
llmc
[EMNLP 2024 Industry Track] This is the official PyTorch implementation of "LLMC: Benchmarking Large Language Model Quantization with a Versatile Compression Toolkit".
Stars: 430
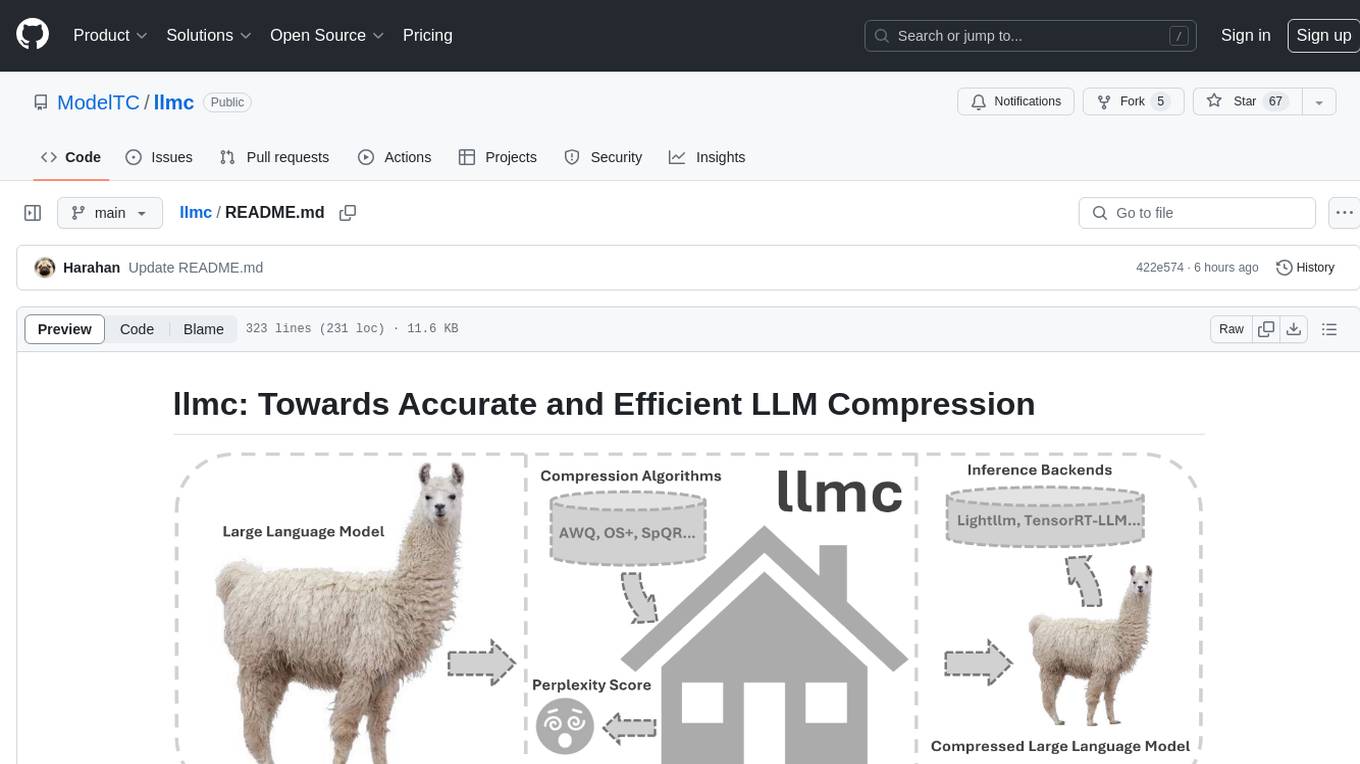
llmc is an off-the-shell tool designed for compressing LLM, leveraging state-of-the-art compression algorithms to enhance efficiency and reduce model size without compromising performance. It provides users with the ability to quantize LLMs, choose from various compression algorithms, export transformed models for further optimization, and directly infer compressed models with a shallow memory footprint. The tool supports a range of model types and quantization algorithms, with ongoing development to include pruning techniques. Users can design their configurations for quantization and evaluation, with documentation and examples planned for future updates. llmc is a valuable resource for researchers working on post-training quantization of large language models.
