
stark
STaRK: Benchmarking LLM Retrieval on Textual and Relational Knowledge Bases (NeurIPS D&B 2024)
Stars: 317
STaRK is a large-scale semi-structure retrieval benchmark on Textual and Relational Knowledge Bases. It provides natural-sounding and practical queries crafted to incorporate rich relational information and complex textual properties, closely mirroring real-life scenarios. The benchmark aims to assess how effectively large language models can handle the interplay between textual and relational requirements in queries, using three diverse knowledge bases constructed from public sources.
README:
- [Oct 2024] Leaderboard: We construct the official leaderboard on Hunggingface and we are calling for submissions!
- [Oct 2024] Camera-ready paper is out! We add multiple retrieval models including BM25, Colbertv2, GritLM.
- [Sep 2024] STaRK is accepted to 2024 NeurIPS Dataset & Benchmark Track!
- [Jun 2024] We make our benchmark as a pip package stark-qa. You can directly load the data from the package now!
- [Jun 2024] We migrate our data to Hugging Face! You don't need to change anything, the data will be automatically downloaded.
- [May 2024] We have augmented our benchmark with three high-quality human-generated query datasets which are open to access. See more details in our updated arxiv!
- [May 9th 2024] We release STaRK SKB Explorer, an interactive interface for you to explore our knowledge bases!
- [May 7th 2024] We present STaRK in the 2024 Stanford Annual Affiliates Meeting and 2024 Stanford Data Science Conference.
- [May 5th 2024] STaRK was reported on Marketpost and 智源社区 BAAI. Thanks for writing about our work!
- [Apr 21st 2024] We release the STaRK benchmark.
STaRK is a large-scale Semi-structured Retrieval Benchmark on Textual and Relational Knowledge bases, covering applications in product search, academic paper search, and biomedicine inquiries.
Featuring diverse, natural-sounding, and practical queries that require context-specific reasoning, STaRK sets a new standard for assessing real-world retrieval systems driven by LLMs and presents significant challenges for future research.
🔥 Check out our website for more overview!
With python >=3.8 and <3.12
pip install stark-qaCreate a conda env with python >=3.8 and <3.12 and install required packages in requirements.txt.
conda create -n stark python=3.11
conda activate stark
pip install -r requirements.txtfrom stark_qa import load_qa, load_skb
dataset_name = 'amazon'
# Load the retrieval dataset
qa_dataset = load_qa(dataset_name)
idx_split = qa_dataset.get_idx_split()
# Load the semi-structured knowledge base
skb = load_skb(dataset_name, download_processed=True, root=None)The root argument for load_skb specifies the location to store SKB data. With default value None, the data will be stored in huggingface cache.
Question answer pairs for the retrieval task will be automatically downloaded in data/{dataset}/stark_qa by default. We provided official split in data/{dataset}/split.
There are two ways to load the knowledge base data:
- (Recommended) Instant downloading: The knowledge base data of all three benchmark will be automatically downloaded and loaded when setting
download_processed=True. - Process data from raw: We also provided all of our preprocessing code for transparency. Therefore, you can process the raw data from scratch via setting
download_processed=False. In this case, STaRK-PrimeKG takes around 5 minutes to download and load the processed data. STaRK-Amazon and STaRK-MAG may takes around an hour to process from the raw data.
If you are running eval, you may install the following packages:
pip install llm2vec gritlm bm25-
Our evaluation requires embed the node documents into
candidate_emb_dict.pt, which is a dictionarynode_id -> torch.Tensor. Query embeddings will be automatically generated if not available. You can either run the following the python script to download query embeddings and document embeddings generated bytext-embedding-ada-002. (We provide them so you can run on our benchmark right away.)python emb_download.py --dataset amazon --emb_dir emb/
Or you can run the following code to generate the query or document embeddings by yourself. E.g.,
python emb_generate.py --dataset amazon --mode query --emb_dir emb/ --emb_model text-embedding-ada-002
-
dataset: one ofamazon,magorprime. -
mode: the content to embed, one ofqueryordoc(node documents). -
emb_dir: the directory to store embeddings. -
emb_model: the LLM name to generate embeddings, such astext-embedding-ada-002,text-embedding-3-large, ,voyage-large-2-instruct,GritLM/GritLM-7B,McGill-NLP/LLM2Vec-Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct-mntp - See
emb_generate.pyfor other arguments.
