
comfyui_LLM_Polymath
An advanced chat node integrating LLMs, real-time web search, image handling, and image scraping. Supports APIs from OpenAI, Google, Anthropic, Grok, DeepSeek, and local Ollama. Includes custom node finder, smart assistant tools, and growing subnodes like text masking and concept eraser.
Stars: 54
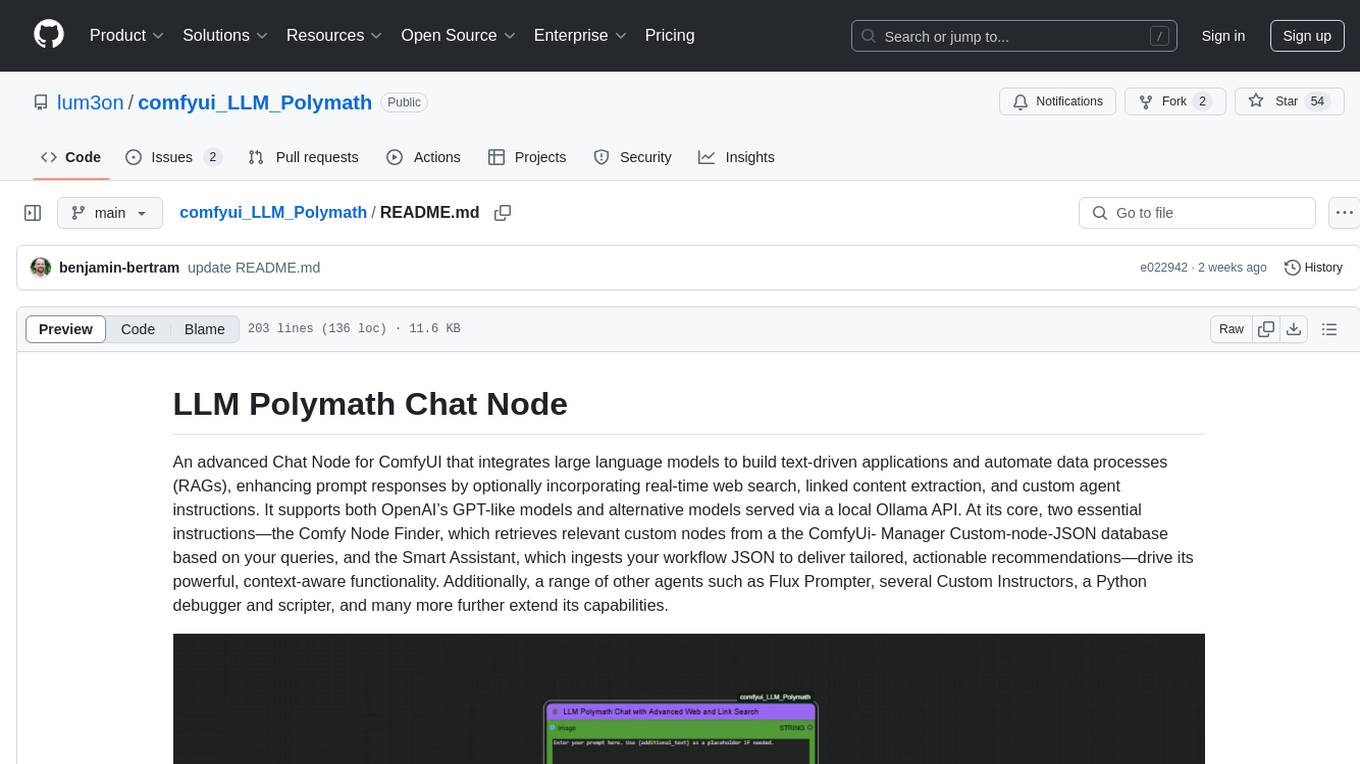
LLM Polymath Chat Node is an advanced Chat Node for ComfyUI that integrates large language models to build text-driven applications and automate data processes, enhancing prompt responses by incorporating real-time web search, linked content extraction, and custom agent instructions. It supports both OpenAI’s GPT-like models and alternative models served via a local Ollama API. The core functionalities include Comfy Node Finder and Smart Assistant, along with additional agents like Flux Prompter, Custom Instructors, Python debugger, and scripter. The tool offers features for prompt processing, web search integration, model & API integration, custom instructions, image handling, logging & debugging, output compression, and more.