README:
LLMC is an off-the-shell tool designed for compressing LLM, leveraging state-of-the-art compression algorithms to enhance efficiency and reduce model size without compromising performance.
English doc is here.
Chinese doc is here.
Docker hub is here.
Aliyun docker: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/yongyang/llmcompression:[tag]
You can download the Docker image that can run llmc with the following command. Users in mainland China are recommended to use Alibaba Cloud Docker.
docker hub
docker pull llmcompression/llmc:pure-latest
aliyun docker
docker pull registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/yongyang/llmcompression:pure-latest
Community:
-
Feb 7, 2025: 🔥 We now fully support quantization of large-scale
MOEmodels likeDeepSeekv3,DeepSeek-R1, andDeepSeek-R1-zerowith671Bparameters. You can now directly load FP8 weights without any extra conversion. AWQ and RTN quantization can run on a single 80GB GPU, and we also support the export of true quantized INT4/INT8 weights. -
Nov 20, 2024: 🔥 We now fully support the quantization of ✨
DeepSeekv2(2.5)and otherMOEmodels, as well as ✨Qwen2VL,Llama3.2, and otherVLMmodels. Supported quantization methods include ✅integer quantization, ✅floating-point quantization, and advanced algorithms like ✅AWQ, ✅GPTQ, ✅SmoothQuant, and ✅Quarot. -
Nov 12, 2024: 🔥 We have added support for 💥
static per-tensor activation quantizationacross various models and algorithms, covering ✅integer quantization and ✅floating-point quantization to further optimize performance and efficiency. Additionally, we now support exporting ✨real quantized modelsand using the VLLM and SGLang backends for inference acceleration. For more details, refer to the VLLM documentation and SGLang documentation. -
Sep 26, 2024: 🔥 We now support exporting 💥
FP8 quantized(E4M3, E5M2)models from 🚀LLMCto advanced inference backends such as VLLM and SGLang. For detailed usage, please refer to the VLLM documentation and SGLang documentation. -
Sep 24, 2024: 🔥 We have officially released ✅INT4 and ✅INT8 models of ✨
Llama-3.1-405B, quantized using 🚀LLMCinsave_lightllmmode. You can download the model parameters here. -
Sep 23, 2024: 🔥 We now support exporting ✨
real quantized(INT4, INT8)models from 🚀LLMCto advanced inference backends such as VLLM, SGLang, AutoAWQ, and MLC-LLM for quantized inference deployment, enabling ✨reduced memory usageand ✨faster inference speeds. For detailed usage, please refer to the VLLM documentation, SGLang documentation, AutoAWQ documentation, and MLC-LLM documentation. -
Sep 9, 2024: 🔥 We provide some configs of our best practice towards superior performance (see Best Practice here).
-
Sep 3, 2024: 🔥 We support opencompass 🤗 to eval 🚀
LLMCmodel. Follow this doc and have a try! -
Aug 22, 2024: 🔥We support lots of small language models, including current SOTA SmolLM(see Supported Model List).
-
Aug 22, 2024: 🔥 Additionally, we also support down stream task evaluation through our modified lm-evaluation-harness 🤗. Specifically, people can first employ
save_transmode(seesavepart in Configuration) to save a weight modified model. After obtaining the transformed model, they can directly evaluate the quantized model referring to run_lm_eval.sh. More details can be found in here. -
Jul 23, 2024: 🍺🍺🍺 We release a brand new version benchmark paper:
LLMC: Benchmarking Large Language Model Quantization with a Versatile Compression Toolkit.
Ruihao Gong*, Yang Yong*, Shiqiao Gu*, Yushi Huang*, Chengtao Lv, Yunchen Zhang, Xianglong Liu📧, Dacheng Tao
(* denotes equal contribution, 📧 denotes corresponding author.)
Previous News
-
Jul 16, 2024: 🔥We support Wanda/Naive(Magnitude) for llm sparsification and layer-wise mix bits quantization now!
-
Jul 14, 2024: 🔥We support rotation based quantization QuaRot now!
