
RAGEN
RAGEN leverages reinforcement learning to train LLM reasoning agents in interactive, stochastic environments.
Stars: 1054
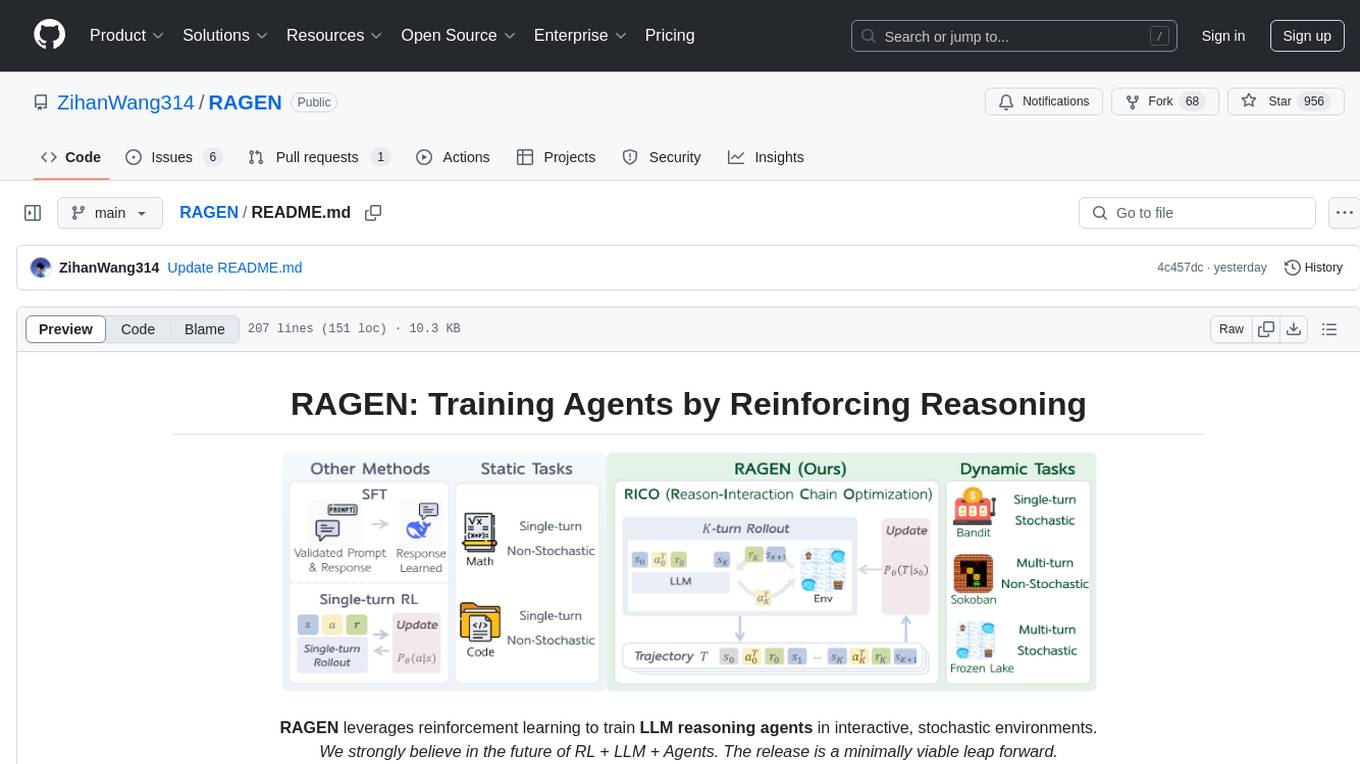
RAGEN is a reinforcement learning framework designed to train reasoning-capable large language model (LLM) agents in interactive, stochastic environments. It addresses challenges such as multi-turn interactions and stochastic environments through a Markov Decision Process (MDP) formulation, Reason-Interaction Chain Optimization (RICO) algorithm, and progressive reward normalization strategies. The framework enables LLMs to reason and interact with the environment, optimizing entire trajectories for long-horizon reasoning while maintaining computational efficiency.
README:
RAGEN leverages reinforcement learning to train LLM reasoning agents in interactive, stochastic environments.
We strongly believe in the future of RL + LLM + Agents. The release is a minimally viable leap forward.
2025.3.8 Update:
- In previous veRL implementation, there is a KL term issue, which has been fixed in recent versions.
- We find evidence from multiple sources that PPO could be more stable than GRPO training in Open-Reasoner-Zero, TinyZero, and Zhihu. We have changed the default advantage estimator to GAE (using PPO) and aim to find more stable while efficient RL optimization methods in later versions.
