
ai_automation_suggester
This custom Home Assistant integration automatically scans your entities, detects new devices, and uses AI (via cloud and local APIs) to suggest tailored automations. It supports multiple AI providers, including OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, Groq, Ollama and more! The integration provides automation suggestions via HASS notifications
Stars: 560
An integration for Home Assistant that leverages AI models to understand your unique home environment and propose intelligent automations. By analyzing your entities, devices, areas, and existing automations, the AI Automation Suggester helps you discover new, context-aware use cases you might not have considered, ultimately streamlining your home management and improving efficiency, comfort, and convenience. The tool acts as a personal automation consultant, providing actionable YAML-based automations that can save energy, improve security, enhance comfort, and reduce manual intervention. It turns the complexity of a large Home Assistant environment into actionable insights and tangible benefits.
README:
An AI‑powered assistant for Home Assistant that leverages large language models to understand your unique smart home environment – your entities, areas, devices, and existing automations. It proposes intelligent, actionable YAML suggestions tailored to your specific setup, helping you unlock your home's full potential.
As your Home Assistant setup grows, managing its complexity and identifying new opportunities for automation can become challenging. You might find yourself with:
- Too many possibilities: Every new device adds countless potential interactions.
- Automation "Writer's Block": Translating a complex idea into functional YAML can be daunting.
- Underutilized Potential: Many devices sit idle or require manual control because the right automation hasn't been thought of or created.
- Maintenance Overload: Keeping existing automations relevant as your home evolves is difficult.
The result is often an under-automated house despite having powerful hardware.
The AI Automation Suggester integration solves these challenges by acting as a personal automation consultant. It intelligently analyzes your Home Assistant instance to:
- Analyze your home's state: Understand your devices, their capabilities, locations, and existing automations.
- Identify opportunities: Spot gaps, synergies, and potential improvements for energy saving, security, comfort, and convenience.