-
May 17, 2024: 🚀 We support some advanced large models, e.g., LLaVA, Mixtral, LLaMA V3 and Qwen V2 now. Have a try!
-
May 13, 2024: 🍺🍺🍺 We release our quantization benchmark paper:
Ruihao Gong*, Yang Yong*, Shiqiao Gu*, Yushi Huang*, Yunchen Zhang, Xianglong Liu📧, Dacheng Tao
(* denotes equal contribution, 📧 denotes corresponding author.)
We modularly and fairly benchmark the quantization techniques considering calibration cost, inference efficiency, and quantized accuracy. Near 600 experiments on diverse models and datasets provide three insightful takeaways on the calibration data, algorithm pipeline, and quantization configuration selection. Based on the takeaways, a best practice for the LLM PTQ pipeline is designed, to achieve the best accuracy and efficiency performance balance under various scenarios.
-
Mar 7, 2024: 🚀 We release the quantization part of a powerful and efficient LLM compression tool. Notably, our benchmark paper is coming soon😊.
-
💥Comprehensive Algorithm Support: Provides a broad range of ✨
SOTA compression algorithms, including ✅quantization, ✅mixed-precision quantization, and ✅sparsity, while maintaining accuracy consistent with the original repositories. ✨Quantization best practices(see 🚀Best Practiceshere) are also available to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. -
💥Supported Formats: Supports both ✨
quantization(integer and floating-point) and ✨sparsity, specifically including ✅weight-activation, ✅weight-only, ✅mixed-precision quantization, as well as ✅structured and ✅unstructured sparsity. -
💥Wide Model Support: Offers support for a diverse array of ✨
LLM models, including ✅LLama, ✅Mistral, ✅InternLM2, ✅Qwen2, among others, as well as ✅MOE(DeepSeekv2, Deepseek-R1) and ✅VLM(Llama3.2-vision, Qwen2-vl) models (see Supported Model List). -
💥Multi-backend Compatibility: Seamlessly integrates with various backends for enhanced deployment flexibility. Multiple quantization settings and model formats are compatible with a wide range of backends and hardware platforms, such as ✅VLLM, ✅Sglang, ✅LightLLM, ✅MLC-LLM, and ✅AutoAWQ, making it highly versatile(see Section
Backendhere). -
💥Performance Efficiency: Enables quantization of large LLMs, such as ✨
Llama3.1-405Band ✨DeepSeek-R1-671B, with PPL evaluation on asingle A100/H100/H800 GPU.
Please refer to the 🚀Quick Start section in the documentation.
✅ BLOOM
✅ LLaMA
✅ LLaMA V2
✅ OPT
✅ Falcon
✅ Mistral
✅ LLaMA V3
✅ Mixtral
✅ Qwen V2
✅ LLaVA
✅ StableLM
✅ Gemma2
✅ Phi2
✅ Phi 1.5
✅ MiniCPM
✅ SmolLM
✅ Qwen MOE
✅ Qwen2-VL
You can add your own model type referring to files under llmc/models/*.py.
