
elyra
Elyra extends JupyterLab with an AI centric approach.
Stars: 1960
Elyra is a set of AI-centric extensions to JupyterLab Notebooks that includes features like Visual Pipeline Editor, running notebooks/scripts as batch jobs, reusable code snippets, hybrid runtime support, script editors with execution capabilities, debugger, version control using Git, and more. It provides a comprehensive environment for data scientists and AI practitioners to develop, test, and deploy machine learning models and workflows efficiently.
README:
Elyra is a set of AI-centric extensions to JupyterLab Notebooks.
Elyra currently includes the following functionality:
- Visual Pipeline Editor
- Ability to run a notebook, Python or R script as a batch job
- Reusable Code Snippets
- Hybrid runtime support based on Jupyter Enterprise Gateway
- Python and R script editors with local/remote execution capabilities
- Python script navigation using auto-generated Table of Contents
- Python script integrated debugger (Experimental)
- Notebook navigation using auto-generated outlines using Table of Contents
- Language Server Protocol integration
- Version control using Git integration
The Elyra Getting Started Guide includes more details on these features. A version-specific summary of new features is located on the releases page.
You can also try Elyra by running one of the container images from Docker Hub or quay.io:
-
elyra/elyra:latesthas the latest released version installed. -
elyra/elyra:x.y.zhas a specific version installed.
Note: You can also build a container image from the main branch ("dev build") to try out features that have not been released yet.
To run one of the container images, issue the following command, specifying a tag of your choice.
docker run -it -p 8888:8888 elyra/elyra:dev jupyter lab --debug
To make a local directory containing your Notebooks (e.g. ${HOME}/opensource/jupyter-notebooks/) available in your docker container, you can use a mount command similar to the following:
docker run -it -p 8888:8888 -v ${HOME}/opensource/jupyter-notebooks/:/home/jovyan/work -w /home/jovyan/work elyra/elyra:dev jupyter lab --debug
These should produce output similar to that below, where you can then find the URL to be used to access Elyra in your local browser.
To access the notebook, open this file in a browser:
file:///home/jovyan/.local/share/jupyter/runtime/nbserver-6-open.html
Or copy and paste one of these URLs:
http://4d17829ecd4c:8888/?token=d690bde267ec75d6f88c64a39825f8b05b919dd084451f82
or http://127.0.0.1:8888/?token=d690bde267ec75d6f88c64a39825f8b05b919dd084451f82
Refer to the installation documentation for details.
For detailed information refer to the installation documentation.
- Node.js 22
- Python 3.9+
- Miniconda / Micromamba (optional)
The current release version is displayed at the top of this page.
-
Install from PyPI
pip3 install --upgrade "elyra[all]" -
Install from conda-forge
conda install -c conda-forge "elyra[all]"
Installation instructions and JupyterLab support vary by release. Note that a JupyterLab build is required. Installation instructions are located in the release-specific documentation, which can be accessed by selecting a specific version.
Elyra 4.x (JupyterLab 4.2.5+)
-
Install from PyPI
pip3 install --upgrade "elyra[all]" -
Install from conda-forge
conda install -c conda-forge "elyra[all]"
Elyra 3.7 < 4.0 (JupyterLab 3.x)
-
Install from PyPI
pip3 install --upgrade "elyra[all]<4.0.0" -
Install from conda-forge
conda install -c conda-forge "elyra[all]<4.0.0"
Elyra 3.1 < 3.7 (JupyterLab 3.x)
-
Install from PyPI
pip3 install --upgrade "elyra[all]>=3.1.0" && jupyter lab build
-
Install from conda-forge
conda install -c conda-forge "elyra[all]>=3.1.0" && jupyter lab build
Elyra 2.0 < 3.1 (JupyterLab 3.x)
-
Install from PyPI
pip3 install --upgrade "elyra>=2.0.1" && jupyter lab build
-
Install from conda-forge
conda install -c conda-forge "elyra>=2.0.1" && jupyter lab build
Run the following commands to verify the installation. Note that in the example output below the [version] placeholder is displayed instead of an actual version identifier, which might change with every release.
