RepoAgent
An LLM-powered repository agent designed to assist developers and teams in generating documentation and understanding repositories quickly.
Stars: 425
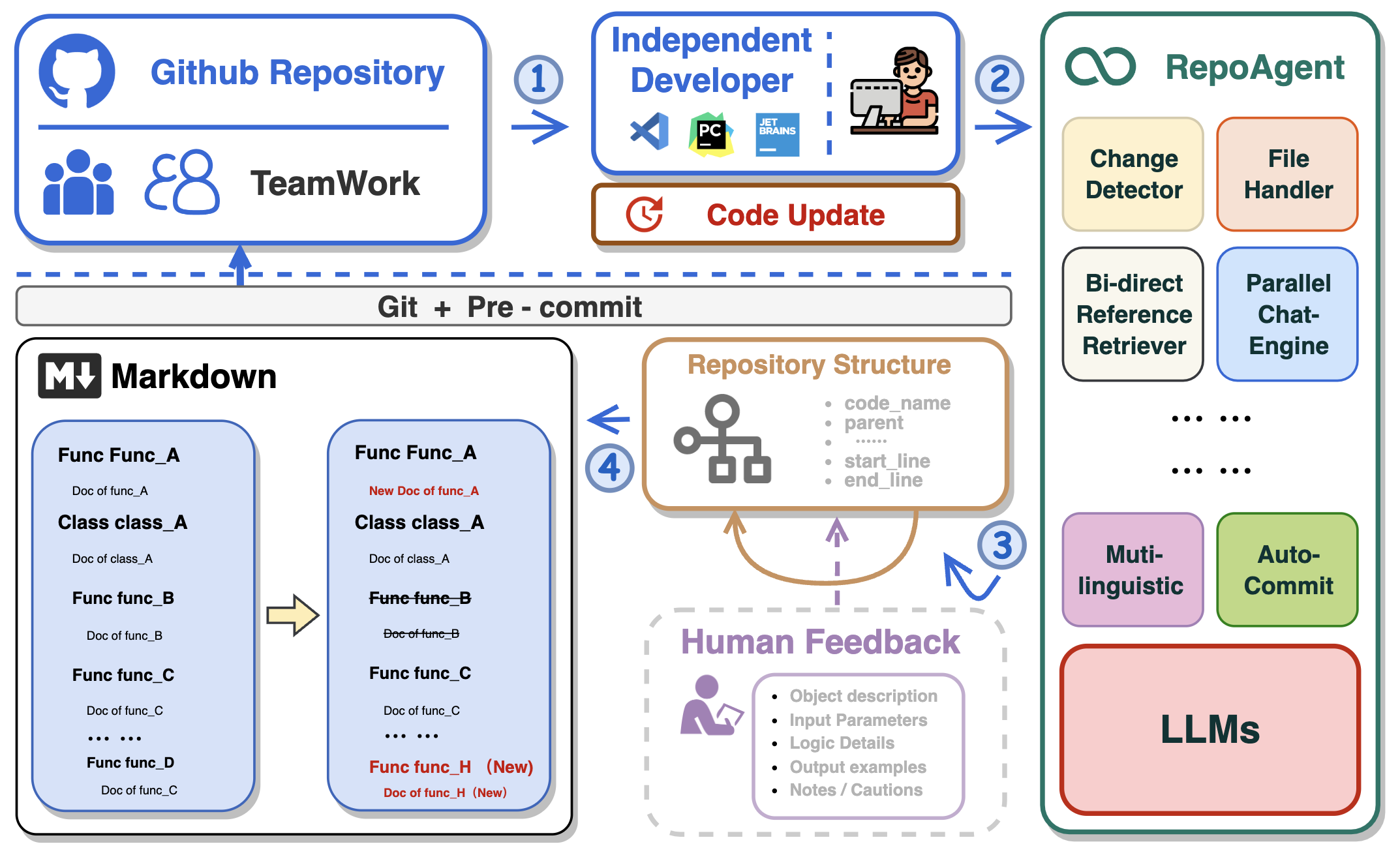
RepoAgent is an LLM-powered framework designed for repository-level code documentation generation. It automates the process of detecting changes in Git repositories, analyzing code structure through AST, identifying inter-object relationships, replacing Markdown content, and executing multi-threaded operations. The tool aims to assist developers in understanding and maintaining codebases by providing comprehensive documentation, ultimately improving efficiency and saving time.
