
DeepPavlov
An open source library for deep learning end-to-end dialog systems and chatbots.
Stars: 6632
DeepPavlov is an open-source conversational AI library built on PyTorch. It is designed for the development of production-ready chatbots and complex conversational systems, as well as for research in the area of NLP and dialog systems. The library offers a wide range of models for tasks such as Named Entity Recognition, Intent/Sentence Classification, Question Answering, Sentence Similarity/Ranking, Syntactic Parsing, and more. DeepPavlov also provides embeddings like BERT, ELMo, and FastText for various languages, along with AutoML capabilities and integrations with REST API, Socket API, and Amazon AWS.
README:
DeepPavlov is an open-source conversational AI library built on PyTorch.
DeepPavlov is designed for
- development of production ready chat-bots and complex conversational systems,
- research in the area of NLP and, particularly, of dialog systems.
- Demo demo.deeppavlov.ai
- Documentation docs.deeppavlov.ai
- Model List docs:features/
- Contribution Guide docs:contribution_guide/
- Issues github/issues/
- Forum forum.deeppavlov.ai
- Blogs medium.com/deeppavlov
- Extended colab tutorials
- Docker Hub hub.docker.com/u/deeppavlov/
- Docker Images Documentation docs:docker-images/
Please leave us your feedback on how we can improve the DeepPavlov framework.
Models
Named Entity Recognition | Intent/Sentence Classification |
Question Answering over Text (SQuAD) | Knowledge Base Question Answering
Sentence Similarity/Ranking | TF-IDF Ranking
Syntactic Parsing | Morphological Tagging
Automatic Spelling Correction | Entity Extraction
Open Domain Questions Answering | Russian SuperGLUE
Embeddings
BERT embeddings for the Russian, Polish, Bulgarian, Czech, and informal English
ELMo embeddings for the Russian language
FastText embeddings for the Russian language
Auto ML
Integrations
-
DeepPavlov supports
Linux,Windows 10+(through WSL/WSL2),MacOS(Big Sur+) platforms,Python 3.6,3.7,3.8,3.9and3.10. Depending on the model used, you may need from 4 to 16 GB RAM. -
Create and activate a virtual environment:
Linux
python -m venv env source ./env/bin/activate -
Install the package inside the environment:
pip install deeppavlov
There is a bunch of great pre-trained NLP models in DeepPavlov. Each model is determined by its config file.
List of models is available on
the doc page in
the deeppavlov.configs (Python):
from deeppavlov import configsWhen you're decided on the model (+ config file), there are two ways to train, evaluate and infer it:
- via Command line interface (CLI) and
- via Python.
By default, DeepPavlov installs models requirements from PyPI. PyTorch from PyPI could not support your device CUDA capability. To run supported DeepPavlov models on GPU you should have CUDA compatible with used GPU and PyTorch version required by DeepPavlov models. See docs for details. GPU with Pascal or newer architecture and 4+ GB VRAM is recommended.
To get predictions from a model interactively through CLI, run
python -m deeppavlov interact <config_path> [-d] [-i]-
-ddownloads required data - pretrained model files and embeddings (optional). -
-iinstalls model requirements (optional).
You can train it in the same simple way:
python -m deeppavlov train <config_path> [-d] [-i]Dataset will be downloaded regardless of whether there was -d flag or not.
To train on your own data you need to modify dataset reader path in the train config doc. The data format is specified in the corresponding model doc page.
There are even more actions you can perform with configs:
python -m deeppavlov <action> <config_path> [-d] [-i]-
<action>can be-
installto install model requirements (same as-i), -
downloadto download model's data (same as-d), -
trainto train the model on the data specified in the config file, -
evaluateto calculate metrics on the same dataset, -
interactto interact via CLI, -
riseapito run a REST API server (see doc), -
predictto get prediction for samples from stdin or from <file_path> if-f <file_path>is specified.
-
-
<config_path>specifies path (or name) of model's config file -
-ddownloads required data -
-iinstalls model requirements
To get predictions from a model interactively through Python, run
from deeppavlov import build_model
model = build_model(<config_path>, install=True, download=True)
# get predictions for 'input_text1', 'input_text2'
model(['input_text1', 'input_text2'])where
-
install=Trueinstalls model requirements (optional), -
download=Truedownloads required data from web - pretrained model files and embeddings (optional), -
<config_path>is model name (e.g.'ner_ontonotes_bert_mult'), path to the chosen model's config file (e.g."deeppavlov/configs/ner/ner_ontonotes_bert_mult.json"), ordeeppavlov.configsattribute (e.g.deeppavlov.configs.ner.ner_ontonotes_bert_multwithout quotation marks).
