
AirSLAM
AirSLAM is an upgrade version of AirVO
Stars: 489
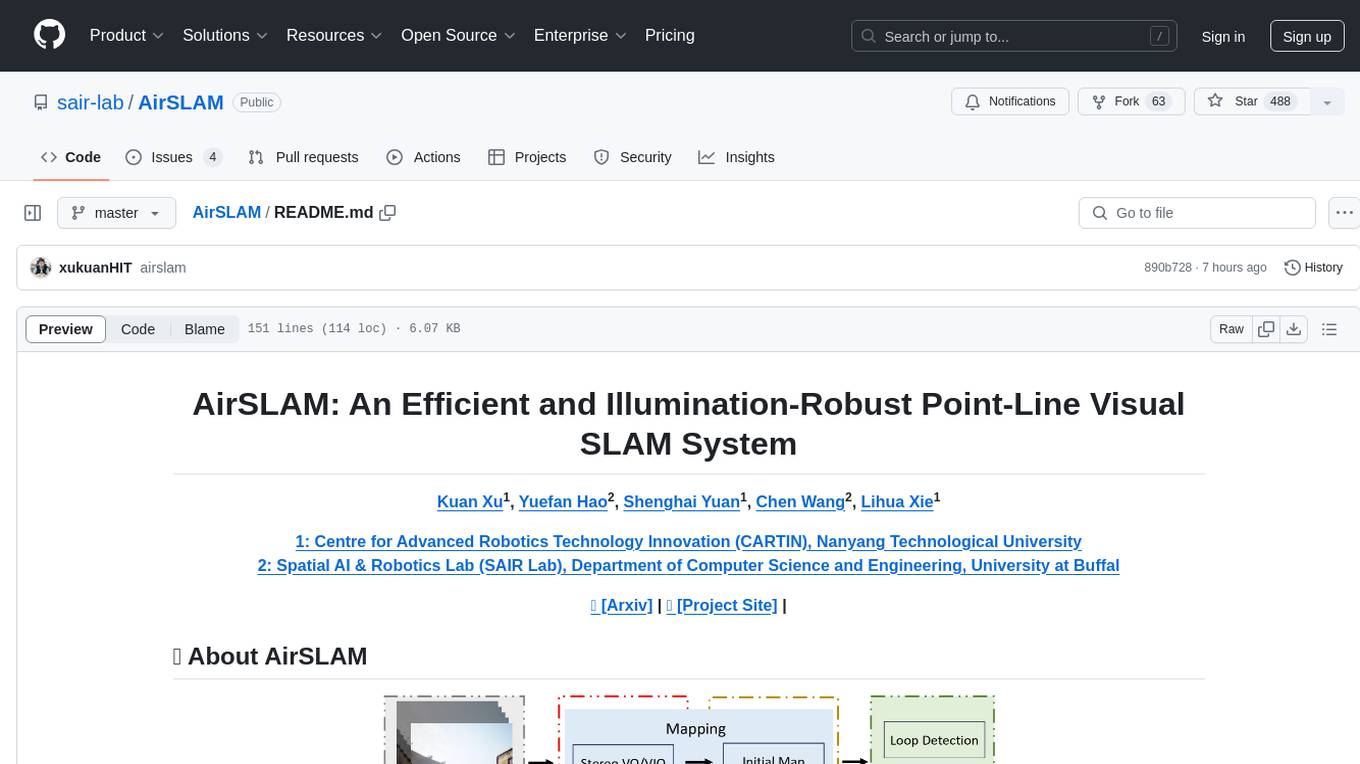
AirSLAM is an efficient visual SLAM system designed to tackle short-term and long-term illumination challenges. It combines deep learning techniques with traditional optimization methods, featuring a unified CNN for keypoint and structural line extraction. The system includes a relocalization pipeline for map reuse, accelerated using C++ and NVIDIA TensorRT. Outperforming other SLAM systems in challenging environments, it runs at 73Hz on PC and 40Hz on embedded platforms.
