aimet
AIMET is a library that provides advanced quantization and compression techniques for trained neural network models.
Stars: 2451
AIMET is a library that provides advanced model quantization and compression techniques for trained neural network models. It provides features that have been proven to improve run-time performance of deep learning neural network models with lower compute and memory requirements and minimal impact to task accuracy. AIMET is designed to work with PyTorch, TensorFlow and ONNX models. We also host the AIMET Model Zoo - a collection of popular neural network models optimized for 8-bit inference. We also provide recipes for users to quantize floating point models using AIMET.
README:
AIMET is a software toolkit for quantizing trained ML models.
AIMET improves the runtime performance of deep learning models by reducing compute load and memory footprint. Models quantized with AIMET facilitate its deployment on edge devices like mobile phones or laptops by reducing memory footprint.
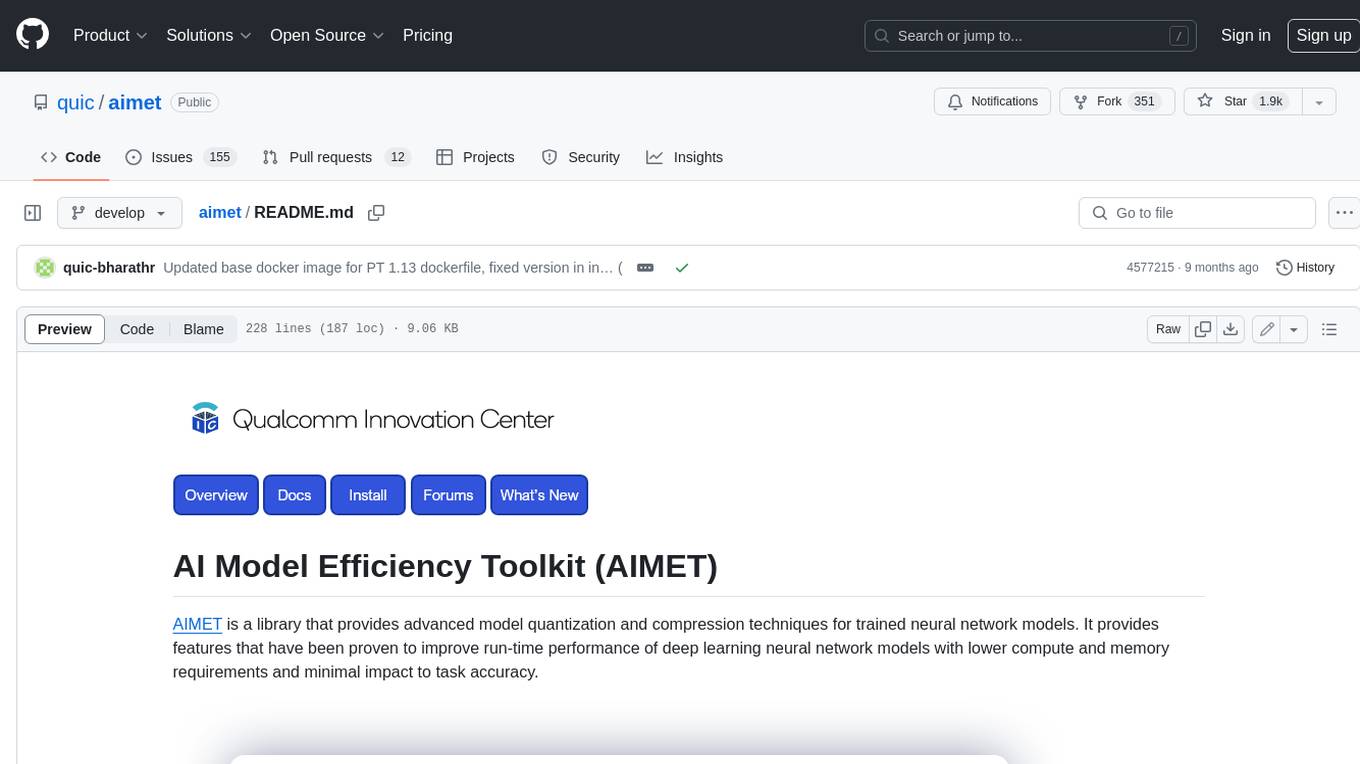
AIMET employs post-training and fine-tuning techniques to minimize accuracy loss during quantization and compression. AIMET supports models from the ONNX and PyTorch frameworks.
