
InfLLM
The code of our paper "InfLLM: Unveiling the Intrinsic Capacity of LLMs for Understanding Extremely Long Sequences with Training-Free Memory"
Stars: 196
InfLLM is a training-free memory-based method that unveils the intrinsic ability of LLMs to process streaming long sequences. It stores distant contexts into additional memory units and employs an efficient mechanism to lookup token-relevant units for attention computation. Thereby, InfLLM allows LLMs to efficiently process long sequences while maintaining the ability to capture long-distance dependencies. Without any training, InfLLM enables LLMs pre-trained on sequences of a few thousand tokens to achieve superior performance than competitive baselines continually training these LLMs on long sequences. Even when the sequence length is scaled to 1, 024K, InfLLM still effectively captures long-distance dependencies.
README:
InfLLM: Unveiling the Intrinsic Capacity of LLMs for Understanding Extremely Long Sequences with Training-Free Memory
The code of our paper "InfLLM: Unveiling the Intrinsic Capacity of LLMs for Understanding Extremely Long Sequences with Training-Free Memory" [pdf].
- March 3, 2024: Initial code release. See init.
- March 24, 2024: Refactor the code. Improve inference speed and reduce GPU memory usage.
- April 4, 2024: Supports topk retrieval using faiss.
- April 20, 2024: Added support for LLaMA 3.
Large language models (LLMs) have emerged as a cornerstone in real-world applications with lengthy streaming inputs, such as LLM-driven agents. However, existing LLMs, pre-trained on sequences with restricted maximum length, cannot generalize to longer sequences due to the out-of-domain and distraction issues. To alleviate these issues, existing efforts employ sliding attention windows and discard distant tokens to achieve the processing of extremely long sequences. Unfortunately, these approaches inevitably fail to capture long-distance dependencies within sequences to deeply understand semantics. This paper introduces a training-free memory-based method, InfLLM, to unveil the intrinsic ability of LLMs to process streaming long sequences. Specifically, InfLLM stores distant contexts into additional memory units and employs an efficient mechanism to lookup token-relevant units for attention computation. Thereby, InfLLM allows LLMs to efficiently process long sequences while maintaining the ability to capture long-distance dependencies. Without any training, InfLLM enables LLMs pre-trained on sequences of a few thousand tokens to achieve superior performance than competitive baselines continually training these LLMs on long sequences. Even when the sequence length is scaled to 1, 024K, InfLLM still effectively captures long-distance dependencies.
torch>=1.13.1
transformers>=4.37.2
fschat>=0.2.35
datasets>=2.17.0
omegaconf
flash-attn
rouge==1.0.1
fuzzywuzzy==0.18.0
jieba==0.42.1
We use YAML files for configuration, and you can see the configuration files we use for benchmark in the config/ directory.
The description of the configuration files is as follows:
model:
