
RLHF-Reward-Modeling
A recipe to train reward models for RLHF.
Stars: 83
This repository contains code for training reward models for Deep Reinforcement Learning-based Reward-modulated Hierarchical Fine-tuning (DRL-based RLHF), Iterative Selection Fine-tuning (Rejection sampling fine-tuning), and iterative Decision Policy Optimization (DPO). The reward models are trained using a Bradley-Terry model based on the Gemma and Mistral language models. The resulting reward models achieve state-of-the-art performance on the RewardBench leaderboard for reward models with base models of up to 13B parameters.
README:
🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥
🔥🔥🚀🚀🚀 Check out our blog post! 🚀🚀🚀🔥🔥
🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥
TL;DL: this is a repo for training the reward model for DRL-based RLHF (PPO), Iterative SFT (Rejection sampling fine-tuning), and iterative DPO.
- 4 x A40 48G: we can train Gemma-7B-it with max_length 4096 by Deepspeed Zero-3 + gradient checkpoint;
- 4 x A100 80G: we can train Gemma-7B-it with max_length 4096 by gradient checkpoint;
- The resulting reward models achieve SOTA performance in the RMs with based model ≤ 13B in the leaderboard of RewardBench.
To be updated.
The current solution is based on the alignment handbook and the environment, which should be sufficient for plain RM training. Before starting, please make sure your linux machine has nvidia-cuda-toolkit installed.
conda create -n newhandbook python=3.10.9
conda activate newhandbook
git clone https://github.com/huggingface/alignment-handbook.git
cd ./alignment-handbook/
python -m pip install .
python -m pip install .
pip install flash-attn
git clone https://github.com/WeiXiongUST/RLHF-Reward-Modeling.gitSome possible problems:
CUDA_HOME may not exist, unable to compile CUDA op(s)AssertionError:[end of output]
conda install nvidia/label/cuda-12.2.0::cuda-nvccYou also need to install wandb to record the training and log in with the huggingface accout to access Gemma.
pip install wandb
wandb login
huggingface-cli loginThe dataset should be preprocessed as the standard format, where each of the sample consists of two conversations 'chosen' and 'rejected' and they share the same prompt. Here is an example of the rejected sample in the comparison pair.
[
{ "content": "Please identify the top 5 rarest animals in the world.", "role": "user" },
{ "content": "Do you mean animals that are really rare, or rare relative to the size of the human population?", "role": "assistant" },
{ "content": "The ones that are really rare.", "role": "user" },
{ "content": "Alright, here’s what I found:", "role": "assistant" },
]We preprocess 4 dataset and upload them to the hugginface hub.
- Version 1: weqweasdas/preference_dataset_mixture
- Version 2: weqweasdas/preference_dataset_mix2
- Version 3: weqweasdas/preference_dataset_mixture2_and_safe_pku
- Version 4: weqweasdas/preference_dataset_mixture2_and_safe_pku150k
- Version 5: llm-blender/Unified-Feedback
Version 1: The model is trained on a mixture1 of
The total number of the comparison pairs is 250K, where we perform the following data selection and cleaning strateges:
- HH-RLHF: we use all the base, rejection sampling, and online subsets but delete the samples whose chosen == rejected, leading to 115547;
- SHP: we only use the samples with score ratio > 2, for each prompt, we only take 1 comparison, leading to 55916;
- Ultrafeedback: similar to UltraFeedback-Binarized, we use the fine-grained score instead of the overall one to rank samples. Meanwhile, for each prompt, we take the best one v.s. random chosen one in the remaining samples. Finally, we delete the selected pairs with equal scores, leading to 62793.
- HelpSteer: we use the mean of helpfulness and correctness to rank samples. Meanwhile, we take the best sample v.s. the random chosen one in the remaining samples. Finally, we delete the selected pairs with equal scores, leading to 8206;
- Capybara: we delete the pairs whose chosen and rejected samples are of the same rating, leading to 7562;
- Orca: we delete the pairs whose chosen and rejected samples are of the same rating, leading to 6405.
Version 2: The model is also trained on a mixture2 of
Difference:
- SHP: we only use the samples with score ratio > 2, for each prompt, we take 5 comparison at most, leading to 109526;
- Ultrafeedback: similar to UltraFeedback-Binarized, we use the fine-grained score instead of the overall one to rank samples. Meanwhile, for each prompt, we take all possible 6 pairs of comparisons. Finally, we delete the selected pairs with equal scores, leading to 267416.
