
Video-MME
✨✨Video-MME: The First-Ever Comprehensive Evaluation Benchmark of Multi-modal LLMs in Video Analysis
Stars: 225
Video-MME is the first-ever comprehensive evaluation benchmark of Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) in Video Analysis. It assesses the capabilities of MLLMs in processing video data, covering a wide range of visual domains, temporal durations, and data modalities. The dataset comprises 900 videos with 256 hours and 2,700 human-annotated question-answer pairs. It distinguishes itself through features like duration variety, diversity in video types, breadth in data modalities, and quality in annotations.
README:
Video-MME applies to both image MLLMs, i.e., generalizing to multiple images, and video MLLMs. 🌟
-
2024.06.15🌟 We have refreshed our evaluation: 1) replace broken and potentially broken video links, and re-annotated them; 2) GPT-4o now samples 384 frames (previously 10 from the website) at 512x512 resolution, boosting overall accuracy to 71.9%. -
2024.06.03🌟 We are very proud to launch Video-MME, the first-ever comprehensive evaluation benchmark of MLLMs in Video Analysis!
In the quest for artificial general intelligence, Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have emerged as a focal point in recent advancements, but their potential in processing sequential visual data is still insufficiently explored. We introduce Video-MME, the first-ever full-spectrum, Multi-Modal Evaluation benchmark of MLLMs in Video analysis. It is designed to comprehensively assess the capabilities of MLLMs in processing video data, covering a wide range of visual domains, temporal durations, and data modalities. Video-MME comprises 900 videos with a total of 254 hours, and 2,700 human-annotated question-answer pairs. Our work distinguishes from existing benchmarks through four key features:
- Duration in temporal dimension. Encompassing both short- (< 2min), medium- (4min~15min), and long-term (30min~60min) videos, ranging from 11 seconds to 1 hour, for robust contextual dynamics;
- Diversity in video types. Spanning 6 primary visual domains, i.e., Knowledge, Film & Television, Sports Competition, Life Record, and Multilingual, with 30 subfields to ensure broad scenario generalizability;
- Breadth in data modalities. Integrating multi-modal inputs besides video frames, including subtitles and audios, to assess the all-round capabilities of MLLMs;
- Quality in annotations. All data are newly collected and annotated by humans, not from any existing video dataset, ensuring diversity and quality.
License:
Video-MME is only used for academic research. Commercial use in any form is prohibited.
The copyright of all videos belongs to the video owners.
If there is any infringement in Video-MME, please email [email protected] and we will remove it immediately.
Without prior approval, you cannot distribute, publish, copy, disseminate, or modify Video-MME in whole or in part.
You must strictly comply with the above restrictions.
Please send an email to [email protected]. 🌟
📍 Extract Frames and Subtitles:
With respect to the setting of adding subtitles, you should only use the subtitles corresponding to the sampled video frames. For example, if you extract 10 frames per video for evaluation, take the 10 subtitles that corresponding to the time of those 10 frames.
There are a total of 900 videos and 744 subtitles, where all long videos have subtitles. If you have already prepared the video and subtitle file, you could refer to this script to extract the frames and subtitles.
📍 Prompt:
The common prompt used in our evaluation follows this format:
This video's subtitles are listed below:
[Subtitles]
Select the best answer to the following multiple-choice question based on the video. Respond with only the letter (A, B, C, or D) of the correct option.
[Question]
The best answer is:
For the subtitles-free setting, you should remove the subtitle content.
Click to expand the prompt examples.
- With subtitles:
This video's subtitles are listed below:
Hi guys, I'm going to show you how to perfectly prepare a ...
Select the best answer to the following multiple-choice question based on the video. Respond with only the letter (A, B, C, or D) of the correct option.
What is the color of the clothing worn by the persons in the video?
A. Black.
B. Gray.
C. Green.
D. Brown.
The best answer is:
- Without subtitles:
Select the best answer to the following multiple-choice question based on the video. Respond with only the letter (A, B, C, or D) of the correct option.
What is the color of the clothing worn by the persons in the video?