AIMET is designed to work with PyTorch and ONNX models.
You can find models quantized with AIMET on Qualcomm AI Hub Models - a collection of optimized and quantized models.
- Advanced quantization techniques: Inference using integer runtimes is significantly faster than using floating-point runtimes. For example, models run 5x-15x faster on the Qualcomm Hexagon DSP than on the Qualcomm Kyro CPU. In addition, 8-bit precision models have a 4x smaller footprint than 32-bit precision models. However, maintaining model accuracy when quantizing ML models is often challenging. AIMET solves this using novel techniques like Data-Free Quantization that provide state-of-the-art INT8 results on several popular models.
- Supports advanced model compression techniques that enable models to run faster at inference-time and require less memory
- AIMET is designed to automate optimization of neural networks avoiding time-consuming and tedious manual tweaking. AIMET also provides user-friendly APIs that allow users to make calls directly from their PyTorch pipelines.
Please visit the AIMET on Github Pages for more details.
aimet-onnx and aimet-torch is available on PyPI.
Check our Quick Start to get started with latest AIMET package.
To build the latest AIMET code from the source, see Build, install and run AIMET from source in Docker environment
Check out guide to get started on PTQ technique.
Following table summarizes basic technique such as Calibration to advanced techniques such as SeqMSE and Adaptive Rounding(AdaRound) that you can use with AIMET.
| Technique | ONNX | PyTorch | What does it do? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration | ✅ | ✅ | Computes Quantization parameters |
| AdaRound | ✅ | ✅ | Rounds quantized weights |
| SeqMSE | ✅ | ✅ | Optimizes encodings for each layer |
| BatchNorm Folding | ✅ | ✅ | Folds batchnorm to bridge the gap between simulation and on-target |
| Cross Layer Equalization | ✅ | ✅ | Rescales the weight to reduce range imbalance |
| BatchNorm re-estimation | ✅ | ✅ | Re-estimates batchnorm statistics |
| AdaScale | ❌ | ✅ | Optimizes quantized weights |
| OmniQuant | ❌ | ✅ | Optimizes quantized weights |
| SpinQuant | ❌ | ✅ | Optimizes quantized weights |
AIMET supports Quantization Aware Training(QAT) via aimet-torch.
If you want to use both QAT and some of the advanced PTQ techniques from AIMET, we recommend the following workflow:
Check detailed QAT guide here
- Spatial SVD: Tensor decomposition technique to split a large layer into two smaller ones
- Channel Pruning: Removes redundant input channels from a layer and reconstructs layer weights
- Per-layer compression-ratio selection: Automatically selects how much to compress each layer in the model
- Weight ranges: Inspect visually if a model is a candidate for applying the Cross Layer Equalization technique. And the effect after applying the technique
- Per-layer compression sensitivity: Visually get feedback about the sensitivity of any given layer in the model to compression
AIMET can quantize an existing 32-bit floating-point model to an 8-bit fixed-point model without sacrificing much accuracy and without model fine-tuning.