-
-
Run the python script for evaluation. E.g.,
python eval.py --dataset amazon --model VSS --emb_dir emb/ --output_dir output/ --emb_model text-embedding-ada-002 --split test --save_predpython eval.py --dataset amazon --model VSS --emb_dir emb/ --output_dir output/ --emb_model GritLM/GritLM-7B --split test-0.1 --save_pred
python eval.py --dataset amazon --model LLMReranker --emb_dir emb/ --output_dir output/ --emb_model text-embedding-ada-002 --split human_generated_eval --llm_model gpt-4-1106-preview --save_pred
Key args:
-
dataset: the dataset to evaluate on, one ofamazon,magorprime. -
model: the model to be evaluated, one ofBM25,Colbertv2,VSS,MultiVSS,LLMReranker.- Please specify the name of embedding model with argument
--emb_model. - If you are using
LLMReranker, please specify the LLM name with argument--llm_model. - Specify API keys in command line
orexport ANTHROPIC_API_KEY=YOUR_API_KEY
orexport OPENAI_API_KEY=YOUR_API_KEY export OPENAI_ORG=YOUR_ORGANIZATIONexport VOYAGE_API_KEY=YOUR_API_KEY
- Please specify the name of embedding model with argument
-
emb_dir: the directory to store embeddings. -
split: the split to evaluate on, one oftrain,val,test,test-0.1(10% random sample), andhuman_generated_eval(to be evaluated on the human generated query dataset). -
output_dir: the directory to store evaluation outputs. -
surfix: Specify when the stored embeddings are in folderdoc{surfix}orquery{surfix}, e.g., _no_compact,
-
Please consider citing our paper if you use our benchmark or code in your work:
@inproceedings{wu24stark,
title = {STaRK: Benchmarking LLM Retrieval on Textual and Relational Knowledge Bases},
author = {
Shirley Wu and Shiyu Zhao and
Michihiro Yasunaga and Kexin Huang and
Kaidi Cao and Qian Huang and
Vassilis N. Ioannidis and Karthik Subbian and
James Zou and Jure Leskovec
},
booktitle = {NeurIPS Datasets and Benchmarks Track},
year = {2024}
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for stark
Similar Open Source Tools

stark
STaRK is a large-scale semi-structure retrieval benchmark on Textual and Relational Knowledge Bases. It provides natural-sounding and practical queries crafted to incorporate rich relational information and complex textual properties, closely mirroring real-life scenarios. The benchmark aims to assess how effectively large language models can handle the interplay between textual and relational requirements in queries, using three diverse knowledge bases constructed from public sources.
ice-score
ICE-Score is a tool designed to instruct large language models to evaluate code. It provides a minimum viable product (MVP) for evaluating generated code snippets using inputs such as problem, output, task, aspect, and model. Users can also evaluate with reference code and enable zero-shot chain-of-thought evaluation. The tool is built on codegen-metrics and code-bert-score repositories and includes datasets like CoNaLa and HumanEval. ICE-Score has been accepted to EACL 2024.
DeepPavlov
DeepPavlov is an open-source conversational AI library built on PyTorch. It is designed for the development of production-ready chatbots and complex conversational systems, as well as for research in the area of NLP and dialog systems. The library offers a wide range of models for tasks such as Named Entity Recognition, Intent/Sentence Classification, Question Answering, Sentence Similarity/Ranking, Syntactic Parsing, and more. DeepPavlov also provides embeddings like BERT, ELMo, and FastText for various languages, along with AutoML capabilities and integrations with REST API, Socket API, and Amazon AWS.
llama_index
LlamaIndex is a data framework for building LLM applications. It provides tools for ingesting, structuring, and querying data, as well as integrating with LLMs and other tools. LlamaIndex is designed to be easy to use for both beginner and advanced users, and it provides a comprehensive set of features for building LLM applications.
PDEBench
PDEBench provides a diverse and comprehensive set of benchmarks for scientific machine learning, including challenging and realistic physical problems. The repository consists of code for generating datasets, uploading and downloading datasets, training and evaluating machine learning models as baselines. It features a wide range of PDEs, realistic and difficult problems, ready-to-use datasets with various conditions and parameters. PDEBench aims for extensibility and invites participation from the SciML community to improve and extend the benchmark.