- HelpSteer: we use the mean of helpfulness and correctness to rank samples. Meanwhile, we take all possible 6 pairs of comparisons. Finally, we delete the selected pairs with equal scores, leading to 21576;
Version 3: Mixture2 + 30K safety is the mixture2 + the training set of PKU-Alignment/PKU-SafeRLHF-30K
Version 4: 1 Mixture2 + 150K safety is the mixture2 + 150K samples from PKU-Alignment/PKU-SafeRLHF
Version 5 Directly leverage the dataset from llm-blender/Unified-Feedback, which includes 886K preference samples from 8 prior datasets: openai/summarize_from_feedback, openai/webgpt_comparisons, Dahoas/instruct-synthetic-prompt-responses, Anthropic/hh-rlhf, lmsys/chatbot_arena_conversations, openbmb/UltraFeedback, argilla/ultrafeedback-binarized-preferences-cleaned, berkeley-nest/Nectar.
Running the code with Gemma-2b-it.
accelerate launch rm.py --model_name google/gemma-2b-it --max_length 4096 --train_set_path weqweasdas/preference_dataset_mix2You can also modify the learning rate, batch size, output_path.. with either command or modify the ScriptArguments in the rm_gemma.py
If you encounter out-of-memory issue. Running the code with Gemma-2b-it with deepspeed stage 3. If OOM still exists, use a smaller max length and per_device_batch_size.
accelerate launch rm.py --model_name google/gemma-2b-it --max_length 4096 --train_set_path weqweasdas/preference_dataset_mix2 --deepspeed deepspeed_3.jsonREMARK: note that with deepspeed stage 3, the final mode saving does not work normally. You should set the save_every_steps as the total number of training steps - 1 so that the trainer will save a model for you just before finishing the training.
You can evaluate the resulting reward model with the dataset provided by benchmark by the following command.
accelerate launch eval_bench_mark.py --reward_name_or_path ./models/gemma_2b_mixture2_last_checkpoint --record_dir ./bench_mark_eval.txtSome models trained by our script are competitive in the leaderboard.
- [x] Bradley-Terry Reward Model based on Gemma and Mistral.
- [ ] Bradley-Terry Reward Model based on Mixtral;
- [ ] Preference model;
- [ ] Regression-based reward model;
- [ ] Multi-objective reward model.
The repo was part of the iterative rejection sampling fine-tuning and iterative DPO. If you find the content of this repo useful in your work, please consider cite it as follows:
@article{dong2023raft,
title={Raft: Reward ranked finetuning for generative foundation model alignment},
author={Dong, Hanze and Xiong, Wei and Goyal, Deepanshu and Pan, Rui and Diao, Shizhe and Zhang, Jipeng and Shum, Kashun and Zhang, Tong},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2304.06767},
year={2023}
}
@misc{xiong2024iterative,
title={Iterative Preference Learning from Human Feedback: Bridging Theory and Practice for RLHF under KL-Constraint},
author={Wei Xiong and Hanze Dong and Chenlu Ye and Ziqi Wang and Han Zhong and Heng Ji and Nan Jiang and Tong Zhang},
year={2024},
eprint={2312.11456},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.LG}
}For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for RLHF-Reward-Modeling
Similar Open Source Tools

RLHF-Reward-Modeling
This repository contains code for training reward models for Deep Reinforcement Learning-based Reward-modulated Hierarchical Fine-tuning (DRL-based RLHF), Iterative Selection Fine-tuning (Rejection sampling fine-tuning), and iterative Decision Policy Optimization (DPO). The reward models are trained using a Bradley-Terry model based on the Gemma and Mistral language models. The resulting reward models achieve state-of-the-art performance on the RewardBench leaderboard for reward models with base models of up to 13B parameters.

llm-reasoners
LLM Reasoners is a library that enables LLMs to conduct complex reasoning, with advanced reasoning algorithms. It approaches multi-step reasoning as planning and searches for the optimal reasoning chain, which achieves the best balance of exploration vs exploitation with the idea of "World Model" and "Reward". Given any reasoning problem, simply define the reward function and an optional world model (explained below), and let LLM reasoners take care of the rest, including Reasoning Algorithms, Visualization, LLM calling, and more!