jupyter server extension listShould output:
Config dir: /.../.jupyter
Config dir: /.../etc/jupyter
elyra enabled
- Validating elyra...
elyra OK
jupyter_lsp enabled
- Validating jupyter_lsp...
jupyter_lsp [version] OK
jupyter_resource_usage enabled
- Validating jupyter_resource_usage...
jupyter_resource_usage [version] OK
jupyter_server_mathjax enabled
- Validating jupyter_server_mathjax...
jupyter_server_mathjax OK
jupyterlab enabled
- Validating jupyterlab...
jupyterlab [version] OK
jupyterlab_git enabled
- Validating jupyterlab_git...
jupyterlab_git [version] OK
nbclassic enabled
- Validating nbclassic...
nbclassic OK
nbdime enabled
- Validating nbdime...
nbdime [version] OK
Config dir: /.../etc/jupyter
NOTE: If you don't see the Elyra server extension enabled, you may need to explicitly enable
it with jupyter server extension enable elyra
jupyter labextension listShould output:
JupyterLab [version]
/.../share/jupyter/labextensions
nbdime-jupyterlab [version] enabled OK
@jupyter-server/resource-usage [version] enabled OK (python, jupyter-resource-usage)
@krassowski/jupyterlab-lsp [version] enabled OK (python, jupyterlab_lsp)
@elyra/code-snippet-extension [version] enabled OK
@elyra/metadata-extension [version] enabled OK
@elyra/pipeline-editor-extension [version] enabled OK
@elyra/python-editor-extension [version] enabled OK
@elyra/scala-editor-extension [version] enabled OK
@elyra/r-editor-extension [version] enabled OK
@elyra/theme-extension [version] enabled OK
@jupyterlab/git [version] enabled OK (python, jupyterlab-git)
Other labextensions (built into JupyterLab)
app dir: /.../share/jupyter/lab
After verifying Elyra has been installed, start Elyra with:
jupyter labWe welcome your questions, ideas, and feedback. Check the Getting Help section in the Getting Started guide to learn more about the channels you can use to get in touch with us.
If you are interested in helping make Elyra better, we encourage you to take a look at our Contributing page, Development Workflow documentation, and invite you to attend our weekly dev community meetings.
Our daily and weekly community meeting schedule can be found here.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for elyra
Similar Open Source Tools

elyra
Elyra is a set of AI-centric extensions to JupyterLab Notebooks that includes features like Visual Pipeline Editor, running notebooks/scripts as batch jobs, reusable code snippets, hybrid runtime support, script editors with execution capabilities, debugger, version control using Git, and more. It provides a comprehensive environment for data scientists and AI practitioners to develop, test, and deploy machine learning models and workflows efficiently.
obs-localvocal
LocalVocal is a live-streaming AI assistant plugin for OBS that allows you to transcribe audio speech into text and perform various language processing functions on the text using AI / LLMs (Large Language Models). It's privacy-first, with all data staying on your machine, and requires no GPU, cloud costs, network, or downtime.
backend.ai-webui
Backend.AI Web UI is a user-friendly web and app interface designed to make AI accessible for end-users, DevOps, and SysAdmins. It provides features for session management, inference service management, pipeline management, storage management, node management, statistics, configurations, license checking, plugins, help & manuals, kernel management, user management, keypair management, manager settings, proxy mode support, service information, and integration with the Backend.AI Web Server. The tool supports various devices, offers a built-in websocket proxy feature, and allows for versatile usage across different platforms. Users can easily manage resources, run environment-supported apps, access a web-based terminal, use Visual Studio Code editor, manage experiments, set up autoscaling, manage pipelines, handle storage, monitor nodes, view statistics, configure settings, and more.