Pixel-Reasoner
Pixel Reasoner is a framework that introduces reasoning in the pixel-space for Vision-Language Models (VLMs), enabling them to directly inspect, interrogate, and infer from visual evidences. This enhances reasoning fidelity for visual tasks by equipping VLMs with visual reasoning operations like zoom-in and select-frame. The framework addresses challenges like model's imbalanced competence and reluctance to adopt pixel-space operations through a two-phase training approach involving instruction tuning and curiosity-driven reinforcement learning. With these visual operations, VLMs can interact with complex visual inputs such as images or videos to gather necessary information, leading to improved performance across visual reasoning benchmarks.
AirspeedVelocity.jl
AirspeedVelocity.jl is a tool designed to simplify benchmarking of Julia packages over their lifetime. It provides a CLI to generate benchmarks, compare commits/tags/branches, plot benchmarks, and run benchmark comparisons for every submitted PR as a GitHub action. The tool freezes the benchmark script at a specific revision to prevent old history from affecting benchmarks. Users can configure options using CLI flags and visualize benchmark results. AirspeedVelocity.jl can be used to benchmark any Julia package and offers features like generating tables and plots of benchmark results. It also supports custom benchmarks and can be integrated into GitHub actions for automated benchmarking of PRs.
distilabel
Distilabel is a framework for synthetic data and AI feedback for AI engineers that require high-quality outputs, full data ownership, and overall efficiency. It helps you synthesize data and provide AI feedback to improve the quality of your AI models. With Distilabel, you can: * **Synthesize data:** Generate synthetic data to train your AI models. This can help you to overcome the challenges of data scarcity and bias. * **Provide AI feedback:** Get feedback from AI models on your data. This can help you to identify errors and improve the quality of your data. * **Improve your AI output quality:** By using Distilabel to synthesize data and provide AI feedback, you can improve the quality of your AI models and get better results.
llmgraph