README:
Kuan Xu1, Yuefan Hao2, Shenghai Yuan1, Chen Wang2, Lihua Xie1
1: Centre for Advanced Robotics Technology Innovation (CARTIN), Nanyang Technological University
2: Spatial AI & Robotics Lab (SAIR Lab), Department of Computer Science and Engineering, University at Buffal
📄 [Arxiv] | 💾 [Project Site] |
AirSLAM is an efficient visual SLAM system designed to tackle both short-term and long-term illumination challenges. Our system adopts a hybrid approach that combines deep learning techniques for feature detection and matching with traditional backend optimization methods. Specifically, we proposea unified convolutional neural network (CNN) that simultaneously extracts keypoints and structural lines. These features are then associated, matched, triangulated, and optimized in a coupled manner. Additionally, we introduce a lightweight relocalization pipeline that reuses the built map, where keypoints, lines, anda structure graph are used to match the query frame with themap. To enhance the applicability of the proposed system to real-world robots, we deploy and accelerate the feature detection and matching networks using C++ and NVIDIA TensorRT. Extensive experiments conducted on various datasets demonstrate that our system outperforms other state-of-the-art visual SLAM systems in illumination-challenging environments. Efficiency evaluations show that our system can run at a rate of 73Hz on a PC and 40Hz on an embedded platform.
- [2024.08] We release the code and paper for AirSLAM.
- [2023.07] AriVO is accepted by IROS 2023.
- [2022.10] We release the code and paper for AirVO. The code for AirVO can now be found here.
- OpenCV 4.2
- Eigen 3
- Ceres 2.0.0
- G2O (tag:20230223_git)
- TensorRT 8.6
- CUDA 12
- python
- ROS noetic
- Boost
docker pull xukuanhit/air_slam:v4
docker run -it --env DISPLAY=$DISPLAY --volume /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix --privileged --runtime nvidia --gpus all --volume ${PWD}:/workspace --workdir /workspace --name air_slam xukuanhit/air_slam:v4 /bin/bashThe data for mapping should be organized in the following Automous Systems Lab (ASL) dataset format:
dataroot
├── cam0
│ └── data
│ ├── 00001.jpg
│ ├── 00002.jpg
│ ├── 00003.jpg
│ └── ......
├── cam1
│ └── data
│ ├── 00001.jpg
│ ├── 00002.jpg
│ ├── 00003.jpg
│ └── ......
└── imu0
└── data.csv
After the map is built, the relocalization requires only moocular images. Therefore, you only need to place the query images in a folder.
cd ~/catkin_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/sair-lab/AirSLAM.git
cd ../
catkin_make
source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bash
The launch files for VO/VIO, map optimization and relocalization are placed in VO folder, MR folder, and Reloc folder, respectively. Before running them, you need to modify the corresponding configurations according to you data path and the desired map saving path. The following is an example of mapping, optimization, and relocalization with the EuRoC dataset.
1: Change "dataroot" in VO launch file to your own data path. For the EuRoC dataset, "mav0" needs to be included in the path.
2: Change "saving_dir" in the same file to the path where you want to save the map and trajectory. It must be an existing folder.
3: Run the launch file:
roslaunch air_slam vo_euroc.launch
1: Change "map_root" in MR launch file to your own map path.
2: Run the launch file:
roslaunch air_slam mr_euroc.launch
1: Change "dataroot" in Reloc launch file to your own query data path.
2: Change "map_root" in the same file to your own map path.
3: Run the launch file:
roslaunch air_slam reloc_euroc.launch
Launch folder and config folder respectively provide the lauch files and configuration files for other datatsetsin the paper. If you want to run AirSLAM with your own dataset, you need to create your own camera file, configuration file, and launch file.
