
nuxt-llms
Automatically generates /llms.txt markdown documentation for your Nuxt application.
Stars: 117

Nuxt LLMs automatically generates llms.txt markdown documentation for Nuxt applications. It provides runtime hooks to collect data from various sources and generate structured documentation. The tool allows customization of sections directly from nuxt.config.ts and integrates with Nuxt modules via the runtime hooks system. It generates two documentation formats: llms.txt for concise structured documentation and llms_full.txt for detailed documentation. Users can extend documentation using hooks to add sections, links, and metadata. The tool is suitable for developers looking to automate documentation generation for their Nuxt applications.
README:
Nuxt LLMs automatically generates llms.txt markdown documentation for your Nuxt application. It provides runtime hooks to collect data from various sources (CMS, Nuxt Content, etc.) and generate structured documentation in a text-based format.
- Generates & prerenders
/llms.txtautomatically - Generate & prerenders
/llms-full.txtwhen enabled - Customizable sections directly from your
nuxt.config.ts - Integrates with Nuxt modules and your application via the runtime hooks system
- Install the module:
npm i nuxt-llms- Register
nuxt-llmsin yournuxt.config.ts:
export default defineNuxtConfig({
modules: ['nuxt-llms']
})- Configure your application details:
export default defineNuxtConfig({
modules: ['nuxt-llms'],
llms: {
domain: 'https://example.com',
title: 'My Application',
description: 'My Application Description',
sections: [
{
title: 'Section 1',
description: 'Section 1 Description',
links: [
{
title: 'Link 1',
description: 'Link 1 Description',
href: '/link-1',
},
{
title: 'Link 2',
description: 'Link 2 Description',
href: '/link-2',
},
],
},
],
},
})That's it! You can visit /llms.txt to see the generated documentation ✨
-
domain(required): The domain of the application -
title: The title of the application, will be displayed at the top of the documentation -
description: The description of the application, will be displayed at the top of the documentation right after the title -
sections: The sections of the documentation. Section are consisted of a title, one or more paragraphs of description and possibly a list of links. Each section is an object with the following properties:-
title(required): The title of the section -
description: The description of the section -
links: The links of the section-
title(required): The title of the link -
description: The description of the link -
href(required): The href of the link
-
-
-
notes: The notes of the documentation. Notes are a special section which always appears at the end of the documentation. Notes are useful to add any information about the application or documentation itself. -
full: Thellms-full.txtconfiguration. Setting this option will enable thellms-full.txtroute.-
title: The title of the llms-full documentation -
description: The description of the llms-full documentation
-
The module generates two different documentation formats:
The /llms.txt route generates a concise, structured documentation that follows the llms.txt specification. This format is optimized for both human readability and AI consumption. It includes:
- Application title and description
- Organized sections with titles and descriptions
- Links with titles, descriptions, and URLs
- Optional notes section
The /llms-full.txt route provides a more detailed, free-form documentation format. This is useful to reduce crawler traffic on your application and provide a more detailed documentation to your users and LLMs.
By default module does not generate the llms-full.txt route, you need to enable it by setting full.title and full.description in your nuxt.config.ts.
export default defineNuxtConfig({
llms: {
domain: 'https://example.com',
title: 'My Application',
full: {
title: 'Full Documentation',
description: 'Full documentation of the application',
},
},
})The module provides a hooks system that allows you to dynamically extend both documentation formats. There are two main hooks:
This hook is called for every request to /llms.txt. Use this hook to modify the structured documentation, It allows you to add sections, links, and metadata.
Parameters:
-
event: H3Event - The current request event -
options: ModuleOptions - The module options that you can modify to add sections, links, etc.
This hook is called for every request to /llms-full.txt. It allows you to add custom content sections in any format.