The DFQ method applied to several popular networks, such as MobileNet-v2 and ResNet-50, result in less than 0.9% loss in accuracy all the way down to 8-bit quantization, in an automated way without any training data.
| Models | FP32 | INT8 Simulation |
|---|---|---|
| MobileNet v2 (top1) | 71.72% | 71.08% |
| ResNet 50 (top1) | 76.05% | 75.45% |
| DeepLab v3 (mIOU) | 72.65% | 71.91% |
For this example ADAS object detection model, which was challenging to quantize to 8-bit precision, AdaRound can recover the accuracy to within 1% of the FP32 accuracy.
| Configuration | mAP - Mean Average Precision | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FP32 | 82.20% | ||||||||||||||
| Nearest Rounding (INT8 weights, INT8 acts) | 49.85% | ||||||||||||||
| AdaRound (INT8 weights, INT8 acts) | 81.21% | ||||||||||||||
For some models like the DeepLabv3 semantic segmentation model, AdaRound can even quantize the model weights to 4-bit precision without a significant drop in accuracy.
| Configuration | mIOU - Mean intersection over union | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FP32 | 72.94% | ||||||||||||||
| Nearest Rounding (INT4 weights, INT8 acts) | 6.09% | ||||||||||||||
| AdaRound (INT4 weights, INT8 acts) | 70.86% | ||||||||||||||
AIMET supports quantization simulation and quantization-aware training (QAT) for recurrent models (RNN, LSTM, GRU). Using QAT feature in AIMET, a DeepSpeech2 model with bi-directional LSTMs can be quantized to 8-bit precision with minimal drop in accuracy.
| DeepSpeech2 (using bi-directional LSTMs) |
Word Error Rate |
|---|---|
| FP32 | 9.92% |
| INT8 | 10.22% |
AIMET can also significantly compress models. For popular models, such as Resnet-50 and Resnet-18, compression with spatial SVD plus channel pruning achieves 50% MAC (multiply-accumulate) reduction while retaining accuracy within approx. 1% of the original uncompressed model.
| Models | Uncompressed model | 50% Compressed model |
|---|---|---|
| ResNet18 (top1) | 69.76% | 68.56% |
| ResNet 50 (top1) | 76.05% | 75.75% |
Thanks for your interest in contributing to AIMET! Please read our Contributions Page for more information on contributing features or bug fixes. We look forward to your participation!
AIMET aims to be a community-driven project maintained by Qualcomm Innovation Center, Inc.
AIMET is licensed under the BSD 3-clause "New" or "Revised" License. Check out the LICENSE for more details.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for aimet
Similar Open Source Tools

aimet
AIMET is a library that provides advanced model quantization and compression techniques for trained neural network models. It provides features that have been proven to improve run-time performance of deep learning neural network models with lower compute and memory requirements and minimal impact to task accuracy. AIMET is designed to work with PyTorch, TensorFlow and ONNX models. We also host the AIMET Model Zoo - a collection of popular neural network models optimized for 8-bit inference. We also provide recipes for users to quantize floating point models using AIMET.
MMLU-Pro
MMLU-Pro is an enhanced benchmark designed to evaluate language understanding models across broader and more challenging tasks. It integrates more challenging, reasoning-focused questions and increases answer choices per question, significantly raising difficulty. The dataset comprises over 12,000 questions from academic exams and textbooks across 14 diverse domains. Experimental results show a significant drop in accuracy compared to the original MMLU, with greater stability under varying prompts. Models utilizing Chain of Thought reasoning achieved better performance on MMLU-Pro.
arthur-engine
The Arthur Engine is a comprehensive tool for monitoring and governing AI/ML workloads. It provides evaluation and benchmarking of machine learning models, guardrails enforcement, and extensibility for fitting into various application architectures. With support for a wide range of evaluation metrics and customizable features, the tool aims to improve model understanding, optimize generative AI outputs, and prevent data-security and compliance risks. Key features include real-time guardrails, model performance monitoring, feature importance visualization, error breakdowns, and support for custom metrics and models integration.