- [x] Initial release. 🚀
- [ ] Support SuperGlue as feature matecher
- [ ] Optimize the TensorRT acceleration of PLNet
@article{xu2024airslam,
title = {{AirSLAM}: An Efficient and Illumination-Robust Point-Line Visual SLAM System},
author = {Xu, Kuan and Hao, Yuefan and Yuan, Shenghai and Wang, Chen and Xie, Lihua},
journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2408.03520},
year = {2024},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2408.03520},
code = {https://github.com/sair-lab/AirSLAM},
}
@inproceedings{xu2023airvo,
title = {{AirVO}: An Illumination-Robust Point-Line Visual Odometry},
author = {Xu, Kuan and Hao, Yuefan and Yuan, Shenghai and Wang, Chen and Xie, Lihua},
booktitle = {IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS)},
year = {2023},
url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.07595},
code = {https://github.com/sair-lab/AirVO},
video = {https://youtu.be/YfOCLll_PfU},
addendum = {SAIR Lab Recommended}
}For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for AirSLAM
Similar Open Source Tools

AirSLAM
AirSLAM is an efficient visual SLAM system designed to tackle short-term and long-term illumination challenges. It combines deep learning techniques with traditional optimization methods, featuring a unified CNN for keypoint and structural line extraction. The system includes a relocalization pipeline for map reuse, accelerated using C++ and NVIDIA TensorRT. Outperforming other SLAM systems in challenging environments, it runs at 73Hz on PC and 40Hz on embedded platforms.
OpenViking
OpenViking is an open-source Context Database designed specifically for AI Agents. It aims to solve challenges in agent development by unifying memories, resources, and skills in a filesystem management paradigm. The tool offers tiered context loading, directory recursive retrieval, visualized retrieval trajectory, and automatic session management. Developers can interact with OpenViking like managing local files, enabling precise context manipulation and intuitive traceable operations. The tool supports various model services like OpenAI and Volcengine, enhancing semantic retrieval and context understanding for AI Agents.
SoM-LLaVA
SoM-LLaVA is a new data source and learning paradigm for Multimodal LLMs, empowering open-source Multimodal LLMs with Set-of-Mark prompting and improved visual reasoning ability. The repository provides a new dataset that is complementary to existing training sources, enhancing multimodal LLMs with Set-of-Mark prompting and improved general capacity. By adding 30k SoM data to the visual instruction tuning stage of LLaVA, the tool achieves 1% to 6% relative improvements on all benchmarks. Users can train SoM-LLaVA via command line and utilize the implementation to annotate COCO images with SoM. Additionally, the tool can be loaded in Huggingface for further usage.
llmxcpg
LLMxCPG is a framework for vulnerability detection using Code Property Graphs (CPG) and Large Language Models (LLM). It involves a two-phase process: Slice Construction where an LLM generates queries for a CPG to extract a code slice, and Vulnerability Detection where another LLM classifies the code slice as vulnerable or safe. The repository includes implementations of baseline models, information on datasets, scripts for running models, prompt templates, query generation examples, and configurations for fine-tuning models.

MInference
MInference is a tool designed to accelerate pre-filling for long-context Language Models (LLMs) by leveraging dynamic sparse attention. It achieves up to a 10x speedup for pre-filling on an A100 while maintaining accuracy. The tool supports various decoding LLMs, including LLaMA-style models and Phi models, and provides custom kernels for attention computation. MInference is useful for researchers and developers working with large-scale language models who aim to improve efficiency without compromising accuracy.
BIRD-CRITIC-1
BIRD-CRITIC 1.0 is a SQL benchmark designed to evaluate the capability of large language models (LLMs) in diagnosing and solving user issues within real-world database environments. It comprises 600 tasks for development and 200 held-out out-of-distribution tests across 4 prominent open-source SQL dialects. The benchmark expands beyond simple SELECT queries to cover a wider range of SQL operations, reflecting actual application scenarios. An optimized execution-based evaluation environment is included for rigorous and efficient validation.