Reinforcement Learning (RL) with rule-based rewards has shown promise in enhancing reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs). However, existing approaches have primarily focused on static, single-turn tasks like math reasoning and coding. Extending these methods to agent scenarios introduces two fundamental challenges:
- Multi-turn Interactions: Agents must perform sequential decision-making and react to environment feedback
- Stochastic Environments: Uncertainty where identical actions can lead to different outcomes
RAGEN addresses these challenges through:
- A Markov Decision Process (MDP) formulation for agent tasks
- Reason-Interaction Chain Optimization (RICO) algorithm that optimizes entire trajectory distributions
- Progressive reward normalization strategies to handle diverse, complex environments
RAGEN introduces a reinforcement learning framework to train reasoning-capable LLM agents that can operate in interactive, stochastic environments.
The Reasoning-Interaction Chain Optimization (RICO) framework with two interleaved stages: rollout stage and update stage. LLM iteratively generates reasoning-guided actions to interact with the environment to obtain trajectory-level rewards, normalized for LLM update to jointly optimize reasoning and action strategies.
RAGEN introduces a reinforcement learning framework to train reasoning-capable LLM agents that can operate in interactive, stochastic environments. The framework consists of two key components:
We formulate agent-environment interactions as Markov Decision Processes (MDPs) where states and actions are token sequences, allowing LLMs to reason over environment dynamics. At time t, state $s_t$ transitions to the next state through action $a_t$ following a transition function. The policy generates actions given the trajectory history. The objective is to maximize expected cumulative rewards across multiple interaction turns.
RICO enables LLMs to jointly optimize reasoning and action strategies over entire trajectories. The algorithm alternates between two phases:
Given an initial state, the LLM generates multiple trajectories. At each step, the model receives the trajectory history and generates a reasoning-guided action: <think>...</think><ans> action </ans>. The environment receives the action and returns feedback (reward and next state).
After generating trajectories, we train LLMs to optimize expected rewards. Instead of step-by-step optimization, RICO optimizes entire trajectories using importance sampling. This approach enables long-horizon reasoning while maintaining computational efficiency.
We implement three progressive normalization strategies to stabilize training:
- ARPO: Preserves raw rewards directly
- BRPO: Normalizes rewards across each training batch using batch statistics
- GRPO: Normalizes within prompt groups to balance learning across varying task difficulties
For detailed setup instructions, please check our documentation. Here's a quick start guide:
# Setup environment and download data (7MB)
bash scripts/setup_ragen.sh
python scripts/download_data.pyIf this fails, you can follow the manual setup instructions in scripts/setup_ragen.md.
Here's how to train models with RAGEN:
We provide 10k first-round-observation data for both Sokoban and FrozenLake tasks.
# Basic data creation
bash scripts/create_data.sh
# Or for research purposes, create more comprehensive data
bash scripts/create_data_full.shWe provide default configuration in verl/trainer/config/ppo_trainer.yaml. To train:
bash train.sh sokoban \
model.experiment_name=new_test
# Override config parameters as needed
bash train.sh sokoban \
model.experiment_name=new_test_debug \
training.train_batch_size=128 \
training.ppo_batch_size=64For supervised finetuning with LoRA:
- Create supervised finetuning data:
bash sft/generate_data.sh <env_type>- Finetune the model:
bash sft/finetune_lora.sh <env_type> <num_gpus> <save_path>- Merge LoRA weights with the base model:
python sft/utils/merge_lora.py \
--base_model_name <base_model_name> \
--lora_model_path <lora_model_path> \
--output_path <output_path>To visualize agent trajectories:
- Set visualization parameters in
train.sh:
logging.log_images=True
logging.log_image_dir=log/trajectory
logging.log_image_step_size=4
logging.log_n_image_per_batch=32- View the visualizations:
cd log/trajectory
python -m http.server 8000
# Access at http://localhost:8000/[EXP_NAME]/step_[STEP_NUM]/trajectory_data_[ID].html- For proper font rendering:
sudo apt-get install fonts-noto-cjk- Download visualization data from wandb:
from ragen.utils.wandb import download_wandb
download_wandb("RUN_ID") # e.g., 9o465jqjWe evaluate RAGEN across multiple model sizes and configurations. Below are results from our Sokoban experiments using Qwen-2.5-{0.5B, 3B}-{Instruct, None} and DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B.
NOTE: The loss shows the reward curve, where the KL term is considered.
Key observations:
- Instruct-finetuned models show early advantages but the gap narrows as training progresses
- Larger models (3B) generally outperform smaller models (0.5B), though the advantage is not dramatic
- The R1-distilled 1.5B model initially underperforms compared to 0.5B models
- Training has not yet converged in these experiments
Our analysis reveals two key aspects of LLM agent training with RL:
- Prompt diversity: Balancing observation variety and effective response comparison
- Online rollout frequency: Mediating between training stability and data recency
Visualization of agent reasoning on the Sokoban task:
The visualizations show how the agent reasons through sequential steps to solve the puzzle.