- Draft ready-to-paste YAML: Provide concrete, tailored automation ideas as YAML snippets you can review, tweak, and implement directly.
In essence, this integration turns the complexity of a large Home Assistant environment into actionable insights and tangible benefits, guiding you toward a more efficient, comfortable, and secure smart home.
The integration follows a simple, effective process:
| Step | What happens? | Details |
|---|---|---|
| 1 · Snapshot | Collects data about your home. | On manual trigger or schedule, the integration gathers information on your entities (including attributes), devices, areas, and existing automations. You can control the scope using filters and limits. |
| 2 · Prompt Building | Structures the data for the AI. | This snapshot is embedded into a detailed system prompt describing your specific Home Assistant setup. You can enhance this with a custom prompt to steer suggestions towards specific goals (e.g., "focus on presence lighting"). |
| 3 · Provider Call | Sends the prompt to the AI. | The crafted prompt is sent to your configured AI provider (OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, Groq, LocalAI, Ollama, Mistral, Perplexity). |
| 4 · Parsing | Processes the AI's response. | The raw response from the AI is parsed to extract key information: a human-readable description of the suggestion, the actual yaml_block code, and potentially other details. This information is stored on sensor attributes. |
| 5 · Surface | Delivers the suggestions. | Suggestions appear as Home Assistant persistent notifications. You can also use sensor attributes to display suggestions on custom dashboards for easy review and implementation. |
Randomized entity selection (configurable) helps ensure each analysis run can surface fresh ideas rather than repeating the same suggestions.
Suggestions are delivered directly within Home Assistant notifications:
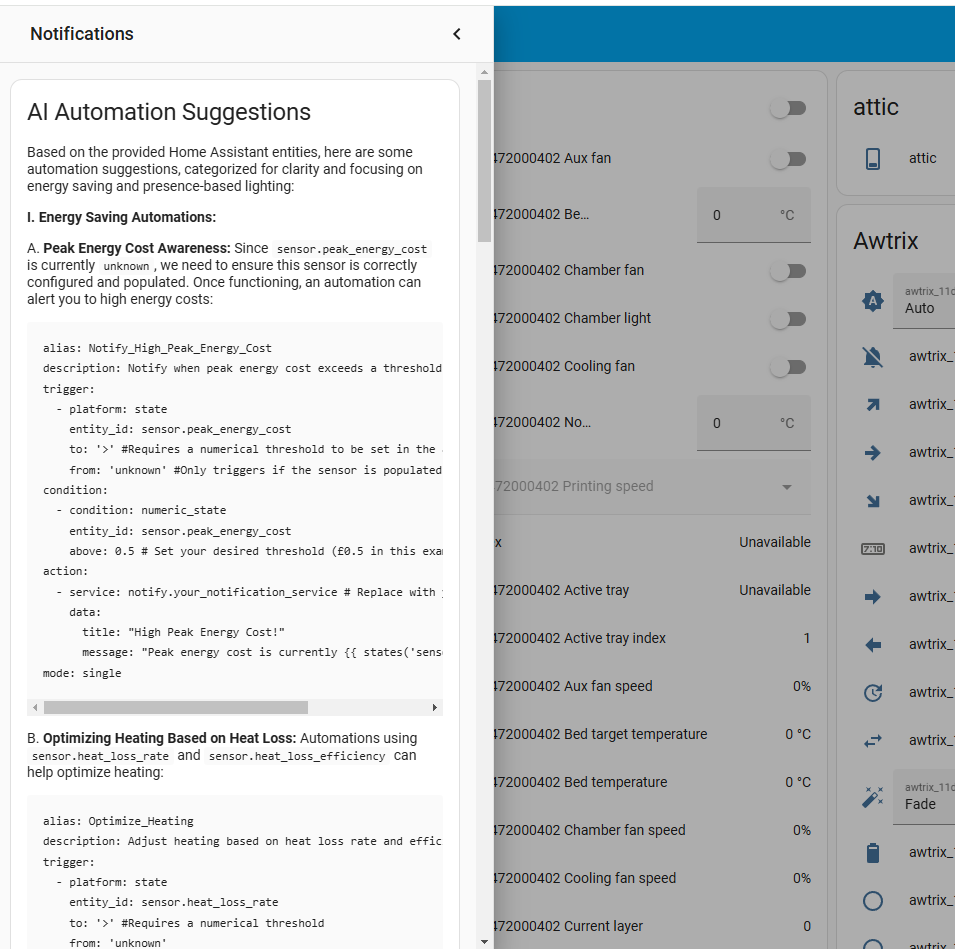
AI suggestions delivered right inside Home Assistant
You can also build custom dashboard cards to display suggestions using sensor attributes:

Dashboard showing human-readable description and extracted YAML block
Here's an example of displaying suggestions on a dashboard:
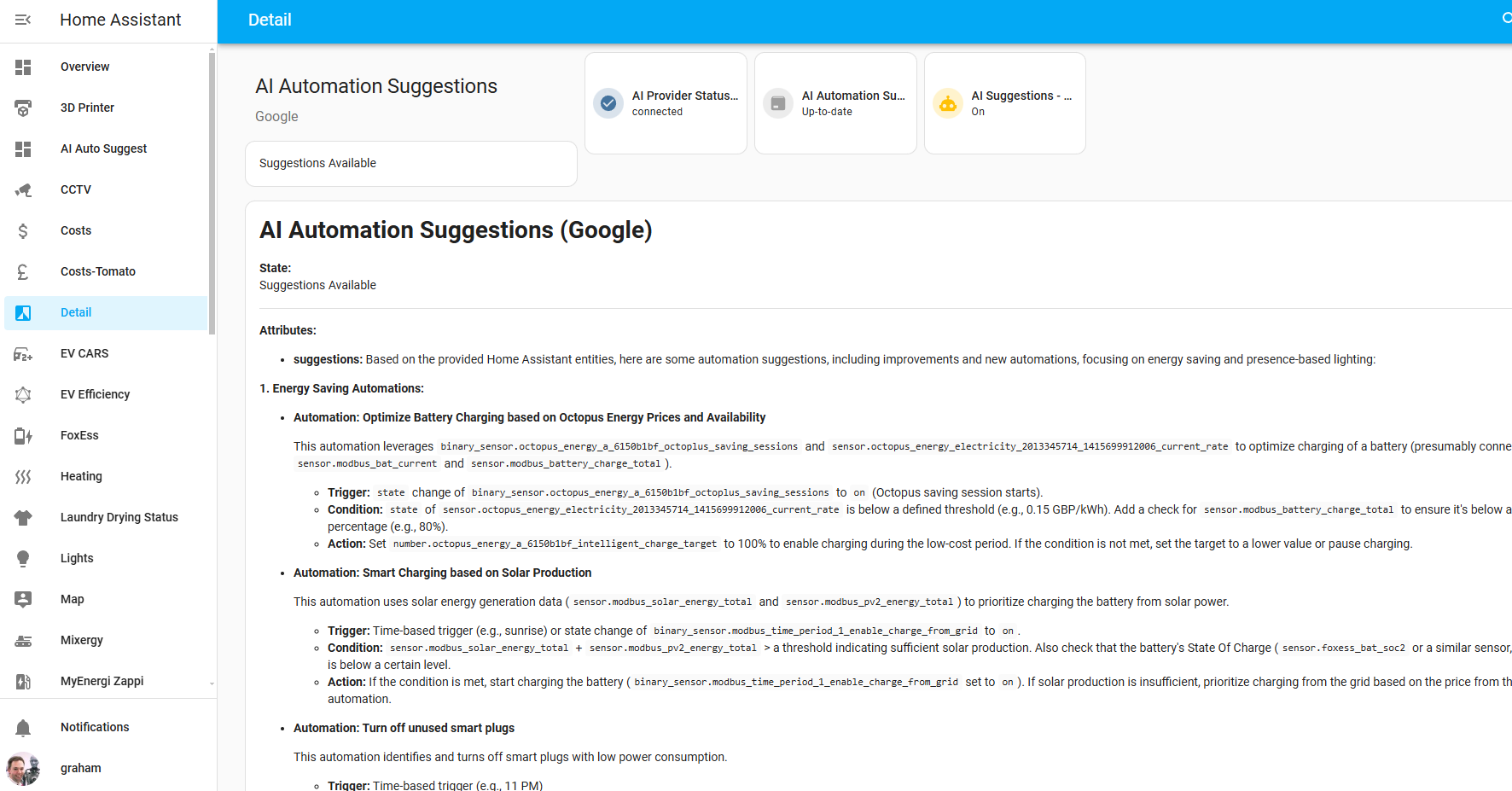
Example of a dashboard displaying AI-suggested automations
Leveraging the AI Automation Suggester provides several key benefits:
- Time Saving: Reduces the effort and guesswork involved in designing complex automations.
