Data-and-AI-Concepts
This repository contains Data Science interview questions covered on my Threads page.
Stars: 152
This repository is a curated collection of data science and AI concepts and IQs, covering topics from foundational mathematics to cutting-edge generative AI concepts. It aims to support learners and professionals preparing for various data science roles by providing detailed explanations and notebooks for each concept.
README:
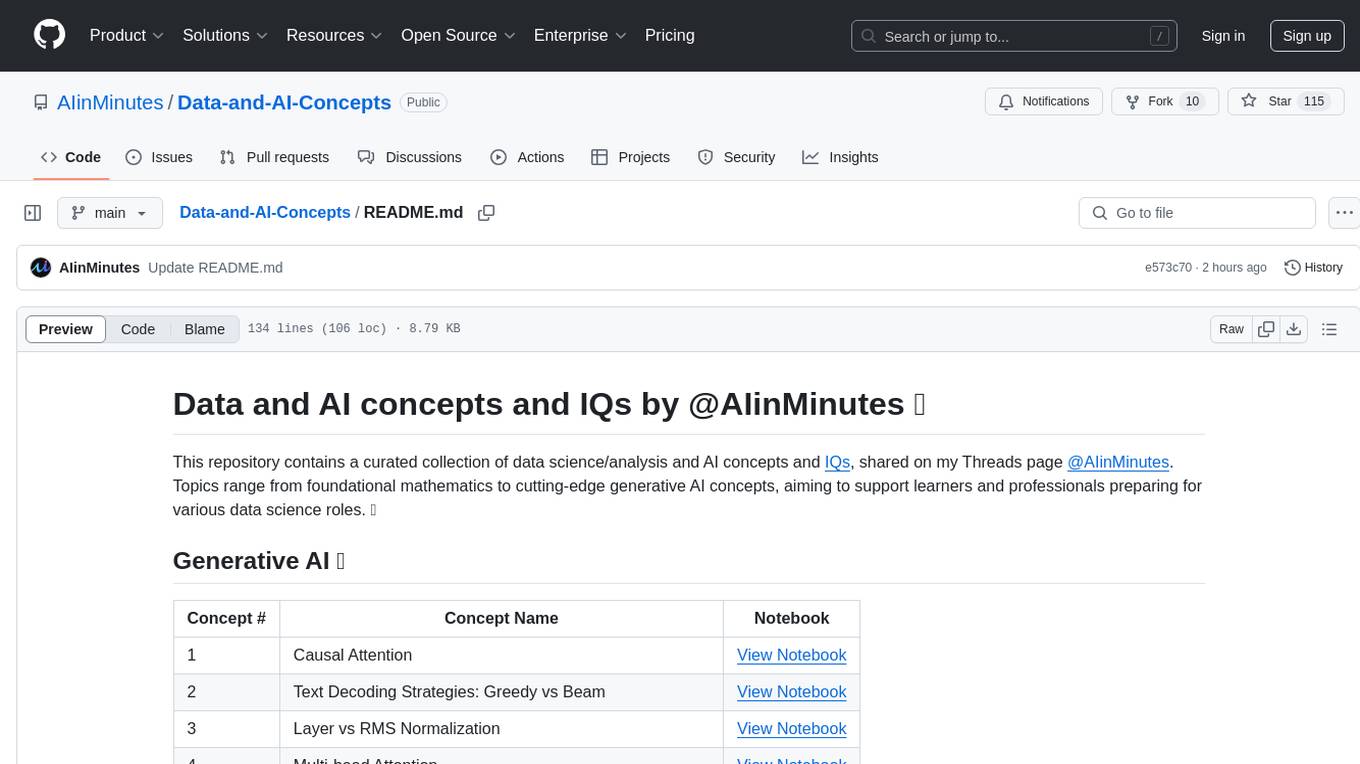
This repository contains a curated collection of data science/analysis and AI concepts and IQs, shared on my Threads page @AIinMinutes. Topics range from foundational mathematics to cutting-edge generative AI concepts, aiming to support learners and professionals preparing for various data science roles. 📚
The book based on this repo is currently under development. Check it out here: AI in Minutes.
| Concept # | Concept Name | Notebook |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Causal Attention | View Notebook |
| 2 | Text Decoding Strategies: Greedy vs Beam | View Notebook |
| 3 | Layer vs RMS Normalization | View Notebook |
| 4 | Multi-head Attention | View Notebook |
| 5 | Energy | View Notebook |
| 6 | Gaussian Mixture Models | View Notebook |
| 7 | Hyperplanes | View Notebook |
| 8 | Inner Product | View Notebook |
| 9 | Moore Penrose Inverse | View Notebook |
| 10 | Jacobians and Gradients behind Multi-class Classification | View Notebook |
| 11 | Norm and Metric | View Notebook |
| 12 | Rank One Matrices | View Notebook |
| 13 | Auto-encoder Latent Space | View Notebook |
| 14 | PCA for Anomaly Detection | View Notebook |
| 15 | Variational AutoEncoder for Anomaly Detection | View Notebook |
| 16 | Variational AutoEncoder Loss Function | View Notebook |
| 17 | Attention Mechanism | View Notebook |
| 18 | GELU | View Notebook |
| 19 | Orthogonality | View Notebook |
| 20 | Perplexity | View Notebook |
| Concept # | Concept Name | Notebook |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Gini Impurity vs Entropy | View Notebook |
| 2 | Agglomerative Clustering | View Notebook |
| 3 | Elastic Net | View Notebook |
| 4 | Huber Loss | View Notebook |
| 5 | Mahalanobis Distance | View Notebook |
| 6 | Natural Breaks | View Notebook |
| 7 | Oversampling | View Notebook |
| 8 | PCA vs Feature Agglomeration | View Notebook |
| 9 | Permutation Importance | View Notebook |
| 10 | Pseudo R^2 | View Notebook |
| Concept # | Concept Name | Notebook |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Balanced Focal Loss | View Notebook |
| 2 | Jensen's Inequality | View Notebook |
| 3 | Reparametrization Trick | View Notebook |
| 4 | Temperature Scaled Softmax | View Notebook |
| Concept # | Concept Name | Notebook |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Logistic Regression Coefficient Interpretation | View Notebook |
| 2 | Shapley values and SHAP for ML | View Notebook |
| 3 | Counterfactuals | View Notebook |
| Concept # | Concept Name | Notebook |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Autocorrelation Function vs Partial Autocorrelation Function | View Notebook |