# attention type.
# inf-llm/infinite-lm/stream-lm/origin(full attention)
type: inf-llm
# huggingface or model-center model path
path: mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2
# Use flash-attention or not.
# For inf-llm/infinite-lm/stream-llm, we implemented multi-stage flash-attention by OpenAI's Triton.
fattn: false
# RoPE base and distance_scale
base: 1000000
distance_scale: 1.0
# inf-llm/infinite-lm/stream-lm settings
# Initital tokens as attention sinks
n_init: 128
# Local sliding window size
n_local: 4096
# inf-llm settings
# Number of memory units to retrieve for attention computation.
topk: 16
# The number of top-scoring tokens per memory unit considered as representative elements.
repr_topk: 4
# Maximum number of memory units stored in GPU memory.
max_cached_block: 32
# Number of tokens queried at a time as an execution block.
# Each execution block retrieves topk memory units once.
exc_block_size: 512
# The strategy for replacing cached memory units.
# Supported strategies include LRU (Least Recently Used), FIFO (First In, First Out),
# and LRU-S (LRU in our paper).
cache_strategy: lru
# score_decay for LRU-S
# score_decay: 0.1
# Use overlap local and global calculation.
# Can accelerate, but may not be compatible.
async_global_stream: false
# Use faiss for topk retrieval of memory units.
# It will increase inference time and ensure constant GPU memory usage.
faiss: false
# Use perhead topk.
# Enabling it will be very time-consuming and is intended for research use only.
# perhead: false
# Model max input length.
# A truncation will be employed if the input length exceeds.
max_len: 2147483647
# truncation type. Now supports suffix only.
truncation: suffix
# Chunked input in decoding.
# To save GPU memory. (FFN block)
chunk_size: 8192
# Conversation type.
# mistral-inst/vicuna/qwen/minicpm/llama-3-inst
conv_type: mistral-instData Preparation We adopt InfiniteBench and LongBench for model evaluation. You can download the datasets by running the following command.
bash scripts/download.sh
Response Generation You can evaluate InfLLM by running the following command. Notably, the provided code is used to run evaluate with only one GPU, and you can accelerate the experiments with multiple GPUs.
bash scripts/[infinitebench,longbench].sh
We integrated fastchat's CLI chat.
python -m inf_llm.chat \
--model-path mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2 \
--inf-llm-config-path config/mistral-inf-llm.yaml
If you find InfLLM useful, please cite the following paper:
@article{xiao2024infllm,
author = {Chaojun Xiao and Pengle Zhang and Xu Han and Guangxuan Xiao and Yankai Lin and Zhengyan Zhang and Zhiyuan Liu and Song Han and Maosong Sun},
title = {InfLLM: Unveiling the Intrinsic Capacity of LLMs for Understanding
Extremely Long Sequences with Training-Free Memory},
journal = {arXiv},
year = {2024}
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for InfLLM
Similar Open Source Tools

InfLLM
InfLLM is a training-free memory-based method that unveils the intrinsic ability of LLMs to process streaming long sequences. It stores distant contexts into additional memory units and employs an efficient mechanism to lookup token-relevant units for attention computation. Thereby, InfLLM allows LLMs to efficiently process long sequences while maintaining the ability to capture long-distance dependencies. Without any training, InfLLM enables LLMs pre-trained on sequences of a few thousand tokens to achieve superior performance than competitive baselines continually training these LLMs on long sequences. Even when the sequence length is scaled to 1, 024K, InfLLM still effectively captures long-distance dependencies.
llm-d-inference-sim
The `llm-d-inference-sim` is a lightweight, configurable, and real-time simulator designed to mimic the behavior of vLLM without the need for GPUs or running heavy models. It operates as an OpenAI-compliant server, allowing developers to test clients, schedulers, and infrastructure using realistic request-response cycles, token streaming, and latency patterns. The simulator offers modes of operation, response generation from predefined text or real datasets, latency simulation, tokenization options, LoRA management, KV cache simulation, failure injection, and deployment options for standalone or Kubernetes testing. It supports a subset of standard vLLM Prometheus metrics for observability.
tinyllm
tinyllm is a lightweight framework designed for developing, debugging, and monitoring LLM and Agent powered applications at scale. It aims to simplify code while enabling users to create complex agents or LLM workflows in production. The core classes, Function and FunctionStream, standardize and control LLM, ToolStore, and relevant calls for scalable production use. It offers structured handling of function execution, including input/output validation, error handling, evaluation, and more, all while maintaining code readability. Users can create chains with prompts, LLM models, and evaluators in a single file without the need for extensive class definitions or spaghetti code. Additionally, tinyllm integrates with various libraries like Langfuse and provides tools for prompt engineering, observability, logging, and finite state machine design.
gepa
GEPA (Genetic-Pareto) is a framework for optimizing arbitrary systems composed of text components like AI prompts, code snippets, or textual specs against any evaluation metric. It employs LLMs to reflect on system behavior, using feedback from execution and evaluation traces to drive targeted improvements. Through iterative mutation, reflection, and Pareto-aware candidate selection, GEPA evolves robust, high-performing variants with minimal evaluations, co-evolving multiple components in modular systems for domain-specific gains. The repository provides the official implementation of the GEPA algorithm as proposed in the paper titled 'GEPA: Reflective Prompt Evolution Can Outperform Reinforcement Learning'.