We provide several case studies showing the model's behavior:
More case studies will be added to showcase both successful reasoning patterns and failure modes.
We welcome all forms of feedback! Please raise an issue for bugs, questions, or suggestions. This helps our team address common problems efficiently and builds a more productive community.
Zihan Wang*, Kangrui Wang*, Qineng Wang*, Pingyue Zhang*, Linjie Li*, Zhengyuan Yang, Kefan Yu, Minh Nhat Nguyen, Monica Lam, Yiping Lu, Kyunghyun Cho, Jiajun Wu, Li Fei-Fei, Lijuan Wang, Yejin Choi, Manling Li
*:Equal Contribution.
We thank DeepSeek for providing the DeepSeek-R1 model and ideas. We thank the veRL team for their infrastructure. We thank the TinyZero team for their discoveries that inspired our early exploration. We thank Han Liu, Xinyu Xing, Li Erran Li, Akari Asai, Eiso Kant, Lu Lu, Runxin Xu, Huajian Xin, Zijun Liu, Weiyi Liu, Weimin Wu, Yibo Wen, Jiarui Liu, Lorenzo Xiao, Ishan Mukherjee, Anabella Isaro, Haosen Sun, How-Yeh Wan, Lester Xue, Weiyi Liu for insightful discussions.
@misc{RAGEN,
author = {Zihan Wang* and Kangrui Wang* and Qineng Wang* and Pingyue Zhang* and Linjie Li* and Zhengyuan Yang and Kefan Yu and Minh Nhat Nguyen and Monica Lam and Yiping Lu and Kyunghyun Cho and Jiajun Wu and Li Fei-Fei and Lijuan Wang and Yejin Choi and Manling Li},
title = {Training Agents by Reinforcing Reasoning},
year = {2025},
organization = {GitHub},
url = {https://github.com/ZihanWang314/ragen},
}For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for RAGEN
Similar Open Source Tools

RAGEN