A. Black.
B. Gray.
C. Green.
D. Brown.
The best answer is:
📍 Evaluation:
To extract the answer and calculate the scores, we add the model response to the provided JSON file. Here we provide an example template output_test_template.json. Once you have prepared the model responses in this format, please execute our evaluation script eval_your_results.py, and you will get the accuracy scores across video_durations, video domains, video subcategories, and task types. The evaluation does not introduce any third-party models, such as ChatGPT.
python eval_your_results.py \
--results_file $YOUR_RESULTS_FILE \
--video_duration_type $VIDEO_DURATION_TYPE \
--return_categories_accuracy \
--return_sub_categories_accuracy \
--return_task_types_accuracyPlease ensure that the results_file follows the specified JSON format stated above, and video_duration_type is specified as either short, medium, or long. If you wish to assess results across various duration types, you can specify multiple types separated by commas or organize them in a list, for example: short,medium,long or ["short","medium","long"].
- Evaluation results of different MLLMs.
- Evaluation results of different MLLMs across different task types.
- Evaluation results of Gemini 1.5 Pro across different video duration types.
- Evaluation results of Gemini 1.5 Pro across different video sub-types.
If you find our work helpful for your research, please consider citing our work.
@article{fu2024video,
title={Video-MME: The First-Ever Comprehensive Evaluation Benchmark of Multi-modal LLMs in Video Analysis},
author={Fu, Chaoyou and Dai, Yuhan and Luo, Yondong and Li, Lei and Ren, Shuhuai and Zhang, Renrui and Wang, Zihan and Zhou, Chenyu and Shen, Yunhang and Zhang, Mengdan and others},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.21075},
year={2024}
}Explore our related researches:
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Video-MME
Similar Open Source Tools

Video-MME
Video-MME is the first-ever comprehensive evaluation benchmark of Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) in Video Analysis. It assesses the capabilities of MLLMs in processing video data, covering a wide range of visual domains, temporal durations, and data modalities. The dataset comprises 900 videos with 256 hours and 2,700 human-annotated question-answer pairs. It distinguishes itself through features like duration variety, diversity in video types, breadth in data modalities, and quality in annotations.
MicroLens
MicroLens is a content-driven micro-video recommendation dataset at scale. It provides a large dataset with multimodal data, including raw text, images, audio, video, and video comments, for tasks such as multi-modal recommendation, foundation model building, and fairness recommendation. The dataset is available in two versions: MicroLens-50K and MicroLens-100K, with extracted features for multimodal recommendation tasks. Researchers can access the dataset through provided links and reach out to the corresponding author for the complete dataset. The repository also includes codes for various algorithms like VideoRec, IDRec, and VIDRec, each implementing different video models and baselines.
MathVerse
MathVerse is an all-around visual math benchmark designed to evaluate the capabilities of Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) in visual math problem-solving. It collects high-quality math problems with diagrams to assess how well MLLMs can understand visual diagrams for mathematical reasoning. The benchmark includes 2,612 problems transformed into six versions each, contributing to 15K test samples. It also introduces a Chain-of-Thought (CoT) Evaluation strategy for fine-grained assessment of output answers.

MInference
MInference is a tool designed to accelerate pre-filling for long-context Language Models (LLMs) by leveraging dynamic sparse attention. It achieves up to a 10x speedup for pre-filling on an A100 while maintaining accuracy. The tool supports various decoding LLMs, including LLaMA-style models and Phi models, and provides custom kernels for attention computation. MInference is useful for researchers and developers working with large-scale language models who aim to improve efficiency without compromising accuracy.
opencompass
OpenCompass is a one-stop platform for large model evaluation, aiming to provide a fair, open, and reproducible benchmark for large model evaluation. Its main features include: * Comprehensive support for models and datasets: Pre-support for 20+ HuggingFace and API models, a model evaluation scheme of 70+ datasets with about 400,000 questions, comprehensively evaluating the capabilities of the models in five dimensions. * Efficient distributed evaluation: One line command to implement task division and distributed evaluation, completing the full evaluation of billion-scale models in just a few hours. * Diversified evaluation paradigms: Support for zero-shot, few-shot, and chain-of-thought evaluations, combined with standard or dialogue-type prompt templates, to easily stimulate the maximum performance of various models. * Modular design with high extensibility: Want to add new models or datasets, customize an advanced task division strategy, or even support a new cluster management system? Everything about OpenCompass can be easily expanded! * Experiment management and reporting mechanism: Use config files to fully record each experiment, and support real-time reporting of results.