README:
An advanced Chat Node for ComfyUI that integrates large language models to build text-driven applications and automate data processes (RAGs), enhancing prompt responses by optionally incorporating real-time web search, linked content extraction, and custom agent instructions. It supports both OpenAI’s GPT-like models and alternative models served via a local Ollama API. At its core, two essential instructions—the Comfy Node Finder, which retrieves relevant custom nodes from a the ComfyUi- Manager Custom-node-JSON database based on your queries, and the Smart Assistant, which ingests your workflow JSON to deliver tailored, actionable recommendations—drive its powerful, context-aware functionality. Additionally, a range of other agents such as Flux Prompter, several Custom Instructors, a Python debugger and scripter, and many more further extend its capabilities.
----
Placeholder Replacement: If your prompt contains the placeholder
{additional_text}, the node replaces it with the provided additional text. Otherwise, any additional text is appended. - Dynamic Augmentation: Depending on the settings, the node can automatically augment your prompt with web-fetched content or search results.
- URL Extraction: Scans the input prompt for URLs and uses BeautifulSoup to extract text from the linked pages.
-
Google Search Results: If enabled, it performs a Google search for your query, retrieves a specified number of results (controlled via
num_search_results), and appends the extracted content to the prompt. - Source Listing: Optionally appends all fetched sources to the prompt so that the language model’s response can reference them.
-
Model Loading: Loads model configurations from a local
config.jsonfile and fetches additional models from an Ollama API endpoint (http://127.0.0.1:11434/api/tags). -
API Selection:
- The model automatically selects the API depending on which model is selected from the list. The polymath currently supports Grok, Gemini, Gemma, Deepseek, and Claude.
- If Ollama is installed and running, the node uses the Ollama API.
- Chat History: Optionally retains context from previous interactions to allow for more natural, continuous conversations.
-
Instruction Files: The node scans a
custom_instructionsdirectory for.txtfiles and makes them available as options. -
Node Finder Specialization: If the custom instruction named “node finder” is selected, the node loads and appends information from a JSON file (
custom-node-list.json) to aid in finding specific nodes.
- Image Conversion: Converts provided image tensors into PIL images and encodes them as base64 strings. These are then included in the payload sent to the language model, enabling multimodal interactions.
-
Console Logging: When enabled (
Console_log), detailed information about the prompt augmentation process and API calls is printed to the console. - Seed Control: Uses a user-provided seed to help manage randomness and reproducibility.
-
Compression Options: If compression is enabled, the node appends a directive to the prompt that instructs the model to produce concise output. Three levels are available:
- Soft: Maximum output size ~250 characters.
- Medium: Maximum output size ~150 characters.
- Hard: Maximum output size ~75 characters.
ComfyUI Node Assistant
An advanced Agent that analyzes your specific use case and strictly uses the provided ../ComfyUI-Manager/custom-node-list.json reference to deliver consistent structured, ranked recommendations featuring node names, detailed descriptions, categories, inputs/outputs, and usage notes; it dynamically refines suggestions based on your requirements, ensuring you access both top-performing and underrated nodes categorized as Best Image Processing Nodes, Top Text-to-Image Nodes, Essential Utility Nodes, Best Inpainting Nodes, Advanced Control Nodes, Performance Optimization Nodes, Hidden Gems, Latent Processing Nodes, Mathematical Nodes, Noise Processing Nodes, Randomization Nodes, and Display & Show Nodes for optimal functionality, efficiency, and compatibility.