magpie
This is the official repository for 'Alignment Data Synthesis from Scratch by Prompting Aligned LLMs with Nothing'. Magpie is a tool designed to synthesize high-quality instruction data at scale by extracting it directly from an aligned Large Language Models (LLMs). It aims to democratize AI by generating large-scale alignment data and enhancing the transparency of model alignment processes. Magpie has been tested on various model families and can be used to fine-tune models for improved performance on alignment benchmarks such as AlpacaEval, ArenaHard, and WildBench.

fuse-med-ml
FuseMedML is a Python framework designed to accelerate machine learning-based discovery in the medical field by promoting code reuse. It provides a flexible design concept where data is stored in a nested dictionary, allowing easy handling of multi-modality information. The framework includes components for creating custom models, loss functions, metrics, and data processing operators. Additionally, FuseMedML offers 'batteries included' key components such as fuse.data for data processing, fuse.eval for model evaluation, and fuse.dl for reusable deep learning components. It supports PyTorch and PyTorch Lightning libraries and encourages the creation of domain extensions for specific medical domains.

aimo-progress-prize
This repository contains the training and inference code needed to replicate the winning solution to the AI Mathematical Olympiad - Progress Prize 1. It consists of fine-tuning DeepSeekMath-Base 7B, high-quality training datasets, a self-consistency decoding algorithm, and carefully chosen validation sets. The training methodology involves Chain of Thought (CoT) and Tool Integrated Reasoning (TIR) training stages. Two datasets, NuminaMath-CoT and NuminaMath-TIR, were used to fine-tune the models. The models were trained using open-source libraries like TRL, PyTorch, vLLM, and DeepSpeed. Post-training quantization to 8-bit precision was done to improve performance on Kaggle's T4 GPUs. The project structure includes scripts for training, quantization, and inference, along with necessary installation instructions and hardware/software specifications.
OREAL
OREAL is a reinforcement learning framework designed for mathematical reasoning tasks, aiming to achieve optimal performance through outcome reward-based learning. The framework utilizes behavior cloning, reshaping rewards, and token-level reward models to address challenges in sparse rewards and partial correctness. OREAL has achieved significant results, with a 7B model reaching 94.0 pass@1 accuracy on MATH-500 and surpassing previous 32B models. The tool provides training tutorials and Hugging Face model repositories for easy access and implementation.
llm-analysis
llm-analysis is a tool designed for Latency and Memory Analysis of Transformer Models for Training and Inference. It automates the calculation of training or inference latency and memory usage for Large Language Models (LLMs) or Transformers based on specified model, GPU, data type, and parallelism configurations. The tool helps users to experiment with different setups theoretically, understand system performance, and optimize training/inference scenarios. It supports various parallelism schemes, communication methods, activation recomputation options, data types, and fine-tuning strategies. Users can integrate llm-analysis in their code using the `LLMAnalysis` class or use the provided entry point functions for command line interface. The tool provides lower-bound estimations of memory usage and latency, and aims to assist in achieving feasible and optimal setups for training or inference.