CogAgent
CogAgent is an advanced intelligent agent model designed for automating operations on graphical interfaces across various computing devices. It supports platforms like Windows, macOS, and Android, enabling users to issue commands, capture device screenshots, and perform automated operations. The model requires a minimum of 29GB of GPU memory for inference at BF16 precision and offers capabilities for executing tasks like sending Christmas greetings and sending emails. Users can interact with the model by providing task descriptions, platform specifications, and desired output formats.
LongBench
LongBench v2 is a benchmark designed to assess the ability of large language models (LLMs) to handle long-context problems requiring deep understanding and reasoning across various real-world multitasks. It consists of 503 challenging multiple-choice questions with contexts ranging from 8k to 2M words, covering six major task categories. The dataset is collected from nearly 100 highly educated individuals with diverse professional backgrounds and is designed to be challenging even for human experts. The evaluation results highlight the importance of enhanced reasoning ability and scaling inference-time compute to tackle the long-context challenges in LongBench v2.

MInference
MInference is a tool designed to accelerate pre-filling for long-context Language Models (LLMs) by leveraging dynamic sparse attention. It achieves up to a 10x speedup for pre-filling on an A100 while maintaining accuracy. The tool supports various decoding LLMs, including LLaMA-style models and Phi models, and provides custom kernels for attention computation. MInference is useful for researchers and developers working with large-scale language models who aim to improve efficiency without compromising accuracy.
k2
K2 (GeoLLaMA) is a large language model for geoscience, trained on geoscience literature and fine-tuned with knowledge-intensive instruction data. It outperforms baseline models on objective and subjective tasks. The repository provides K2 weights, core data of GeoSignal, GeoBench benchmark, and code for further pretraining and instruction tuning. The model is available on Hugging Face for use. The project aims to create larger and more powerful geoscience language models in the future.
MME-RealWorld
MME-RealWorld is a benchmark designed to address real-world applications with practical relevance, featuring 13,366 high-resolution images and 29,429 annotations across 43 tasks. It aims to provide substantial recognition challenges and overcome common barriers in existing Multimodal Large Language Model benchmarks, such as small data scale, restricted data quality, and insufficient task difficulty. The dataset offers advantages in data scale, data quality, task difficulty, and real-world utility compared to existing benchmarks. It also includes a Chinese version with additional images and QA pairs focused on Chinese scenarios.
LLMLingua
LLMLingua is a tool that utilizes a compact, well-trained language model to identify and remove non-essential tokens in prompts. This approach enables efficient inference with large language models, achieving up to 20x compression with minimal performance loss. The tool includes LLMLingua, LongLLMLingua, and LLMLingua-2, each offering different levels of prompt compression and performance improvements for tasks involving large language models.

Trace
Trace is a new AutoDiff-like tool for training AI systems end-to-end with general feedback. It generalizes the back-propagation algorithm by capturing and propagating an AI system's execution trace. Implemented as a PyTorch-like Python library, users can write Python code directly and use Trace primitives to optimize certain parts, similar to training neural networks.
simple_GRPO
simple_GRPO is a very simple implementation of the GRPO algorithm for reproducing r1-like LLM thinking. It provides a codebase that supports saving GPU memory, understanding RL processes, trying various improvements like multi-answer generation, regrouping, penalty on KL, and parameter tuning. The project focuses on simplicity, performance, and core loss calculation based on Hugging Face's trl. It offers a straightforward setup with minimal dependencies and efficient training on multiple GPUs.
xFinder
xFinder is a model specifically designed for key answer extraction from large language models (LLMs). It addresses the challenges of unreliable evaluation methods by optimizing the key answer extraction module. The model achieves high accuracy and robustness compared to existing frameworks, enhancing the reliability of LLM evaluation. It includes a specialized dataset, the Key Answer Finder (KAF) dataset, for effective training and evaluation. xFinder is suitable for researchers and developers working with LLMs to improve answer extraction accuracy.