RAGEN is a reinforcement learning framework designed to train reasoning-capable large language model (LLM) agents in interactive, stochastic environments. It addresses challenges such as multi-turn interactions and stochastic environments through a Markov Decision Process (MDP) formulation, Reason-Interaction Chain Optimization (RICO) algorithm, and progressive reward normalization strategies. The framework enables LLMs to reason and interact with the environment, optimizing entire trajectories for long-horizon reasoning while maintaining computational efficiency.
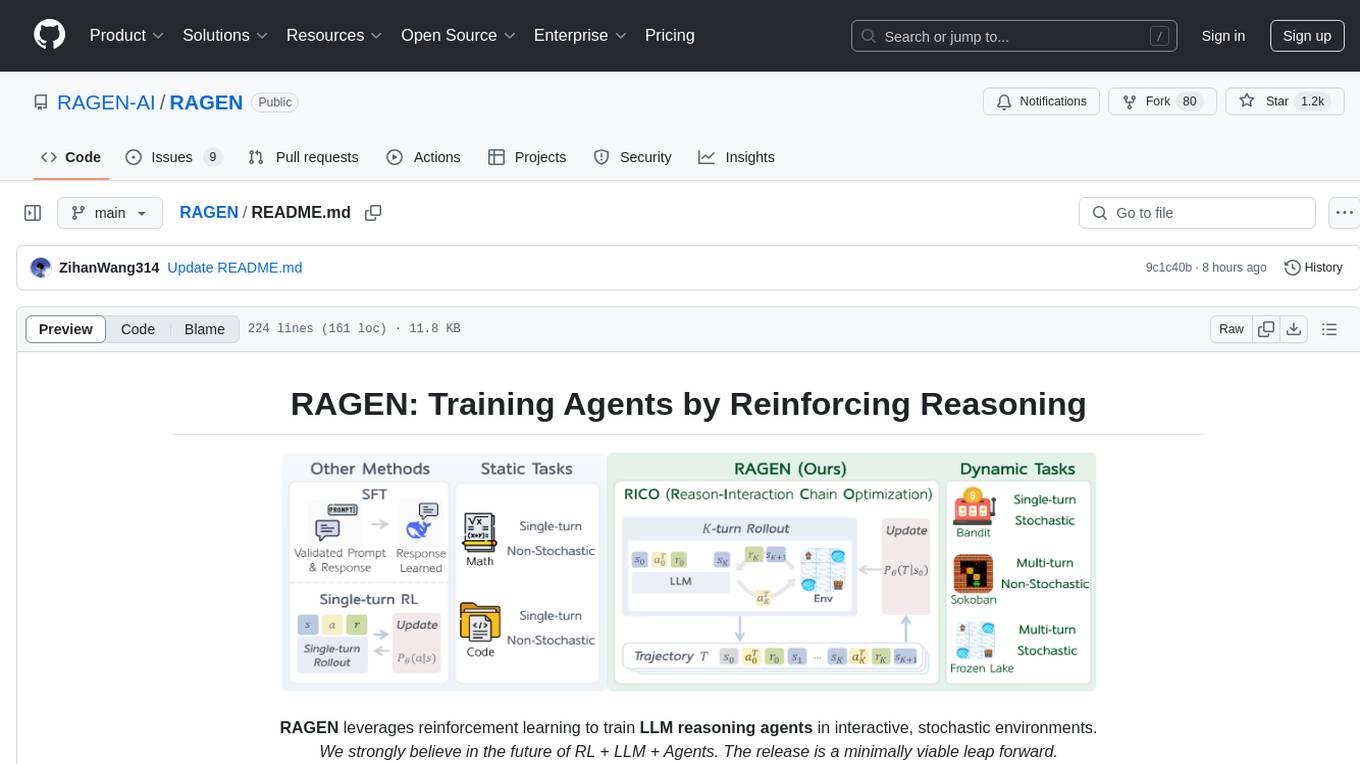
RAGEN
RAGEN is a reinforcement learning framework designed to train reasoning-capable large language model (LLM) agents in interactive, stochastic environments. It addresses challenges such as multi-turn interactions and stochastic environments through a Markov Decision Process (MDP) formulation, Reason-Interaction Chain Optimization (RICO) algorithm, and progressive reward normalization strategies. The framework consists of MDP formulation, RICO algorithm with rollout and update stages, and reward normalization strategies to stabilize training. RAGEN aims to optimize reasoning and action strategies for LLM agents operating in complex environments.
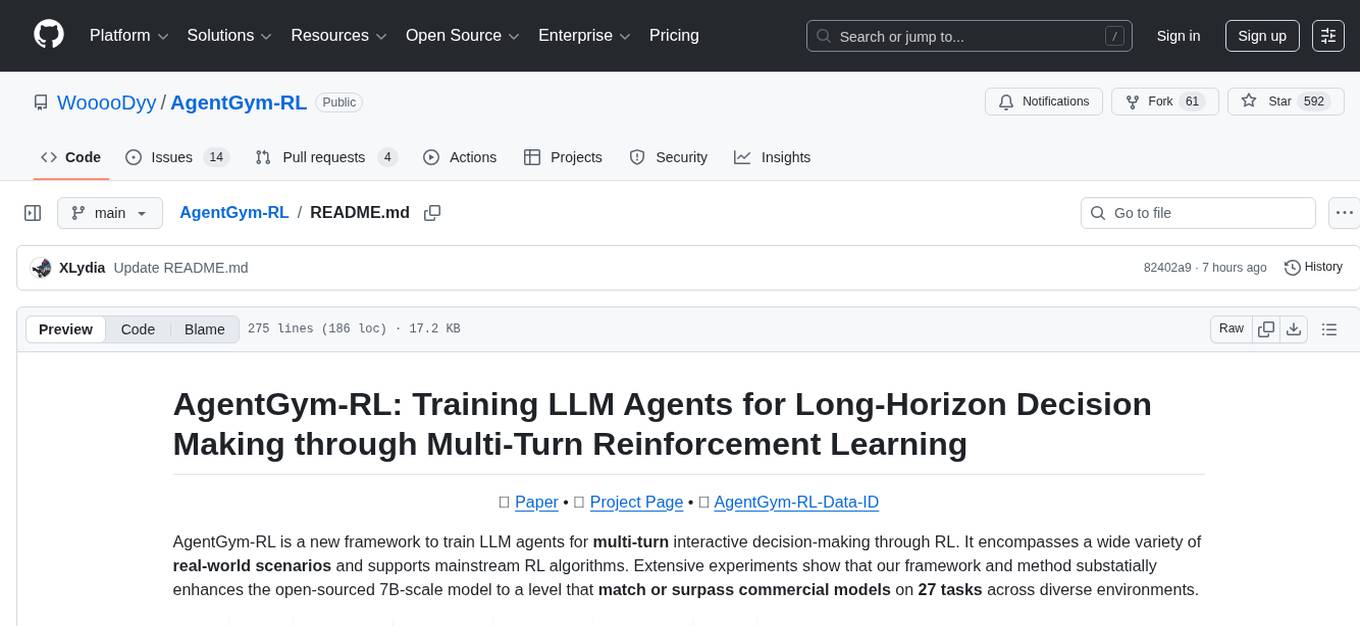
AgentGym-RL
AgentGym-RL is a framework designed to train Long-Long Memory (LLM) agents for multi-turn interactive decision-making through Reinforcement Learning. It addresses challenges in training agents for real-world scenarios by supporting mainstream RL algorithms and introducing the ScalingInter-RL method for stable optimization. The framework includes modular components for environment, agent reasoning, and training pipelines. It offers diverse environments like Web Navigation, Deep Search, Digital Games, Embodied Tasks, and Scientific Tasks. AgentGym-RL also supports various online RL algorithms and post-training strategies. The tool aims to enhance agent performance and exploration capabilities through long-horizon planning and interaction with the environment.