ComfyUI Smart Assistant
ComfyUI Smart Assistant Instruction: An advanced, context-aware AI integration that ingests your workflow JSON to thoroughly analyze your unique use case and deliver tailored, high-impact recommendations presented as structured, ranked insights—with each recommendation accompanied by names, detailed descriptions, categorical breakdowns, input/output specifications, and usage notes—while dynamically adapting to your evolving requirements through in-depth comparisons, alternative methodologies, and layered workflow enhancements; its robust capabilities extend to executing wildcard searches, deploying comprehensive error-handling strategies, offering real-time monitoring insights, and providing seamless integration guidance, all meticulously organized into key sections such as "Best Workflow Enhancements," "Essential Automation Tools," "Performance Optimization Strategies," "Advanced Customization Tips," "Hidden Gems & Lesser-Known Features," "Troubleshooting & Debugging," "Integration & Compatibility Advice," "Wildcard & Exploratory Searches," "Security & Compliance Measures," and "Real-Time Feedback & Monitoring"—ensuring peak functionality, efficiency, and compatibility while maximizing productivity and driving continuous improvement.
Polymath Scraper
An automated web scraper node designed for seamless gallery extraction, allowing users to input a gallery website URL and retrieve image data efficiently. Built on gallery-dl, it supports all websites listed in the official repository. with key keatures such as:
- URL-Based Extraction: Simply input a gallery URL to fetch images.
- Wide Website Support: Compatible with all sites supported by gallery-dl.
-
Output-Ready for Training: Provides structured outputs:
- List of Image Files: Downloaded images ready for use.
- List of Filenames: Organized for captioning and dataset creation.
- Modular Integration: Stack with the LLM Polymath Node for automated captioning, enabling end-to-end dataset preparation.
Ideal for creating large, labeled datasets for AI model training, reducing manual effort and streamlining workflow efficiency.
A versatile configuration node providing essential settings for language models (LLMs) and image generation workflows. Designed for maximum flexibility and control, it allows fine-tuning of generative behavior across multiple engines including text and image generation APIs.
-
Comprehensive LLM Controls: Fine-tune generative text outputs with key parameters:
- Temperature: Adjusts randomness in output (0.0–2.0, default 0.8).
- Top-p (Nucleus Sampling): Controls diversity via probability mass (0.0–1.0, default 0.95).
- Top-k: Limits to top-k most likely tokens (0–100, default 40).
- Max Output Tokens: Sets maximum length of output (-1 to 65536, default 1024).
- Response Format JSON: Toggle structured JSON output (default: False).
- Ollama Keep Alive: Controls idle timeout for Ollama connections (1–10, default 5).
- Request Timeout: Timeout for generation requests (0–600 sec, default 120).
-
DALL·E Image Settings: Customize generation style and quality:
-
Quality: Choose between
"standard"and"hd"(default: standard). -
Style: Select image tone, either
"vivid"or"natural"(default: vivid). - Size: Specify dimensions (1024x1024, 1792x1024, 1024x1792; default: 1024x1024).
- Number of Images: Set number of outputs per request (1–4, default: 1).
-
Quality: Choose between
The node exposes a range of configurable inputs:
-
Prompt: Main query text. Supports
{additional_text}placeholders. - Additional Text: Extra text that supplements or replaces the placeholder in the prompt.
- Seed: Integer seed for reproducibility.
-
Model: Dropdown of available models (merged from
config.jsonand Ollama API). - Custom Instruction: Choose from available instruction files.
- Enable Web Search: Toggle for fetching web content.
- List Sources: Whether to append the fetched sources to the prompt.
- Number of Search Results: Determines how many search results to process.
- Keep Context: Whether to retain chat history across interactions.
- Compress & Compression Level: Enable output compression and choose the level.
- Console Log: Toggle detailed logging.
- Image: Optionally pass an image tensor for multimodal input.