- Context-Aware Suggestions: Ideas consider your specific devices, areas, and current setup for realistic, tailored recommendations.
- Model-Agnostic Flexibility: Supports cloud and local AI models, letting you choose based on cost, privacy, and performance preferences.
- Improved Usability: Makes automation creation more accessible, even for users less familiar with YAML.
- Dynamic Inspiration: Provides fresh ideas as your home and devices change, keeping your automations evolving.
- Enhanced Control: Custom prompts, entity limits, and domain filters give you command over the suggestion generation process.
- Safe to Try: Suggestions are presented for review; nothing is automatically implemented without your explicit action.
-
Multi-Provider Support: Connect to OpenAI, OpenAI Azure, Anthropic, Google, Groq, LocalAI, Ollama, Mistral, Perplexity, or OpenRouter with full configuration options:
- Temperature control for all providers (0.0 - 2.0)
- Model selection with provider-specific defaults
- Secure API key storage
- Custom endpoints for compatible providers
- Advanced options like Ollama's think mode control
- Customizable Prompts and Filters: Tailor suggestions using system prompts, domain filters, and entity limits.
- Randomized Entity Selection: Prevent repetitive suggestions and discover new opportunities.
- Context-Rich Insights: Incorporates device and area information for smarter, more relevant ideas.
- Persistent Notifications: Receive suggestions directly in your Home Assistant interface.
-
Service Call Integration: Manually trigger suggestions via the
ai_automation_suggester.generate_suggestionsservice with full parameter control. - Diagnostics Sensors: Monitor suggestion status and provider connection health.
- Example Automations: Includes built-in examples for new entity detection and weekly reviews.
- Dashboard-Friendly Output: Sensor attributes provide description and YAML blocks ready for Lovelace cards.
- Home Assistant: Version 2023.5 or later.
-
AI Provider Setup: You will need access to an AI model.
- For cloud providers (OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, Groq, Mistral, Perplexity), you’ll need API keys.
- For local models (LocalAI, Ollama), ensure the local servers are running and accessible from Home Assistant.
- Install HACS if you haven't already.
- In HACS → Integrations, click the
+button. - Search for
AI Automation Suggester. - Select the integration and click Download.
- Restart Home Assistant.
- Go to Settings → Devices & Services → + Add Integration and search for
AI Automation Suggester.
- Download the contents of this repository.
-
Copy the
custom_components/ai_automation_suggesterfolder to your Home Assistantcustom_componentsdirectory.<homeassistant_config_dir>/ └── custom_components/ └── ai_automation_suggester/ ├── __init__.py └── ... (other files)
- Restart Home Assistant.
- Go to Settings → Devices & Services → + Add Integration and search for
AI Automation Suggester.
- Add the integration via the Home Assistant UI: Settings → Devices & Services → + Add Integration →
AI Automation Suggester. - Follow the setup wizard:
- Select your AI Provider: Choose from the dropdown list.
- Enter API Keys or Endpoint: Provide the necessary credentials or local server URL based on your provider choice.
- Select Model: Choose the specific model variant you wish to use.
- Set Max Tokens: Define the maximum length for the AI's response (influences the length of suggestions).
- (Optional) Custom System Prompt: Provide an initial prompt to guide the AI's overall perspective (e.g., "You are an expert in energy-saving automations for smart homes.").
You can adjust these settings later via the integration options in Settings → Devices & Services.
-
Temperature Control:
- Available for all providers
- Range: 0.0 (more focused) to 2.0 (more creative)
- Default: 0.7
- Configurable in both initial setup and options
-
Token Management:
- Separate input/output token limits
- Prevents excessive API usage
- Optimizes response length
The integration comes with example automations you can enable or adapt:
- On New Entities: Automatically generates suggestions when new entities are added to Home Assistant, helping you quickly integrate them.
- Weekly Reviews: Triggers a comprehensive analysis weekly (or at a custom interval you define in the automation), providing ongoing ideas.
Find and enable these examples in Settings → Automations.
You can trigger the suggestion generation manually using the service call:
- Go to Developer Tools → Services.
- Select the service
ai_automation_suggester.generate_suggestions. - Call the service. You can pass parameters to customize the request:
-
all_entities(boolean, default:false): Set totrueto consider all eligible entities,falseto only consider entities added since the last successful run. -
domains(list of strings, optional): Limit the analysis to entities within specific domains (e.g.,['light', 'sensor']). -
entity_limit(integer, optional): Set a maximum number of entities the AI should consider in this run. Useful for controlling prompt length and cost. -
custom_prompt(string, optional): Add a specific instruction for this particular run (e.g., "Suggest security automations for doors and windows.").
-
The main sensor (sensor.ai_automation_suggestions_<provider_name>) exposes useful attributes for display on dashboards. Replace <provider_name> with the name you gave the integration instance (e.g., openai, ollama).
-
Displaying the Description:
{{ state_attr('sensor.ai_automation_suggestions_<provider_name>', 'description') }} -
Displaying the YAML Block:
{{ state_attr('sensor.ai_automation_suggestions_<provider_name>', 'yaml_block') }}
You can use Markdown cards or other card types to present this information cleanly in your Home Assistant dashboard.