README:
In the realm of computer programming, the significance of comprehensive project documentation, including detailed explanations for each Python file, cannot be overstated. Such documentation serves as the cornerstone for understanding, maintaining, and enhancing the codebase. It provides essential context and rationale for the code, making it easier for current and future developers to comprehend the purpose, functionality, and structure of the software. It not only facilitates current and future developers in grasping the project's purpose and structure but also ensures that the project remains accessible and modifiable over time, significantly easing the learning curve for new team members.
Traditionally, creating and maintaining software documentation demanded significant human effort and expertise, a challenge for small teams without dedicated personnel. The introduction of Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT has transformed this, enabling AI to handle much of the documentation process. This shift allows human developers to focus on verification and fine-tuning, greatly reducing the manual burden of documentation.
🏆 Our goal is to create an intelligent document assistant that helps people read and understand repositories and generate documents, ultimately helping people improve efficiency and save time.
- 🤖 Automatically detects changes in Git repositories, tracking additions, deletions, and modifications of files.
- 📝 Independently analyzes the code structure through AST, generating documents for individual objects.
- 🔍 Accurate identification of inter-object bidirectional invocation relationships, enriching the global perspective of document content.
- 📚 Seamlessly replaces Markdown content based on changes, maintaining consistency in documentation.
- 🕙 Executes multi-threaded concurrent operations, enhancing the efficiency of document generation.
- 👭 Offer a sustainable, automated documentation update method for team collaboration.
- 😍 Display Code Documentation in an amazing way. (with document book per project powered by Gitbook)
This repository supports GitHub Actions for automating workflows such as building, testing, and deploying. For detailed instructions on setting up and using GitHub Actions with this repository, please refer to the actions/run-repoagent.
Install the repoagent package directly using pip:
pip install repoagentIf you're looking to contribute or set up a development environment:
-
Install PDM: If you haven't already, install PDM.
-
Use CodeSpace, or Clone the Repository:
- Use CodeSpace The easiest way to get RepoAgent enviornment. Click below to use the GitHub Codespace, then go to the next step.
- Clone the Repository
git clone https://github.com/LOGIC-10/RepoAgent.git cd RepoAgent -
Setup with PDM
-
Initialize the Python virtual environment. Make sure to run the below cmd in
/RepoAgentdirectory:pdm venv create --name repoagent
-
Install dependencies using PDM
pdm install
-
Before configuring specific parameters for RepoAgent, please ensure that the OpenAI API is configured as an environment variable in the command line:
export OPENAI_API_KEY=YOUR_API_KEY # on Linux/Mac
set OPENAI_API_KEY=YOUR_API_KEY # on Windows
$Env:OPENAI_API_KEY = "YOUR_API_KEY" # on Windows (PowerShell)Enter the root directory of RepoAgent and try the following command in the terminal:
repoagent run #this command will generate doc, or update docs(pre-commit-hook will automatically call this)
repoagent run --print-hierarchy # Print how repo-agent parse the target repoThe run command supports the following optional flags (if set, will override config defaults):
-
-m,--modelTEXT: Specifies the model to use for completion. Default:gpt-3.5-turbo -
-t,--temperatureFLOAT: Sets the generation temperature for the model. Lower values make the model more deterministic. Default:0.2 -
-r,--request-timeoutINTEGER: Defines the timeout in seconds for the API request. Default:60 -
-b,--base-urlTEXT: The base URL for the API calls. Default:https://api.openai.com/v1 -
-tp,--target-repo-pathPATH: The file system path to the target repository. Used as the root for documentation generation. Default:path/to/your/target/repository -
-hp,--hierarchy-pathTEXT: The name or path for the project hierarchy file, used to organize documentation structure. Default:.project_doc_record -
-mdp,--markdown-docs-pathTEXT: The folder path where Markdown documentation will be stored or generated. Default:markdown_docs -
-i,--ignore-listTEXT: A list of files or directories to ignore during documentation generation, separated by commas. -
-l,--languageTEXT: The ISO 639 code or language name for the documentation. Default:Chinese -
-ll,--log-level[DEBUG|INFO|WARNING|ERROR|CRITICAL]: Sets the logging level for the application. Default:INFO
You can also try the following feature
repoagent clean # Remove repoagent-related cache
repoagent diff # Check what docs will be updated/generated based on current code changeIf it's your first time generating documentation for the target repository, RepoAgent will automatically create a JSON file maintaining the global structure information and a folder named Markdown_Docs in the root directory of the target repository for storing documents.