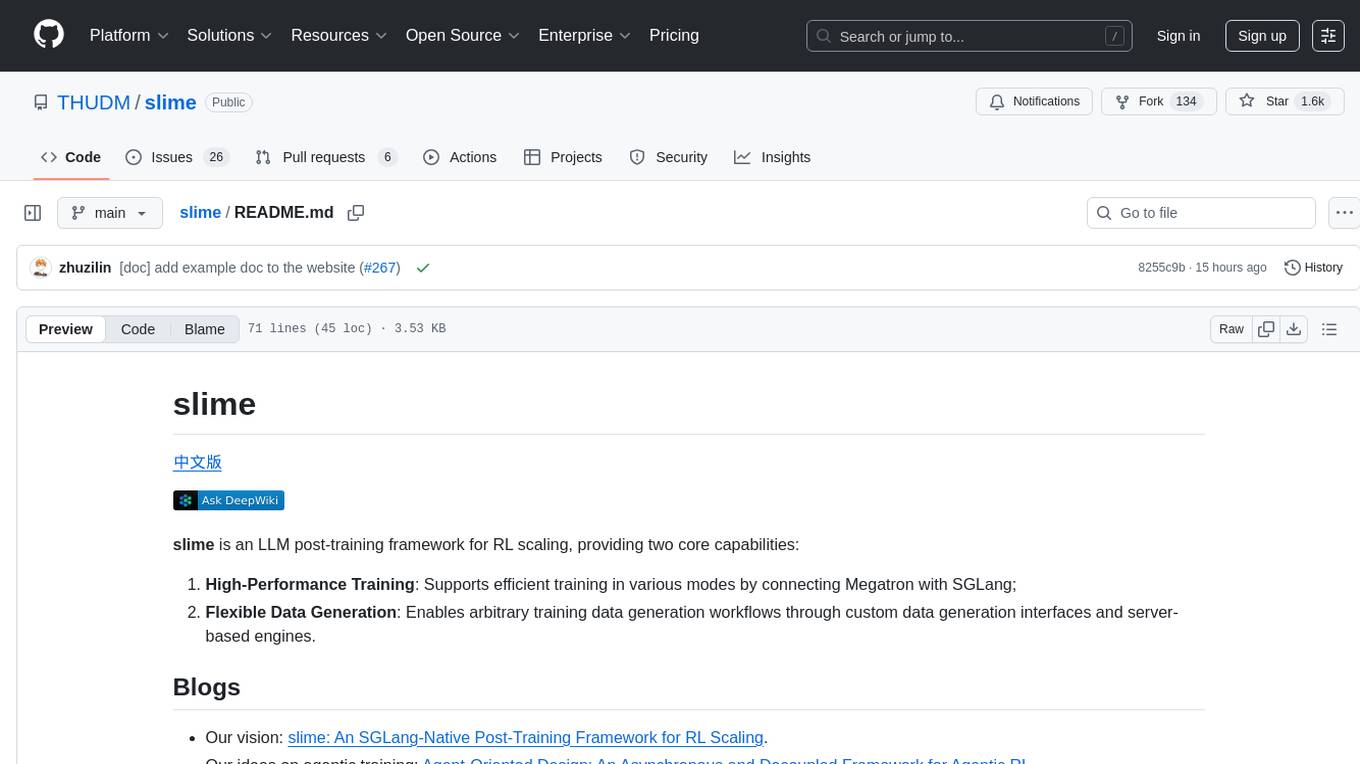
slime
Slime is an LLM post-training framework for RL scaling that provides high-performance training and flexible data generation capabilities. It connects Megatron with SGLang for efficient training and enables custom data generation workflows through server-based engines. The framework includes modules for training, rollout, and data buffer management, offering a comprehensive solution for RL scaling.