mlflow
MLflow is a platform to streamline machine learning development, including tracking experiments, packaging code into reproducible runs, and sharing and deploying models. MLflow offers a set of lightweight APIs that can be used with any existing machine learning application or library (TensorFlow, PyTorch, XGBoost, etc), wherever you currently run ML code (e.g. in notebooks, standalone applications or the cloud). MLflow's current components are:
* `MLflow Tracking

sdialog
SDialog is an MIT-licensed open-source toolkit for building, simulating, and evaluating LLM-based conversational agents end-to-end. It aims to bridge agent construction, user simulation, dialog generation, and evaluation in a single reproducible workflow, enabling the generation of reliable, controllable dialog systems or data at scale. The toolkit standardizes a Dialog schema, offers persona-driven multi-agent simulation with LLMs, provides composable orchestration for precise control over behavior and flow, includes built-in evaluation metrics, and offers mechanistic interpretability. It allows for easy creation of user-defined components and interoperability across various AI platforms.

slideflow
Slideflow is a deep learning library for digital pathology, offering a user-friendly interface for model development. It is designed for medical researchers and AI enthusiasts, providing an accessible platform for developing state-of-the-art pathology models. Slideflow offers customizable training pipelines, robust slide processing and stain normalization toolkit, support for weakly-supervised or strongly-supervised labels, built-in foundation models, multiple-instance learning, self-supervised learning, generative adversarial networks, explainability tools, layer activation analysis tools, uncertainty quantification, interactive user interface for model deployment, and more. It supports both PyTorch and Tensorflow, with optional support for Libvips for slide reading. Slideflow can be installed via pip, Docker container, or from source, and includes non-commercial add-ons for additional tools and pretrained models. It allows users to create projects, extract tiles from slides, train models, and provides evaluation tools like heatmaps and mosaic maps.
mobius
Mobius is an AI infra platform including realtime computing and training. It is built on Ray, a distributed computing framework, and provides a number of features that make it well-suited for online machine learning tasks. These features include: * **Cross Language**: Mobius can run in multiple languages (only Python and Java are supported currently) with high efficiency. You can implement your operator in different languages and run them in one job. * **Single Node Failover**: Mobius has a special failover mechanism that only needs to rollback the failed node itself, in most cases, to recover the job. This is a huge benefit if your job is sensitive about failure recovery time. * **AutoScaling**: Mobius can generate a new graph with different configurations in runtime without stopping the job. * **Fusion Training**: Mobius can combine TensorFlow/Pytorch and streaming, then building an e2e online machine learning pipeline. Mobius is still under development, but it has already been used to power a number of real-world applications, including: * A real-time recommendation system for a major e-commerce company * A fraud detection system for a large financial institution * A personalized news feed for a major news organization If you are interested in using Mobius for your own online machine learning projects, you can find more information in the documentation.

petals
Petals is a tool that allows users to run large language models at home in a BitTorrent-style manner. It enables fine-tuning and inference up to 10x faster than offloading. Users can generate text with distributed models like Llama 2, Falcon, and BLOOM, and fine-tune them for specific tasks directly from their desktop computer or Google Colab. Petals is a community-run system that relies on people sharing their GPUs to increase its capacity and offer a distributed network for hosting model layers.
LightAgent
LightAgent is a lightweight, open-source Agentic AI development framework with memory, tools, and a tree of thought. It supports multi-agent collaboration, autonomous learning, tool integration, complex task handling, and multi-model support. It also features a streaming API, tool generator, agent self-learning, adaptive tool mechanism, and more. LightAgent is designed for intelligent customer service, data analysis, automated tools, and educational assistance.
MotionLLM
MotionLLM is a framework for human behavior understanding that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to jointly model videos and motion sequences. It provides a unified training strategy, dataset MoVid, and MoVid-Bench for evaluating human behavior comprehension. The framework excels in captioning, spatial-temporal comprehension, and reasoning abilities.