MiniCheck
MiniCheck is an efficient fact-checking tool designed to verify claims against grounding documents using large language models. It provides a sentence-level fact-checking model that can be used to evaluate the consistency of claims with the provided documents. MiniCheck offers different models, including Bespoke-MiniCheck-7B, which is the state-of-the-art and commercially usable. The tool enables users to fact-check multi-sentence claims by breaking them down into individual sentences for optimal performance. It also supports automatic prefix caching for faster inference when repeatedly fact-checking the same document with different claims.
storm
STORM is a LLM system that writes Wikipedia-like articles from scratch based on Internet search. While the system cannot produce publication-ready articles that often require a significant number of edits, experienced Wikipedia editors have found it helpful in their pre-writing stage. **Try out our [live research preview](https://storm.genie.stanford.edu/) to see how STORM can help your knowledge exploration journey and please provide feedback to help us improve the system 🙏!**
Quantus
Quantus is a toolkit designed for the evaluation of neural network explanations. It offers more than 30 metrics in 6 categories for eXplainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) evaluation. The toolkit supports different data types (image, time-series, tabular, NLP) and models (PyTorch, TensorFlow). It provides built-in support for explanation methods like captum, tf-explain, and zennit. Quantus is under active development and aims to provide a comprehensive set of quantitative evaluation metrics for XAI methods.
langevals
LangEvals is an all-in-one Python library for testing and evaluating LLM models. It can be used in notebooks for exploration, in pytest for writing unit tests, or as a server API for live evaluations and guardrails. The library is modular, with 20+ evaluators including Ragas for RAG quality, OpenAI Moderation, and Azure Jailbreak detection. LangEvals powers LangWatch evaluations and provides tools for batch evaluations on notebooks and unit test evaluations with PyTest. It also offers LangEvals evaluators for LLM-as-a-Judge scenarios and out-of-the-box evaluators for language detection and answer relevancy checks.

zshot
Zshot is a highly customizable framework for performing Zero and Few shot named entity and relationships recognition. It can be used for mentions extraction, wikification, zero and few shot named entity recognition, zero and few shot named relationship recognition, and visualization of zero-shot NER and RE extraction. The framework consists of two main components: the mentions extractor and the linker. There are multiple mentions extractors and linkers available, each serving a specific purpose. Zshot also includes a relations extractor and a knowledge extractor for extracting relations among entities and performing entity classification. The tool requires Python 3.6+ and dependencies like spacy, torch, transformers, evaluate, and datasets for evaluation over datasets like OntoNotes. Optional dependencies include flair and blink for additional functionalities. Zshot provides examples, tutorials, and evaluation methods to assess the performance of the components.
For similar tasks

RLHF-Reward-Modeling
This repository contains code for training reward models for Deep Reinforcement Learning-based Reward-modulated Hierarchical Fine-tuning (DRL-based RLHF), Iterative Selection Fine-tuning (Rejection sampling fine-tuning), and iterative Decision Policy Optimization (DPO). The reward models are trained using a Bradley-Terry model based on the Gemma and Mistral language models. The resulting reward models achieve state-of-the-art performance on the RewardBench leaderboard for reward models with base models of up to 13B parameters.

h2o-llmstudio
H2O LLM Studio is a framework and no-code GUI designed for fine-tuning state-of-the-art large language models (LLMs). With H2O LLM Studio, you can easily and effectively fine-tune LLMs without the need for any coding experience. The GUI is specially designed for large language models, and you can finetune any LLM using a large variety of hyperparameters. You can also use recent finetuning techniques such as Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) and 8-bit model training with a low memory footprint. Additionally, you can use Reinforcement Learning (RL) to finetune your model (experimental), use advanced evaluation metrics to judge generated answers by the model, track and compare your model performance visually, and easily export your model to the Hugging Face Hub and share it with the community.
MathCoder
MathCoder is a repository focused on enhancing mathematical reasoning by fine-tuning open-source language models to use code for modeling and deriving math equations. It introduces MathCodeInstruct dataset with solutions interleaving natural language, code, and execution results. The repository provides MathCoder models capable of generating code-based solutions for challenging math problems, achieving state-of-the-art scores on MATH and GSM8K datasets. It offers tools for model deployment, inference, and evaluation, along with a citation for referencing the work.
Awesome-Text2SQL
Awesome Text2SQL is a curated repository containing tutorials and resources for Large Language Models, Text2SQL, Text2DSL, Text2API, Text2Vis, and more. It provides guidelines on converting natural language questions into structured SQL queries, with a focus on NL2SQL. The repository includes information on various models, datasets, evaluation metrics, fine-tuning methods, libraries, and practice projects related to Text2SQL. It serves as a comprehensive resource for individuals interested in working with Text2SQL and related technologies.