gitingest
GitIngest is a tool that allows users to turn any Git repository into a prompt-friendly text ingest for LLMs. It provides easy code context by generating a text digest from a git repository URL or directory. The tool offers smart formatting for optimized output format for LLM prompts and provides statistics about file and directory structure, size of the extract, and token count. GitIngest can be used as a CLI tool on Linux and as a Python package for code integration. The tool is built using Tailwind CSS for frontend, FastAPI for backend framework, tiktoken for token estimation, and apianalytics.dev for simple analytics. Users can self-host GitIngest by building the Docker image and running the container. Contributions to the project are welcome, and the tool aims to be beginner-friendly for first-time contributors with a simple Python and HTML codebase.
mLoRA
mLoRA (Multi-LoRA Fine-Tune) is an open-source framework for efficient fine-tuning of multiple Large Language Models (LLMs) using LoRA and its variants. It allows concurrent fine-tuning of multiple LoRA adapters with a shared base model, efficient pipeline parallelism algorithm, support for various LoRA variant algorithms, and reinforcement learning preference alignment algorithms. mLoRA helps save computational and memory resources when training multiple adapters simultaneously, achieving high performance on consumer hardware.
steel-browser
Steel is an open-source browser API designed for AI agents and applications, simplifying the process of building live web agents and browser automation tools. It serves as a core building block for a production-ready, containerized browser sandbox with features like stealth capabilities, text-to-markdown session management, UI for session viewing/debugging, and full browser control through popular automation frameworks. Steel allows users to control, run, and manage a production-ready browser environment via a REST API, offering features such as full browser control, session management, proxy support, extension support, debugging tools, anti-detection mechanisms, resource management, and various browser tools. It aims to streamline complex browsing tasks programmatically, enabling users to focus on their AI applications while Steel handles the underlying complexity.

pebblo
Pebblo enables developers to safely load data and promote their Gen AI app to deployment without worrying about the organization’s compliance and security requirements. The project identifies semantic topics and entities found in the loaded data and summarizes them on the UI or a PDF report.
desktop
ComfyUI Desktop is a packaged desktop application that allows users to easily use ComfyUI with bundled features like ComfyUI source code, ComfyUI-Manager, and uv. It automatically installs necessary Python dependencies and updates with stable releases. The app comes with Electron, Chromium binaries, and node modules. Users can store ComfyUI files in a specified location and manage model paths. The tool requires Python 3.12+ and Visual Studio with Desktop C++ workload for Windows. It uses nvm to manage node versions and yarn as the package manager. Users can install ComfyUI and dependencies using comfy-cli, download uv, and build/launch the code. Troubleshooting steps include rebuilding modules and installing missing libraries. The tool supports debugging in VSCode and provides utility scripts for cleanup. Crash reports can be sent to help debug issues, but no personal data is included.
browser
Lightpanda Browser is an open-source headless browser designed for fast web automation, AI agents, LLM training, scraping, and testing. It features ultra-low memory footprint, exceptionally fast execution, and compatibility with Playwright and Puppeteer through CDP. Built for performance, Lightpanda offers Javascript execution, support for Web APIs, and is optimized for minimal memory usage. It is a modern solution for web scraping and automation tasks, providing a lightweight alternative to traditional browsers like Chrome.
obs-localvocal
LocalVocal is a Speech AI assistant OBS Plugin that enables users to transcribe speech into text and translate it into any language locally on their machine. The plugin runs OpenAI's Whisper for real-time speech processing and prediction. It supports features like transcribing audio in real-time, displaying captions on screen, sending captions to files, syncing captions with recordings, and translating captions to major languages. Users can bring their own Whisper model, filter or replace captions, and experience partial transcriptions for streaming. The plugin is privacy-focused, requiring no GPU, cloud costs, network, or downtime.
langstream
LangStream is a tool for natural language processing tasks, providing a CLI for easy installation and usage. Users can try sample applications like Chat Completions and create their own applications using the developer documentation. It supports running on Kubernetes for production-ready deployment, with support for various Kubernetes distributions and external components like Apache Kafka or Apache Pulsar cluster. Users can deploy LangStream locally using minikube and manage the cluster with mini-langstream. Development requirements include Docker, Java 17, Git, Python 3.11+, and PIP, with the option to test local code changes using mini-langstream.