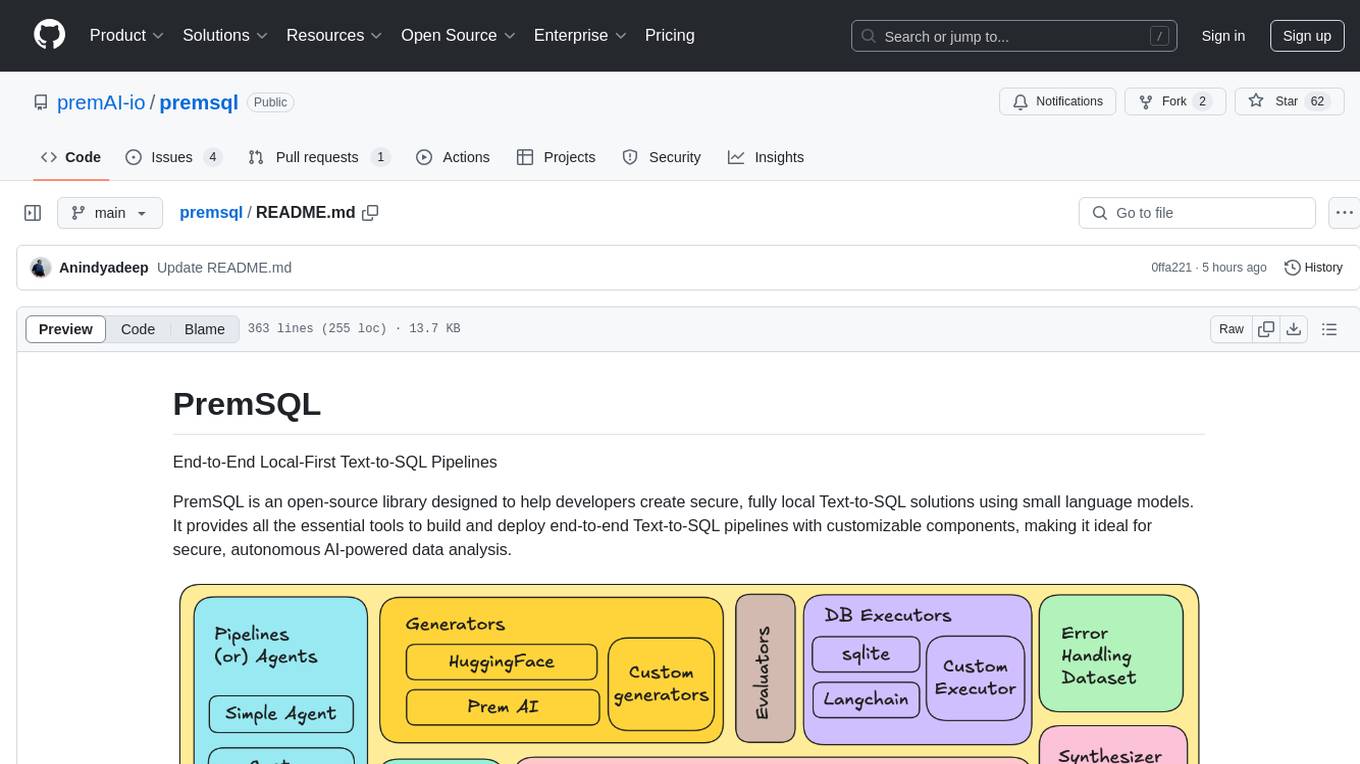
premsql
PremSQL is an open-source library designed to help developers create secure, fully local Text-to-SQL solutions using small language models. It provides essential tools for building and deploying end-to-end Text-to-SQL pipelines with customizable components, ideal for secure, autonomous AI-powered data analysis. The library offers features like Local-First approach, Customizable Datasets, Robust Executors and Evaluators, Advanced Generators, Error Handling and Self-Correction, Fine-Tuning Support, and End-to-End Pipelines. Users can fine-tune models, generate SQL queries from natural language inputs, handle errors, and evaluate model performance against predefined metrics. PremSQL is extendible for customization and private data usage.
EDA-GPT
EDA GPT is an open-source data analysis companion that offers a comprehensive solution for structured and unstructured data analysis. It streamlines the data analysis process, empowering users to explore, visualize, and gain insights from their data. EDA GPT supports analyzing structured data in various formats like CSV, XLSX, and SQLite, generating graphs, and conducting in-depth analysis of unstructured data such as PDFs and images. It provides a user-friendly interface, powerful features, and capabilities like comparing performance with other tools, analyzing large language models, multimodal search, data cleaning, and editing. The tool is optimized for maximal parallel processing, searching internet and documents, and creating analysis reports from structured and unstructured data.