Parameters:
-
event: H3Event - The current request event -
options: ModuleOptions - The module options that you can modify to add sections, links, etc. -
contents: string[] - Array of content sections you can add to or modify
Create a server plugin in your server/plugins directory:
// server/plugins/llms.ts
export default defineNitroPlugin((nitroApp) => {
// Method 1: Using the hooks directly
nitroApp.hooks.hook('llms:generate', (event, options) => {
// Add a new section to llms.txt
options.sections.push({
title: 'API Documentation',
description: 'REST API endpoints and usage',
links: [
{
title: 'Authentication',
description: 'API authentication methods',
href: `${options.domain}/api/auth`
}
]
})
})
// Method 2: Using the helper function
nitroApp.hooks.hook('llms:generate:full', (event, options, contents) => {
// Add detailed documentation to llms-full.txt
contents.push(`## API Authentication
### Bearer Token
To authenticate API requests, include a Bearer token in the Authorization header:
\`\`\`
Authorization: Bearer <your-token>
\`\`\`
### API Keys
For server-to-server communication, use API keys:
\`\`\`
X-API-Key: <your-api-key>
\`\`\`
`)
})
})If you're developing a Nuxt module that needs to extend the LLMs documentation:
- Create a server plugin in your module:
// module/runtime/server/plugins/my-module-llms.ts
export default defineNitroPlugin((nitroApp) => {
nitroApp.hooks.hook('llms:generate', (event, options) => {
options.sections.push({
title: 'My Module',
description: 'Documentation for my module features',
links: [/* ... */]
})
})
})- Register the plugin in your module setup:
import { defineNuxtModule, addServerPlugin } from '@nuxt/kit'
import { fileURLToPath } from 'url'
export default defineNuxtModule({
setup(options, nuxt) {
const runtimeDir = fileURLToPath(new URL('./runtime', import.meta.url))
addServerPlugin(resolve(runtimeDir, 'server/plugins/my-module-llms'))
}
})Nuxt Content ^3.2.0 comes with built-in support for LLMs documentation. You can use nuxt-llms with @nuxt/content to efficiently write content and documentation for your website and generate LLM-friendly documentation without extra effort. Content module uses nuxt-llms hooks and automatically adds all your contents into llms.txt and llms-full.txt documentation.
All you need is to install both modules and write your content files in the content directory.
export default defineNuxtConfig({
modules: ['nuxt-llms', '@nuxt/content'],
llms: {
domain: 'https://example.com',
title: 'My Application',
description: 'My Application Description',
},
})Checkout the Nuxt Content documentation for more information on how to write your content files.
And checkout the Nuxt Content llms documentation for more information on how to customize LLMs contents with nuxt-llms and @nuxt/content.
- Clone repository
- Install dependencies using
pnpm install - Prepare using
pnpm dev:prepare - Build using
pnpm prepack - Try playground using
pnpm dev - Test using
pnpm test
Copyright (c) NuxtLabs
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for nuxt-llms
Similar Open Source Tools

nuxt-llms
Nuxt LLMs automatically generates llms.txt markdown documentation for Nuxt applications. It provides runtime hooks to collect data from various sources and generate structured documentation. The tool allows customization of sections directly from nuxt.config.ts and integrates with Nuxt modules via the runtime hooks system. It generates two documentation formats: llms.txt for concise structured documentation and llms_full.txt for detailed documentation. Users can extend documentation using hooks to add sections, links, and metadata. The tool is suitable for developers looking to automate documentation generation for their Nuxt applications.
Lumos
Lumos is a Chrome extension powered by a local LLM co-pilot for browsing the web. It allows users to summarize long threads, news articles, and technical documentation. Users can ask questions about reviews and product pages. The tool requires a local Ollama server for LLM inference and embedding database. Lumos supports multimodal models and file attachments for processing text and image content. It also provides options to customize models, hosts, and content parsers. The extension can be easily accessed through keyboard shortcuts and offers tools for automatic invocation based on prompts.
laravel-crod
Laravel Crod is a package designed to facilitate the implementation of CRUD operations in Laravel projects. It allows users to quickly generate controllers, models, migrations, services, repositories, views, and requests with various customization options. The package simplifies tasks such as creating resource controllers, making models fillable, querying repositories and services, and generating additional files like seeders and factories. Laravel Crod aims to streamline the process of building CRUD functionalities in Laravel applications by providing a set of commands and tools for developers.
shortest
Shortest is an AI-powered natural language end-to-end testing framework built on Playwright. It provides a seamless testing experience by allowing users to write tests in natural language and execute them using Anthropic Claude API. The framework also offers GitHub integration with 2FA support, making it suitable for testing web applications with complex authentication flows. Shortest simplifies the testing process by enabling users to run tests locally or in CI/CD pipelines, ensuring the reliability and efficiency of web applications.