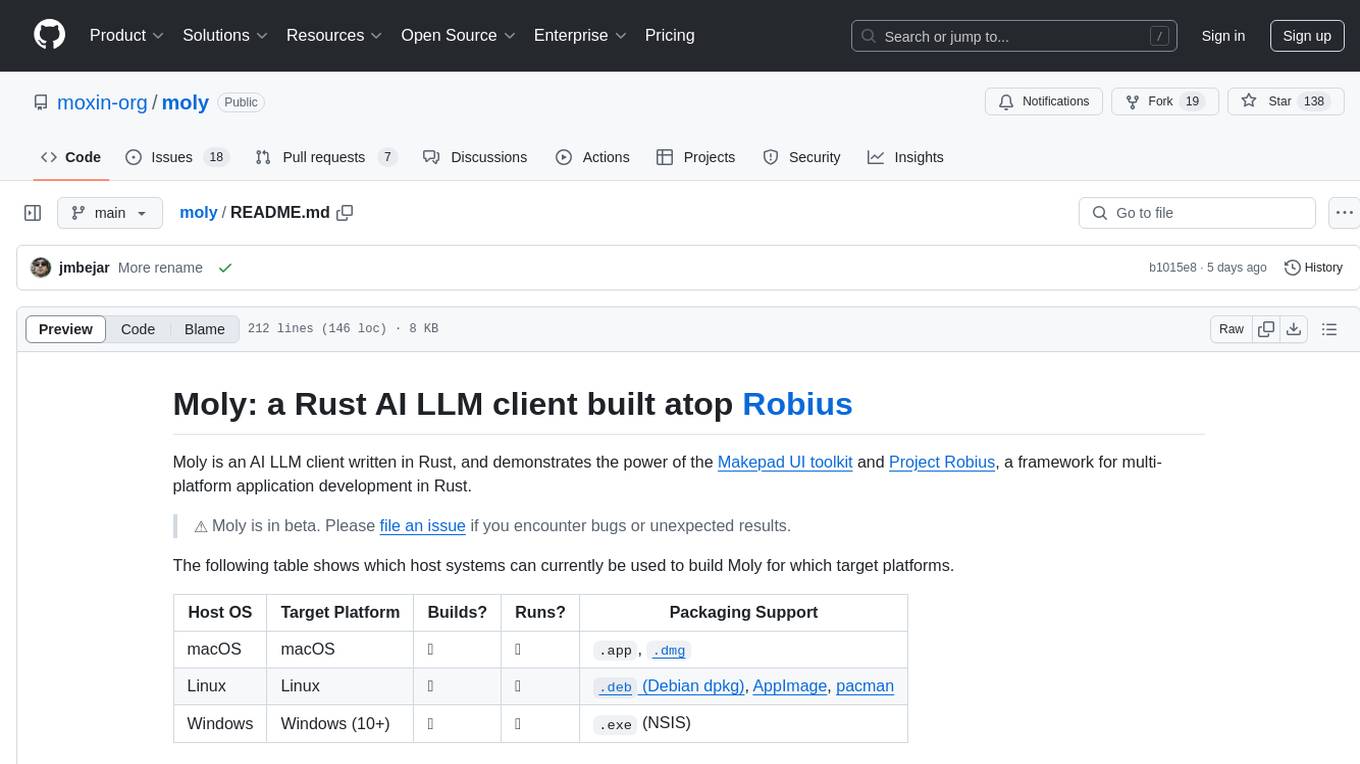
moly
Moly is an AI LLM client written in Rust, showcasing the capabilities of the Makepad UI toolkit and Project Robius, a framework for multi-platform application development in Rust. It is currently in beta, allowing users to build and run Moly on macOS, Linux, and Windows. The tool provides packaging support for different platforms, such as `.app`, `.dmg`, `.deb`, AppImage, pacman, and `.exe` (NSIS). Users can easily set up WasmEdge using `moly-runner` and leverage `cargo` commands to build and run Moly. Additionally, Moly offers pre-built releases for download and supports packaging for distribution on Linux, Windows, and macOS.