Agent-R1
Agent-R1 is an open-source framework designed to accelerate research and development at the critical intersection of RL and Agent. It employs End-to-End reinforcement learning to train agents in specific environments. Developers define domain-specific tools and reward functions to extend Agent-R1 to unique use cases, eliminating the need for complex workflow engineering. Key features include multi-turn tool calling, multi-tool coordination, process rewards, custom tools and environments, support for multiple RL algorithms, and multi-modal support. It aims to make it easier for researchers and developers to create and explore agents in their own domains, collectively advancing the development of autonomous agents.
LLM-as-HH
LLM-as-HH is a codebase that accompanies the paper ReEvo: Large Language Models as Hyper-Heuristics with Reflective Evolution. It introduces Language Hyper-Heuristics (LHHs) that leverage LLMs for heuristic generation with minimal manual intervention and open-ended heuristic spaces. Reflective Evolution (ReEvo) is presented as a searching framework that emulates the reflective design approach of human experts while surpassing human capabilities with scalable LLM inference, Internet-scale domain knowledge, and powerful evolutionary search. The tool can improve various algorithms on problems like Traveling Salesman Problem, Capacitated Vehicle Routing Problem, Orienteering Problem, Multiple Knapsack Problems, Bin Packing Problem, and Decap Placement Problem in both black-box and white-box settings.

AgentCPM
AgentCPM is a series of open-source LLM agents jointly developed by THUNLP, Renmin University of China, ModelBest, and the OpenBMB community. It addresses challenges faced by agents in real-world applications such as limited long-horizon capability, autonomy, and generalization. The team focuses on building deep research capabilities for agents, releasing AgentCPM-Explore, a deep-search LLM agent, and AgentCPM-Report, a deep-research LLM agent. AgentCPM-Explore is the first open-source agent model with 4B parameters to appear on widely used long-horizon agent benchmarks. AgentCPM-Report is built on the 8B-parameter base model MiniCPM4.1, autonomously generating long-form reports with extreme performance and minimal footprint, designed for high-privacy scenarios with offline and agile local deployment.

MInference
MInference is a tool designed to accelerate pre-filling for long-context Language Models (LLMs) by leveraging dynamic sparse attention. It achieves up to a 10x speedup for pre-filling on an A100 while maintaining accuracy. The tool supports various decoding LLMs, including LLaMA-style models and Phi models, and provides custom kernels for attention computation. MInference is useful for researchers and developers working with large-scale language models who aim to improve efficiency without compromising accuracy.
oat
Oat is a simple and efficient framework for running online LLM alignment algorithms. It implements a distributed Actor-Learner-Oracle architecture, with components optimized using state-of-the-art tools. Oat simplifies the experimental pipeline of LLM alignment by serving an Oracle online for preference data labeling and model evaluation. It provides a variety of oracles for simulating feedback and supports verifiable rewards. Oat's modular structure allows for easy inheritance and modification of classes, enabling rapid prototyping and experimentation with new algorithms. The framework implements cutting-edge online algorithms like PPO for math reasoning and various online exploration algorithms.
VeritasGraph
VeritasGraph is an enterprise-grade graph RAG framework designed for secure, on-premise AI applications. It leverages a knowledge graph to perform complex, multi-hop reasoning, providing transparent, auditable reasoning paths with full source attribution. The framework excels at answering complex questions that traditional vector search engines struggle with, ensuring trust and reliability in enterprise AI. VeritasGraph offers full control over data and AI models, verifiable attribution for every claim, advanced graph reasoning capabilities, and open-source deployment with sovereignty and customization.

raga-llm-hub
Raga LLM Hub is a comprehensive evaluation toolkit for Language and Learning Models (LLMs) with over 100 meticulously designed metrics. It allows developers and organizations to evaluate and compare LLMs effectively, establishing guardrails for LLMs and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) applications. The platform assesses aspects like Relevance & Understanding, Content Quality, Hallucination, Safety & Bias, Context Relevance, Guardrails, and Vulnerability scanning, along with Metric-Based Tests for quantitative analysis. It helps teams identify and fix issues throughout the LLM lifecycle, revolutionizing reliability and trustworthiness.
Controllable-RAG-Agent
This repository contains a sophisticated deterministic graph-based solution for answering complex questions using a controllable autonomous agent. The solution is designed to ensure that answers are solely based on the provided data, avoiding hallucinations. It involves various steps such as PDF loading, text preprocessing, summarization, database creation, encoding, and utilizing large language models. The algorithm follows a detailed workflow involving planning, retrieval, answering, replanning, content distillation, and performance evaluation. Heuristics and techniques implemented focus on content encoding, anonymizing questions, task breakdown, content distillation, chain of thought answering, verification, and model performance evaluation.