SheetCopilot
SheetCopilot is an assistant agent that manipulates spreadsheets by following user commands. It leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to interact with spreadsheets like a human expert, enabling non-expert users to complete tasks on complex software such as Google Sheets and Excel via a language interface. The tool observes spreadsheet states, polishes generated solutions based on external action documents and error feedback, and aims to improve success rate and efficiency. SheetCopilot offers a dataset with diverse task categories and operations, supporting operations like entry & manipulation, management, formatting, charts, and pivot tables. Users can interact with SheetCopilot in Excel or Google Sheets, executing tasks like calculating revenue, creating pivot tables, and plotting charts. The tool's evaluation includes performance comparisons with leading LLMs and VBA-based methods on specific datasets, showcasing its capabilities in controlling various aspects of a spreadsheet.
k2
K2 (GeoLLaMA) is a large language model for geoscience, trained on geoscience literature and fine-tuned with knowledge-intensive instruction data. It outperforms baseline models on objective and subjective tasks. The repository provides K2 weights, core data of GeoSignal, GeoBench benchmark, and code for further pretraining and instruction tuning. The model is available on Hugging Face for use. The project aims to create larger and more powerful geoscience language models in the future.

YuE
YuE (乐) is an open-source foundation model designed for music generation, specifically transforming lyrics into full songs. It can generate complete songs in various genres and vocal styles, ensuring a polished and cohesive result. The model requires significant GPU memory for generating long sequences and recommends specific configurations for optimal performance. Users can customize the number of sessions for memory usage. The tool provides a quickstart guide for generating music using Transformers and includes tips for execution time and tag selection. The project is licensed under Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial 4.0.
Reflection_Tuning
Reflection-Tuning is a project focused on improving the quality of instruction-tuning data through a reflection-based method. It introduces Selective Reflection-Tuning, where the student model can decide whether to accept the improvements made by the teacher model. The project aims to generate high-quality instruction-response pairs by defining specific criteria for the oracle model to follow and respond to. It also evaluates the efficacy and relevance of instruction-response pairs using the r-IFD metric. The project provides code for reflection and selection processes, along with data and model weights for both V1 and V2 methods.

cleanlab
Cleanlab helps you **clean** data and **lab** els by automatically detecting issues in a ML dataset. To facilitate **machine learning with messy, real-world data** , this data-centric AI package uses your _existing_ models to estimate dataset problems that can be fixed to train even _better_ models.
TileRT
TileRT is a project designed to serve large language models (LLMs) in ultra-low-latency scenarios. It aims to push the latency limits of LLMs without compromising model size or quality, enabling models with hundreds of billions of parameters to achieve millisecond-level time per output token. TileRT prioritizes responsiveness for applications like high-frequency trading, interactive AI, real-time decision-making, long-running agents, and AI-assisted coding. It introduces a tile-level runtime engine that dynamically reschedules computation, I/O, and communication across multiple devices to minimize idle time and improve hardware utilization. The project is actively evolving, with compiler techniques gradually shared with the community through TileLang and TileScale.
swiftide
Swiftide is a fast, streaming indexing and query library tailored for Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) in AI applications. It is built in Rust, utilizing parallel, asynchronous streams for blazingly fast performance. With Swiftide, users can easily build AI applications from idea to production in just a few lines of code. The tool addresses frustrations around performance, stability, and ease of use encountered while working with Python-based tooling. It offers features like fast streaming indexing pipeline, experimental query pipeline, integrations with various platforms, loaders, transformers, chunkers, embedders, and more. Swiftide aims to provide a platform for data indexing and querying to advance the development of automated Large Language Model (LLM) applications.