Trellis
Trellis is an all-in-one AI framework and toolkit designed for Claude Code, Cursor, and iFlow. It offers features such as auto-injection of required specs and workflows, auto-updated spec library, parallel sessions for running multiple agents simultaneously, team sync for sharing specs, and session persistence. Trellis helps users educate their AI, work on multiple features in parallel, define custom workflows, and provides a structured project environment with workflow guides, spec library, personal journal, task management, and utilities. The tool aims to enhance code review, introduce skill packs, integrate with broader tools, improve session continuity, and visualize progress for each agent.
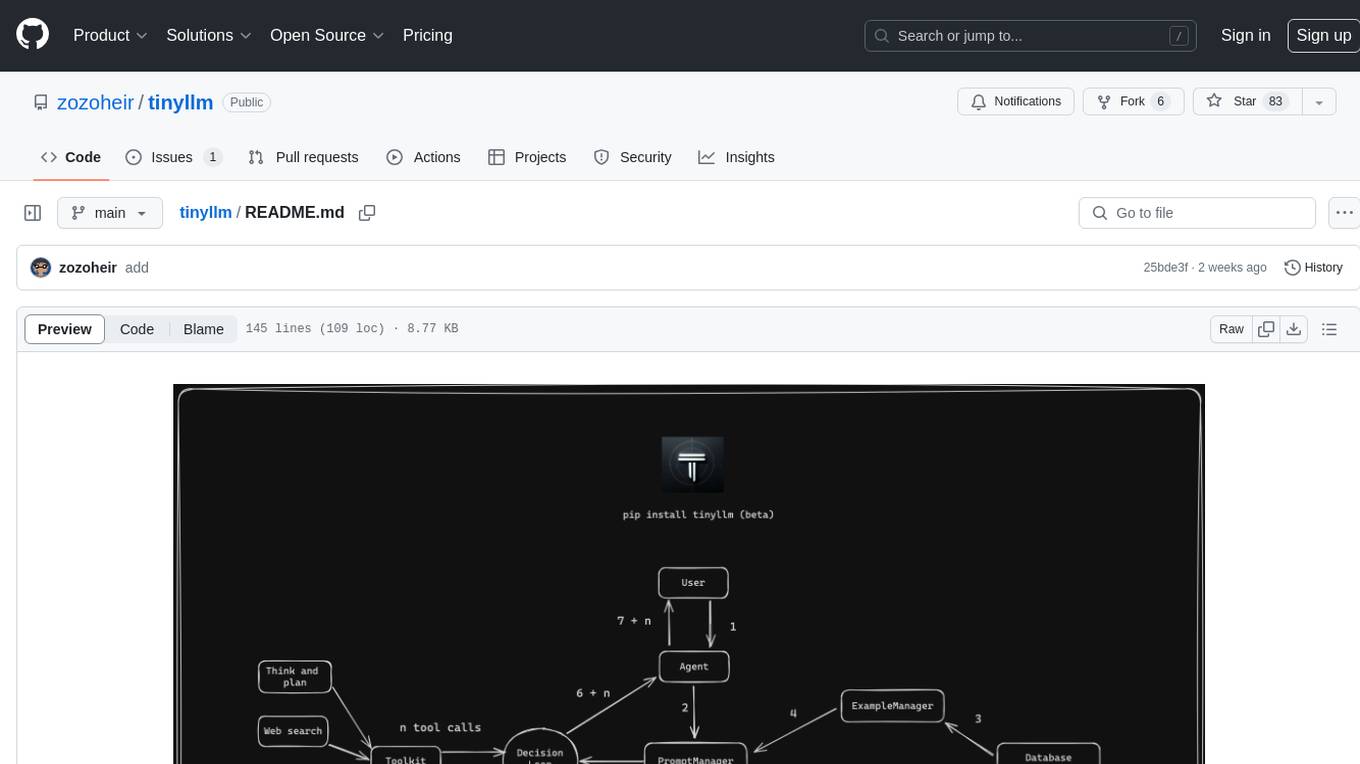
tinyllm
tinyllm is a lightweight framework designed for developing, debugging, and monitoring LLM and Agent powered applications at scale. It aims to simplify code while enabling users to create complex agents or LLM workflows in production. The core classes, Function and FunctionStream, standardize and control LLM, ToolStore, and relevant calls for scalable production use. It offers structured handling of function execution, including input/output validation, error handling, evaluation, and more, all while maintaining code readability. Users can create chains with prompts, LLM models, and evaluators in a single file without the need for extensive class definitions or spaghetti code. Additionally, tinyllm integrates with various libraries like Langfuse and provides tools for prompt engineering, observability, logging, and finite state machine design.