The integration provides several sensors for monitoring:
-
AI Automation Suggestions: (
sensor.ai_automation_suggestions_<provider_name>)- State:
No Suggestions,New Suggestions Available,Suggestions Available - Attributes:
-
description: Human-readable suggestion description -
yaml_block: Ready-to-use automation YAML -
last_update: Timestamp of last update -
entities_processed: List of analyzed entities -
entities_processed_count: Number of entities analyzed
-
- State:
-
AI Provider Status: (
sensor.ai_provider_status_<provider_name>)- State:
connected,error,disconnected,initializing - Attributes:
-
last_error_message: Details of any errors -
last_attempted_update: Timestamp of last attempt
-
- State:
-
Max Input/Output Tokens: (
sensor.max_input_tokens_<provider_name>,sensor.max_output_tokens_<provider_name>)- Shows configured token limits
- Helps monitor API usage
-
AI Model: (
sensor.ai_model_in_use_<provider_name>)- Shows current model configuration
- Useful for multi-instance setups
-
Last Error: (
sensor.last_error_message_<provider_name>)- Detailed error tracking
- Includes stack traces for unexpected errors
-
Stack Traces:
- Detailed error logging for unexpected issues
- Available in Home Assistant logs
- Helpful for debugging API issues
-
Common Error Scenarios:
- API authentication failures
- Network connectivity issues
- Token limit exceeded
- Model availability problems
- Response parsing errors
-
Error Monitoring:
- Use the Last Error sensor for real-time error tracking
- Check Home Assistant logs for stack traces
- Monitor provider status sensor for connection issues
- All API keys are stored securely using Home Assistant's secure storage
- Password fields are properly masked in the UI
- Local providers (Ollama, LocalAI) can be used for complete data privacy
Beyond the basic configuration and service call parameters, you can further customize the integration's behavior:
By default, the integration uses randomized entity selection when all_entities is true (or the automatic weekly scan runs). This helps ensure variety in suggestions and prevents the AI from focusing only on the same initial set of entities.
Use the domains parameter in the service call or your automation configuration to narrow the focus. This is very effective for getting suggestions for specific areas (e.g., only analyze light and switch entities in the living_room area - though area filtering is implicit based on the entities selected).
The entity_limit parameter is crucial for managing prompt size, particularly with models sensitive to input length or cost. Experiment to find a limit that provides good suggestions without hitting token limits or incurring excessive costs.
The custom_prompt parameter allows you to be very specific about the type of suggestions you want for a particular run. Combine it with domain filtering for highly targeted results (e.g., domains: ['climate'], custom_prompt: "Suggest automations to optimize heating/cooling based on occupancy and weather.").
- Review Suggestions: Check the persistent notifications or your dashboard card for new suggestions.
-
Copy YAML: The suggestions are provided as ready-to-use Home Assistant YAML snippets. Copy the
yaml_blockcontent. -
Add to Home Assistant:
- Paste the YAML into your
automations.yamlfile and restart Home Assistant. - Alternatively, use the Home Assistant Automation Editor UI: create a new automation, switch to YAML mode, and paste the snippet.
- Paste the YAML into your
- Adapt as Needed: While the suggestions are tailored, you may need to make minor adjustments to triggers, conditions, delays, or actions to perfectly match your preferences and devices.
- Test: Always test new automations to ensure they function as expected before relying on them.
The integration provides two key sensors for monitoring:
-
AI Automation Suggestions Sensor:
sensor.ai_automation_suggestions_<provider_name>- State indicates the status (e.g.,
idle,generating,suggestions_available). - Attributes contain the latest suggestions, including
description,yaml_block, and potentially other details depending on the AI provider's response format.
- State indicates the status (e.g.,
-
AI Provider Status Sensor:
sensor.ai_provider_status_<provider_name>- State indicates the connection health (e.g.,
connected,error,unavailable). - Attributes may provide additional details about the provider status or any errors encountered.
- State indicates the connection health (e.g.,
Monitor these sensors to ensure the integration is functioning correctly.
- Privacy Considerations: If using cloud-based AI providers, be aware that entity data (names, states, attributes) is sent to their servers. Consider using local AI models (LocalAI, Ollama) for full data control if privacy is a major concern.
-
API Costs: Some cloud providers charge for API usage based on tokens processed. Be mindful of this and use features like
entity_limitand scheduled run frequency to manage potential costs. Monitor your provider's billing. - No Guarantees: The AI's suggestions are based on patterns and logical inference from the data provided. They are not guaranteed to be perfect or the most efficient solution for every scenario. Always review suggestions thoroughly before implementing them in your live system.
- AI Limitations: Large language models can sometimes hallucinate or provide illogical suggestions. Use your judgment and knowledge of your home setup when reviewing.