llmgraph is a tool that enables users to create knowledge graphs in GraphML, GEXF, and HTML formats by extracting world knowledge from large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT. It supports various entity types and relationships, offers cache support for efficient graph growth, and provides insights into LLM costs. Users can customize the model used and interact with different LLM providers. The tool allows users to generate interactive graphs based on a specified entity type and Wikipedia link, making it a valuable resource for knowledge graph creation and exploration.
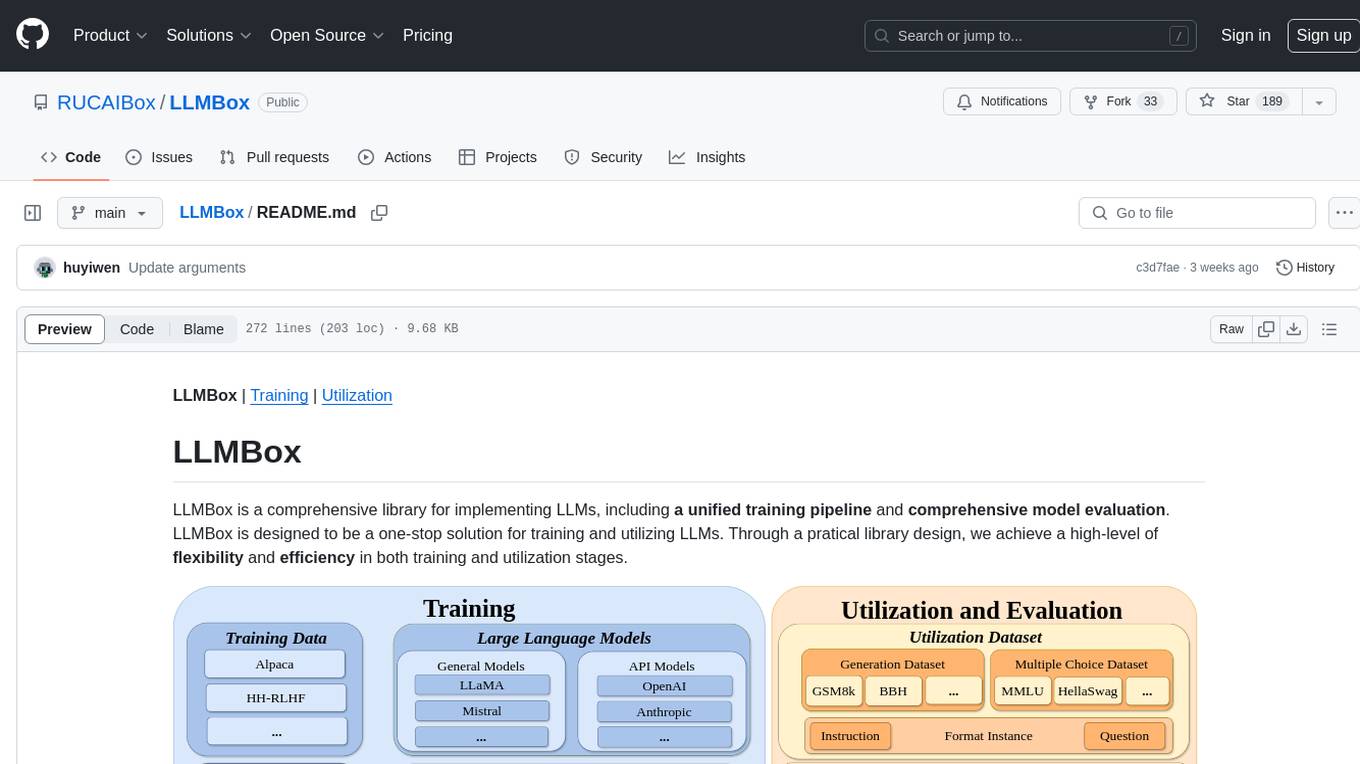
LLMBox
LLMBox is a comprehensive library designed for implementing Large Language Models (LLMs) with a focus on a unified training pipeline and comprehensive model evaluation. It serves as a one-stop solution for training and utilizing LLMs, offering flexibility and efficiency in both training and utilization stages. The library supports diverse training strategies, comprehensive datasets, tokenizer vocabulary merging, data construction strategies, parameter efficient fine-tuning, and efficient training methods. For utilization, LLMBox provides comprehensive evaluation on various datasets, in-context learning strategies, chain-of-thought evaluation, evaluation methods, prefix caching for faster inference, support for specific LLM models like vLLM and Flash Attention, and quantization options. The tool is suitable for researchers and developers working with LLMs for natural language processing tasks.
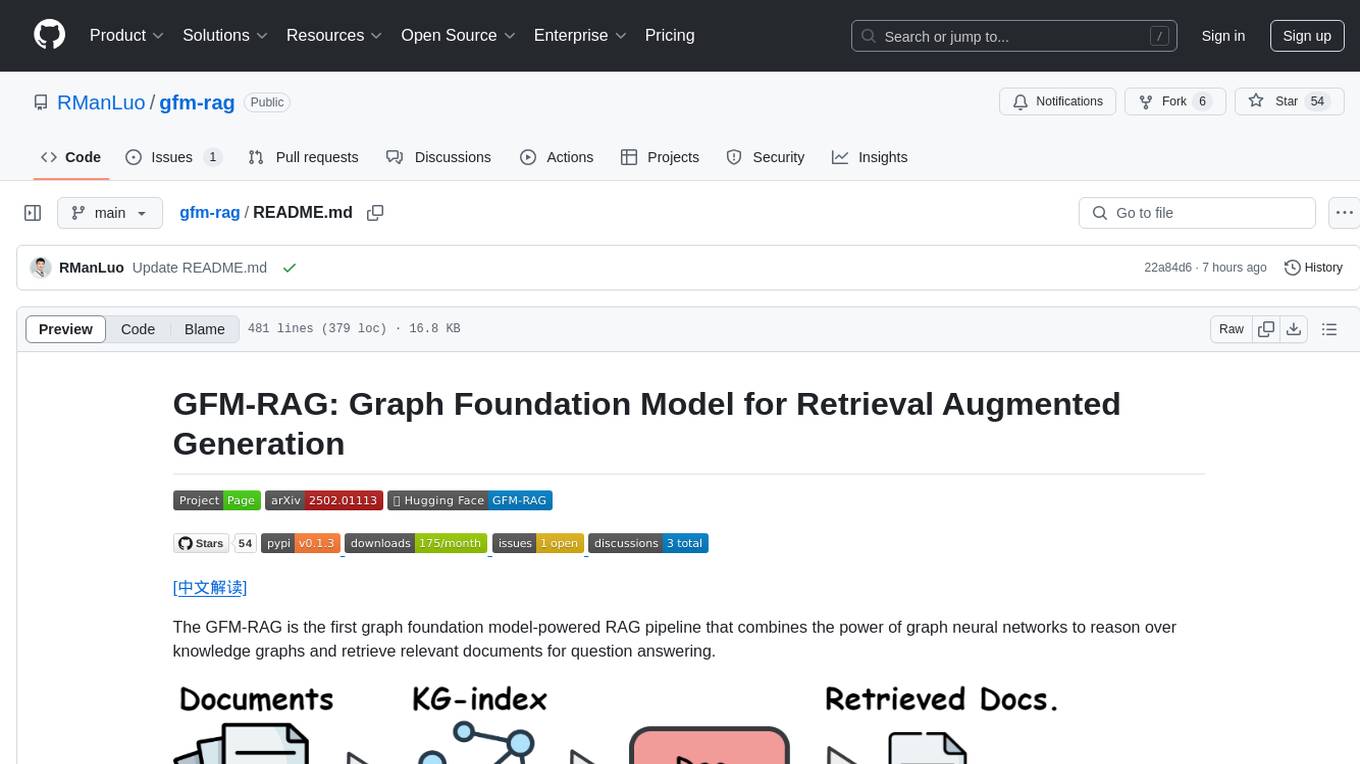
gfm-rag
The GFM-RAG is a graph foundation model-powered pipeline that combines graph neural networks to reason over knowledge graphs and retrieve relevant documents for question answering. It features a knowledge graph index, efficiency in multi-hop reasoning, generalizability to unseen datasets, transferability for fine-tuning, compatibility with agent-based frameworks, and interpretability of reasoning paths. The tool can be used for conducting retrieval and question answering tasks using pre-trained models or fine-tuning on custom datasets.
minja