✅ VLLM
✅ LightLLM
✅ Sglang
✅ MLC-LLM
✅ AutoAWQ
✅ Naive
✅ AWQ
✅ GPTQ
✅ OS+
✅ AdaDim
✅ QUIK
✅ SpQR
✅ DGQ
✅ OWQ
✅ HQQ
✅ QuaRot
✅ TesseraQ
✅ Naive(Magnitude)
✅ Wanda
✅ ShortGPT
We develop our code referring to the following repos:
- https://github.com/mit-han-lab/llm-awq
- https://github.com/mit-han-lab/smoothquant
- https://github.com/OpenGVLab/OmniQuant
- https://github.com/IST-DASLab/gptq
- https://github.com/ModelTC/Outlier_Suppression_Plus
- https://github.com/IST-DASLab/QUIK
- https://github.com/Vahe1994/SpQR
- https://github.com/ilur98/DGQ
- https://github.com/xvyaward/owq
- https://github.com/TimDettmers/bitsandbytes
- https://github.com/mobiusml/hqq
- https://github.com/spcl/QuaRot
- https://github.com/locuslab/wanda
- https://github.com/EleutherAI/lm-evaluation-harness
- https://github.com/facebookresearch/SpinQuant
- https://github.com/Intelligent-Computing-Lab-Yale/TesseraQ
If you find our LLM-QBench paper/llmc toolkit useful or relevant to your research, please kindly cite our paper:
@misc{llmc,
author = {llmc contributors},
title = {llmc: Towards Accurate and Efficient LLM Compression},
year = {2024},
publisher = {GitHub},
journal = {GitHub repository},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/ModelTC/llmc}},
}
@misc{gong2024llmqbench,
title={LLM-QBench: A Benchmark Towards the Best Practice for Post-training Quantization of Large Language Models},
author={Ruihao Gong and Yang Yong and Shiqiao Gu and Yushi Huang and Yunchen Zhang and Xianglong Liu and Dacheng Tao},
year={2024},
eprint={2405.06001},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.LG}
}
@misc{gong2024llmcbenchmarkinglargelanguage,
title={LLMC: Benchmarking Large Language Model Quantization with a Versatile Compression Toolkit},
author={Ruihao Gong and Yang Yong and Shiqiao Gu and Yushi Huang and Chentao Lv and Yunchen Zhang and Xianglong Liu and Dacheng Tao},
year={2024},
eprint={2405.06001},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.LG},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2405.06001},
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for llmc
Similar Open Source Tools

llmc
llmc is an off-the-shell tool designed for compressing LLM, leveraging state-of-the-art compression algorithms to enhance efficiency and reduce model size without compromising performance. It provides users with the ability to quantize LLMs, choose from various compression algorithms, export transformed models for further optimization, and directly infer compressed models with a shallow memory footprint. The tool supports a range of model types and quantization algorithms, with ongoing development to include pruning techniques. Users can design their configurations for quantization and evaluation, with documentation and examples planned for future updates. llmc is a valuable resource for researchers working on post-training quantization of large language models.
LLM-as-HH
LLM-as-HH is a codebase that accompanies the paper ReEvo: Large Language Models as Hyper-Heuristics with Reflective Evolution. It introduces Language Hyper-Heuristics (LHHs) that leverage LLMs for heuristic generation with minimal manual intervention and open-ended heuristic spaces. Reflective Evolution (ReEvo) is presented as a searching framework that emulates the reflective design approach of human experts while surpassing human capabilities with scalable LLM inference, Internet-scale domain knowledge, and powerful evolutionary search. The tool can improve various algorithms on problems like Traveling Salesman Problem, Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem, Orienteering Problem, Multiple Knapsack Problems, Bin Packing Problem, and Decap Placement Problem in both black-box and white-box settings.
MathCoder
MathCoder is a repository focused on enhancing mathematical reasoning by fine-tuning open-source language models to use code for modeling and deriving math equations. It introduces MathCodeInstruct dataset with solutions interleaving natural language, code, and execution results. The repository provides MathCoder models capable of generating code-based solutions for challenging math problems, achieving state-of-the-art scores on MATH and GSM8K datasets. It offers tools for model deployment, inference, and evaluation, along with a citation for referencing the work.

MM-RLHF
MM-RLHF is a comprehensive project for aligning Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) with human preferences. It includes a high-quality MLLM alignment dataset, a Critique-Based MLLM reward model, a novel alignment algorithm MM-DPO, and benchmarks for reward models and multimodal safety. The dataset covers image understanding, video understanding, and safety-related tasks with model-generated responses and human-annotated scores. The reward model generates critiques of candidate texts before assigning scores for enhanced interpretability. MM-DPO is an alignment algorithm that achieves performance gains with simple adjustments to the DPO framework. The project enables consistent performance improvements across 10 dimensions and 27 benchmarks for open-source MLLMs.
dash-infer
DashInfer is a C++ runtime tool designed to deliver production-level implementations highly optimized for various hardware architectures, including x86 and ARMv9. It supports Continuous Batching and NUMA-Aware capabilities for CPU, and can fully utilize modern server-grade CPUs to host large language models (LLMs) up to 14B in size. With lightweight architecture, high precision, support for mainstream open-source LLMs, post-training quantization, optimized computation kernels, NUMA-aware design, and multi-language API interfaces, DashInfer provides a versatile solution for efficient inference tasks. It supports x86 CPUs with AVX2 instruction set and ARMv9 CPUs with SVE instruction set, along with various data types like FP32, BF16, and InstantQuant. DashInfer also offers single-NUMA and multi-NUMA architectures for model inference, with detailed performance tests and inference accuracy evaluations available. The tool is supported on mainstream Linux server operating systems and provides documentation and examples for easy integration and usage.