llm-vscode
llm-vscode is an extension designed for all things LLM, utilizing llm-ls as its backend. It offers features such as code completion with 'ghost-text' suggestions, the ability to choose models for code generation via HTTP requests, ensuring prompt size fits within the context window, and code attribution checks. Users can configure the backend, suggestion behavior, keybindings, llm-ls settings, and tokenization options. Additionally, the extension supports testing models like Code Llama 13B, Phind/Phind-CodeLlama-34B-v2, and WizardLM/WizardCoder-Python-34B-V1.0. Development involves cloning llm-ls, building it, and setting up the llm-vscode extension for use.
code2prompt
Code2Prompt is a powerful command-line tool that generates comprehensive prompts from codebases, designed to streamline interactions between developers and Large Language Models (LLMs) for code analysis, documentation, and improvement tasks. It bridges the gap between codebases and LLMs by converting projects into AI-friendly prompts, enabling users to leverage AI for various software development tasks. The tool offers features like holistic codebase representation, intelligent source tree generation, customizable prompt templates, smart token management, Gitignore integration, flexible file handling, clipboard-ready output, multiple output options, and enhanced code readability.
swarmzero
SwarmZero SDK is a library that simplifies the creation and execution of AI Agents and Swarms of Agents. It supports various LLM Providers such as OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, Anthropic, MistralAI, Gemini, Nebius, and Ollama. Users can easily install the library using pip or poetry, set up the environment and configuration, create and run Agents, collaborate with Swarms, add tools for complex tasks, and utilize retriever tools for semantic information retrieval. Sample prompts are provided to help users explore the capabilities of the agents and swarms. The SDK also includes detailed examples and documentation for reference.
langchainrb
Langchain.rb is a Ruby library that makes it easy to build LLM-powered applications. It provides a unified interface to a variety of LLMs, vector search databases, and other tools, making it easy to build and deploy RAG (Retrieval Augmented Generation) systems and assistants. Langchain.rb is open source and available under the MIT License.

langserve
LangServe helps developers deploy `LangChain` runnables and chains as a REST API. This library is integrated with FastAPI and uses pydantic for data validation. In addition, it provides a client that can be used to call into runnables deployed on a server. A JavaScript client is available in LangChain.js.
instructor
Instructor is a popular Python library for managing structured outputs from large language models (LLMs). It offers a user-friendly API for validation, retries, and streaming responses. With support for various LLM providers and multiple languages, Instructor simplifies working with LLM outputs. The library includes features like response models, retry management, validation, streaming support, and flexible backends. It also provides hooks for logging and monitoring LLM interactions, and supports integration with Anthropic, Cohere, Gemini, Litellm, and Google AI models. Instructor facilitates tasks such as extracting user data from natural language, creating fine-tuned models, managing uploaded files, and monitoring usage of OpenAI models.
mcpdoc
The MCP LLMS-TXT Documentation Server is an open-source server that provides developers full control over tools used by applications like Cursor, Windsurf, and Claude Code/Desktop. It allows users to create a user-defined list of `llms.txt` files and use a `fetch_docs` tool to read URLs within these files, enabling auditing of tool calls and context returned. The server supports various applications and provides a way to connect to them, configure rules, and test tool calls for tasks related to documentation retrieval and processing.
models.dev
Models.dev is an open-source database providing detailed specifications, pricing, and capabilities of various AI models. It serves as a centralized platform for accessing information on AI models, allowing users to contribute and utilize the data through an API. The repository contains data stored in TOML files, organized by provider and model, along with SVG logos. Users can contribute by adding new models following specific guidelines and submitting pull requests for validation. The project aims to maintain an up-to-date and comprehensive database of AI model information.
parsera
Parsera is a lightweight Python library designed for scraping websites using LLMs. It offers simplicity and efficiency by minimizing token usage, enhancing speed, and reducing costs. Users can easily set up and run the tool to extract specific elements from web pages, generating JSON output with relevant data. Additionally, Parsera supports integration with various chat models, such as Azure, expanding its functionality and customization options for web scraping tasks.
forge
Forge is a powerful open-source tool for building modern web applications. It provides a simple and intuitive interface for developers to quickly scaffold and deploy projects. With Forge, you can easily create custom components, manage dependencies, and streamline your development workflow. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced developer, Forge offers a flexible and efficient solution for your web development needs.