Once you have initially generated the global documentation for the target repository, or if the project you cloned already contains global documentation information, you can then seamlessly and automatically maintain internal project documentation with your team by configuring the pre-commit hook in the target repository!
RepoAgent currently supports generating documentation for projects, which requires some configuration in the target repository.
First, ensure that the target repository is a git repository and has been initialized.
git initInstall pre-commit in the target repository to detect changes in the git repository.
pip install pre-commitCreate a file named .pre-commit-config.yaml in the root directory of the target repository. An example is as follows:
repos:
- repo: local
hooks:
- id: repo-agent
name: RepoAgent
entry: repoagent
language: system
pass_filenames: false # prevent from passing filenames to the hook
# You can specify the file types that trigger the hook, but currently only python is supported.
types: [python]For specific configuration methods of hooks, please refer to pre-commit. After configuring the yaml file, execute the following command to install the hook.
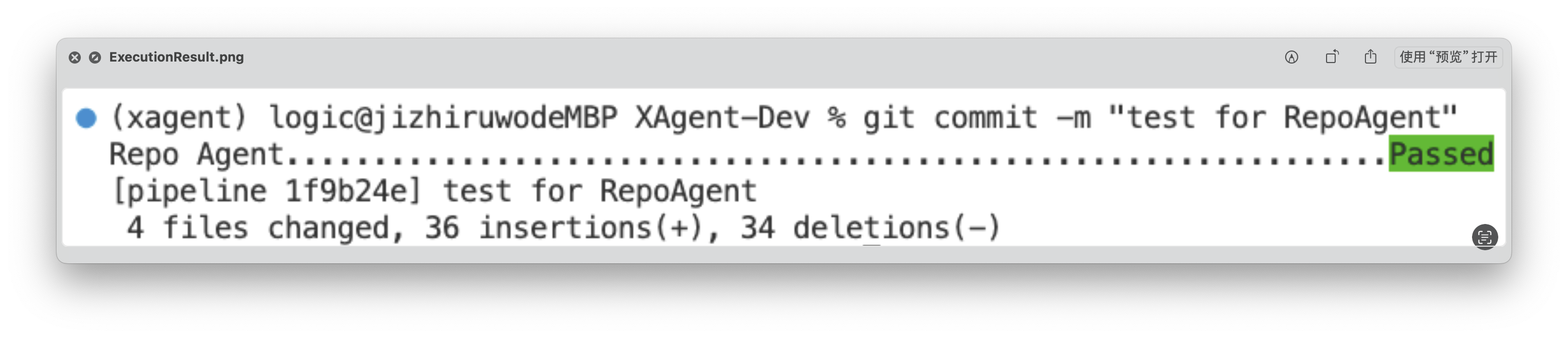
pre-commit installIn this way, each git commit will trigger the RepoAgent's hook, automatically detecting changes in the target repository and generating corresponding documents. Next, you can make some modifications to the target repository, such as adding a new file to the target repository, or modifying an existing file. You just need to follow the normal git workflow: git add, git commit -m "your commit message", git push The RepoAgent hook will automatically trigger at git commit, detect the files you added in the previous step, and generate corresponding documents.