eole
EOLE is an open language modeling toolkit based on PyTorch. It aims to provide a research-friendly approach with a comprehensive yet compact and modular codebase for experimenting with various types of language models. The toolkit includes features such as versatile training and inference, dynamic data transforms, comprehensive large language model support, advanced quantization, efficient finetuning, flexible inference, and tensor parallelism. EOLE is a work in progress with ongoing enhancements in configuration management, command line entry points, reproducible recipes, core API simplification, and plans for further simplification, refactoring, inference server development, additional recipes, documentation enhancement, test coverage improvement, logging enhancements, and broader model support.
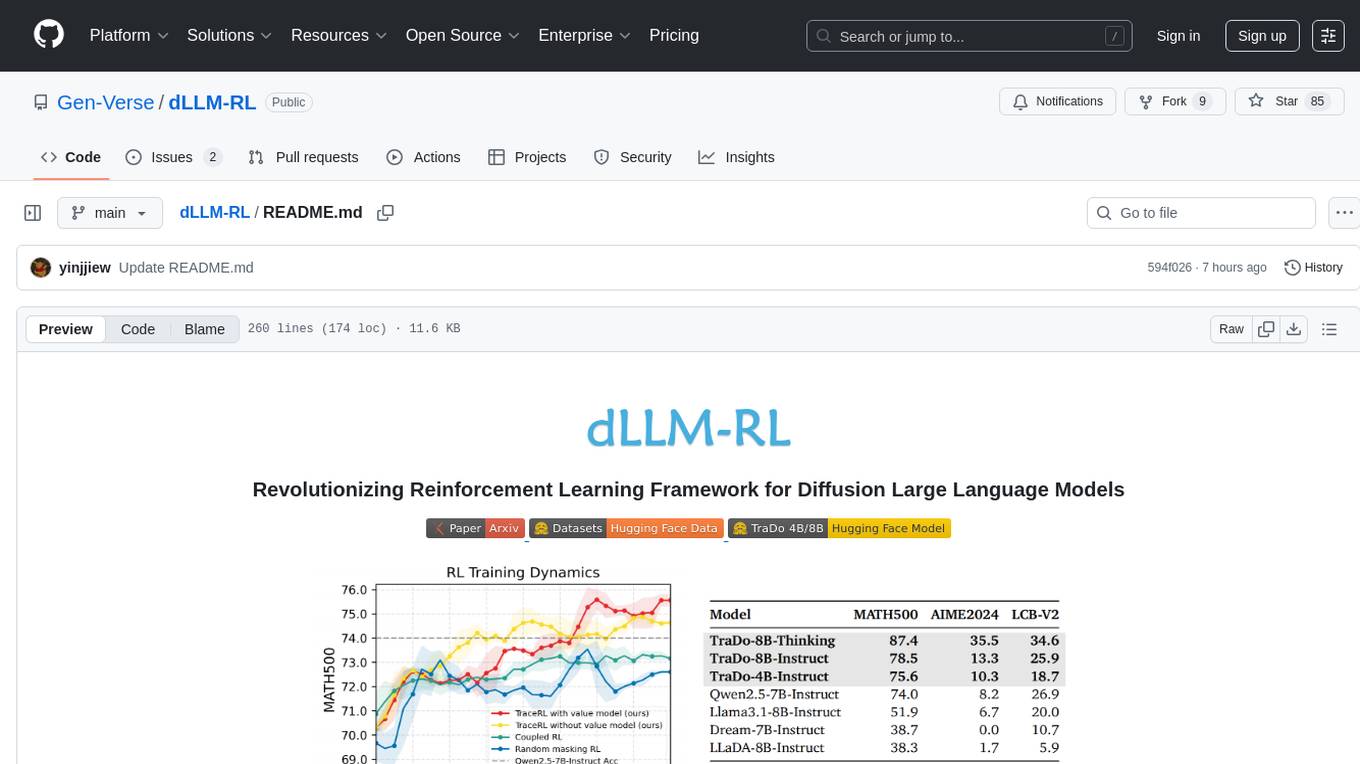
dLLM-RL
dLLM-RL is a revolutionary reinforcement learning framework designed for Diffusion Large Language Models. It supports various models with diverse structures, offers inference acceleration, RL training capabilities, and SFT functionalities. The tool introduces TraceRL for trajectory-aware RL and diffusion-based value models for optimization stability. Users can download and try models like TraDo-4B-Instruct and TraDo-8B-Instruct. The tool also provides support for multi-node setups and easy building of reinforcement learning methods. Additionally, it offers supervised fine-tuning strategies for different models and tasks.