| Symptom | Check / Action |
|---|---|
| No suggestions available | - Verify API key is correct. - Check the AI Provider Status sensor for errors.- Check the Home Assistant logs for errors related to the integration. - Try triggering the service manually with a small entity_limit and no domain filters.- Ensure you have enough entities/devices for meaningful suggestions. |
AI Provider Status shows error |
- Inspect the Home Assistant log (home-assistant.log) for detailed error messages (look for ai_automation_suggester and processing error).- Check your network connection to the provider's server (if cloud-based) or your local server. - Confirm your API key is active and has permissions. - Ensure your local AI server is running and accessible. |
| Suggestion prompt is too long | - Reduce the entity_limit parameter when triggering the service or configuring the automation.- Use the domains filter to narrow the scope of entities analyzed.- Shorten or simplify your custom_prompt if you are using one. |
| Unintended startup suggestions | - Review your Home Assistant automations and scripts to ensure none are configured to call ai_automation_suggester.generate_suggestions on startup or via events you didn't intend. |
| Suggestions are repetitive | - Ensure all_entities is used (e.g., in a weekly automation) and consider enabling randomized entity selection.- Try different custom_prompt values to steer the AI in a new direction.- Increase the entity_limit to give the AI more data points (if prompt length allows). |
| Image links are broken in HACS/GitHub | This has been addressed in this README version. Ensure the README file in your repository uses the corrected URLs provided. Clear your browser cache or wait for GitHub/HACS to refresh. |
If you encounter issues not covered here, please open an issue on the GitHub repository with details from your Home Assistant logs.
Future planned features and improvements:
- More Interactive Suggestions: Explore feedback mechanisms to help the AI learn from user acceptance or rejection of suggestions.
- One-Click Automation Creation: Streamline the process from reviewing a suggestion to creating the automation in Home Assistant.
- Expanded Localization: Support for more languages through community contributions.
- Improved Entity/Device Context: Enhance the information provided to the AI about device types, capabilities, and relationships.
This project is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for details.
- Home Assistant Community: For providing a robust and extensible smart home platform.
- AI Providers: OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, Groq, LocalAI, Ollama, Mistral, and Perplexity for developing and providing access to powerful language models.
- Contributors and Users: For valuable feedback, testing, and contributions that help improve this project.
We welcome contributions! If you have ideas for new features, improvements, bug fixes, or translations, please feel free to open an issue or submit a pull request on the GitHub repository. Please follow standard development practices.
This is a custom component developed independently. It is not affiliated with, endorsed by, or officially supported by Home Assistant, Nabu Casa, or any of the mentioned AI providers. Use at your own discretion.
If you find this integration helpful and it saves you time and effort in automating your home, please consider supporting its development. Your support helps with maintenance, adding new features, and covering any potential costs associated with development and testing.
For further questions, discussions, or assistance, please visit the GitHub repository or the Home Assistant Community Forums thread (if one exists). Your feedback is highly valuable and helps shape the future direction of this project.
1. How do I update the integration?
If installed via HACS, update directly through the HACS interface in Home Assistant. If installed manually, download the latest version of the files from the repository and replace the existing ones in your custom_components/ai_automation_suggester folder, then restart Home Assistant.
2. Can I use this integration without a cloud API key? Yes! You can use local AI models like those provided by LocalAI or Ollama running on your local network. This requires setting up and running the local AI server separately.
3. Is my Home Assistant data safe? When using cloud-based AI providers, specific entity data (names, states, attributes) is sent to the provider's API for processing. Refer to the privacy policies of your chosen AI provider. Using local models keeps all data processing within your local network.
4. I found a bug or have a feature request. What should I do? Please open an issue on the GitHub repository. Provide as much detail as possible, including steps to reproduce the bug, screenshots, and relevant logs. For feature requests, clearly describe the desired functionality and use case.
5. Can I get suggestions in languages other than English? The quality of suggestions in other languages depends heavily on the AI model used. The integration structures the prompt in English, but you can experiment with custom prompts in other languages and see how the model responds. Community translations of the integration's UI and documentation are welcome!
With the AI Automation Suggester, you gain an AI-powered ally to help you unlock your home’s full potential. Instead of being overwhelmed by possibilities, receive thoughtful, context-aware suggestions that make your Home Assistant automations more impactful, efficient, and enjoyable.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for ai_automation_suggester
Similar Open Source Tools

ai_automation_suggester
An integration for Home Assistant that leverages AI models to understand your unique home environment and propose intelligent automations. By analyzing your entities, devices, areas, and existing automations, the AI Automation Suggester helps you discover new, context-aware use cases you might not have considered, ultimately streamlining your home management and improving efficiency, comfort, and convenience. The tool acts as a personal automation consultant, providing actionable YAML-based automations that can save energy, improve security, enhance comfort, and reduce manual intervention. It turns the complexity of a large Home Assistant environment into actionable insights and tangible benefits.
LLMstudio
LLMstudio by TensorOps is a platform that offers prompt engineering tools for accessing models from providers like OpenAI, VertexAI, and Bedrock. It provides features such as Python Client Gateway, Prompt Editing UI, History Management, and Context Limit Adaptability. Users can track past runs, log costs and latency, and export history to CSV. The tool also supports automatic switching to larger-context models when needed. Coming soon features include side-by-side comparison of LLMs, automated testing, API key administration, project organization, and resilience against rate limits. LLMstudio aims to streamline prompt engineering, provide execution history tracking, and enable effortless data export, offering an evolving environment for teams to experiment with advanced language models.