ProactiveAgent
Proactive Agent is a project aimed at constructing a fully active agent that can anticipate user's requirements and offer assistance without explicit requests. It includes a data collection and generation pipeline, automatic evaluator, and training agent. The project provides datasets, evaluation scripts, and prompts to finetune LLM for proactive agent. Features include environment sensing, assistance annotation, dynamic data generation, and construction pipeline with a high F1 score on the test set. The project is intended for coding, writing, and daily life scenarios, distributed under Apache License 2.0.
kubesphere
KubeSphere is a distributed operating system for cloud-native application management, using Kubernetes as its kernel. It provides a plug-and-play architecture, allowing third-party applications to be seamlessly integrated into its ecosystem. KubeSphere is also a multi-tenant container platform with full-stack automated IT operation and streamlined DevOps workflows. It provides developer-friendly wizard web UI, helping enterprises to build out a more robust and feature-rich platform, which includes most common functionalities needed for enterprise Kubernetes strategy.

fenic
fenic is an opinionated DataFrame framework from typedef.ai for building AI and agentic applications. It transforms unstructured and structured data into insights using familiar DataFrame operations enhanced with semantic intelligence. With support for markdown, transcripts, and semantic operators, plus efficient batch inference across various model providers. fenic is purpose-built for LLM inference, providing a query engine designed for AI workloads, semantic operators as first-class citizens, native unstructured data support, production-ready infrastructure, and a familiar DataFrame API.
OmAgent
OmAgent is an open-source agent framework designed to streamline the development of on-device multimodal agents. It enables agents to empower various hardware devices, integrates speed-optimized SOTA multimodal models, provides SOTA multimodal agent algorithms, and focuses on optimizing the end-to-end computing pipeline for real-time user interaction experience. Key features include easy connection to diverse devices, scalability, flexibility, and workflow orchestration. The architecture emphasizes graph-based workflow orchestration, native multimodality, and device-centricity, allowing developers to create bespoke intelligent agent programs.

MiniAI-Face-Recognition-LivenessDetection-WindowsSDK
This repository contains a C++ application that demonstrates face recognition capabilities using computer vision techniques. The demo utilizes OpenCV and dlib libraries for efficient face detection and recognition with 3D passive face liveness detection (face anti-spoofing). Key Features: Face detection: The SDK utilizes advanced computer vision techniques to detect faces in images or video frames, enabling a wide range of applications. Face recognition: It can recognize known faces by comparing them with a pre-defined database of individuals. Age estimation: It can estimate the age of detected faces. Gender detection: It can determine the gender of detected faces. Liveness detection: It can detect whether a face is from a live person or a static image.
CuMo
CuMo is a project focused on scaling multimodal Large Language Models (LLMs) with Co-Upcycled Mixture-of-Experts. It introduces CuMo, which incorporates Co-upcycled Top-K sparsely-gated Mixture-of-experts blocks into the vision encoder and the MLP connector, enhancing the capabilities of multimodal LLMs. The project adopts a three-stage training approach with auxiliary losses to stabilize the training process and maintain a balanced loading of experts. CuMo achieves comparable performance to other state-of-the-art multimodal LLMs on various Visual Question Answering (VQA) and visual-instruction-following benchmarks.
maxtext
MaxText is a high performance, highly scalable, open-source Large Language Model (LLM) written in pure Python/Jax targeting Google Cloud TPUs and GPUs for training and inference. It aims to be a launching off point for ambitious LLM projects in research and production, supporting TPUs and GPUs, models like Llama2, Mistral, and Gemma. MaxText provides specific instructions for getting started, runtime performance results, comparison to alternatives, and features like stack trace collection, ahead of time compilation for TPUs and GPUs, and automatic upload of logs to Vertex Tensorboard.
sqlcoder
Defog's SQLCoder is a family of state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs) designed for converting natural language questions into SQL queries. It outperforms popular open-source models like gpt-4 and gpt-4-turbo on SQL generation tasks. SQLCoder has been trained on more than 20,000 human-curated questions based on 10 different schemas, and the model weights are licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0. Users can interact with SQLCoder through the 'transformers' library and run queries using the 'sqlcoder launch' command in the terminal. The tool has been tested on NVIDIA GPUs with more than 16GB VRAM and Apple Silicon devices with some limitations. SQLCoder offers a demo on their website and supports quantized versions of the model for consumer GPUs with sufficient memory.