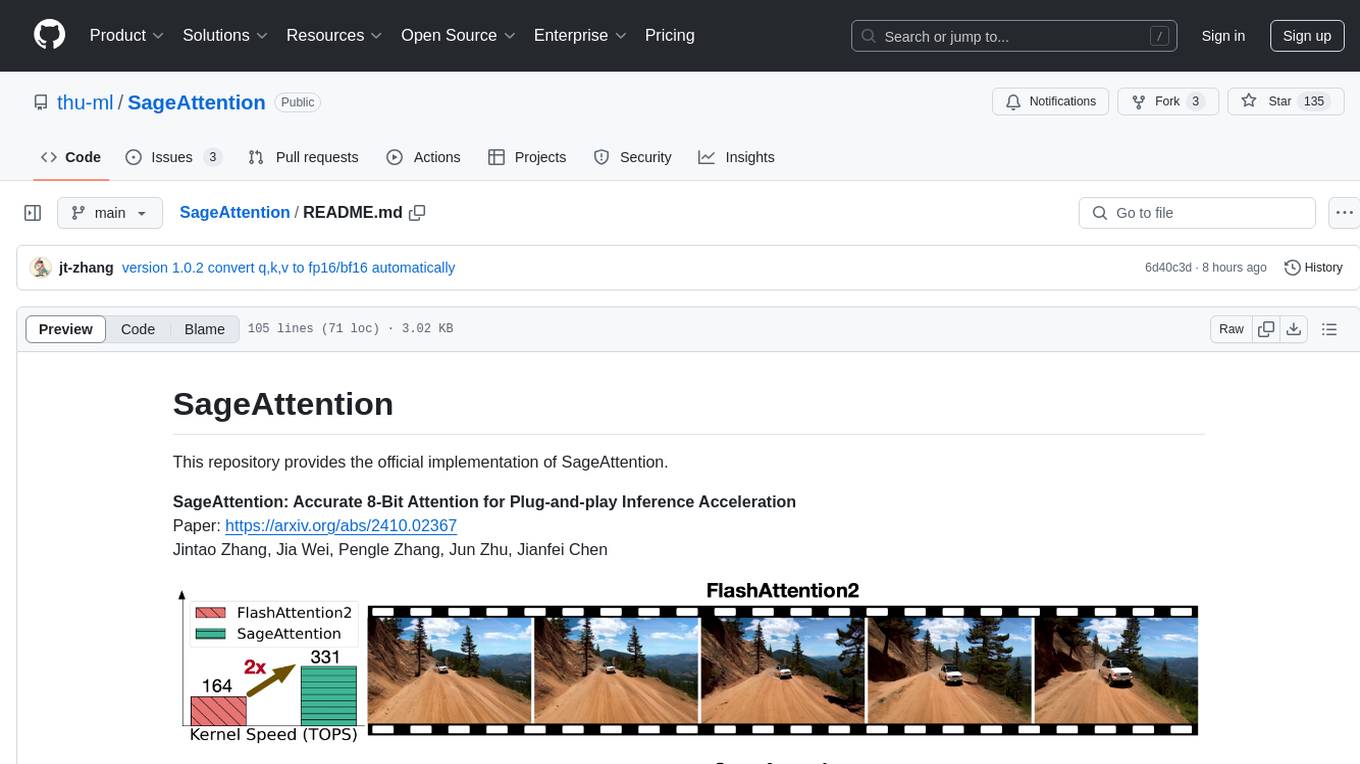
SageAttention
SageAttention is an official implementation of an accurate 8-bit attention mechanism for plug-and-play inference acceleration. It is optimized for RTX4090 and RTX3090 GPUs, providing performance improvements for specific GPU architectures. The tool offers a technique called 'smooth_k' to ensure accuracy in processing FP16/BF16 data. Users can easily replace 'scaled_dot_product_attention' with SageAttention for faster video processing.