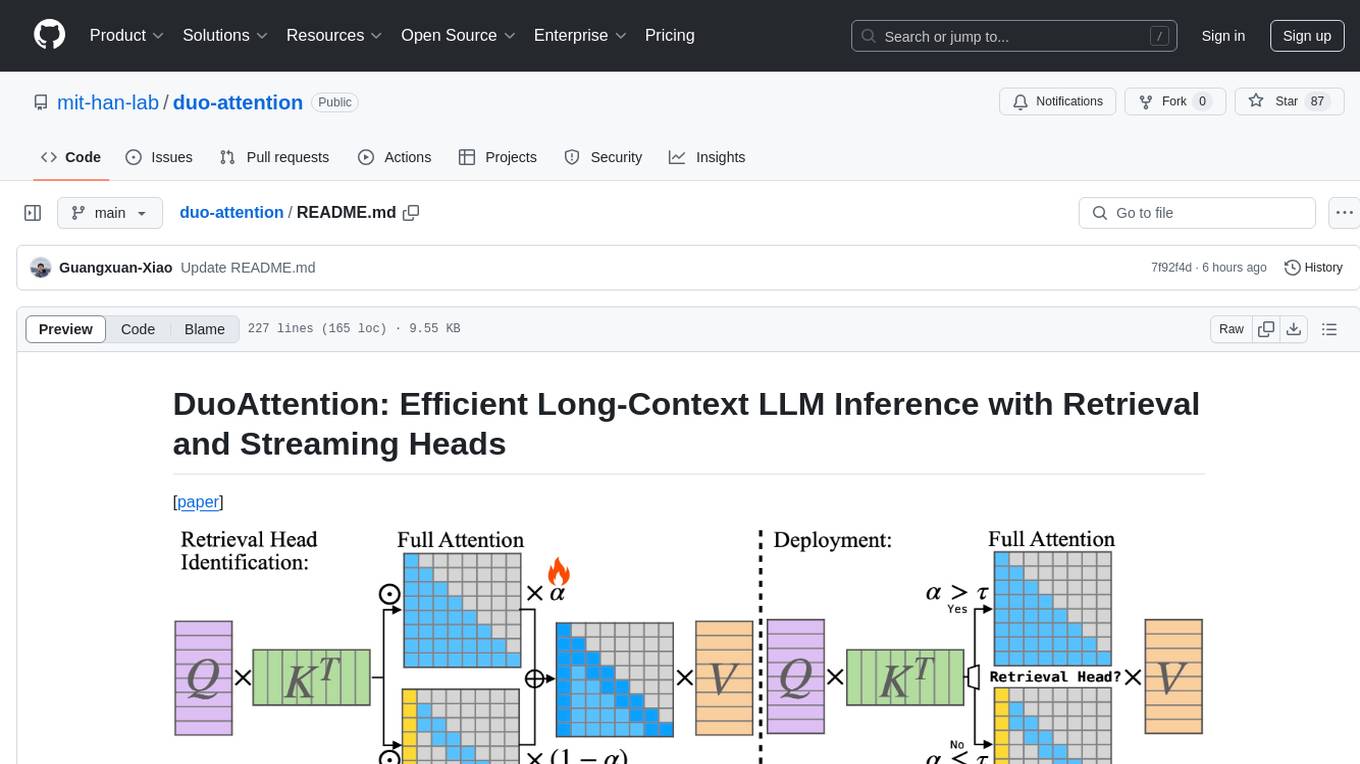
duo-attention
DuoAttention is a framework designed to optimize long-context large language models (LLMs) by reducing memory and latency during inference without compromising their long-context abilities. It introduces a concept of Retrieval Heads and Streaming Heads to efficiently manage attention across tokens. By applying a full Key and Value (KV) cache to retrieval heads and a lightweight, constant-length KV cache to streaming heads, DuoAttention achieves significant reductions in memory usage and decoding time for LLMs. The framework uses an optimization-based algorithm with synthetic data to accurately identify retrieval heads, enabling efficient inference with minimal accuracy loss compared to full attention. DuoAttention also supports quantization techniques for further memory optimization, allowing for decoding of up to 3.3 million tokens on a single GPU.
LongBench
LongBench v2 is a benchmark designed to assess the ability of large language models (LLMs) to handle long-context problems requiring deep understanding and reasoning across various real-world multitasks. It consists of 503 challenging multiple-choice questions with contexts ranging from 8k to 2M words, covering six major task categories. The dataset is collected from nearly 100 highly educated individuals with diverse professional backgrounds and is designed to be challenging even for human experts. The evaluation results highlight the importance of enhanced reasoning ability and scaling inference-time compute to tackle the long-context challenges in LongBench v2.