PowerInfer
PowerInfer is a high-speed Large Language Model (LLM) inference engine designed for local deployment on consumer-grade hardware, leveraging activation locality to optimize efficiency. It features a locality-centric design, hybrid CPU/GPU utilization, easy integration with popular ReLU-sparse models, and support for various platforms. PowerInfer achieves high speed with lower resource demands and is flexible for easy deployment and compatibility with existing models like Falcon-40B, Llama2 family, ProSparse Llama2 family, and Bamboo-7B.
fish-identification
Fishial.ai is a project focused on training and validating scripts for fish segmentation and classification models. It includes various scripts for automatic training with different loss functions, dataset manipulation, and model setup using Detectron2 API. The project also provides tools for converting classification models to TorchScript format and creating training datasets. The models available include MaskRCNN for fish segmentation and various versions of ResNet18 for fish classification with different class counts and features. The project aims to facilitate fish identification and analysis through machine learning techniques.
mlcraft
Synmetrix (prev. MLCraft) is an open source data engineering platform and semantic layer for centralized metrics management. It provides a complete framework for modeling, integrating, transforming, aggregating, and distributing metrics data at scale. Key features include data modeling and transformations, semantic layer for unified data model, scheduled reports and alerts, versioning, role-based access control, data exploration, caching, and collaboration on metrics modeling. Synmetrix leverages Cube (Cube.js) for flexible data models that consolidate metrics from various sources, enabling downstream distribution via a SQL API for integration into BI tools, reporting, dashboards, and data science. Use cases include data democratization, business intelligence, embedded analytics, and enhancing accuracy in data handling and queries. The tool speeds up data-driven workflows from metrics definition to consumption by combining data engineering best practices with self-service analytics capabilities.
synmetrix
Synmetrix is an open source data engineering platform and semantic layer for centralized metrics management. It provides a complete framework for modeling, integrating, transforming, aggregating, and distributing metrics data at scale. Key features include data modeling and transformations, semantic layer for unified data model, scheduled reports and alerts, versioning, role-based access control, data exploration, caching, and collaboration on metrics modeling. Synmetrix leverages Cube.js to consolidate metrics from various sources and distribute them downstream via a SQL API. Use cases include data democratization, business intelligence and reporting, embedded analytics, and enhancing accuracy in data handling and queries. The tool speeds up data-driven workflows from metrics definition to consumption by combining data engineering best practices with self-service analytics capabilities.
Pearl
Pearl is a production-ready Reinforcement Learning AI agent library open-sourced by the Applied Reinforcement Learning team at Meta. It enables researchers and practitioners to develop Reinforcement Learning AI agents that prioritize cumulative long-term feedback over immediate feedback and can adapt to environments with limited observability, sparse feedback, and high stochasticity. Pearl offers a diverse set of unique features for production environments, including dynamic action spaces, offline learning, intelligent neural exploration, safe decision making, history summarization, and data augmentation.
For similar tasks

aimet
AIMET is a library that provides advanced model quantization and compression techniques for trained neural network models. It provides features that have been proven to improve run-time performance of deep learning neural network models with lower compute and memory requirements and minimal impact to task accuracy. AIMET is designed to work with PyTorch, TensorFlow and ONNX models. We also host the AIMET Model Zoo - a collection of popular neural network models optimized for 8-bit inference. We also provide recipes for users to quantize floating point models using AIMET.
hqq
HQQ is a fast and accurate model quantizer that skips the need for calibration data. It's super simple to implement (just a few lines of code for the optimizer). It can crunch through quantizing the Llama2-70B model in only 4 minutes! 🚀
llm-resource
llm-resource is a comprehensive collection of high-quality resources for Large Language Models (LLM). It covers various aspects of LLM including algorithms, training, fine-tuning, alignment, inference, data engineering, compression, evaluation, prompt engineering, AI frameworks, AI basics, AI infrastructure, AI compilers, LLM application development, LLM operations, AI systems, and practical implementations. The repository aims to gather and share valuable resources related to LLM for the community to benefit from.