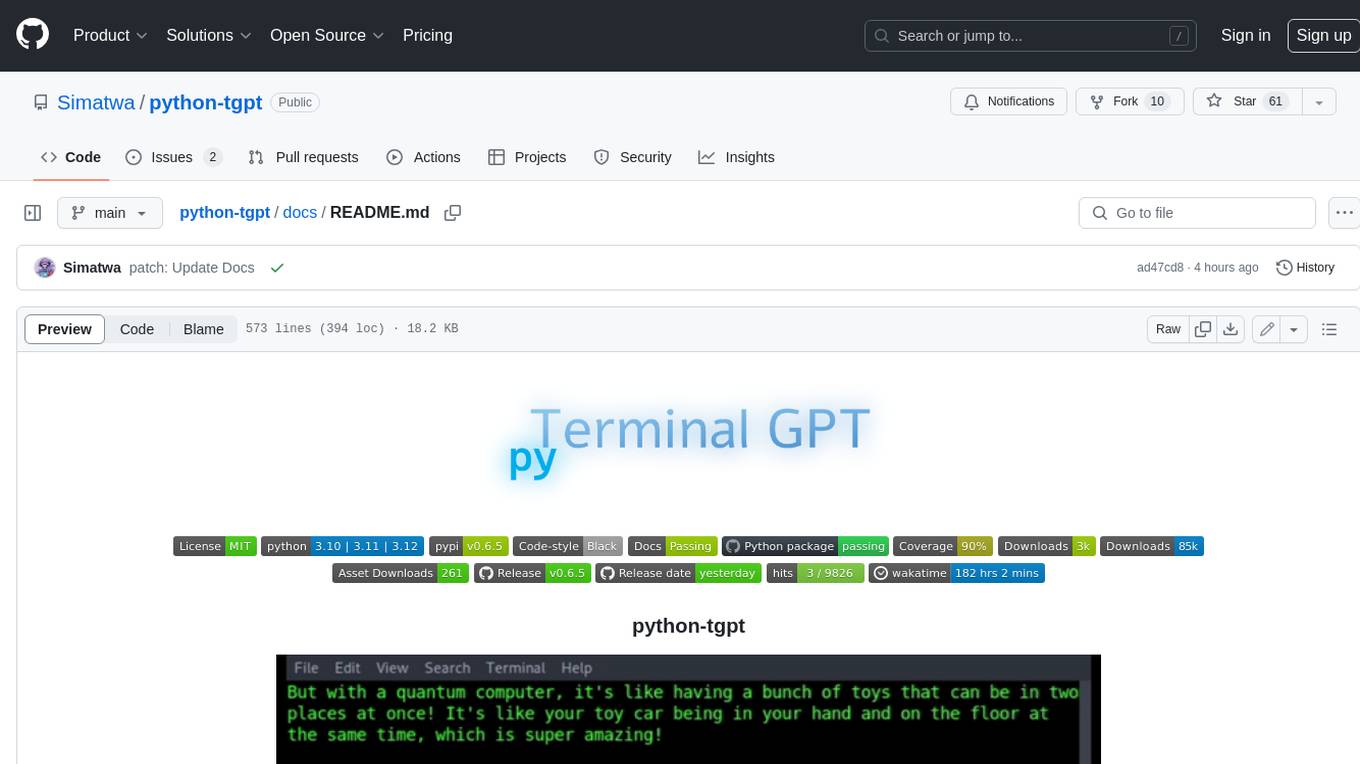
python-tgpt
Python-tgpt is a Python package that enables seamless interaction with over 45 free LLM providers without requiring an API key. It also provides image generation capabilities. The name _python-tgpt_ draws inspiration from its parent project tgpt, which operates on Golang. Through this Python adaptation, users can effortlessly engage with a number of free LLMs available, fostering a smoother AI interaction experience.
odoo-expert
RAG-Powered Odoo Documentation Assistant is a comprehensive documentation processing and chat system that converts Odoo's documentation to a searchable knowledge base with an AI-powered chat interface. It supports multiple Odoo versions (16.0, 17.0, 18.0) and provides semantic search capabilities powered by OpenAI embeddings. The tool automates the conversion of RST to Markdown, offers real-time semantic search, context-aware AI-powered chat responses, and multi-version support. It includes a Streamlit-based web UI, REST API for programmatic access, and a CLI for document processing and chat. The system operates through a pipeline of data processing steps and an interface layer for UI and API access to the knowledge base.