| 2 | Adjusted R^2 | View Notebook |
| 3 | Condition Number | View Notebook |
| 4 | Cramer's V | View Notebook |
| 5 | Exponentially Weighted Average and Bias Correction | View Notebook |
| 6 | Kendall's Tau Rank Correlation | View Notebook |
| 7 | Kruskal Wallis | View Notebook |
| 8 | Spurious Correlation | View Notebook |
| 9 | Leave One Out Cross Validation and PRESS | View Notebook |
| Concept # | Concept Name | Notebook |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Canonical Correlation Analysis | View Notebook |
| 2 | Correspondence Analysis | View Notebook |
| 3 | Factor Analysis | View Notebook |
| 4 | Hotelling's T^2 | View Notebook |
| 5 | Principal Component Analysis | View Notebook |
| Concept # | Concept Name | Notebook |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chebyshev's Inequality | View Notebook |
| 2 | Distribution of Minimum | View Notebook |
| 3 | Matrix Calculus Jacobians and Gradients | View Notebook |
| 4 | Multivariate Normal Distribution | View Notebook |
| 5 | Mutual Information | View Notebook |
| 6 | Point Biserial Correlation Coefficient | View Notebook |
| 7 | Unbiasesd vs Consistent Estimator | View Notebook |
| 8 | ECDF | View Notebook |
| Concept # | Concept Name | Notebook |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | User Item Interaction Matrix | View Notebook |
| Concept # | Concept Name | Notebook |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Spectral Decomposition | View Notebook |
| Concept # | Concept Name | Notebook |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kadane's Algorithm | View Notebook |
| 2 | Prefix Sum and Sliding Window | View Notebook |
| 3 | Pivoting in Pandas | View Notebook |
| Concept # | Concept Name | Notebook |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Plotnine: Python's ggplot2 | View Notebook |
I follow a structured approach to sharing knowledge on Threads, posting concepts and thought-provoking questions (IQs) that stem from my professional experience, academic background, and interview scenarios. These questions are either ones I have encountered, been asked in interviews, or would consider posing in a data science discussion. I refine each question to maximize conceptual coverage and, at times, deliberately choose intellectually stimulating topics to encourage deeper engagement.
Contributions are welcome! If you have suggestions for new questions, additional resources, or improvements to the current answers, feel free to submit a pull request or open an issue.
- Code in this repository is licensed under the MIT License.
- Content (text, explanations, visualizations, etc.) is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 (CC BY 4.0).
This means:
- You are free to use and modify the code as per the MIT license.
- You may reuse and share content, but you must provide proper attribution.
For details, check the LICENSE file.
Email: [email protected]
For more updates, follow me on Threads @AIinMinutes.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Data-and-AI-Concepts
Similar Open Source Tools