Minja is a minimalistic C++ Jinja templating engine designed specifically for integration with C++ LLM projects, such as llama.cpp or gemma.cpp. It is not a general-purpose tool but focuses on providing a limited set of filters, tests, and language features tailored for chat templates. The library is header-only, requires C++17, and depends only on nlohmann::json. Minja aims to keep the codebase small, easy to understand, and offers decent performance compared to Python. Users should be cautious when using Minja due to potential security risks, and it is not intended for producing HTML or JavaScript output.
chatWeb
ChatWeb is a tool that can crawl web pages, extract text from PDF, DOCX, TXT files, and generate an embedded summary. It can answer questions based on text content using chatAPI and embeddingAPI based on GPT3.5. The tool calculates similarity scores between text vectors to generate summaries, performs nearest neighbor searches, and designs prompts to answer user questions. It aims to extract relevant content from text and provide accurate search results based on keywords. ChatWeb supports various modes, languages, and settings, including temperature control and PostgreSQL integration.
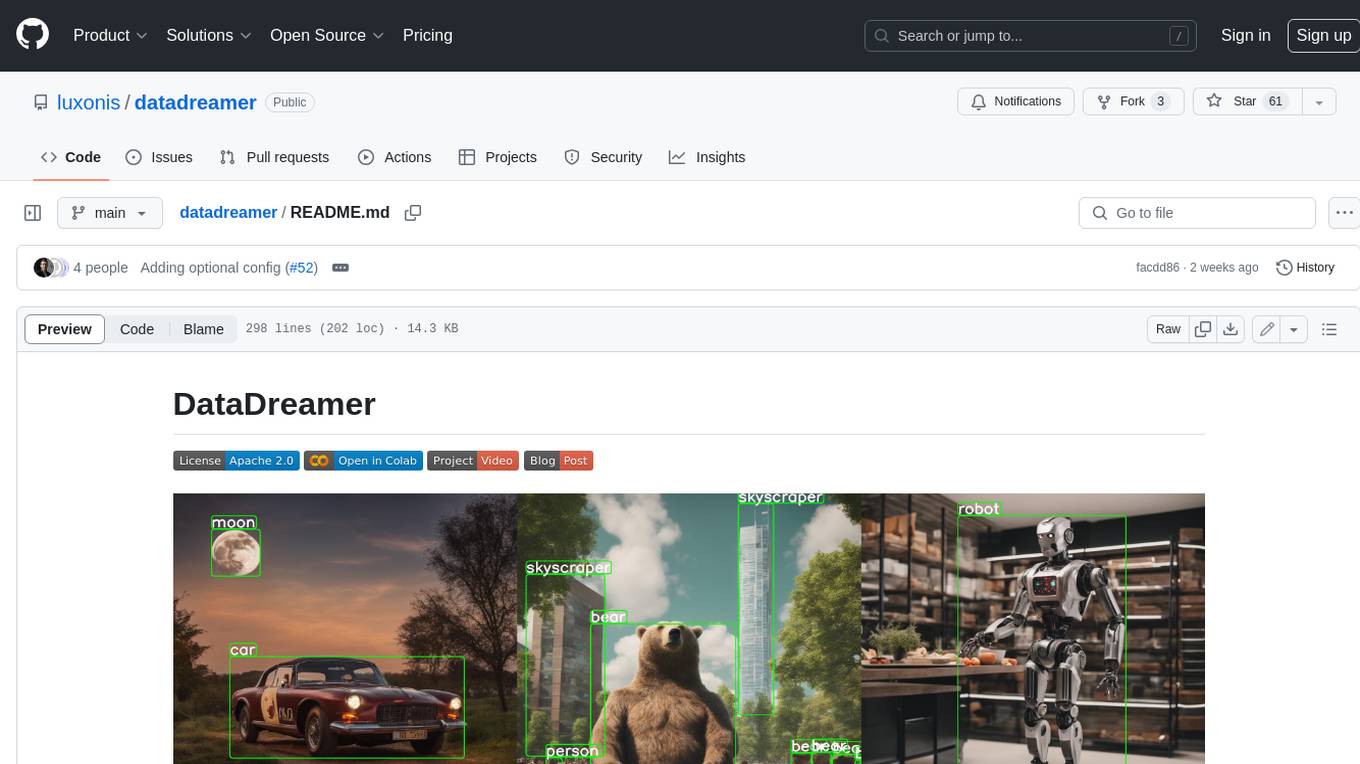
datadreamer
DataDreamer is an advanced toolkit designed to facilitate the development of edge AI models by enabling synthetic data generation, knowledge extraction from pre-trained models, and creation of efficient and potent models. It eliminates the need for extensive datasets by generating synthetic datasets, leverages latent knowledge from pre-trained models, and focuses on creating compact models suitable for integration into any device and performance for specialized tasks. The toolkit offers features like prompt generation, image generation, dataset annotation, and tools for training small-scale neural networks for edge deployment. It provides hardware requirements, usage instructions, available models, and limitations to consider while using the library.
probsem