LLM-Drop
LLM-Drop is an official implementation of the paper 'What Matters in Transformers? Not All Attention is Needed'. The tool investigates redundancy in transformer-based Large Language Models (LLMs) by analyzing the architecture of Blocks, Attention layers, and MLP layers. It reveals that dropping certain Attention layers can enhance computational and memory efficiency without compromising performance. The tool provides a pipeline for Block Drop and Layer Drop based on LLaMA-Factory, and implements quantization using AutoAWQ and AutoGPTQ.
MiniCheck
MiniCheck is an efficient fact-checking tool designed to verify claims against grounding documents using large language models. It provides a sentence-level fact-checking model that can be used to evaluate the consistency of claims with the provided documents. MiniCheck offers different models, including Bespoke-MiniCheck-7B, which is the state-of-the-art and commercially usable. The tool enables users to fact-check multi-sentence claims by breaking them down into individual sentences for optimal performance. It also supports automatic prefix caching for faster inference when repeatedly fact-checking the same document with different claims.
simple_GRPO
simple_GRPO is a very simple implementation of the GRPO algorithm for reproducing r1-like LLM thinking. It provides a codebase that supports saving GPU memory, understanding RL processes, trying various improvements like multi-answer generation, regrouping, penalty on KL, and parameter tuning. The project focuses on simplicity, performance, and core loss calculation based on Hugging Face's trl. It offers a straightforward setup with minimal dependencies and efficient training on multiple GPUs.
For similar tasks

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

onnxruntime-genai
ONNX Runtime Generative AI is a library that provides the generative AI loop for ONNX models, including inference with ONNX Runtime, logits processing, search and sampling, and KV cache management. Users can call a high level `generate()` method, or run each iteration of the model in a loop. It supports greedy/beam search and TopP, TopK sampling to generate token sequences, has built in logits processing like repetition penalties, and allows for easy custom scoring.

jupyter-ai
Jupyter AI connects generative AI with Jupyter notebooks. It provides a user-friendly and powerful way to explore generative AI models in notebooks and improve your productivity in JupyterLab and the Jupyter Notebook. Specifically, Jupyter AI offers: * An `%%ai` magic that turns the Jupyter notebook into a reproducible generative AI playground. This works anywhere the IPython kernel runs (JupyterLab, Jupyter Notebook, Google Colab, Kaggle, VSCode, etc.). * A native chat UI in JupyterLab that enables you to work with generative AI as a conversational assistant. * Support for a wide range of generative model providers, including AI21, Anthropic, AWS, Cohere, Gemini, Hugging Face, NVIDIA, and OpenAI. * Local model support through GPT4All, enabling use of generative AI models on consumer grade machines with ease and privacy.

khoj
Khoj is an open-source, personal AI assistant that extends your capabilities by creating always-available AI agents. You can share your notes and documents to extend your digital brain, and your AI agents have access to the internet, allowing you to incorporate real-time information. Khoj is accessible on Desktop, Emacs, Obsidian, Web, and Whatsapp, and you can share PDF, markdown, org-mode, notion files, and GitHub repositories. You'll get fast, accurate semantic search on top of your docs, and your agents can create deeply personal images and understand your speech. Khoj is self-hostable and always will be.

langchain_dart
LangChain.dart is a Dart port of the popular LangChain Python framework created by Harrison Chase. LangChain provides a set of ready-to-use components for working with language models and a standard interface for chaining them together to formulate more advanced use cases (e.g. chatbots, Q&A with RAG, agents, summarization, extraction, etc.). The components can be grouped into a few core modules: * **Model I/O:** LangChain offers a unified API for interacting with various LLM providers (e.g. OpenAI, Google, Mistral, Ollama, etc.), allowing developers to switch between them with ease. Additionally, it provides tools for managing model inputs (prompt templates and example selectors) and parsing the resulting model outputs (output parsers). * **Retrieval:** assists in loading user data (via document loaders), transforming it (with text splitters), extracting its meaning (using embedding models), storing (in vector stores) and retrieving it (through retrievers) so that it can be used to ground the model's responses (i.e. Retrieval-Augmented Generation or RAG). * **Agents:** "bots" that leverage LLMs to make informed decisions about which available tools (such as web search, calculators, database lookup, etc.) to use to accomplish the designated task. The different components can be composed together using the LangChain Expression Language (LCEL).