Data-and-AI-Concepts
This repository is a curated collection of data science and AI concepts and IQs, covering topics from foundational mathematics to cutting-edge generative AI concepts. It aims to support learners and professionals preparing for various data science roles by providing detailed explanations and notebooks for each concept.
models
The Intel® AI Reference Models repository contains links to pre-trained models, sample scripts, best practices, and tutorials for popular open-source machine learning models optimized by Intel to run on Intel® Xeon® Scalable processors and Intel® Data Center GPUs. It aims to replicate the best-known performance of target model/dataset combinations in optimally-configured hardware environments. The repository will be deprecated upon the publication of v3.2.0 and will no longer be maintained or published.
ai-reference-models
The Intel® AI Reference Models repository contains links to pre-trained models, sample scripts, best practices, and tutorials for popular open-source machine learning models optimized by Intel to run on Intel® Xeon® Scalable processors and Intel® Data Center GPUs. The purpose is to quickly replicate complete software environments showcasing the AI capabilities of Intel platforms. It includes optimizations for popular deep learning frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch, with additional plugins/extensions for improved performance. The repository is licensed under Apache License Version 2.0.
Azure-AIGEN-demos
Microsoft Foundry is a unified Azure platform-as-a-service offering for enterprise AI operations, model builders, and application development. This foundation combines production-grade infrastructure with friendly interfaces, enabling developers to focus on building applications rather than managing infrastructure. Microsoft Foundry unifies agents, models, and tools under a single management grouping with built-in enterprise-readiness capabilities including tracing, monitoring, evaluations, and customizable enterprise setup configurations. The platform provides streamlined management through unified Role-based access control (RBAC), networking, and policies under one Azure resource provider namespace.
Model-References
The 'Model-References' repository contains examples for training and inference using Intel Gaudi AI Accelerator. It includes models for computer vision, natural language processing, audio, generative models, MLPerf™ training, and MLPerf™ inference. The repository provides performance data and model validation information for various frameworks like PyTorch. Users can find examples of popular models like ResNet, BERT, and Stable Diffusion optimized for Intel Gaudi AI accelerator.
ai-game-development-tools
Here we will keep track of the AI Game Development Tools, including LLM, Agent, Code, Writer, Image, Texture, Shader, 3D Model, Animation, Video, Audio, Music, Singing Voice and Analytics. 🔥 * Tool (AI LLM) * Game (Agent) * Code * Framework * Writer * Image * Texture * Shader * 3D Model * Avatar * Animation * Video * Audio * Music * Singing Voice * Speech * Analytics * Video Tool
LLM-KG4QA
LLM-KG4QA is a repository focused on the integration of Large Language Models (LLMs) and Knowledge Graphs (KGs) for Question Answering (QA). It covers various aspects such as using KGs as background knowledge, reasoning guideline, and refiner/filter. The repository provides detailed information on pre-training, fine-tuning, and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) techniques for enhancing QA performance. It also explores complex QA tasks like Explainable QA, Multi-Modal QA, Multi-Document QA, Multi-Hop QA, Multi-run and Conversational QA, Temporal QA, Multi-domain and Multilingual QA, along with advanced topics like Optimization and Data Management. Additionally, it includes benchmark datasets, industrial and scientific applications, demos, and related surveys in the field.
Multiverse_of_100-_data_science_project_series
This repository contains a series of 100+ data science projects covering a wide range of topics and techniques. Each project is designed to help learners practice and improve their data science skills by working on real-world datasets and problems. The projects include data cleaning, exploratory data analysis, machine learning modeling, and data visualization. Whether you are a beginner looking to build a portfolio or an experienced data scientist wanting to sharpen your skills, this repository offers a diverse set of projects to work on.
LLM4EC
LLM4EC is an interdisciplinary research repository focusing on the intersection of Large Language Models (LLM) and Evolutionary Computation (EC). It provides a comprehensive collection of papers and resources exploring various applications, enhancements, and synergies between LLM and EC. The repository covers topics such as LLM-assisted optimization, EA-based LLM architecture search, and applications in code generation, software engineering, neural architecture search, and other generative tasks. The goal is to facilitate research and development in leveraging LLM and EC for innovative solutions in diverse domains.
open-llms
Open LLMs is a repository containing various Large Language Models licensed for commercial use. It includes models like T5, GPT-NeoX, UL2, Bloom, Cerebras-GPT, Pythia, Dolly, and more. These models are designed for tasks such as transfer learning, language understanding, chatbot development, code generation, and more. The repository provides information on release dates, checkpoints, papers/blogs, parameters, context length, and licenses for each model. Contributions to the repository are welcome, and it serves as a resource for exploring the capabilities of different language models.
AudioLLM
AudioLLMs is a curated collection of research papers focusing on developing, implementing, and evaluating language models for audio data. The repository aims to provide researchers and practitioners with a comprehensive resource to explore the latest advancements in AudioLLMs. It includes models for speech interaction, speech recognition, speech translation, audio generation, and more. Additionally, it covers methodologies like multitask audioLLMs and segment-level Q-Former, as well as evaluation benchmarks like AudioBench and AIR-Bench. Adversarial attacks such as VoiceJailbreak are also discussed.
awesome-llm-planning-reasoning
The 'Awesome LLMs Planning Reasoning' repository is a curated collection focusing on exploring the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) in planning and reasoning tasks. It includes research papers, code repositories, and benchmarks that delve into innovative techniques, reasoning limitations, and standardized evaluations related to LLMs' performance in complex cognitive tasks. The repository serves as a comprehensive resource for researchers, developers, and enthusiasts interested in understanding the advancements and challenges in leveraging LLMs for planning and reasoning in real-world scenarios.
LLM4Opt
LLM4Opt is a collection of references and papers focusing on applying Large Language Models (LLMs) for diverse optimization tasks. The repository includes research papers, tutorials, workshops, competitions, and related collections related to LLMs in optimization. It covers a wide range of topics such as algorithm search, code generation, machine learning, science, industry, and more. The goal is to provide a comprehensive resource for researchers and practitioners interested in leveraging LLMs for optimization tasks.
watsonx-ai-samples
Sample notebooks for IBM Watsonx.ai for IBM Cloud and IBM Watsonx.ai software product. The notebooks demonstrate capabilities such as running experiments on model building using AutoAI or Deep Learning, deploying third-party models as web services or batch jobs, monitoring deployments with OpenScale, managing model lifecycles, inferencing Watsonx.ai foundation models, and integrating LangChain with Watsonx.ai. Notebooks with Python code and the Python SDK can be found in the `python_sdk` folder. The REST API examples are organized in the `rest_api` folder.
For similar tasks