After execution, RepoAgent will automatically modify the staged files in the target repository and formally submit the commit. After the execution is completed, the green "Passed" will be displayed, as shown in the figure below:
The generated document will be stored in the specified folder in the root directory of the target warehouse. The rendering of the generated document is as shown below:
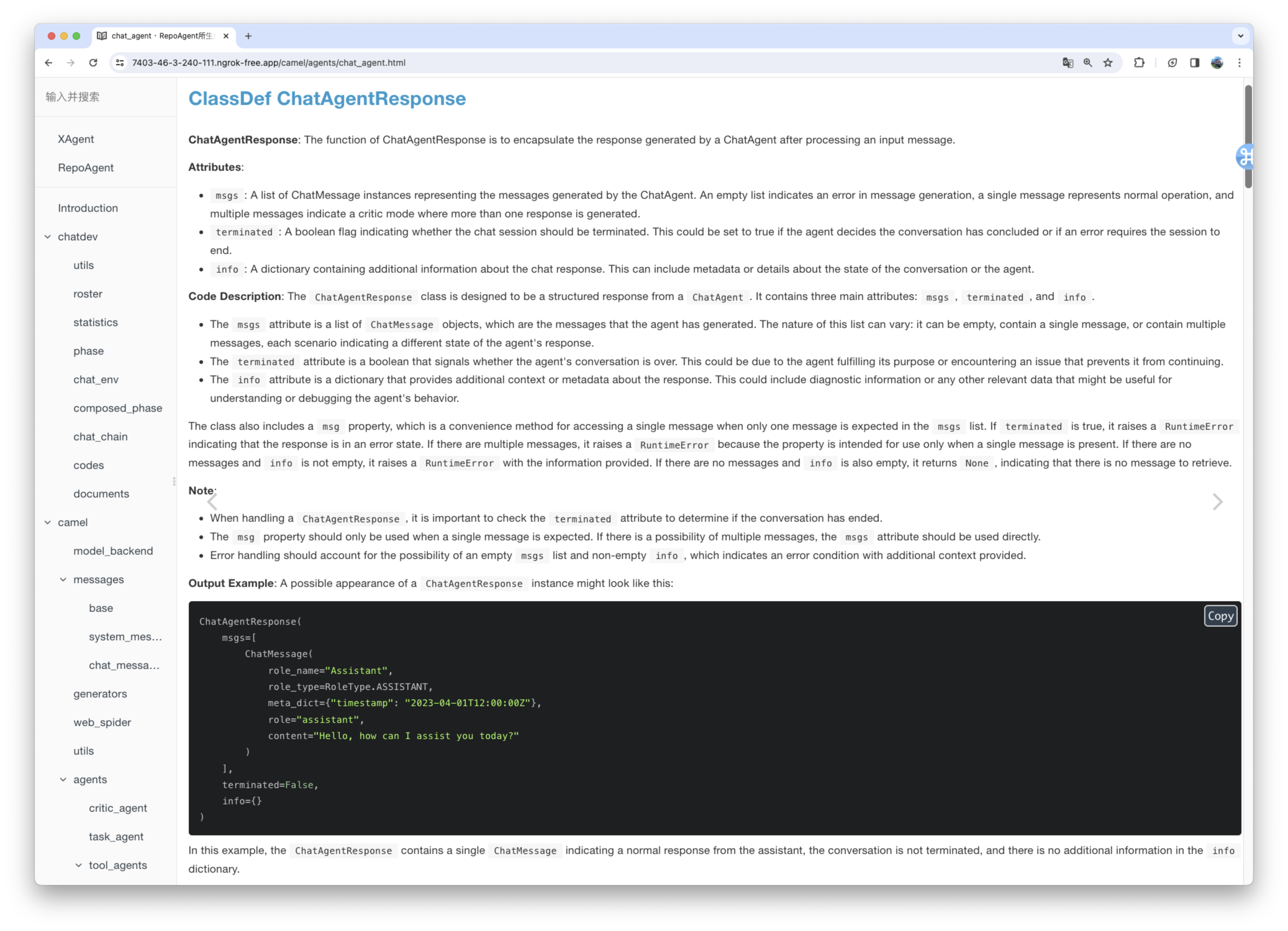
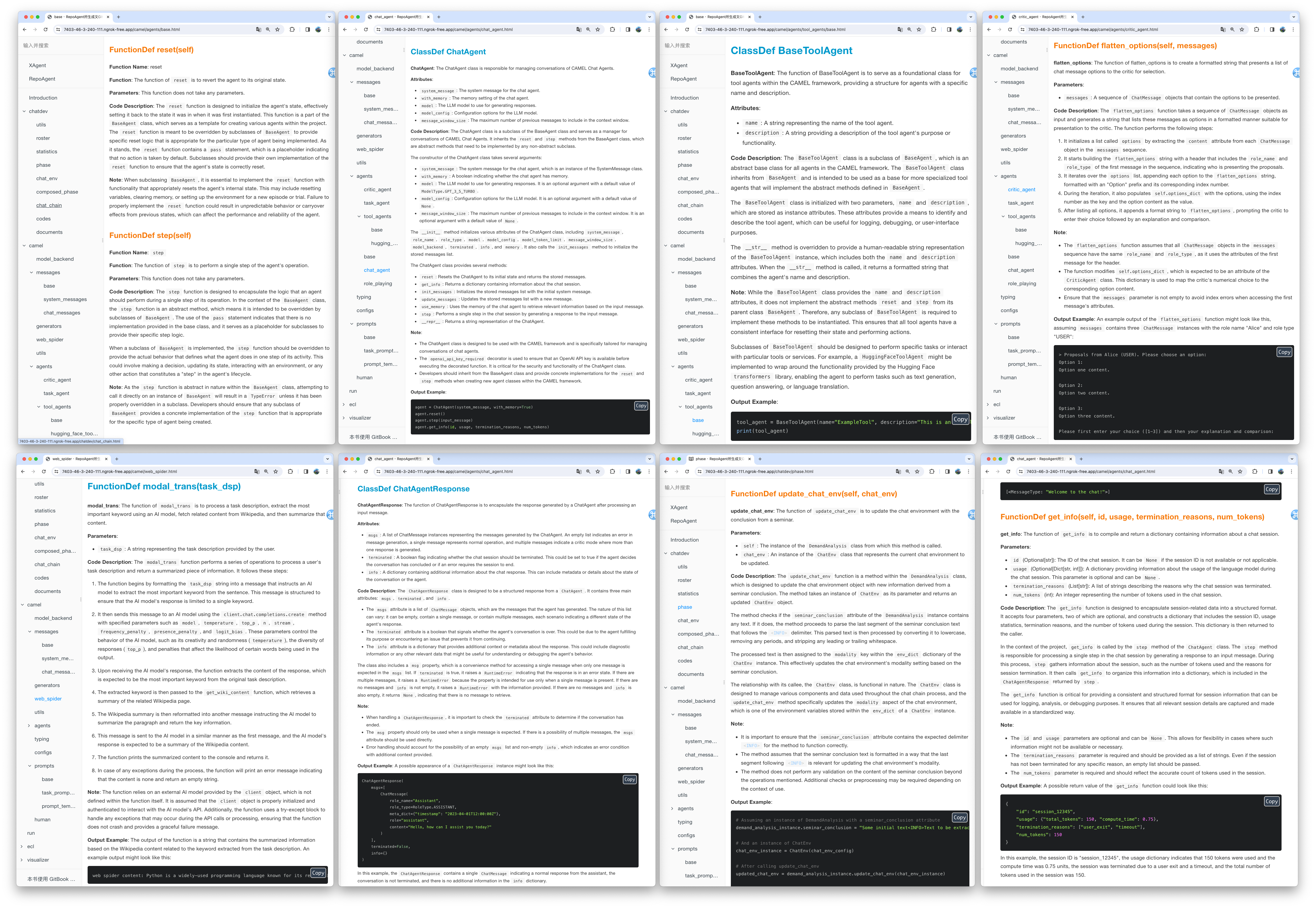
We utilized the default model gpt-3.5-turbo to generate documentation for the XAgent project, which comprises approximately 270,000 lines of code. You can view the results of this generation in the Markdown_Docs directory of the XAgent project on GitHub. For enhanced documentation quality, we suggest considering more advanced models like gpt-4-1106 or gpt-4-0125-preview.
In the end, you can flexibly adjust the output format, template, and other aspects of the document by customizing the prompt. We are excited about your exploration of a more scientific approach to Automated Technical Writing and your contributions to the community.
We conceptualize Chat With Repo as a unified gateway for these downstream applications, acting as a connector that links RepoAgent to human users and other AI agents. Our future research will focus on adapting the interface to various downstream applications and customizing it to meet their unique characteristics and implementation requirements.
Here we demonstrate a preliminary prototype of one of our downstream tasks: Automatic Q&A for Issues and Code Explanation. You can start the server by running the following code.
pip install repoagent[chat-with-repo]
repoagent chat-with-repo- [ ] Generate README.md automatically combining with the global documentation
- [ ] Multi-programming-language support Support more programming languages like Java, C or C++, etc.
- [x] Local model support like Llama, chatGLM, Qwen, GLM4, etc.
Here are featured cases that have adopted RepoAgent.
- MiniCPM: An edge-side LLM of 2B size, comparable to 7B model.
- ChatDev: Collaborative AI agents for software development.
- XAgent: An Autonomous LLM Agent for Complex Task Solving.
- EasyRL4Rec: A user-friendly RL library for recommender systems.