ProbSem is a repository that provides a framework to leverage large language models (LLMs) for assigning context-conditional probability distributions over queried strings. It supports OpenAI engines and HuggingFace CausalLM models, and is flexible for research applications in linguistics, cognitive science, program synthesis, and NLP. Users can define prompts, contexts, and queries to derive probability distributions over possible completions, enabling tasks like cloze completion, multiple-choice QA, semantic parsing, and code completion. The repository offers CLI and API interfaces for evaluation, with options to customize models, normalize scores, and adjust temperature for probability distributions.
topicGPT
TopicGPT is a repository containing scripts and prompts for the paper 'TopicGPT: Topic Modeling by Prompting Large Language Models' (NAACL'24). The 'topicgpt_python' package offers functions to generate high-level and specific topics, refine topics, assign topics to input text, and correct generated topics. It supports various APIs like OpenAI, VertexAI, Azure, Gemini, and vLLM for inference. Users can prepare data in JSONL format, run the pipeline using provided scripts, and evaluate topic alignment with ground-truth labels.
For similar tasks

stark
STaRK is a large-scale semi-structure retrieval benchmark on Textual and Relational Knowledge Bases. It provides natural-sounding and practical queries crafted to incorporate rich relational information and complex textual properties, closely mirroring real-life scenarios. The benchmark aims to assess how effectively large language models can handle the interplay between textual and relational requirements in queries, using three diverse knowledge bases constructed from public sources.
monitors4codegen
This repository hosts the official code and data artifact for the paper 'Monitor-Guided Decoding of Code LMs with Static Analysis of Repository Context'. It introduces Monitor-Guided Decoding (MGD) for code generation using Language Models, where a monitor uses static analysis to guide the decoding. The repository contains datasets, evaluation scripts, inference results, a language server client 'multilspy' for static analyses, and implementation of various monitors monitoring for different properties in 3 programming languages. The monitors guide Language Models to adhere to properties like valid identifier dereferences, correct number of arguments to method calls, typestate validity of method call sequences, and more.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.