-
Clone the Repository:
git clone https://github.com/lum3on/comfyui_LLM_Polymath.git cd comfyui_LLM_Polymath -
Install Dependencies: The node automatically attempts to install missing Python packages (such as
googlesearch,requests, andbs4). However, you can also manually install dependencies using:pip install -r requirements.txt
-
Set the key in your Environment Variables: create a .env file in your comfy root folder and set your api-keys in the file like this:
OPENAI_API_KEY="your_api_key_here" ANTHROPIC_API_KEY="your_anthropic_api_key_here" XAI_API_KEY="your_xai_api_key_here" DEEPSEEK_API_KEY="your_deepseek_api_key_here" GEMINI_API_KEY="your_gemini_api_key_here"
OLLAMA (Ollama) enables you to run large language models locally with a few simple commands. Follow these instructions to install OLLAMA and download models.
Download the installer from the official website or install via Homebrew:
brew install ollamaRun the installation script directly from your terminal:
curl -fsSL https://ollama.com/install.sh | shVisit the Ollama Download Page and run the provided installer.
Once OLLAMA is installed, you can easily pull and run models. For example, to download the lightweight Gemma 2B model:
ollama pull gemma:2bAfter downloading, you can start interacting with the model using:
ollama run gemma:2bFor a full list of available models (including various sizes and specialized variants), please visit the official Ollama Model Library.
After you download a model via Ollama, it will automatically be listed in the model dropdown in Comfy after you restart it. This seamless integration means you don’t need to perform any additional configuration—the model is ready for use immediately within Comfy.
- Install OLLAMA on your system using the method appropriate for your operating system.
-
Download a Model with the
ollama pullcommand or use the run command and the model gets auto downloaded. -
Run the Model with
ollama run <model-name>to start a REPL and interact with it. - Keep the Cli open so that Comfy can acess the local Olama api
- Restart Comfy to have the downloaded model automatically appear in the model dropdown for easy selection.
By following these steps, you can quickly set up OLLAMA on your machine and begin experimenting with different large language models locally.
For further details on model customization and advanced usage, refer to the official documentation at Ollama Docs.
The following features are planned for the next Update.
- [ ] Node Finder Implementation in ComfyUI Manager: Integrate a full-featured node finder in the Comfy Manager
- [X] Advanced Parameter Node: Introduce an enhanced parameter node offering additional customization and control.
- [ ] Speed Improvements: Optimize processing and API response times for a more fluid user experience.
This project is licensed under the MIT License. See the LICENSE file for details.
This node integrates several libraries and APIs to deliver an advanced multimodal, web-augmented chat experience. Special thanks to all contributors and open source projects that made this work possible.
For any questions or further assistance, please open an issue on GitHub or contact the maintainer.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for comfyui_LLM_Polymath
Similar Open Source Tools

comfyui_LLM_Polymath
LLM Polymath Chat Node is an advanced Chat Node for ComfyUI that integrates large language models to build text-driven applications and automate data processes, enhancing prompt responses by incorporating real-time web search, linked content extraction, and custom agent instructions. It supports both OpenAI’s GPT-like models and alternative models served via a local Ollama API. The core functionalities include Comfy Node Finder and Smart Assistant, along with additional agents like Flux Prompter, Custom Instructors, Python debugger, and scripter. The tool offers features for prompt processing, web search integration, model & API integration, custom instructions, image handling, logging & debugging, output compression, and more.
Ollama-Colab-Integration
Ollama Colab Integration V4 is a tool designed to enhance the interaction and management of large language models. It allows users to quantize models within their notebook environment, access a variety of models through a user-friendly interface, and manage public endpoints efficiently. The tool also provides features like LiteLLM proxy control, model insights, and customizable model file templating. Users can troubleshoot model loading issues, CPU fallback strategies, and manage VRAM and RAM effectively. Additionally, the tool offers functionalities for downloading model files from Hugging Face, model conversion with high precision, model quantization using Q and Kquants, and securely uploading converted models to Hugging Face.
