related to LLM-based autonomous agents, making it a valuable resource for researchers, developers, and enthusiasts in the field of AI.
CodeFuse-muAgent
CodeFuse-muAgent is a Multi-Agent framework designed to streamline Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) orchestration for agents. It integrates toolkits, code libraries, knowledge bases, and sandbox environments for rapid construction of complex Multi-Agent interactive applications. The framework enables efficient execution and handling of multi-layered and multi-dimensional tasks.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.