nanobrowser
Nanobrowser is an open-source AI web automation tool that runs in your browser. It is a free alternative to OpenAI Operator with flexible LLM options and a multi-agent system. Nanobrowser offers premium web automation capabilities while keeping users in complete control, with features like a multi-agent system, interactive side panel, task automation, follow-up questions, and multiple LLM support. Users can easily download and install Nanobrowser as a Chrome extension, configure agent models, and accomplish tasks such as news summary, GitHub research, and shopping research with just a sentence. The tool uses a specialized multi-agent system powered by large language models to understand and execute complex web tasks. Nanobrowser is actively developed with plans to expand LLM support, implement security measures, optimize memory usage, enable session replay, and develop specialized agents for domain-specific tasks. Contributions from the community are welcome to improve Nanobrowser and build the future of web automation.
agent-zero
Agent Zero is a personal and organic AI framework designed to be dynamic, organically growing, and learning as you use it. It is fully transparent, readable, comprehensible, customizable, and interactive. The framework uses the computer as a tool to accomplish tasks, with no single-purpose tools pre-programmed. It emphasizes multi-agent cooperation, complete customization, and extensibility. Communication is key in this framework, allowing users to give proper system prompts and instructions to achieve desired outcomes. Agent Zero is capable of dangerous actions and should be run in an isolated environment. The framework is prompt-based, highly customizable, and requires a specific environment to run effectively.
promptbook
Promptbook is a library designed to build responsible, controlled, and transparent applications on top of large language models (LLMs). It helps users overcome limitations of LLMs like hallucinations, off-topic responses, and poor quality output by offering features such as fine-tuning models, prompt-engineering, and orchestrating multiple prompts in a pipeline. The library separates concerns, establishes a common format for prompt business logic, and handles low-level details like model selection and context size. It also provides tools for pipeline execution, caching, fine-tuning, anomaly detection, and versioning. Promptbook supports advanced techniques like Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and knowledge utilization to enhance output quality.
kollektiv
Kollektiv is a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) system designed to enable users to chat with their favorite documentation easily. It aims to provide LLMs with access to the most up-to-date knowledge, reducing inaccuracies and improving productivity. The system utilizes intelligent web crawling, advanced document processing, vector search, multi-query expansion, smart re-ranking, AI-powered responses, and dynamic system prompts. The technical stack includes Python/FastAPI for backend, Supabase, ChromaDB, and Redis for storage, OpenAI and Anthropic Claude 3.5 Sonnet for AI/ML, and Chainlit for UI. Kollektiv is licensed under a modified version of the Apache License 2.0, allowing free use for non-commercial purposes.
spacy-llm
This package integrates Large Language Models (LLMs) into spaCy, featuring a modular system for **fast prototyping** and **prompting** , and turning unstructured responses into **robust outputs** for various NLP tasks, **no training data** required. It supports open-source LLMs hosted on Hugging Face 🤗: Falcon, Dolly, Llama 2, OpenLLaMA, StableLM, Mistral. Integration with LangChain 🦜️🔗 - all `langchain` models and features can be used in `spacy-llm`. Tasks available out of the box: Named Entity Recognition, Text classification, Lemmatization, Relationship extraction, Sentiment analysis, Span categorization, Summarization, Entity linking, Translation, Raw prompt execution for maximum flexibility. Soon: Semantic role labeling. Easy implementation of **your own functions** via spaCy's registry for custom prompting, parsing and model integrations. For an example, see here. Map-reduce approach for splitting prompts too long for LLM's context window and fusing the results back together
plandex
Plandex is an open source, terminal-based AI coding engine designed for complex tasks. It uses long-running agents to break up large tasks into smaller subtasks, helping users work through backlogs, navigate unfamiliar technologies, and save time on repetitive tasks. Plandex supports various AI models, including OpenAI, Anthropic Claude, Google Gemini, and more. It allows users to manage context efficiently in the terminal, experiment with different approaches using branches, and review changes before applying them. The tool is platform-independent and runs from a single binary with no dependencies.

AIOStreams
AIOStreams is a versatile tool that combines streams from various addons into one platform, offering extensive customization options. Users can change result formats, filter results by various criteria, remove duplicates, prioritize services, sort results, specify size limits, and more. The tool scrapes results from selected addons, applies user configurations, and presents the results in a unified manner. It simplifies the process of finding and accessing desired content from multiple sources, enhancing user experience and efficiency.
TaskingAI
TaskingAI brings Firebase's simplicity to **AI-native app development**. The platform enables the creation of GPTs-like multi-tenant applications using a wide range of LLMs from various providers. It features distinct, modular functions such as Inference, Retrieval, Assistant, and Tool, seamlessly integrated to enhance the development process. TaskingAI’s cohesive design ensures an efficient, intelligent, and user-friendly experience in AI application development.
mikupad
mikupad is a lightweight and efficient language model front-end powered by ReactJS, all packed into a single HTML file. Inspired by the likes of NovelAI, it provides a simple yet powerful interface for generating text with the help of various backends.
chatnio
Chat Nio is a next-generation AI one-stop solution that provides a rich and user-friendly interface for interacting with various AI models. It offers features such as AI chat conversation, rich format compatibility, markdown support, message menu support, multi-platform adaptation, dialogue memory, full-model file parsing, full-model DuckDuckGo online search, full-screen large text editing, model marketplace, preset support, site announcements, preference settings, internationalization support, and a rich admin system. Chat Nio also boasts a powerful channel management system that utilizes a self-developed channel distribution algorithm, supports multi-channel management, is compatible with multiple formats, allows for custom models, supports channel retries, enables balanced load within the same channel, and provides channel model mapping and user grouping. Additionally, Chat Nio offers forwarding API services that are compatible with multiple formats in the OpenAI universal format and support multiple model compatible layers. It also provides a custom build and install option for highly customizable deployments. Chat Nio is an open-source project licensed under the Apache License 2.0 and welcomes contributions from the community.