ChatDev
ChatDev is a virtual software company powered by intelligent agents like CEO, CPO, CTO, programmer, reviewer, tester, and art designer. These agents collaborate to revolutionize the digital world through programming. The platform offers an easy-to-use, highly customizable, and extendable framework based on large language models, ideal for studying collective intelligence. ChatDev introduces innovative methods like Iterative Experience Refinement and Experiential Co-Learning to enhance software development efficiency. It supports features like incremental development, Docker integration, Git mode, and Human-Agent-Interaction mode. Users can customize ChatChain, Phase, and Role settings, and share their software creations easily. The project is open-source under the Apache 2.0 License and utilizes data licensed under CC BY-NC 4.0.
sec-parser
The `sec-parser` project simplifies extracting meaningful information from SEC EDGAR HTML documents by organizing them into semantic elements and a tree structure. It helps in parsing SEC filings for financial and regulatory analysis, analytics and data science, AI and machine learning, causal AI, and large language models. The tool is especially beneficial for AI, ML, and LLM applications by streamlining data pre-processing and feature extraction.
basiclingua-LLM-Based-NLP
BasicLingua is a Python library that provides functionalities for linguistic tasks such as tokenization, stemming, lemmatization, and many others. It is based on the Gemini Language Model, which has demonstrated promising results in dealing with text data. BasicLingua can be used as an API or through a web demo. It is available under the MIT license and can be used in various projects.

sdialog
SDialog is an MIT-licensed open-source toolkit for building, simulating, and evaluating LLM-based conversational agents end-to-end. It aims to bridge agent construction, user simulation, dialog generation, and evaluation in a single reproducible workflow, enabling the generation of reliable, controllable dialog systems or data at scale. The toolkit standardizes a Dialog schema, offers persona-driven multi-agent simulation with LLMs, provides composable orchestration for precise control over behavior and flow, includes built-in evaluation metrics, and offers mechanistic interpretability. It allows for easy creation of user-defined components and interoperability across various AI platforms.
For similar tasks
Awesome-LLMs-for-Video-Understanding
Awesome-LLMs-for-Video-Understanding is a repository dedicated to exploring Video Understanding with Large Language Models. It provides a comprehensive survey of the field, covering models, pretraining, instruction tuning, and hybrid methods. The repository also includes information on tasks, datasets, and benchmarks related to video understanding. Contributors are encouraged to add new papers, projects, and materials to enhance the repository.

Video-MME
Video-MME is the first-ever comprehensive evaluation benchmark of Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) in Video Analysis. It assesses the capabilities of MLLMs in processing video data, covering a wide range of visual domains, temporal durations, and data modalities. The dataset comprises 900 videos with 256 hours and 2,700 human-annotated question-answer pairs. It distinguishes itself through features like duration variety, diversity in video types, breadth in data modalities, and quality in annotations.
ControlLLM
ControlLLM is a framework that empowers large language models to leverage multi-modal tools for solving complex real-world tasks. It addresses challenges like ambiguous user prompts, inaccurate tool selection, and inefficient tool scheduling by utilizing a task decomposer, a Thoughts-on-Graph paradigm, and an execution engine with a rich toolbox. The framework excels in tasks involving image, audio, and video processing, showcasing superior accuracy, efficiency, and versatility compared to existing methods.
gen-cv
This repository is a rich resource offering examples of synthetic image generation, manipulation, and reasoning using Azure Machine Learning, Computer Vision, OpenAI, and open-source frameworks like Stable Diffusion. It provides practical insights into image processing applications, including content generation, video analysis, avatar creation, and image manipulation with various tools and APIs.

outspeed
Outspeed is a PyTorch-inspired SDK for building real-time AI applications on voice and video input. It offers low-latency processing of streaming audio and video, an intuitive API familiar to PyTorch users, flexible integration of custom AI models, and tools for data preprocessing and model deployment. Ideal for developing voice assistants, video analytics, and other real-time AI applications processing audio-visual data.
starter-applets
This repository contains the source code for Google AI Studio's starter apps — a collection of small apps that demonstrate how Gemini can be used to create interactive experiences. These apps are built to run inside AI Studio, but the versions included here can run standalone using the Gemini API. The apps cover spatial understanding, video analysis, and map exploration, showcasing Gemini's capabilities in these areas. Developers can use these starter applets to kickstart their projects and learn how to leverage Gemini for spatial reasoning and interactive experiences.