llmc
llmc is an off-the-shell tool designed for compressing LLM, leveraging state-of-the-art compression algorithms to enhance efficiency and reduce model size without compromising performance. It provides users with the ability to quantize LLMs, choose from various compression algorithms, export transformed models for further optimization, and directly infer compressed models with a shallow memory footprint. The tool supports a range of model types and quantization algorithms, with ongoing development to include pruning techniques. Users can design their configurations for quantization and evaluation, with documentation and examples planned for future updates. llmc is a valuable resource for researchers working on post-training quantization of large language models.
Awesome-Efficient-LLM
Awesome-Efficient-LLM is a curated list focusing on efficient large language models. It includes topics such as knowledge distillation, network pruning, quantization, inference acceleration, efficient MOE, efficient architecture of LLM, KV cache compression, text compression, low-rank decomposition, hardware/system, tuning, and survey. The repository provides a collection of papers and projects related to improving the efficiency of large language models through various techniques like sparsity, quantization, and compression.
TensorRT-Model-Optimizer
The NVIDIA TensorRT Model Optimizer is a library designed to quantize and compress deep learning models for optimized inference on GPUs. It offers state-of-the-art model optimization techniques including quantization and sparsity to reduce inference costs for generative AI models. Users can easily stack different optimization techniques to produce quantized checkpoints from torch or ONNX models. The quantized checkpoints are ready for deployment in inference frameworks like TensorRT-LLM or TensorRT, with planned integrations for NVIDIA NeMo and Megatron-LM. The tool also supports 8-bit quantization with Stable Diffusion for enterprise users on NVIDIA NIM. Model Optimizer is available for free on NVIDIA PyPI, and this repository serves as a platform for sharing examples, GPU-optimized recipes, and collecting community feedback.
Awesome_LLM_System-PaperList
Since the emergence of chatGPT in 2022, the acceleration of Large Language Model has become increasingly important. Here is a list of papers on LLMs inference and serving.
llm-compressor
llm-compressor is an easy-to-use library for optimizing models for deployment with vllm. It provides a comprehensive set of quantization algorithms, seamless integration with Hugging Face models and repositories, and supports mixed precision, activation quantization, and sparsity. Supported algorithms include PTQ, GPTQ, SmoothQuant, and SparseGPT. Installation can be done via git clone and local pip install. Compression can be easily applied by selecting an algorithm and calling the oneshot API. The library also offers end-to-end examples for model compression. Contributions to the code, examples, integrations, and documentation are appreciated.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

agentcloud
AgentCloud is an open-source platform that enables companies to build and deploy private LLM chat apps, empowering teams to securely interact with their data. It comprises three main components: Agent Backend, Webapp, and Vector Proxy. To run this project locally, clone the repository, install Docker, and start the services. The project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 only. Contributions and feedback are welcome from the community.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.
executorch
ExecuTorch is an end-to-end solution for enabling on-device inference capabilities across mobile and edge devices including wearables, embedded devices and microcontrollers. It is part of the PyTorch Edge ecosystem and enables efficient deployment of PyTorch models to edge devices. Key value propositions of ExecuTorch are: * **Portability:** Compatibility with a wide variety of computing platforms, from high-end mobile phones to highly constrained embedded systems and microcontrollers. * **Productivity:** Enabling developers to use the same toolchains and SDK from PyTorch model authoring and conversion, to debugging and deployment to a wide variety of platforms. * **Performance:** Providing end users with a seamless and high-performance experience due to a lightweight runtime and utilizing full hardware capabilities such as CPUs, NPUs, and DSPs.
autogen
AutoGen is a framework that enables the development of LLM applications using multiple agents that can converse with each other to solve tasks. AutoGen agents are customizable, conversable, and seamlessly allow human participation. They can operate in various modes that employ combinations of LLMs, human inputs, and tools.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.