Eco2AI
Eco2AI is a python library for CO2 emission tracking that monitors energy consumption of CPU & GPU devices and estimates equivalent carbon emissions based on regional emission coefficients. Users can easily integrate Eco2AI into their Python scripts by adding a few lines of code. The library records emissions data and device information in a local file, providing detailed session logs with project names, experiment descriptions, start times, durations, power consumption, CO2 emissions, CPU and GPU names, operating systems, and countries.
For similar tasks

AirSLAM
AirSLAM is an efficient visual SLAM system designed to tackle short-term and long-term illumination challenges. It combines deep learning techniques with traditional optimization methods, featuring a unified CNN for keypoint and structural line extraction. The system includes a relocalization pipeline for map reuse, accelerated using C++ and NVIDIA TensorRT. Outperforming other SLAM systems in challenging environments, it runs at 73Hz on PC and 40Hz on embedded platforms.
For similar jobs
DriveLM
DriveLM is a multimodal AI model that enables autonomous driving by combining computer vision and natural language processing. It is designed to understand and respond to complex driving scenarios using visual and textual information. DriveLM can perform various tasks related to driving, such as object detection, lane keeping, and decision-making. It is trained on a massive dataset of images and text, which allows it to learn the relationships between visual cues and driving actions. DriveLM is a powerful tool that can help to improve the safety and efficiency of autonomous vehicles.
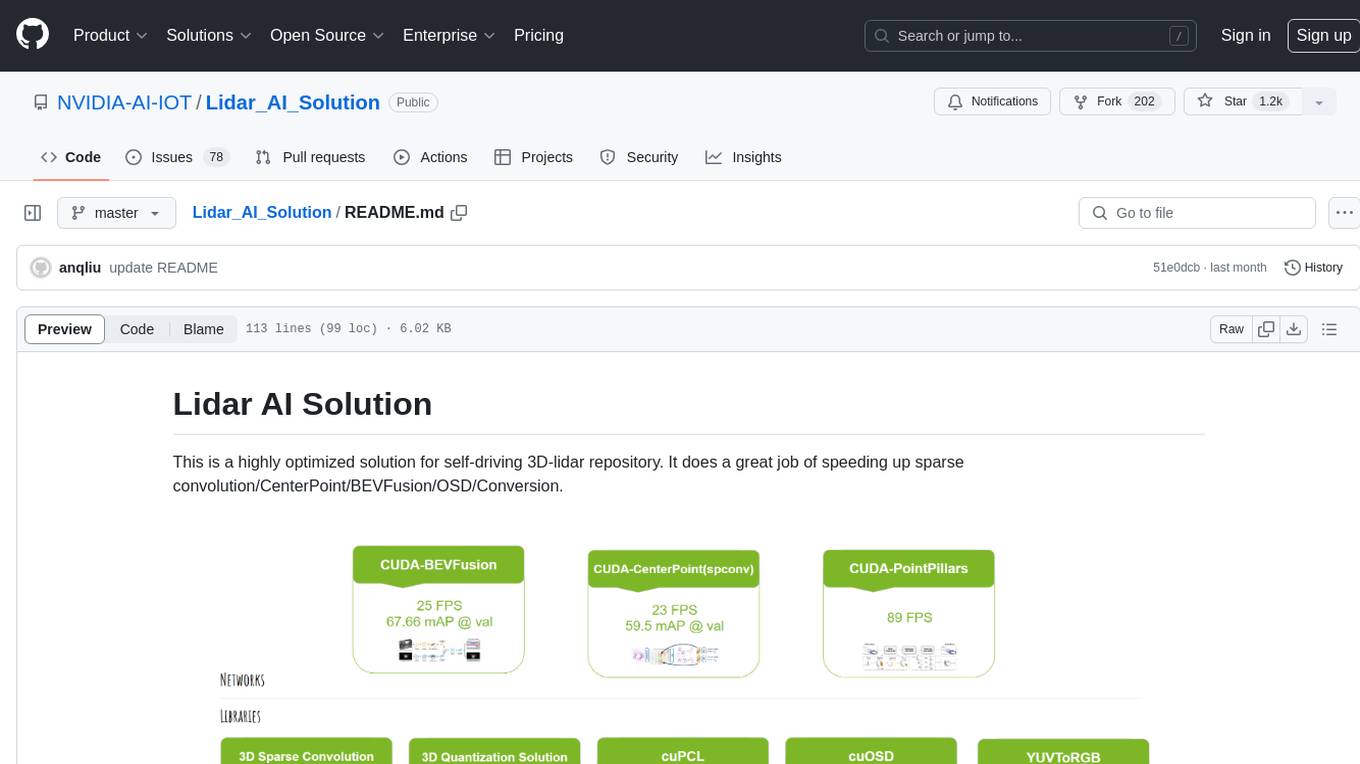
Lidar_AI_Solution
Lidar AI Solution is a highly optimized repository for self-driving 3D lidar, providing solutions for sparse convolution, BEVFusion, CenterPoint, OSD, and Conversion. It includes CUDA and TensorRT implementations for various tasks such as 3D sparse convolution, BEVFusion, CenterPoint, PointPillars, V2XFusion, cuOSD, cuPCL, and YUV to RGB conversion. The repository offers easy-to-use solutions, high accuracy, low memory usage, and quantization options for different tasks related to self-driving technology.

AirSLAM