TRACE
TRACE is a temporal grounding video model that utilizes causal event modeling to capture videos' inherent structure. It presents a task-interleaved video LLM model tailored for sequential encoding/decoding of timestamps, salient scores, and textual captions. The project includes various model checkpoints for different stages and fine-tuning on specific datasets. It provides evaluation codes for different tasks like VTG, MVBench, and VideoMME. The repository also offers annotation files and links to raw videos preparation projects. Users can train the model on different tasks and evaluate the performance based on metrics like CIDER, METEOR, SODA_c, F1, mAP, Hit@1, etc. TRACE has been enhanced with trace-retrieval and trace-uni models, showing improved performance on dense video captioning and general video understanding tasks.
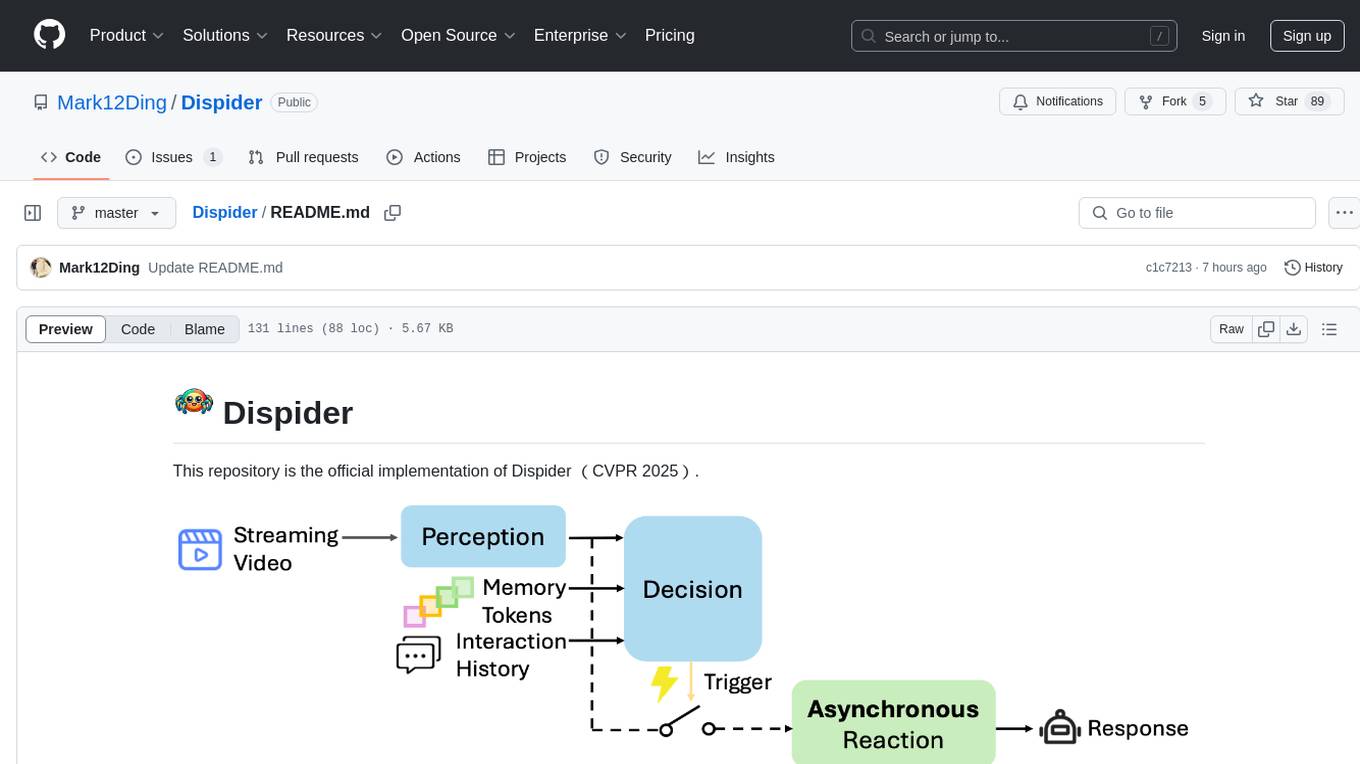
Dispider
Dispider is an implementation enabling real-time interactions with streaming videos, providing continuous feedback in live scenarios. It separates perception, decision-making, and reaction into asynchronous modules, ensuring timely interactions. Dispider outperforms VideoLLM-online on benchmarks like StreamingBench and excels in temporal reasoning. The tool requires CUDA 11.8 and specific library versions for optimal performance.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.