AirCasting
AirCasting is a platform for gathering, visualizing, and sharing environmental data. It aims to provide a central hub for environmental data, making it easier for people to access and use this information to make informed decisions about their environment.
ai-containers
This repository contains Dockerfiles, scripts, yaml files, Helm charts, etc. used to scale out AI containers with versions of TensorFlow and PyTorch optimized for Intel platforms. Scaling is done with python, Docker, kubernetes, kubeflow, cnvrg.io, Helm, and other container orchestration frameworks for use in the cloud and on-premise.
shortest
Shortest is a project for local development that helps set up environment variables and services for a web application. It provides a guide for setting up Node.js and pnpm dependencies, configuring services like Clerk, Vercel Postgres, Anthropic, Stripe, and GitHub OAuth, and running the application and tests locally.
screeps-starter-rust
screeps-starter-rust is a Rust AI starter kit for Screeps: World, a JavaScript-based MMO game. It utilizes the screeps-game-api bindings from the rustyscreeps organization and wasm-pack for building Rust code to WebAssembly. The example includes Rollup for bundling javascript, Babel for transpiling code, and screeps-api Node.js package for deployment. Users can refer to the Rust version of game APIs documentation at https://docs.rs/screeps-game-api/. The tool supports most crates on crates.io, except those interacting with OS APIs.
For similar tasks

zenml
ZenML is an extensible, open-source MLOps framework for creating portable, production-ready machine learning pipelines. By decoupling infrastructure from code, ZenML enables developers across your organization to collaborate more effectively as they develop to production.
pipeline
Pipeline is a Python library designed for constructing computational flows for AI/ML models. It supports both development and production environments, offering capabilities for inference, training, and finetuning. The library serves as an interface to Mystic, enabling the execution of pipelines at scale and on enterprise GPUs. Users can also utilize this SDK with Pipeline Core on a private hosted cluster. The syntax for defining AI/ML pipelines is reminiscent of sessions in Tensorflow v1 and Flows in Prefect.

elyra