speculators
Speculators is a unified library for building, training, and storing speculative decoding algorithms for large language model (LLM) inference. It speeds up LLM inference by using a smaller, faster draft model (the speculator) to propose tokens, which are then verified by the larger base model, reducing latency without compromising output quality. Trained models can seamlessly run in vLLM, enabling the deployment of speculative decoding in production-grade inference servers.
APOLLO
APOLLO is a memory-efficient optimizer designed for large language model (LLM) pre-training and full-parameter fine-tuning. It offers SGD-like memory cost with AdamW-level performance. The optimizer integrates low-rank approximation and optimizer state redundancy reduction to achieve significant memory savings while maintaining or surpassing the performance of Adam(W). Key contributions include structured learning rate updates for LLM training, approximated channel-wise gradient scaling in a low-rank auxiliary space, and minimal-rank tensor-wise gradient scaling. APOLLO aims to optimize memory efficiency during training large language models.
open-unlearning
OpenUnlearning is an easily extensible framework that unifies LLM unlearning evaluation benchmarks. It provides efficient implementations of TOFU and MUSE unlearning benchmarks, supporting 5 unlearning methods, 3+ datasets, 6+ evaluation metrics, and 7+ LLMs. Users can easily extend the framework to incorporate more variants, collaborate by adding new benchmarks, unlearning methods, datasets, and evaluation metrics, and drive progress in the field.

only_train_once
Only Train Once (OTO) is an automatic, architecture-agnostic DNN training and compression framework that allows users to train a general DNN from scratch or a pretrained checkpoint to achieve high performance and slimmer architecture simultaneously in a one-shot manner without fine-tuning. The framework includes features for automatic structured pruning and erasing operators, as well as hybrid structured sparse optimizers for efficient model compression. OTO provides tools for pruning zero-invariant group partitioning, constructing pruned models, and visualizing pruning and erasing dependency graphs. It supports the HESSO optimizer and offers a sanity check for compliance testing on various DNNs. The repository also includes publications, installation instructions, quick start guides, and a roadmap for future enhancements and collaborations.

cleanlab
Cleanlab helps you **clean** data and **lab** els by automatically detecting issues in a ML dataset. To facilitate **machine learning with messy, real-world data** , this data-centric AI package uses your _existing_ models to estimate dataset problems that can be fixed to train even _better_ models.
opencompass
OpenCompass is a one-stop platform for large model evaluation, aiming to provide a fair, open, and reproducible benchmark for large model evaluation. Its main features include: * Comprehensive support for models and datasets: Pre-support for 20+ HuggingFace and API models, a model evaluation scheme of 70+ datasets with about 400,000 questions, comprehensively evaluating the capabilities of the models in five dimensions. * Efficient distributed evaluation: One line command to implement task division and distributed evaluation, completing the full evaluation of billion-scale models in just a few hours. * Diversified evaluation paradigms: Support for zero-shot, few-shot, and chain-of-thought evaluations, combined with standard or dialogue-type prompt templates, to easily stimulate the maximum performance of various models. * Modular design with high extensibility: Want to add new models or datasets, customize an advanced task division strategy, or even support a new cluster management system? Everything about OpenCompass can be easily expanded! * Experiment management and reporting mechanism: Use config files to fully record each experiment, and support real-time reporting of results.

petals
Petals is a tool that allows users to run large language models at home in a BitTorrent-style manner. It enables fine-tuning and inference up to 10x faster than offloading. Users can generate text with distributed models like Llama 2, Falcon, and BLOOM, and fine-tune them for specific tasks directly from their desktop computer or Google Colab. Petals is a community-run system that relies on people sharing their GPUs to increase its capacity and offer a distributed network for hosting model layers.