Awesome-LLM
Awesome-LLM is a curated list of resources related to large language models, focusing on papers, projects, frameworks, tools, tutorials, courses, opinions, and other useful resources in the field. It covers trending LLM projects, milestone papers, other papers, open LLM projects, LLM training frameworks, LLM evaluation frameworks, tools for deploying LLM, prompting libraries & tools, tutorials, courses, books, and opinions. The repository provides a comprehensive overview of the latest advancements and resources in the field of large language models.
langserve_ollama
LangServe Ollama is a tool that allows users to fine-tune Korean language models for local hosting, including RAG. Users can load HuggingFace gguf files, create model chains, and monitor GPU usage. The tool provides a seamless workflow for customizing and deploying language models in a local environment.

k2
K2 (GeoLLaMA) is a large language model for geoscience, trained on geoscience literature and fine-tuned with knowledge-intensive instruction data. It outperforms baseline models on objective and subjective tasks. The repository provides K2 weights, core data of GeoSignal, GeoBench benchmark, and code for further pretraining and instruction tuning. The model is available on Hugging Face for use. The project aims to create larger and more powerful geoscience language models in the future.
LLM-Fine-Tuning
This GitHub repository contains examples of fine-tuning open source large language models. It showcases the process of fine-tuning and quantizing large language models using efficient techniques like Lora and QLora. The repository serves as a practical guide for individuals looking to optimize the performance of language models through fine-tuning.
For similar jobs
llm2vec
LLM2Vec is a simple recipe to convert decoder-only LLMs into text encoders. It consists of 3 simple steps: 1) enabling bidirectional attention, 2) training with masked next token prediction, and 3) unsupervised contrastive learning. The model can be further fine-tuned to achieve state-of-the-art performance.
Friend
Friend is an open-source AI wearable device that records everything you say, gives you proactive feedback and advice. It has real-time AI audio processing capabilities, low-powered Bluetooth, open-source software, and a wearable design. The device is designed to be affordable and easy to use, with a total cost of less than $20. To get started, you can clone the repo, choose the version of the app you want to install, and follow the instructions for installing the firmware and assembling the device. Friend is still a prototype project and is provided "as is", without warranty of any kind. Use of the device should comply with all local laws and regulations concerning privacy and data protection.
open-parse
Open Parse is a Python library for visually discerning document layouts and chunking them effectively. It is designed to fill the gap in open-source libraries for handling complex documents. Unlike text splitting, which converts a file to raw text and slices it up, Open Parse visually analyzes documents for superior LLM input. It also supports basic markdown for parsing headings, bold, and italics, and has high-precision table support, extracting tables into clean Markdown formats with accuracy that surpasses traditional tools. Open Parse is extensible, allowing users to easily implement their own post-processing steps. It is also intuitive, with great editor support and completion everywhere, making it easy to use and learn.

RLHF-Reward-Modeling
This repository contains code for training reward models for Deep Reinforcement Learning-based Reward-modulated Hierarchical Fine-tuning (DRL-based RLHF), Iterative Selection Fine-tuning (Rejection sampling fine-tuning), and iterative Decision Policy Optimization (DPO). The reward models are trained using a Bradley-Terry model based on the Gemma and Mistral language models. The resulting reward models achieve state-of-the-art performance on the RewardBench leaderboard for reward models with base models of up to 13B parameters.
hqq
HQQ is a fast and accurate model quantizer that skips the need for calibration data. It's super simple to implement (just a few lines of code for the optimizer). It can crunch through quantizing the Llama2-70B model in only 4 minutes! 🚀
curated-transformers
Curated Transformers is a transformer library for PyTorch that provides state-of-the-art models composed of reusable components. It supports various transformer architectures, including encoders like ALBERT, BERT, and RoBERTa, and decoders like Falcon, Llama, and MPT. The library emphasizes consistent type annotations, minimal dependencies, and ease of use for education and research. It has been production-tested by Explosion and will be the default transformer implementation in spaCy 3.7.

clarifai-python
The Clarifai Python SDK offers a comprehensive set of tools to integrate Clarifai's AI platform to leverage computer vision capabilities like classification , detection ,segementation and natural language capabilities like classification , summarisation , generation , Q&A ,etc into your applications. With just a few lines of code, you can leverage cutting-edge artificial intelligence to unlock valuable insights from visual and textual content.