@misc{luo2024repoagent,
title={RepoAgent: An LLM-Powered Open-Source Framework for Repository-level Code Documentation Generation},
author={Qinyu Luo and Yining Ye and Shihao Liang and Zhong Zhang and Yujia Qin and Yaxi Lu and Yesai Wu and Xin Cong and Yankai Lin and Yingli Zhang and Xiaoyin Che and Zhiyuan Liu and Maosong Sun},
year={2024},
eprint={2402.16667},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CL}
}For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for RepoAgent
Similar Open Source Tools

RepoAgent
RepoAgent is an LLM-powered framework designed for repository-level code documentation generation. It automates the process of detecting changes in Git repositories, analyzing code structure through AST, identifying inter-object relationships, replacing Markdown content, and executing multi-threaded operations. The tool aims to assist developers in understanding and maintaining codebases by providing comprehensive documentation, ultimately improving efficiency and saving time.
langmanus
LangManus is a community-driven AI automation framework that combines language models with specialized tools for tasks like web search, crawling, and Python code execution. It implements a hierarchical multi-agent system with agents like Coordinator, Planner, Supervisor, Researcher, Coder, Browser, and Reporter. The framework supports LLM integration, search and retrieval tools, Python integration, workflow management, and visualization. LangManus aims to give back to the open-source community and welcomes contributions in various forms.

patchwork
PatchWork is an open-source framework designed for automating development tasks using large language models. It enables users to automate workflows such as PR reviews, bug fixing, security patching, and more through a self-hosted CLI agent and preferred LLMs. The framework consists of reusable atomic actions called Steps, customizable LLM prompts known as Prompt Templates, and LLM-assisted automations called Patchflows. Users can run Patchflows locally in their CLI/IDE or as part of CI/CD pipelines. PatchWork offers predefined patchflows like AutoFix, PRReview, GenerateREADME, DependencyUpgrade, and ResolveIssue, with the flexibility to create custom patchflows. Prompt templates are used to pass queries to LLMs and can be customized. Contributions to new patchflows, steps, and the core framework are encouraged, with chat assistants available to aid in the process. The roadmap includes expanding the patchflow library, introducing a debugger and validation module, supporting large-scale code embeddings, parallelization, fine-tuned models, and an open-source GUI. PatchWork is licensed under AGPL-3.0 terms, while custom patchflows and steps can be shared using the Apache-2.0 licensed patchwork template repository.
agents
Polymarket Agents is a developer framework and set of utilities for building AI agents to trade autonomously on Polymarket. It integrates with Polymarket API, provides AI agent utilities for prediction markets, supports local and remote RAG, sources data from various services, and offers comprehensive LLM tools for prompt engineering. The architecture features modular components like APIs and scripts for managing local environments, server set-up, and CLI for end-user commands.
honcho
Honcho is a platform for creating personalized AI agents and LLM powered applications for end users. The repository is a monorepo containing the server/API for managing database interactions and storing application state, along with a Python SDK. It utilizes FastAPI for user context management and Poetry for dependency management. The API can be run using Docker or manually by setting environment variables. The client SDK can be installed using pip or Poetry. The project is open source and welcomes contributions, following a fork and PR workflow. Honcho is licensed under the AGPL-3.0 License.
SWELancer-Benchmark
SWE-Lancer is a benchmark repository containing datasets and code for the paper 'SWE-Lancer: Can Frontier LLMs Earn $1 Million from Real-World Freelance Software Engineering?'. It provides instructions for package management, building Docker images, configuring environment variables, and running evaluations. Users can use this tool to assess the performance of language models in real-world freelance software engineering tasks.
TaskWeaver
TaskWeaver is a code-first agent framework designed for planning and executing data analytics tasks. It interprets user requests through code snippets, coordinates various plugins to execute tasks in a stateful manner, and preserves both chat history and code execution history. It supports rich data structures, customized algorithms, domain-specific knowledge incorporation, stateful execution, code verification, easy debugging, security considerations, and easy extension. TaskWeaver is easy to use with CLI and WebUI support, and it can be integrated as a library. It offers detailed documentation, demo examples, and citation guidelines.
cover-agent
CodiumAI Cover Agent is a tool designed to help increase code coverage by automatically generating qualified tests to enhance existing test suites. It utilizes Generative AI to streamline development workflows and is part of a suite of utilities aimed at automating the creation of unit tests for software projects. The system includes components like Test Runner, Coverage Parser, Prompt Builder, and AI Caller to simplify and expedite the testing process, ensuring high-quality software development. Cover Agent can be run via a terminal and is planned to be integrated into popular CI platforms. The tool outputs debug files locally, such as generated_prompt.md, run.log, and test_results.html, providing detailed information on generated tests and their status. It supports multiple LLMs and allows users to specify the model to use for test generation.