AI2BMD
AI2BMD is a program for efficiently simulating protein molecular dynamics with ab initio accuracy. The repository contains datasets, simulation programs, and public materials related to AI2BMD. It provides a Docker image for easy deployment and a standalone launcher program. Users can run simulations by downloading the launcher script and specifying simulation parameters. The repository also includes ready-to-use protein structures for testing. AI2BMD is designed for x86-64 GNU/Linux systems with recommended hardware specifications. The related research includes model architectures like ViSNet, Geoformer, and fine-grained force metrics for MLFF. Citation information and contact details for the AI2BMD Team are provided.
siiRL
siiRL is a novel, fully distributed reinforcement learning (RL) framework designed to break the scaling barriers in Large Language Models (LLMs) post-training. Developed by researchers from Shanghai Innovation Institute, siiRL delivers near-linear scalability, dramatic throughput gains, and unprecedented flexibility for RL-based LLM development. It eliminates the centralized controller common in other frameworks, enabling scalability to thousands of GPUs, achieving state-of-the-art throughput, and supporting cross-hardware compatibility. siiRL is extensively benchmarked and excels in data-intensive workloads such as long-context and multi-modal training.
HuixiangDou2
HuixiangDou2 is a robustly optimized GraphRAG approach that integrates multiple open-source projects to improve performance in graph-based augmented generation. It conducts comparative experiments and achieves a significant score increase, leading to a GraphRAG implementation with recognized performance. The repository provides code improvements, dense retrieval for querying entities and relationships, real domain knowledge testing, and impact analysis on accuracy.
eole
EOLE is an open language modeling toolkit based on PyTorch. It aims to provide a research-friendly approach with a comprehensive yet compact and modular codebase for experimenting with various types of language models. The toolkit includes features such as versatile training and inference, dynamic data transforms, comprehensive large language model support, advanced quantization, efficient finetuning, flexible inference, and tensor parallelism. EOLE is a work in progress with ongoing enhancements in configuration management, command line entry points, reproducible recipes, core API simplification, and plans for further simplification, refactoring, inference server development, additional recipes, documentation enhancement, test coverage improvement, logging enhancements, and broader model support.
For similar tasks
lighteval
LightEval is a lightweight LLM evaluation suite that Hugging Face has been using internally with the recently released LLM data processing library datatrove and LLM training library nanotron. We're releasing it with the community in the spirit of building in the open. Note that it is still very much early so don't expect 100% stability ^^' In case of problems or question, feel free to open an issue!
Firefly
Firefly is an open-source large model training project that supports pre-training, fine-tuning, and DPO of mainstream large models. It includes models like Llama3, Gemma, Qwen1.5, MiniCPM, Llama, InternLM, Baichuan, ChatGLM, Yi, Deepseek, Qwen, Orion, Ziya, Xverse, Mistral, Mixtral-8x7B, Zephyr, Vicuna, Bloom, etc. The project supports full-parameter training, LoRA, QLoRA efficient training, and various tasks such as pre-training, SFT, and DPO. Suitable for users with limited training resources, QLoRA is recommended for fine-tuning instructions. The project has achieved good results on the Open LLM Leaderboard with QLoRA training process validation. The latest version has significant updates and adaptations for different chat model templates.
Awesome-Text2SQL
Awesome Text2SQL is a curated repository containing tutorials and resources for Large Language Models, Text2SQL, Text2DSL, Text2API, Text2Vis, and more. It provides guidelines on converting natural language questions into structured SQL queries, with a focus on NL2SQL. The repository includes information on various models, datasets, evaluation metrics, fine-tuning methods, libraries, and practice projects related to Text2SQL. It serves as a comprehensive resource for individuals interested in working with Text2SQL and related technologies.
create-million-parameter-llm-from-scratch
The 'create-million-parameter-llm-from-scratch' repository provides a detailed guide on creating a Large Language Model (LLM) with 2.3 million parameters from scratch. The blog replicates the LLaMA approach, incorporating concepts like RMSNorm for pre-normalization, SwiGLU activation function, and Rotary Embeddings. The model is trained on a basic dataset to demonstrate the ease of creating a million-parameter LLM without the need for a high-end GPU.
StableToolBench
StableToolBench is a new benchmark developed to address the instability of Tool Learning benchmarks. It aims to balance stability and reality by introducing features such as a Virtual API System with caching and API simulators, a new set of solvable queries determined by LLMs, and a Stable Evaluation System using GPT-4. The Virtual API Server can be set up either by building from source or using a prebuilt Docker image. Users can test the server using provided scripts and evaluate models with Solvable Pass Rate and Solvable Win Rate metrics. The tool also includes model experiments results comparing different models' performance.
BetaML.jl
The Beta Machine Learning Toolkit is a package containing various algorithms and utilities for implementing machine learning workflows in multiple languages, including Julia, Python, and R. It offers a range of supervised and unsupervised models, data transformers, and assessment tools. The models are implemented entirely in Julia and are not wrappers for third-party models. Users can easily contribute new models or request implementations. The focus is on user-friendliness rather than computational efficiency, making it suitable for educational and research purposes.