portia-sdk-python
Portia AI is an open source developer framework for predictable, stateful, authenticated agentic workflows. It allows developers to have oversight over their multi-agent deployments and focuses on production readiness. The framework supports iterating on agents' reasoning, extensive tool support including MCP support, authentication for API and web agents, and is production-ready with features like attribute multi-agent runs, large inputs and outputs storage, and connecting any LLM. Portia AI aims to provide a flexible and reliable platform for developing AI agents with tools, authentication, and smart control.
comfyui_LLM_Polymath
LLM Polymath Chat Node is an advanced Chat Node for ComfyUI that integrates large language models to build text-driven applications and automate data processes, enhancing prompt responses by incorporating real-time web search, linked content extraction, and custom agent instructions. It supports both OpenAI’s GPT-like models and alternative models served via a local Ollama API. The core functionalities include Comfy Node Finder and Smart Assistant, along with additional agents like Flux Prompter, Custom Instructors, Python debugger, and scripter. The tool offers features for prompt processing, web search integration, model & API integration, custom instructions, image handling, logging & debugging, output compression, and more.
trip_planner_agent
VacAIgent is an AI tool that automates and enhances trip planning by leveraging the CrewAI framework. It integrates a user-friendly Streamlit interface for interactive travel planning. Users can input preferences and receive tailored travel plans with the help of autonomous AI agents. The tool allows for collaborative decision-making on cities and crafting complete itineraries based on specified preferences, all accessible via a streamlined Streamlit user interface. VacAIgent can be customized to use different AI models like GPT-3.5 or local models like Ollama for enhanced privacy and customization.
ROSGPT_Vision
ROSGPT_Vision is a new robotic framework designed to command robots using only two prompts: a Visual Prompt for visual semantic features and an LLM Prompt to regulate robotic reactions. It is based on the Prompting Robotic Modalities (PRM) design pattern and is used to develop CarMate, a robotic application for monitoring driver distractions and providing real-time vocal notifications. The framework leverages state-of-the-art language models to facilitate advanced reasoning about image data and offers a unified platform for robots to perceive, interpret, and interact with visual data through natural language. LangChain is used for easy customization of prompts, and the implementation includes the CarMate application for driver monitoring and assistance.
For similar tasks

MiniAI-Face-Recognition-LivenessDetection-ServerSDK
The MiniAiLive Face Recognition LivenessDetection Server SDK provides system integrators with fast, flexible, and extremely precise facial recognition that can be deployed across various scenarios, including security, access control, public safety, fintech, smart retail, and home protection. The SDK is fully on-premise, meaning all processing happens on the hosting server, and no data leaves the server. The project structure includes bin, cpp, flask, model, python, test_image, and Dockerfile directories. To set up the project on Linux, download the repo, install system dependencies, and copy libraries into the system folder. For Windows, contact MiniAiLive via email. The C++ example involves replacing the license key in main.cpp, building the project, and running it. The Python example requires installing dependencies and running the project. The Python Flask example involves replacing the license key in app.py, installing dependencies, and running the project. The Docker Flask example includes building the docker image and running it. To request a license, contact MiniAiLive. Contributions to the project are welcome by following specific steps. An online demo is available at https://demo.miniai.live. Related products include MiniAI-Face-Recognition-LivenessDetection-AndroidSDK, MiniAI-Face-Recognition-LivenessDetection-iOS-SDK, MiniAI-Face-LivenessDetection-AndroidSDK, MiniAI-Face-LivenessDetection-iOS-SDK, MiniAI-Face-Matching-AndroidSDK, and MiniAI-Face-Matching-iOS-SDK. MiniAiLive is a leading AI solutions company specializing in computer vision and machine learning technologies.

MiniAI-Face-LivenessDetection-AndroidSDK
The MiniAiLive Face Liveness Detection Android SDK provides advanced computer vision techniques to enhance security and accuracy on Android platforms. It offers 3D Passive Face Liveness Detection capabilities, ensuring that users are physically present and not using spoofing methods to access applications or services. The SDK is fully on-premise, with all processing happening on the hosting server, ensuring data privacy and security.

blinkid-ios
BlinkID iOS is a mobile SDK that enables developers to easily integrate ID scanning and data extraction capabilities into their iOS applications. The SDK supports scanning and processing various types of identity documents, such as passports, driver's licenses, and ID cards. It provides accurate and fast data extraction, including personal information and document details. With BlinkID iOS, developers can enhance their apps with secure and reliable ID verification functionality, improving user experience and streamlining identity verification processes.
cheat-sheet-pdf
The Cheat-Sheet Collection for DevOps, Engineers, IT professionals, and more is a curated list of cheat sheets for various tools and technologies commonly used in the software development and IT industry. It includes cheat sheets for Nginx, Docker, Ansible, Python, Go (Golang), Git, Regular Expressions (Regex), PowerShell, VIM, Jenkins, CI/CD, Kubernetes, Linux, Redis, Slack, Puppet, Google Cloud Developer, AI, Neural Networks, Machine Learning, Deep Learning & Data Science, PostgreSQL, Ajax, AWS, Infrastructure as Code (IaC), System Design, and Cyber Security.