AirSLAM is an efficient visual SLAM system designed to tackle short-term and long-term illumination challenges. It combines deep learning techniques with traditional optimization methods, featuring a unified CNN for keypoint and structural line extraction. The system includes a relocalization pipeline for map reuse, accelerated using C++ and NVIDIA TensorRT. Outperforming other SLAM systems in challenging environments, it runs at 73Hz on PC and 40Hz on embedded platforms.
sdk-examples
Spectacular AI SDK fuses data from cameras and IMU sensors to output an accurate 6-degree-of-freedom pose of a device, enabling Visual-Inertial SLAM for tracking robots and vehicles, as well as Augmented, Mixed, and Virtual Reality. The SDK includes a Mapping API for real-time and offline 3D reconstruction use cases.

awesome-and-novel-works-in-slam
This repository contains a curated list of cutting-edge works in Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM). It includes research papers, projects, and tools related to various aspects of SLAM, such as 3D reconstruction, semantic mapping, novel algorithms, large-scale mapping, and more. The repository aims to showcase the latest advancements in SLAM technology and provide resources for researchers and practitioners in the field.
retinify
Retinify is an advanced AI-powered stereo vision library designed for robotics, enabling real-time, high-precision 3D perception by leveraging GPU and NPU acceleration. It is open source under Apache-2.0 license, offers high precision 3D mapping and object recognition, runs computations on GPU for fast performance, accepts stereo images from any rectified camera setup, is cost-efficient using minimal hardware, and has minimal dependencies on CUDA Toolkit, cuDNN, and TensorRT. The tool provides a pipeline for stereo matching and supports various image data types independently of OpenCV.
Autopilot-Notes
Autopilot Notes is an open-source knowledge base for systematically learning autonomous driving technology. It covers basic theory, hardware, algorithms, tools, and practical engineering practices across 10+ chapters. The repository provides daily updates on industry trends, in-depth analysis of mainstream solutions like Tesla, Baidu Apollo, and Openpilot, and hands-on content including simulation, deployment, and optimization. Contributors are welcome to submit pull requests to improve the documentation.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.