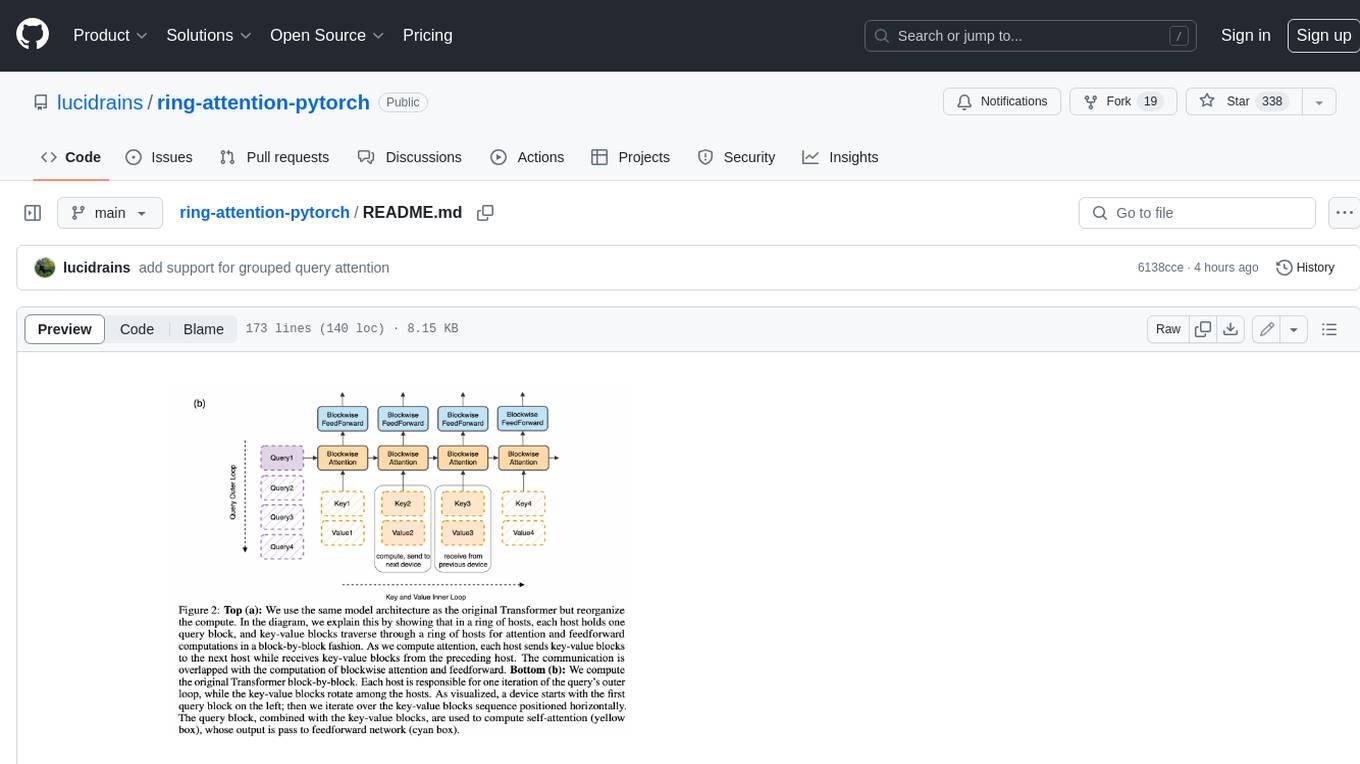
ring-attention-pytorch
This repository contains an implementation of Ring Attention, a technique for processing large sequences in transformers. Ring Attention splits the data across the sequence dimension and applies ring reduce to the processing of the tiles of the attention matrix, similar to flash attention. It also includes support for Striped Attention, a follow-up paper that permutes the sequence for better workload balancing for autoregressive transformers, and grouped query attention, which saves on communication costs during the ring reduce. The repository includes a CUDA version of the flash attention kernel, which is used for the forward and backward passes of the ring attention. It also includes logic for splitting the sequence evenly among ranks, either within the attention function or in the external ring transformer wrapper, and basic test cases with two processes to check for equivalent output and gradients.