For similar tasks

screenpipe
24/7 Screen & Audio Capture Library to build personalized AI powered by what you've seen, said, or heard. Works with Ollama. Alternative to Rewind.ai. Open. Secure. You own your data. Rust. We are shipping daily, make suggestions, post bugs, give feedback. Building a reliable stream of audio and screenshot data, simplifying life for developers by solving non-trivial problems. Multiple installation options available. Experimental tool with various integrations and features for screen and audio capture, OCR, STT, and more. Open source project focused on enabling tooling & infrastructure for a wide range of applications.

nuxt-llms
Nuxt LLMs automatically generates llms.txt markdown documentation for Nuxt applications. It provides runtime hooks to collect data from various sources and generate structured documentation. The tool allows customization of sections directly from nuxt.config.ts and integrates with Nuxt modules via the runtime hooks system. It generates two documentation formats: llms.txt for concise structured documentation and llms_full.txt for detailed documentation. Users can extend documentation using hooks to add sections, links, and metadata. The tool is suitable for developers looking to automate documentation generation for their Nuxt applications.

OSA
OSA (Open-Source-Advisor) is a tool designed to improve the quality of scientific open source projects by automating the generation of README files, documentation, CI/CD scripts, and providing advice and recommendations for repositories. It supports various LLMs accessible via API, local servers, or osa_bot hosted on ITMO servers. OSA is currently under development with features like README file generation, documentation generation, automatic implementation of changes, LLM integration, and GitHub Action Workflow generation. It requires Python 3.10 or higher and tokens for GitHub/GitLab/Gitverse and LLM API key. Users can install OSA using PyPi or build from source, and run it using CLI commands or Docker containers.
pr-agent
PR-Agent is a tool that helps to efficiently review and handle pull requests by providing AI feedbacks and suggestions. It supports various commands such as generating PR descriptions, providing code suggestions, answering questions about the PR, and updating the CHANGELOG.md file. PR-Agent can be used via CLI, GitHub Action, GitHub App, Docker, and supports multiple git providers and models. It emphasizes real-life practical usage, with each tool having a single GPT-4 call for quick and affordable responses. The PR Compression strategy enables effective handling of both short and long PRs, while the JSON prompting strategy allows for modular and customizable tools. PR-Agent Pro, the hosted version by CodiumAI, provides additional benefits such as full management, improved privacy, priority support, and extra features.
shell_gpt
ShellGPT is a command-line productivity tool powered by AI large language models (LLMs). This command-line tool offers streamlined generation of shell commands, code snippets, documentation, eliminating the need for external resources (like Google search). Supports Linux, macOS, Windows and compatible with all major Shells like PowerShell, CMD, Bash, Zsh, etc.
gpt-pilot
GPT Pilot is a core technology for the Pythagora VS Code extension, aiming to provide the first real AI developer companion. It goes beyond autocomplete, helping with writing full features, debugging, issue discussions, and reviews. The tool utilizes LLMs to generate production-ready apps, with developers overseeing the implementation. GPT Pilot works step by step like a developer, debugging issues as they arise. It can work at any scale, filtering out code to show only relevant parts to the AI during tasks. Contributions are welcome, with debugging and telemetry being key areas of focus for improvement.
sirji
Sirji is an agentic AI framework for software development where various AI agents collaborate via a messaging protocol to solve software problems. It uses standard or user-generated recipes to list tasks and tips for problem-solving. Agents in Sirji are modular AI components that perform specific tasks based on custom pseudo code. The framework is currently implemented as a Visual Studio Code extension, providing an interactive chat interface for problem submission and feedback. Sirji sets up local or remote development environments by installing dependencies and executing generated code.
awesome-ai-devtools
Awesome AI-Powered Developer Tools is a curated list of AI-powered developer tools that leverage AI to assist developers in tasks such as code completion, refactoring, debugging, documentation, and more. The repository includes a wide range of tools, from IDEs and Git clients to assistants, agents, app generators, UI generators, snippet generators, documentation tools, code generation tools, agent platforms, OpenAI plugins, search tools, and testing tools. These tools are designed to enhance developer productivity and streamline various development tasks by integrating AI capabilities.