You can train it in the same simple way:
from deeppavlov import train_model
model = train_model(<config_path>, install=True, download=True)To train on your own data you need to modify dataset reader path in the train config doc. The data format is specified in the corresponding model doc page.
You can also calculate metrics on the dataset specified in your config file:
from deeppavlov import evaluate_model
model = evaluate_model(<config_path>, install=True, download=True)DeepPavlov also allows to build a model from components for inference using Python.
DeepPavlov is Apache 2.0 - licensed.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for DeepPavlov
Similar Open Source Tools

DeepPavlov
DeepPavlov is an open-source conversational AI library built on PyTorch. It is designed for the development of production-ready chatbots and complex conversational systems, as well as for research in the area of NLP and dialog systems. The library offers a wide range of models for tasks such as Named Entity Recognition, Intent/Sentence Classification, Question Answering, Sentence Similarity/Ranking, Syntactic Parsing, and more. DeepPavlov also provides embeddings like BERT, ELMo, and FastText for various languages, along with AutoML capabilities and integrations with REST API, Socket API, and Amazon AWS.
uzu
uzu is a high-performance inference engine for AI models on Apple Silicon. It features a simple, high-level API, hybrid architecture for GPU kernel computation, unified model configurations, traceable computations, and utilizes unified memory on Apple devices. The tool provides a CLI mode for running models, supports its own model format, and offers prebuilt Swift and TypeScript frameworks for bindings. Users can quickly start by adding the uzu dependency to their Cargo.toml and creating an inference Session with a specific model and configuration. Performance benchmarks show metrics for various models on Apple M2, highlighting the tokens/s speed for each model compared to llama.cpp with bf16/f16 precision.
stark
STaRK is a large-scale semi-structure retrieval benchmark on Textual and Relational Knowledge Bases. It provides natural-sounding and practical queries crafted to incorporate rich relational information and complex textual properties, closely mirroring real-life scenarios. The benchmark aims to assess how effectively large language models can handle the interplay between textual and relational requirements in queries, using three diverse knowledge bases constructed from public sources.
consult-llm-mcp
Consult LLM MCP is an MCP server that enables users to consult powerful AI models like GPT-5.2, Gemini 3.0 Pro, and DeepSeek Reasoner for complex problem-solving. It supports multi-turn conversations, direct queries with optional file context, git changes inclusion for code review, comprehensive logging with cost estimation, and various CLI modes for Gemini and Codex. The tool is designed to simplify the process of querying AI models for assistance in resolving coding issues and improving code quality.
AgentKit
AgentKit is a framework for constructing complex human thought processes from simple natural language prompts. It offers a unified way to represent and execute these processes as graphs, making it easy to design and tune agents without any programming experience. AgentKit can be used for a variety of tasks, including generating text, answering questions, and making decisions.
paxml
Pax is a framework to configure and run machine learning experiments on top of Jax.
py-llm-core
PyLLMCore is a light-weighted interface with Large Language Models with native support for llama.cpp, OpenAI API, and Azure deployments. It offers a Pythonic API that is simple to use, with structures provided by the standard library dataclasses module. The high-level API includes the assistants module for easy swapping between models. PyLLMCore supports various models including those compatible with llama.cpp, OpenAI, and Azure APIs. It covers use cases such as parsing, summarizing, question answering, hallucinations reduction, context size management, and tokenizing. The tool allows users to interact with language models for tasks like parsing text, summarizing content, answering questions, reducing hallucinations, managing context size, and tokenizing text.

langserve
LangServe helps developers deploy `LangChain` runnables and chains as a REST API. This library is integrated with FastAPI and uses pydantic for data validation. In addition, it provides a client that can be used to call into runnables deployed on a server. A JavaScript client is available in LangChain.js.
minja
Minja is a minimalistic C++ Jinja templating engine designed specifically for integration with C++ LLM projects, such as llama.cpp or gemma.cpp. It is not a general-purpose tool but focuses on providing a limited set of filters, tests, and language features tailored for chat templates. The library is header-only, requires C++17, and depends only on nlohmann::json. Minja aims to keep the codebase small, easy to understand, and offers decent performance compared to Python. Users should be cautious when using Minja due to potential security risks, and it is not intended for producing HTML or JavaScript output.