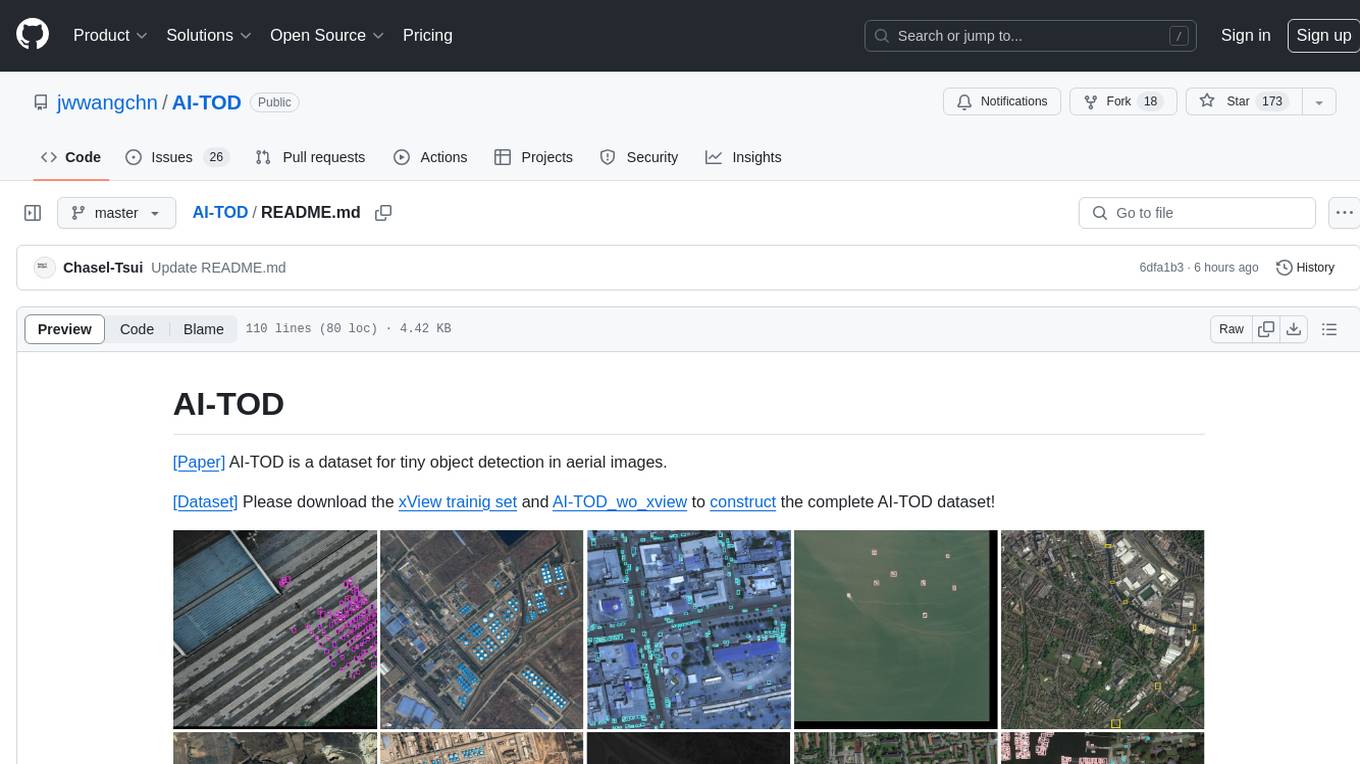
AI-TOD
AI-TOD is a dataset for tiny object detection in aerial images, containing 700,621 object instances across 28,036 images. Objects in AI-TOD are smaller with a mean size of 12.8 pixels compared to other aerial image datasets. To use AI-TOD, download xView training set and AI-TOD_wo_xview, then generate the complete dataset using the provided synthesis tool. The dataset is publicly available for academic and research purposes under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license.
UMOE-Scaling-Unified-Multimodal-LLMs
Uni-MoE is a MoE-based unified multimodal model that can handle diverse modalities including audio, speech, image, text, and video. The project focuses on scaling Unified Multimodal LLMs with a Mixture of Experts framework. It offers enhanced functionality for training across multiple nodes and GPUs, as well as parallel processing at both the expert and modality levels. The model architecture involves three training stages: building connectors for multimodal understanding, developing modality-specific experts, and incorporating multiple trained experts into LLMs using the LoRA technique on mixed multimodal data. The tool provides instructions for installation, weights organization, inference, training, and evaluation on various datasets.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.