unitycatalog
Unity Catalog is an open and interoperable catalog for data and AI, supporting multi-format tables, unstructured data, and AI assets. It offers plugin support for extensibility and interoperates with Delta Sharing protocol. The catalog is fully open with OpenAPI spec and OSS implementation, providing unified governance for data and AI with asset-level access control enforced through REST APIs.
NeoGPT
NeoGPT is an AI assistant that transforms your local workspace into a powerhouse of productivity from your CLI. With features like code interpretation, multi-RAG support, vision models, and LLM integration, NeoGPT redefines how you work and create. It supports executing code seamlessly, multiple RAG techniques, vision models, and interacting with various language models. Users can run the CLI to start using NeoGPT and access features like Code Interpreter, building vector database, running Streamlit UI, and changing LLM models. The tool also offers magic commands for chat sessions, such as resetting chat history, saving conversations, exporting settings, and more. Join the NeoGPT community to experience a new era of efficiency and contribute to its evolution.

DevDocs
DevDocs is a platform designed to simplify the process of digesting technical documentation for software engineers and developers. It automates the extraction and conversion of web content into markdown format, making it easier for users to access and understand the information. By crawling through child pages of a given URL, DevDocs provides a streamlined approach to gathering relevant data and integrating it into various tools for software development. The tool aims to save time and effort by eliminating the need for manual research and content extraction, ultimately enhancing productivity and efficiency in the development process.
pipecat-flows
Pipecat Flows is a framework designed for building structured conversations in AI applications. It allows users to create both predefined conversation paths and dynamically generated flows, handling state management and LLM interactions. The framework includes a Python module for building conversation flows and a visual editor for designing and exporting flow configurations. Pipecat Flows is suitable for scenarios such as customer service scripts, intake forms, personalized experiences, and complex decision trees.
lmql
LMQL is a programming language designed for large language models (LLMs) that offers a unique way of integrating traditional programming with LLM interaction. It allows users to write programs that combine algorithmic logic with LLM calls, enabling model reasoning capabilities within the context of the program. LMQL provides features such as Python syntax integration, rich control-flow options, advanced decoding techniques, powerful constraints via logit masking, runtime optimization, sync and async API support, multi-model compatibility, and extensive applications like JSON decoding and interactive chat interfaces. The tool also offers library integration, flexible tooling, and output streaming options for easy model output handling.
middleware
Middleware is an open-source engineering management tool that helps engineering leaders measure and analyze team effectiveness using DORA metrics. It integrates with CI/CD tools, automates DORA metric collection and analysis, visualizes key performance indicators, provides customizable reports and dashboards, and integrates with project management platforms. Users can set up Middleware using Docker or manually, generate encryption keys, set up backend and web servers, and access the application to view DORA metrics. The tool calculates DORA metrics using GitHub data, including Deployment Frequency, Lead Time for Changes, Mean Time to Restore, and Change Failure Rate. Middleware aims to provide DORA metrics to users based on their Git data, simplifying the process of tracking software delivery performance and operational efficiency.
torchchat
torchchat is a codebase showcasing the ability to run large language models (LLMs) seamlessly. It allows running LLMs using Python in various environments such as desktop, server, iOS, and Android. The tool supports running models via PyTorch, chatting, generating text, running chat in the browser, and running models on desktop/server without Python. It also provides features like AOT Inductor for faster execution, running in C++ using the runner, and deploying and running on iOS and Android. The tool supports popular hardware and OS including Linux, Mac OS, Android, and iOS, with various data types and execution modes available.

lhotse
Lhotse is a Python library designed to make speech and audio data preparation flexible and accessible. It aims to attract a wider community to speech processing tasks by providing a Python-centric design and an expressive command-line interface. Lhotse offers standard data preparation recipes, PyTorch Dataset classes for speech tasks, and efficient data preparation for model training with audio cuts. It supports data augmentation, feature extraction, and feature-space cut mixing. The tool extends Kaldi's data preparation recipes with seamless PyTorch integration, human-readable text manifests, and convenient Python classes.