Elyra is a set of AI-centric extensions to JupyterLab Notebooks that includes features like Visual Pipeline Editor, running notebooks/scripts as batch jobs, reusable code snippets, hybrid runtime support, script editors with execution capabilities, debugger, version control using Git, and more. It provides a comprehensive environment for data scientists and AI practitioners to develop, test, and deploy machine learning models and workflows efficiently.
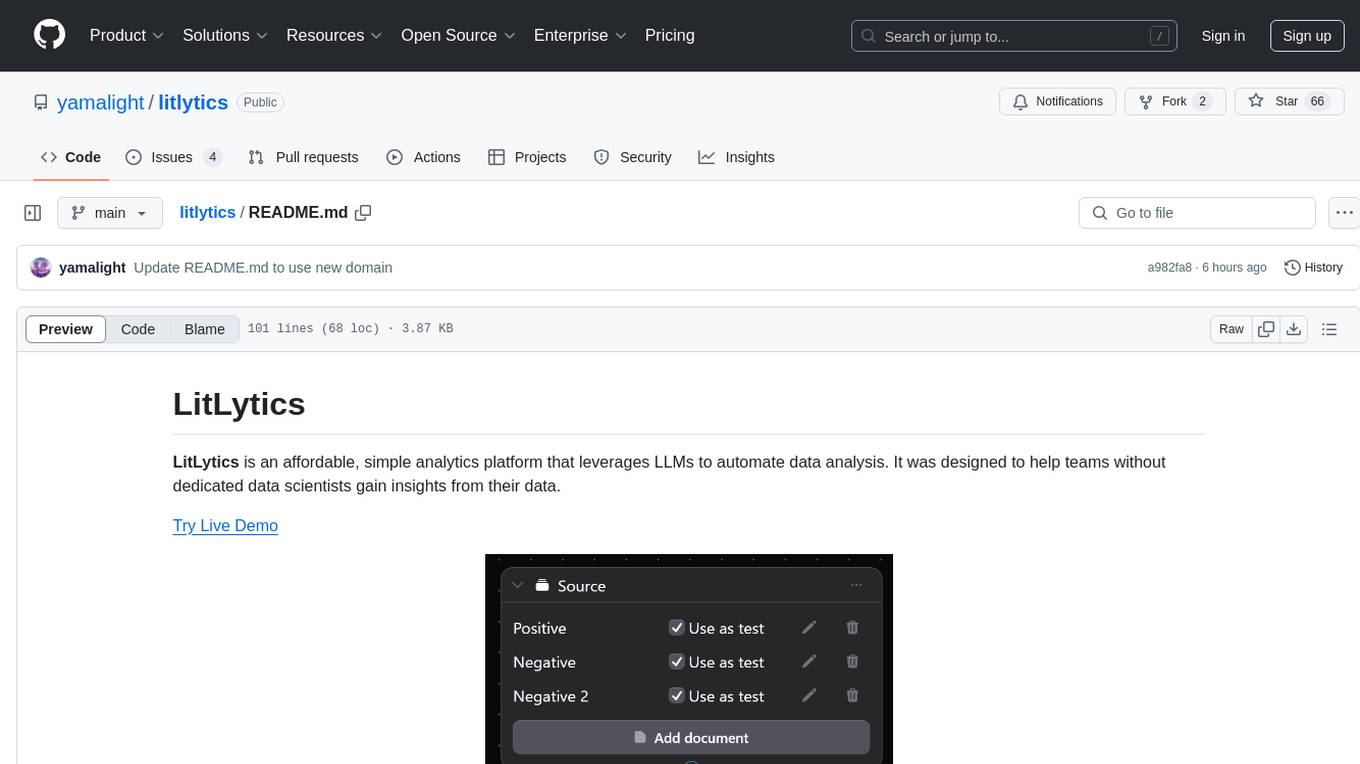
litlytics
LitLytics is an affordable analytics platform leveraging LLMs for automated data analysis. It simplifies analytics for teams without data scientists, generates custom pipelines, and allows customization. Cost-efficient with low data processing costs. Scalable and flexible, works with CSV, PDF, and plain text data formats.
xorq
Xorq (formerly LETSQL) is a data processing library built on top of Ibis and DataFusion to write multi-engine data workflows. It provides a flexible and powerful tool for processing and analyzing data from various sources, enabling users to create complex data pipelines and perform advanced data transformations.
pyscripter
PyScripter is a free and open-source Python Integrated Development Environment (IDE) aiming to compete with commercial Windows-based IDEs for other languages. It offers features like LLM-assisted coding and provides support for Python development projects. The tool is designed to enhance the coding experience for Python developers by providing a user-friendly interface and a range of functionalities to streamline the development process.
HEC-Commander
HEC-Commander Tools is a suite of python notebooks developed with AI assistance for water resource engineering workflows, focused on providing automation for HEC-RAS and HEC-HMS through Jupyter Notebooks. It contains automation scripts for HEC-HMS and HEC-RAS, tools for plotting results, and miscellaneous scripts for workflow assistance. The repository also includes blog posts, ChatGPT assistants, and presentations related to H&H modeling and the use of LLM's for water resources workflows.
nvim-repl
Neovim REPL is a tool that allows users to create, use, and remove interactive Read-Eval-Print Loops (REPLs) within Neovim. It supports various REPLs including aider, ipython, and utop. Users can easily send code cells, lines, or visual selections to the REPL. The tool provides default settings and allows for customization through Lua configuration. Documentation is available within Neovim's help file. Users can seamlessly integrate Neovim with aider for AI pair programming by following recommended configurations.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.