rl
TorchRL is an open-source Reinforcement Learning (RL) library for PyTorch. It provides pytorch and **python-first** , low and high level abstractions for RL that are intended to be **efficient** , **modular** , **documented** and properly **tested**. The code is aimed at supporting research in RL. Most of it is written in python in a highly modular way, such that researchers can easily swap components, transform them or write new ones with little effort.
For similar tasks
aimet
AIMET is a library that provides advanced model quantization and compression techniques for trained neural network models. It provides features that have been proven to improve run-time performance of deep learning neural network models with lower compute and memory requirements and minimal impact to task accuracy. AIMET is designed to work with PyTorch, TensorFlow and ONNX models. We also host the AIMET Model Zoo - a collection of popular neural network models optimized for 8-bit inference. We also provide recipes for users to quantize floating point models using AIMET.
hqq
HQQ is a fast and accurate model quantizer that skips the need for calibration data. It's super simple to implement (just a few lines of code for the optimizer). It can crunch through quantizing the Llama2-70B model in only 4 minutes! 🚀
llm-resource
llm-resource is a comprehensive collection of high-quality resources for Large Language Models (LLM). It covers various aspects of LLM including algorithms, training, fine-tuning, alignment, inference, data engineering, compression, evaluation, prompt engineering, AI frameworks, AI basics, AI infrastructure, AI compilers, LLM application development, LLM operations, AI systems, and practical implementations. The repository aims to gather and share valuable resources related to LLM for the community to benefit from.

llmc
llmc is an off-the-shell tool designed for compressing LLM, leveraging state-of-the-art compression algorithms to enhance efficiency and reduce model size without compromising performance. It provides users with the ability to quantize LLMs, choose from various compression algorithms, export transformed models for further optimization, and directly infer compressed models with a shallow memory footprint. The tool supports a range of model types and quantization algorithms, with ongoing development to include pruning techniques. Users can design their configurations for quantization and evaluation, with documentation and examples planned for future updates. llmc is a valuable resource for researchers working on post-training quantization of large language models.
Awesome-Efficient-LLM
Awesome-Efficient-LLM is a curated list focusing on efficient large language models. It includes topics such as knowledge distillation, network pruning, quantization, inference acceleration, efficient MOE, efficient architecture of LLM, KV cache compression, text compression, low-rank decomposition, hardware/system, tuning, and survey. The repository provides a collection of papers and projects related to improving the efficiency of large language models through various techniques like sparsity, quantization, and compression.
TensorRT-Model-Optimizer
The NVIDIA TensorRT Model Optimizer is a library designed to quantize and compress deep learning models for optimized inference on GPUs. It offers state-of-the-art model optimization techniques including quantization and sparsity to reduce inference costs for generative AI models. Users can easily stack different optimization techniques to produce quantized checkpoints from torch or ONNX models. The quantized checkpoints are ready for deployment in inference frameworks like TensorRT-LLM or TensorRT, with planned integrations for NVIDIA NeMo and Megatron-LM. The tool also supports 8-bit quantization with Stable Diffusion for enterprise users on NVIDIA NIM. Model Optimizer is available for free on NVIDIA PyPI, and this repository serves as a platform for sharing examples, GPU-optimized recipes, and collecting community feedback.
Awesome_LLM_System-PaperList
Since the emergence of chatGPT in 2022, the acceleration of Large Language Model has become increasingly important. Here is a list of papers on LLMs inference and serving.
llm-compressor
llm-compressor is an easy-to-use library for optimizing models for deployment with vllm. It provides a comprehensive set of quantization algorithms, seamless integration with Hugging Face models and repositories, and supports mixed precision, activation quantization, and sparsity. Supported algorithms include PTQ, GPTQ, SmoothQuant, and SparseGPT. Installation can be done via git clone and local pip install. Compression can be easily applied by selecting an algorithm and calling the oneshot API. The library also offers end-to-end examples for model compression. Contributions to the code, examples, integrations, and documentation are appreciated.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.