For similar jobs
ai-admin-jqadm
Aimeos JQAdm is a VueJS and Bootstrap based admin backend for Aimeos. It provides a user-friendly interface for managing your Aimeos e-commerce website. With Aimeos JQAdm, you can easily add, edit, and delete products, categories, orders, and customers. You can also manage your website's settings, such as payment methods, shipping methods, and taxes. Aimeos JQAdm is a powerful and easy-to-use tool that can help you manage your Aimeos website more efficiently.

quantizr
Quanta is a new kind of Content Management platform, with powerful features including: Wikis & micro-blogging, ChatGPT Question Answering, Document collaboration and publishing, PDF Generation, Secure messaging with (E2E Encryption), Video/audio recording & sharing, File sharing, Podcatcher (RSS Reader), and many other features related to managing hierarchical content.
ai-cms-grapesjs
The Aimeos GrapesJS CMS extension provides a simple to use but powerful page editor for creating content pages based on extensible components. It integrates seamlessly with Laravel applications and allows users to easily manage and display CMS content. The tool also supports Google reCAPTCHA v3 for enhanced security. Users can create and customize pages with various components and manage multi-language setups effortlessly. The extension simplifies the process of creating and managing content pages, making it ideal for developers and businesses looking to enhance their website's content management capabilities.

nuxt-llms
Nuxt LLMs automatically generates llms.txt markdown documentation for Nuxt applications. It provides runtime hooks to collect data from various sources and generate structured documentation. The tool allows customization of sections directly from nuxt.config.ts and integrates with Nuxt modules via the runtime hooks system. It generates two documentation formats: llms.txt for concise structured documentation and llms_full.txt for detailed documentation. Users can extend documentation using hooks to add sections, links, and metadata. The tool is suitable for developers looking to automate documentation generation for their Nuxt applications.
mushroom
MRCMS is a Java-based content management system that uses data model + template + plugin implementation, providing built-in article model publishing functionality. The goal is to quickly build small to medium websites.

PandaWiki
PandaWiki is a collaborative platform for creating and editing wiki pages. It allows users to easily collaborate on documentation, knowledge sharing, and information dissemination. With features like version control, user permissions, and rich text editing, PandaWiki simplifies the process of creating and managing wiki content. Whether you are working on a team project, organizing information for personal use, or building a knowledge base for your organization, PandaWiki provides a user-friendly and efficient solution for creating and maintaining wiki pages.
nsfw_ai_model_server
This project is dedicated to creating and running AI models that can automatically select appropriate tags for images and videos, providing invaluable information to help manage content and find content without manual effort. The AI models deliver highly accurate time-based tags, enhance searchability, improve content management, and offer future content recommendations. The project offers a free open source AI model supporting 10 tags and several paid Patreon models with 151 tags and additional variations for different tradeoffs between accuracy and speed. The project has limitations related to usage restrictions, hardware requirements, performance on CPU, complexity, and model access.

DocsGPT
DocsGPT is an open-source documentation assistant powered by GPT models. It simplifies the process of searching for information in project documentation by allowing developers to ask questions and receive accurate answers. With DocsGPT, users can say goodbye to manual searches and quickly find the information they need. The tool aims to revolutionize project documentation experiences and offers features like live previews, Discord community, guides, and contribution opportunities. It consists of a Flask app, Chrome extension, similarity search index creation script, and a frontend built with Vite and React. Users can quickly get started with DocsGPT by following the provided setup instructions and can contribute to its development by following the guidelines in the CONTRIBUTING.md file. The project follows a Code of Conduct to ensure a harassment-free community environment for all participants. DocsGPT is licensed under MIT and is built with LangChain.