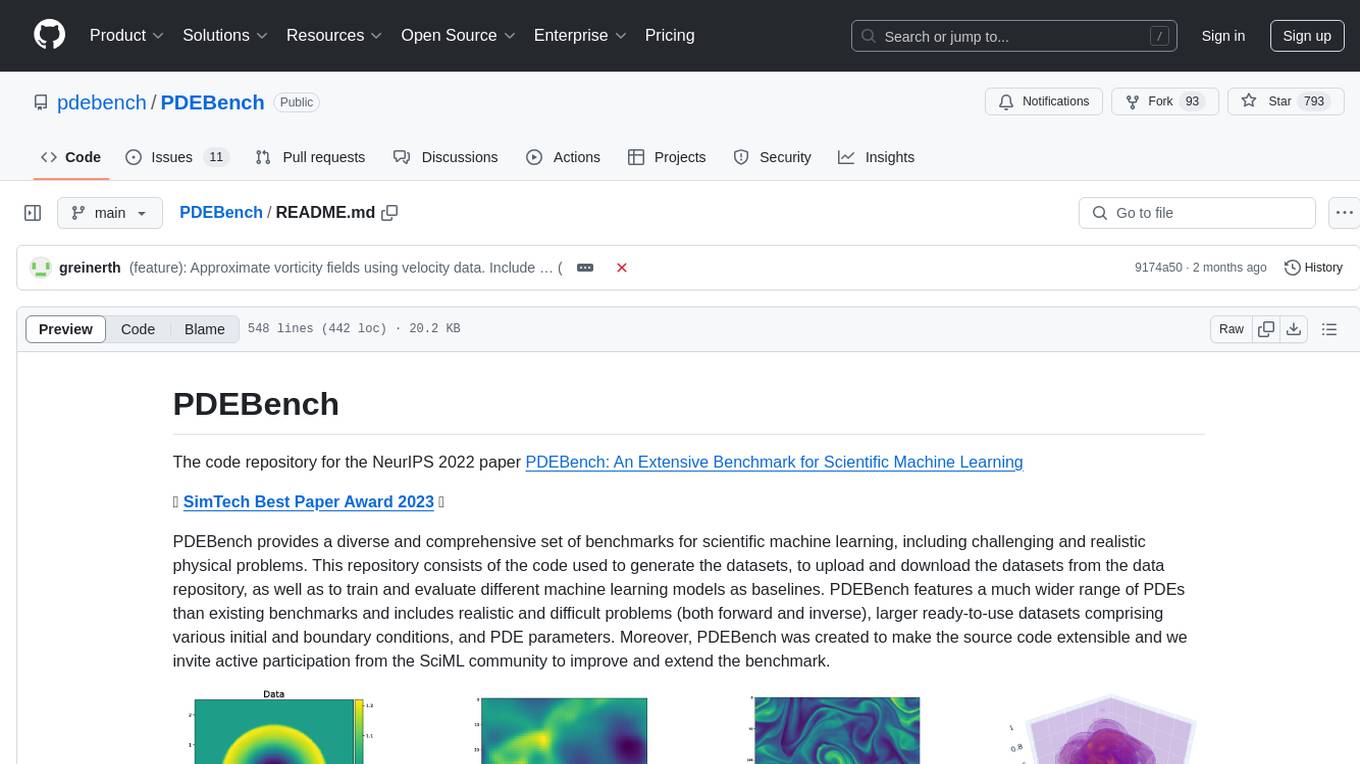
PDEBench
PDEBench provides a diverse and comprehensive set of benchmarks for scientific machine learning, including challenging and realistic physical problems. The repository consists of code for generating datasets, uploading and downloading datasets, training and evaluating machine learning models as baselines. It features a wide range of PDEs, realistic and difficult problems, ready-to-use datasets with various conditions and parameters. PDEBench aims for extensibility and invites participation from the SciML community to improve and extend the benchmark.
IntelliNode
IntelliNode is a javascript module that integrates cutting-edge AI models like ChatGPT, LLaMA, WaveNet, Gemini, and Stable diffusion into projects. It offers functions for generating text, speech, and images, as well as semantic search, multi-model evaluation, and chatbot capabilities. The module provides a wrapper layer for low-level model access, a controller layer for unified input handling, and a function layer for abstract functionality tailored to various use cases.