Vodalus-Expert-LLM-Forge
Vodalus Expert LLM Forge is a tool designed for crafting datasets and efficiently fine-tuning models using free open-source tools. It includes components for data generation, LLM interaction, RAG engine integration, model training, fine-tuning, and quantization. The tool is suitable for users at all levels and is accompanied by comprehensive documentation. Users can generate synthetic data, interact with LLMs, train models, and optimize performance for local execution. The tool provides detailed guides and instructions for setup, usage, and customization.
chatnio
Chat Nio is a next-generation AI one-stop solution that provides a rich and user-friendly interface for interacting with various AI models. It offers features such as AI chat conversation, rich format compatibility, markdown support, message menu support, multi-platform adaptation, dialogue memory, full-model file parsing, full-model DuckDuckGo online search, full-screen large text editing, model marketplace, preset support, site announcements, preference settings, internationalization support, and a rich admin system. Chat Nio also boasts a powerful channel management system that utilizes a self-developed channel distribution algorithm, supports multi-channel management, is compatible with multiple formats, allows for custom models, supports channel retries, enables balanced load within the same channel, and provides channel model mapping and user grouping. Additionally, Chat Nio offers forwarding API services that are compatible with multiple formats in the OpenAI universal format and support multiple model compatible layers. It also provides a custom build and install option for highly customizable deployments. Chat Nio is an open-source project licensed under the Apache License 2.0 and welcomes contributions from the community.
logicstudio.ai
LogicStudio.ai is a powerful visual canvas-based tool for building, managing, and visualizing complex logic flows involving AI agents, data inputs, and outputs. It provides an intuitive interface to streamline development processes by offering features like drag-and-drop canvas design, dynamic components, real-time connections, import/export capabilities, zoom & pan controls, file management, AI integration, editable views, and various output formats. Users can easily add, connect, configure, and manage components to create interactive systems and workflows.
greenmask
Greenmask is a powerful open-source utility designed for logical database backup dumping, anonymization, synthetic data generation, and restoration. It is highly customizable, stateless, and backward-compatible with existing PostgreSQL utilities. Greenmask supports advanced subset systems, deterministic transformers, dynamic parameters, transformation conditions, and more. It is cross-platform, database type safe, extensible, and supports parallel execution and various storage options. Ideal for backup and restoration tasks, anonymization, transformation, and data masking.
Zentara-Code
Zentara Code is an AI coding assistant for VS Code that turns chat instructions into precise, auditable changes in the codebase. It is optimized for speed, safety, and correctness through parallel execution, LSP semantics, and integrated runtime debugging. It offers features like parallel subagents, integrated LSP tools, and runtime debugging for efficient code modification and analysis.

cline-based-code-generator
HAI Code Generator is a cutting-edge tool designed to simplify and automate task execution while enhancing code generation workflows. Leveraging Specif AI, it streamlines processes like task execution, file identification, and code documentation through intelligent automation and AI-driven capabilities. Built on Cline's powerful foundation for AI-assisted development, HAI Code Generator boosts productivity and precision by automating task execution and integrating file management capabilities. It combines intelligent file indexing, context generation, and LLM-driven automation to minimize manual effort and ensure task accuracy. Perfect for developers and teams aiming to enhance their workflows.
ai_automation_suggester
An integration for Home Assistant that leverages AI models to understand your unique home environment and propose intelligent automations. By analyzing your entities, devices, areas, and existing automations, the AI Automation Suggester helps you discover new, context-aware use cases you might not have considered, ultimately streamlining your home management and improving efficiency, comfort, and convenience. The tool acts as a personal automation consultant, providing actionable YAML-based automations that can save energy, improve security, enhance comfort, and reduce manual intervention. It turns the complexity of a large Home Assistant environment into actionable insights and tangible benefits.
eole
EOLE is an open language modeling toolkit based on PyTorch. It aims to provide a research-friendly approach with a comprehensive yet compact and modular codebase for experimenting with various types of language models. The toolkit includes features such as versatile training and inference, dynamic data transforms, comprehensive large language model support, advanced quantization, efficient finetuning, flexible inference, and tensor parallelism. EOLE is a work in progress with ongoing enhancements in configuration management, command line entry points, reproducible recipes, core API simplification, and plans for further simplification, refactoring, inference server development, additional recipes, documentation enhancement, test coverage improvement, logging enhancements, and broader model support.