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.

sorrentum
Sorrentum is an open-source project that aims to combine open-source development, startups, and brilliant students to build machine learning, AI, and Web3 / DeFi protocols geared towards finance and economics. The project provides opportunities for internships, research assistantships, and development grants, as well as the chance to work on cutting-edge problems, learn about startups, write academic papers, and get internships and full-time positions at companies working on Sorrentum applications.

tidb
TiDB is an open-source distributed SQL database that supports Hybrid Transactional and Analytical Processing (HTAP) workloads. It is MySQL compatible and features horizontal scalability, strong consistency, and high availability.

zep-python
Zep is an open-source platform for building and deploying large language model (LLM) applications. It provides a suite of tools and services that make it easy to integrate LLMs into your applications, including chat history memory, embedding, vector search, and data enrichment. Zep is designed to be scalable, reliable, and easy to use, making it a great choice for developers who want to build LLM-powered applications quickly and easily.

telemetry-airflow
This repository codifies the Airflow cluster that is deployed at workflow.telemetry.mozilla.org (behind SSO) and commonly referred to as "WTMO" or simply "Airflow". Some links relevant to users and developers of WTMO: * The `dags` directory in this repository contains some custom DAG definitions * Many of the DAGs registered with WTMO don't live in this repository, but are instead generated from ETL task definitions in bigquery-etl * The Data SRE team maintains a WTMO Developer Guide (behind SSO)

mojo
Mojo is a new programming language that bridges the gap between research and production by combining Python syntax and ecosystem with systems programming and metaprogramming features. Mojo is still young, but it is designed to become a superset of Python over time.

pandas-ai
PandasAI is a Python library that makes it easy to ask questions to your data in natural language. It helps you to explore, clean, and analyze your data using generative AI.

databend
Databend is an open-source cloud data warehouse that serves as a cost-effective alternative to Snowflake. With its focus on fast query execution and data ingestion, it's designed for complex analysis of the world's largest datasets.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.