wllama
Wllama is a WebAssembly binding for llama.cpp, a high-performance and lightweight language model library. It enables you to run inference directly on the browser without the need for a backend or GPU. Wllama provides both high-level and low-level APIs, allowing you to perform various tasks such as completions, embeddings, tokenization, and more. It also supports model splitting, enabling you to load large models in parallel for faster download. With its Typescript support and pre-built npm package, Wllama is easy to integrate into your React Typescript projects.
clarifai-python-grpc
This is the official Clarifai gRPC Python client for interacting with their recognition API. Clarifai offers a platform for data scientists, developers, researchers, and enterprises to utilize artificial intelligence for image, video, and text analysis through computer vision and natural language processing. The client allows users to authenticate, predict concepts in images, and access various functionalities provided by the Clarifai API. It follows a versioning scheme that aligns with the backend API updates and includes specific instructions for installation and troubleshooting. Users can explore the Clarifai demo, sign up for an account, and refer to the documentation for detailed information.
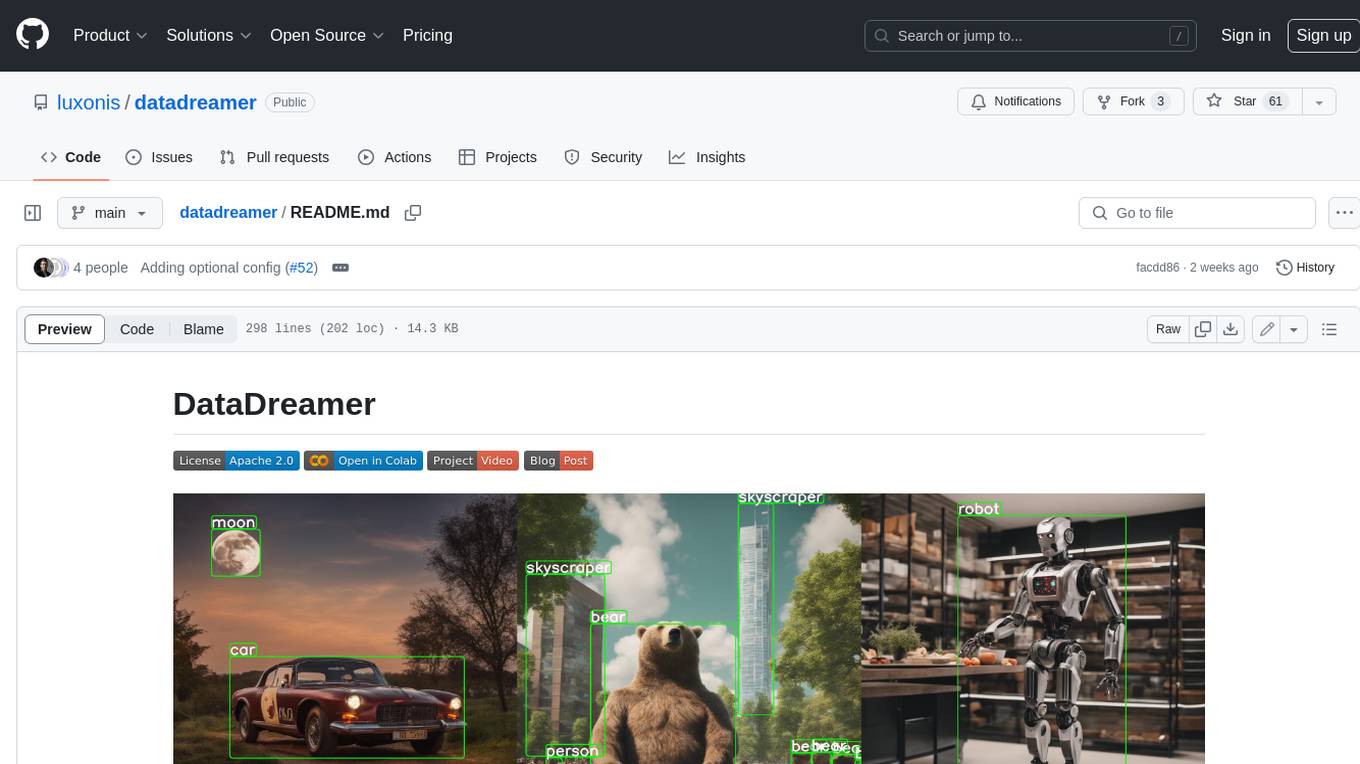
datadreamer
DataDreamer is an advanced toolkit designed to facilitate the development of edge AI models by enabling synthetic data generation, knowledge extraction from pre-trained models, and creation of efficient and potent models. It eliminates the need for extensive datasets by generating synthetic datasets, leverages latent knowledge from pre-trained models, and focuses on creating compact models suitable for integration into any device and performance for specialized tasks. The toolkit offers features like prompt generation, image generation, dataset annotation, and tools for training small-scale neural networks for edge deployment. It provides hardware requirements, usage instructions, available models, and limitations to consider while using the library.