UltraRAG
The UltraRAG framework is a researcher and developer-friendly RAG system solution that simplifies the process from data construction to model fine-tuning in domain adaptation. It introduces an automated knowledge adaptation technology system, supporting no-code programming, one-click synthesis and fine-tuning, multidimensional evaluation, and research-friendly exploration work integration. The architecture consists of Frontend, Service, and Backend components, offering flexibility in customization and optimization. Performance evaluation in the legal field shows improved results compared to VanillaRAG, with specific metrics provided. The repository is licensed under Apache-2.0 and encourages citation for support.

swark
Swark is a VS Code extension that automatically generates architecture diagrams from code using large language models (LLMs). It is directly integrated with GitHub Copilot, requires no authentication or API key, and supports all languages. Swark helps users learn new codebases, review AI-generated code, improve documentation, understand legacy code, spot design flaws, and gain test coverage insights. It saves output in a 'swark-output' folder with diagram and log files. Source code is only shared with GitHub Copilot for privacy. The extension settings allow customization for file reading, file extensions, exclusion patterns, and language model selection. Swark is open source under the GNU Affero General Public License v3.0.
FunGen-AI-Powered-Funscript-Generator
FunGen is a Python-based tool that uses AI to generate Funscript files from VR and 2D POV videos. It enables fully automated funscript creation for individual scenes or entire folders of videos. The tool includes features like automatic system scaling support, quick installation guides for Windows, Linux, and macOS, manual installation instructions, NVIDIA GPU setup, AMD GPU acceleration, YOLO model download, GUI settings, GitHub token setup, command-line usage, modular systems for funscript filtering and motion tracking, performance and parallel processing tips, and more. The project is still in early development stages and is not intended for commercial use.
langmanus
LangManus is a community-driven AI automation framework that combines language models with specialized tools for tasks like web search, crawling, and Python code execution. It implements a hierarchical multi-agent system with agents like Coordinator, Planner, Supervisor, Researcher, Coder, Browser, and Reporter. The framework supports LLM integration, search and retrieval tools, Python integration, workflow management, and visualization. LangManus aims to give back to the open-source community and welcomes contributions in various forms.