For similar tasks

RepoAgent
RepoAgent is an LLM-powered framework designed for repository-level code documentation generation. It automates the process of detecting changes in Git repositories, analyzing code structure through AST, identifying inter-object relationships, replacing Markdown content, and executing multi-threaded operations. The tool aims to assist developers in understanding and maintaining codebases by providing comprehensive documentation, ultimately improving efficiency and saving time.

brokk
Brokk is a code assistant tool named after the Norse god of the forge. It is designed to understand code semantically, enabling LLMs to work effectively on large codebases. Users can sign up at Brokk.ai, install jbang, and follow instructions to run Brokk. The tool uses Gradle with Scala support and requires JDK 21 or newer for building. Brokk aims to enhance code comprehension and productivity by providing semantic understanding of code.
python-repomix
Repomix is a powerful tool that packs your entire repository into a single, AI-friendly file. It formats your codebase for easy AI comprehension, provides token counts, is simple to use with one command, customizable, git-aware, security-focused, and offers advanced code compression. It supports multiprocessing or threading for faster analysis, automatically handles various file encodings, and includes built-in security checks. Repomix can be used with uvx, pipx, or Docker. It offers various configuration options for output style, security checks, compression modes, ignore patterns, and remote repository processing. The tool can be used for code review, documentation generation, test case generation, code quality assessment, library overview, API documentation review, code architecture analysis, and configuration analysis. Repomix can also run as an MCP server for AI assistants like Claude, providing tools for packaging codebases, reading output files, searching within outputs, reading files from the filesystem, listing directory contents, generating Claude Agent Skills, and more.
awesome-ai-coding
Awesome-AI-Coding is a curated list of AI coding topics, projects, datasets, LLM models, embedding models, papers, blogs, products, startups, and peer awesome lists related to artificial intelligence in coding. It includes tools for code completion, code generation, code documentation, and code search, as well as AI models and techniques for improving developer productivity. The repository also features information on various AI-powered developer tools, copilots, and related resources in the AI coding domain.
gitmesh
GitMesh is an AI-powered Git collaboration network designed to address contributor dropout in open source projects. It offers real-time branch-level insights, intelligent contributor-task matching, and automated workflows. The platform transforms complex codebases into clear contribution journeys, fostering engagement through gamified rewards and integration with open source support programs. GitMesh's mascot, Meshy/Mesh Wolf, symbolizes agility, resilience, and teamwork, reflecting the platform's ethos of efficiency and power through collaboration.
WebMasterLog
WebMasterLog is a comprehensive repository showcasing various web development projects built with front-end and back-end technologies. It highlights interactive user interfaces, dynamic web applications, and a spectrum of web development solutions. The repository encourages contributions in areas such as adding new projects, improving existing projects, updating documentation, fixing bugs, implementing responsive design, enhancing code readability, and optimizing project functionalities. Contributors are guided to follow specific guidelines for project submissions, including directory naming conventions, README file inclusion, project screenshots, and commit practices. Pull requests are reviewed based on criteria such as proper PR template completion, originality of work, code comments for clarity, and sharing screenshots for frontend updates. The repository also participates in various open-source programs like JWOC, GSSoC, Hacktoberfest, KWOC, 24 Pull Requests, IWOC, SWOC, and DWOC, welcoming valuable contributors.
UltraContextAI
UltraContextAI is a comprehensive system for managing AI interactions through memory management, lessons learned tracking, and dual-mode operation (Plan/Agent). It ensures consistent, high-quality development while maintaining detailed project documentation and knowledge retention. The system includes core components like Memory System, Lessons Learned, and Scratchpad. It operates in Plan Mode for information gathering and planning, and Agent Mode for execution. Users can create new features, fix bugs, set up projects, and update documentation using the system. Real-time updates, version control, and cross-referencing are key aspects of the system. Best practices include memory management, task tracking, and documentation standards. Tips and tricks are provided for handling AI and Cursor issues. Contributions to the system are welcome, and it is licensed under MIT License.
docs-mcp-server
The docs-mcp-server repository contains the server-side code for the documentation management system. It provides functionalities for managing, storing, and retrieving documentation files. Users can upload, update, and delete documents through the server. The server also supports user authentication and authorization to ensure secure access to the documentation system. Additionally, the server includes APIs for integrating with other systems and tools, making it a versatile solution for managing documentation in various projects and organizations.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.