shellChatGPT
ShellChatGPT is a shell wrapper for OpenAI's ChatGPT, DALL-E, Whisper, and TTS, featuring integration with LocalAI, Ollama, Gemini, Mistral, Groq, and GitHub Models. It provides text and chat completions, vision, reasoning, and audio models, voice-in and voice-out chatting mode, text editor interface, markdown rendering support, session management, instruction prompt manager, integration with various service providers, command line completion, file picker dialogs, color scheme personalization, stdin and text file input support, and compatibility with Linux, FreeBSD, MacOS, and Termux for a responsive experience.

yzma
yzma is a tool that allows you to write Go applications integrating llama.cpp for local inference using hardware acceleration. It supports running Vision Language Models (VLM) and Large/Small/Tiny Language Models (LLM) on Linux, macOS, or Windows with hardware acceleration like CUDA, Metal, or Vulkan. yzma uses purego and ffi packages, eliminating the need for CGo. It works with the latest llama.cpp releases, enabling users to leverage the newest features and model support.
For similar tasks

agentcloud
AgentCloud is an open-source platform that enables companies to build and deploy private LLM chat apps, empowering teams to securely interact with their data. It comprises three main components: Agent Backend, Webapp, and Vector Proxy. To run this project locally, clone the repository, install Docker, and start the services. The project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 only. Contributions and feedback are welcome from the community.

zep-python
Zep is an open-source platform for building and deploying large language model (LLM) applications. It provides a suite of tools and services that make it easy to integrate LLMs into your applications, including chat history memory, embedding, vector search, and data enrichment. Zep is designed to be scalable, reliable, and easy to use, making it a great choice for developers who want to build LLM-powered applications quickly and easily.
lollms
LoLLMs Server is a text generation server based on large language models. It provides a Flask-based API for generating text using various pre-trained language models. This server is designed to be easy to install and use, allowing developers to integrate powerful text generation capabilities into their applications.
LlamaIndexTS
LlamaIndex.TS is a data framework for your LLM application. Use your own data with large language models (LLMs, OpenAI ChatGPT and others) in Typescript and Javascript.
semantic-kernel
Semantic Kernel is an SDK that integrates Large Language Models (LLMs) like OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, and Hugging Face with conventional programming languages like C#, Python, and Java. Semantic Kernel achieves this by allowing you to define plugins that can be chained together in just a few lines of code. What makes Semantic Kernel _special_ , however, is its ability to _automatically_ orchestrate plugins with AI. With Semantic Kernel planners, you can ask an LLM to generate a plan that achieves a user's unique goal. Afterwards, Semantic Kernel will execute the plan for the user.
botpress
Botpress is a platform for building next-generation chatbots and assistants powered by OpenAI. It provides a range of tools and integrations to help developers quickly and easily create and deploy chatbots for various use cases.
BotSharp
BotSharp is an open-source machine learning framework for building AI bot platforms. It provides a comprehensive set of tools and components for developing and deploying intelligent virtual assistants. BotSharp is designed to be modular and extensible, allowing developers to easily integrate it with their existing systems and applications. With BotSharp, you can quickly and easily create AI-powered chatbots, virtual assistants, and other conversational AI applications.

qdrant
Qdrant is a vector similarity search engine and vector database. It is written in Rust, which makes it fast and reliable even under high load. Qdrant can be used for a variety of applications, including: * Semantic search * Image search * Product recommendations * Chatbots * Anomaly detection Qdrant offers a variety of features, including: * Payload storage and filtering * Hybrid search with sparse vectors * Vector quantization and on-disk storage * Distributed deployment * Highlighted features such as query planning, payload indexes, SIMD hardware acceleration, async I/O, and write-ahead logging Qdrant is available as a fully managed cloud service or as an open-source software that can be deployed on-premises.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.