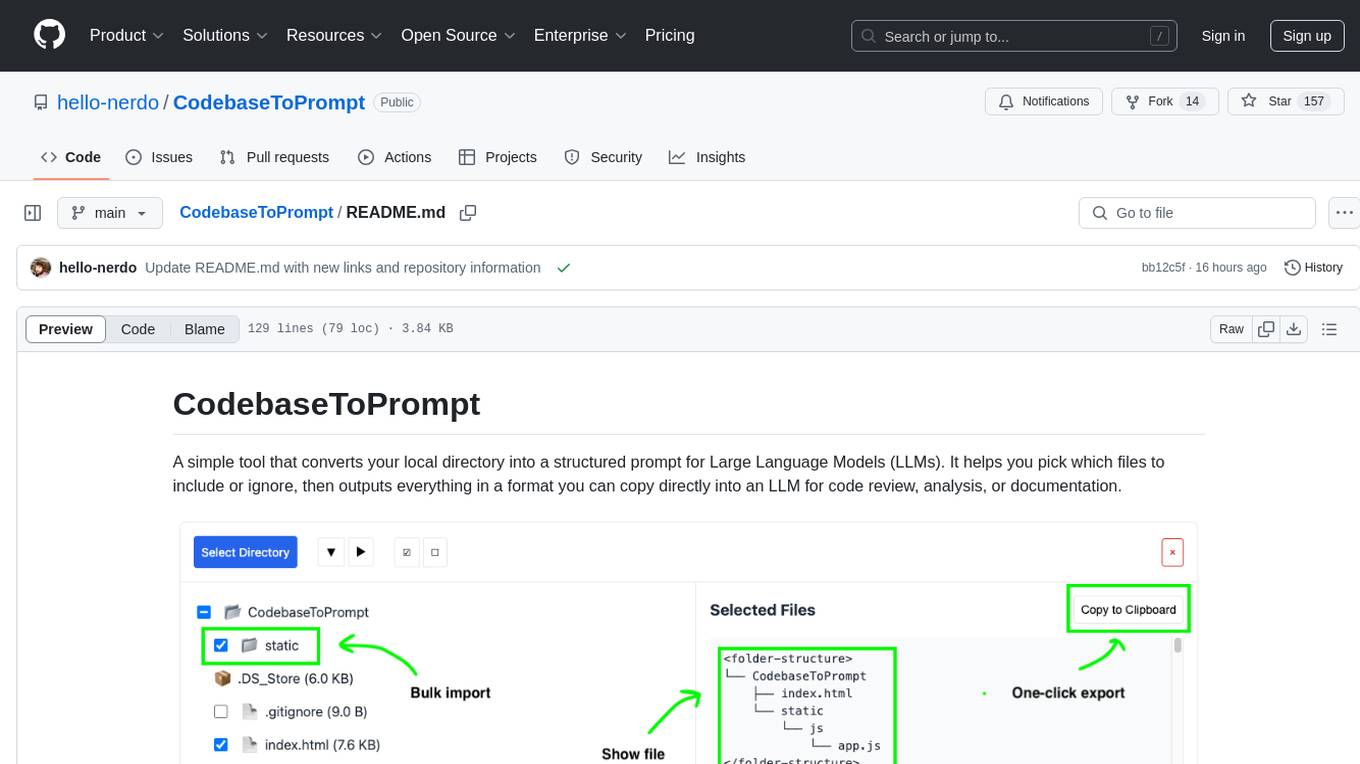
CodebaseToPrompt
CodebaseToPrompt is a tool that converts a local directory into a structured prompt for Large Language Models (LLMs). It allows users to select specific files for code review, analysis, or documentation by exploring and filtering through the file tree in an interactive interface. The tool generates a formatted output that can be directly used with LLMs, estimates token count, and supports flexible text selection. Users can deploy the tool using Docker for self-contained usage and can contribute to the project by opening issues or submitting pull requests.
yn
Yank Note is a highly extensible Markdown editor designed for productivity. It offers features like easy-to-use interface, powerful support for version control and various embedded content, high compatibility with local Markdown files, plug-in extension support, and encryption for saving private files. Users can write their own plug-ins to expand the editor's functionality. However, for more extendability, security protection is sacrificed. The tool supports sync scrolling, outline navigation, version control, encryption, auto-save, editing assistance, image pasting, attachment embedding, code running, to-do list management, quick file opening, integrated terminal, Katex expression, GitHub-style Markdown, multiple data locations, external link conversion, HTML resolving, multiple formats export, TOC generation, table cell editing, title link copying, embedded applets, various graphics embedding, mind map display, custom container support, macro replacement, image hosting service, OpenAI auto completion, and custom plug-ins development.
For similar tasks

comfyui_LLM_Polymath
LLM Polymath Chat Node is an advanced Chat Node for ComfyUI that integrates large language models to build text-driven applications and automate data processes, enhancing prompt responses by incorporating real-time web search, linked content extraction, and custom agent instructions. It supports both OpenAI’s GPT-like models and alternative models served via a local Ollama API. The core functionalities include Comfy Node Finder and Smart Assistant, along with additional agents like Flux Prompter, Custom Instructors, Python debugger, and scripter. The tool offers features for prompt processing, web search integration, model & API integration, custom instructions, image handling, logging & debugging, output compression, and more.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.