L1B3RT45
L1B3RT45 is a tool designed for jailbreaking all flagship AI models. It is part of the FREEAI project and is named LIBERTAS. Users can join the BASI Discord community for support. The tool was created with love by Pliny the Prompter.
card-scanner-flutter
Card Scanner Flutter is a fast, accurate, and secure plugin for Flutter that allows users to scan debit and credit cards offline. It can scan card details such as the card number, expiry date, card holder name, and card issuer. Powered by Google's Machine Learning models, the plugin offers great performance and accuracy. Users can control parameters for speed and accuracy balance and benefit from an intuitive API. Suitable for various jobs such as mobile app developer, fintech product manager, software engineer, data scientist, and UI/UX designer. AI keywords include card scanner, flutter plugin, debit card, credit card, machine learning. Users can use this tool to scan cards, verify card details, extract card information, validate card numbers, and enhance security.
AwesomeLLM4APR
Awesome LLM for APR is a repository dedicated to exploring the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) in Automated Program Repair (APR). It provides a comprehensive collection of research papers, tools, and resources related to using LLMs for various scenarios such as repairing semantic bugs, security vulnerabilities, syntax errors, programming problems, static warnings, self-debugging, type errors, web UI tests, smart contracts, hardware bugs, performance bugs, API misuses, crash bugs, test case repairs, formal proofs, GitHub issues, code reviews, motion planners, human studies, and patch correctness assessments. The repository serves as a valuable reference for researchers and practitioners interested in leveraging LLMs for automated program repair.

ai_automation_suggester
An integration for Home Assistant that leverages AI models to understand your unique home environment and propose intelligent automations. By analyzing your entities, devices, areas, and existing automations, the AI Automation Suggester helps you discover new, context-aware use cases you might not have considered, ultimately streamlining your home management and improving efficiency, comfort, and convenience. The tool acts as a personal automation consultant, providing actionable YAML-based automations that can save energy, improve security, enhance comfort, and reduce manual intervention. It turns the complexity of a large Home Assistant environment into actionable insights and tangible benefits.
For similar jobs

ai_automation_suggester
An integration for Home Assistant that leverages AI models to understand your unique home environment and propose intelligent automations. By analyzing your entities, devices, areas, and existing automations, the AI Automation Suggester helps you discover new, context-aware use cases you might not have considered, ultimately streamlining your home management and improving efficiency, comfort, and convenience. The tool acts as a personal automation consultant, providing actionable YAML-based automations that can save energy, improve security, enhance comfort, and reduce manual intervention. It turns the complexity of a large Home Assistant environment into actionable insights and tangible benefits.
hass-ollama-conversation
The Ollama Conversation integration adds a conversation agent powered by Ollama in Home Assistant. This agent can be used in automations to query information provided by Home Assistant about your house, including areas, devices, and their states. Users can install the integration via HACS and configure settings such as API timeout, model selection, context size, maximum tokens, and other parameters to fine-tune the responses generated by the AI language model. Contributions to the project are welcome, and discussions can be held on the Home Assistant Community platform.
ComfyUI-Tara-LLM-Integration
Tara is a powerful node for ComfyUI that integrates Large Language Models (LLMs) to enhance and automate workflow processes. With Tara, you can create complex, intelligent workflows that refine and generate content, manage API keys, and seamlessly integrate various LLMs into your projects. It comprises nodes for handling OpenAI-compatible APIs, saving and loading API keys, composing multiple texts, and using predefined templates for OpenAI and Groq. Tara supports OpenAI and Grok models with plans to expand support to together.ai and Replicate. Users can install Tara via Git URL or ComfyUI Manager and utilize it for tasks like input guidance, saving and loading API keys, and generating text suitable for chaining in workflows.
aiscript
AiScript is a lightweight scripting language that runs on JavaScript. It supports arrays, objects, and functions as first-class citizens, and is easy to write without the need for semicolons or commas. AiScript runs in a secure sandbox environment, preventing infinite loops from freezing the host. It also allows for easy provision of variables and functions from the host.
askui
AskUI is a reliable, automated end-to-end automation tool that only depends on what is shown on your screen instead of the technology or platform you are running on.
bots
The 'bots' repository is a collection of guides, tools, and example bots for programming bots to play video games. It provides resources on running bots live, installing the BotLab client, debugging bots, testing bots in simulated environments, and more. The repository also includes example bots for games like EVE Online, Tribal Wars 2, and Elvenar. Users can learn about developing bots for specific games, syntax of the Elm programming language, and tools for memory reading development. Additionally, there are guides on bot programming, contributing to BotLab, and exploring Elm syntax and core library.
ain
Ain is a terminal HTTP API client designed for scripting input and processing output via pipes. It allows flexible organization of APIs using files and folders, supports shell-scripts and executables for common tasks, handles url-encoding, and enables sharing the resulting curl, wget, or httpie command-line. Users can put things that change in environment variables or .env-files, and pipe the API output for further processing. Ain targets users who work with many APIs using a simple file format and uses curl, wget, or httpie to make the actual calls.
LaVague
LaVague is an open-source Large Action Model framework that uses advanced AI techniques to compile natural language instructions into browser automation code. It leverages Selenium or Playwright for browser actions. Users can interact with LaVague through an interactive Gradio interface to automate web interactions. The tool requires an OpenAI API key for default examples and offers a Playwright integration guide. Contributors can help by working on outlined tasks, submitting PRs, and engaging with the community on Discord. The project roadmap is available to track progress, but users should exercise caution when executing LLM-generated code using 'exec'.