danswer
Danswer is an open-source Gen-AI Chat and Unified Search tool that connects to your company's docs, apps, and people. It provides a Chat interface and plugs into any LLM of your choice. Danswer can be deployed anywhere and for any scale - on a laptop, on-premise, or to cloud. Since you own the deployment, your user data and chats are fully in your own control. Danswer is MIT licensed and designed to be modular and easily extensible. The system also comes fully ready for production usage with user authentication, role management (admin/basic users), chat persistence, and a UI for configuring Personas (AI Assistants) and their Prompts. Danswer also serves as a Unified Search across all common workplace tools such as Slack, Google Drive, Confluence, etc. By combining LLMs and team specific knowledge, Danswer becomes a subject matter expert for the team. Imagine ChatGPT if it had access to your team's unique knowledge! It enables questions such as "A customer wants feature X, is this already supported?" or "Where's the pull request for feature Y?"

infinity
Infinity is an AI-native database designed for LLM applications, providing incredibly fast full-text and vector search capabilities. It supports a wide range of data types, including vectors, full-text, and structured data, and offers a fused search feature that combines multiple embeddings and full text. Infinity is easy to use, with an intuitive Python API and a single-binary architecture that simplifies deployment. It achieves high performance, with 0.1 milliseconds query latency on million-scale vector datasets and up to 15K QPS.
For similar jobs
h2ogpt
h2oGPT is an Apache V2 open-source project that allows users to query and summarize documents or chat with local private GPT LLMs. It features a private offline database of any documents (PDFs, Excel, Word, Images, Video Frames, Youtube, Audio, Code, Text, MarkDown, etc.), a persistent database (Chroma, Weaviate, or in-memory FAISS) using accurate embeddings (instructor-large, all-MiniLM-L6-v2, etc.), and efficient use of context using instruct-tuned LLMs (no need for LangChain's few-shot approach). h2oGPT also offers parallel summarization and extraction, reaching an output of 80 tokens per second with the 13B LLaMa2 model, HYDE (Hypothetical Document Embeddings) for enhanced retrieval based upon LLM responses, a variety of models supported (LLaMa2, Mistral, Falcon, Vicuna, WizardLM. With AutoGPTQ, 4-bit/8-bit, LORA, etc.), GPU support from HF and LLaMa.cpp GGML models, and CPU support using HF, LLaMa.cpp, and GPT4ALL models. Additionally, h2oGPT provides Attention Sinks for arbitrarily long generation (LLaMa-2, Mistral, MPT, Pythia, Falcon, etc.), a UI or CLI with streaming of all models, the ability to upload and view documents through the UI (control multiple collaborative or personal collections), Vision Models LLaVa, Claude-3, Gemini-Pro-Vision, GPT-4-Vision, Image Generation Stable Diffusion (sdxl-turbo, sdxl) and PlaygroundAI (playv2), Voice STT using Whisper with streaming audio conversion, Voice TTS using MIT-Licensed Microsoft Speech T5 with multiple voices and Streaming audio conversion, Voice TTS using MPL2-Licensed TTS including Voice Cloning and Streaming audio conversion, AI Assistant Voice Control Mode for hands-free control of h2oGPT chat, Bake-off UI mode against many models at the same time, Easy Download of model artifacts and control over models like LLaMa.cpp through the UI, Authentication in the UI by user/password via Native or Google OAuth, State Preservation in the UI by user/password, Linux, Docker, macOS, and Windows support, Easy Windows Installer for Windows 10 64-bit (CPU/CUDA), Easy macOS Installer for macOS (CPU/M1/M2), Inference Servers support (oLLaMa, HF TGI server, vLLM, Gradio, ExLLaMa, Replicate, OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, Anthropic), OpenAI-compliant, Server Proxy API (h2oGPT acts as drop-in-replacement to OpenAI server), Python client API (to talk to Gradio server), JSON Mode with any model via code block extraction. Also supports MistralAI JSON mode, Claude-3 via function calling with strict Schema, OpenAI via JSON mode, and vLLM via guided_json with strict Schema, Web-Search integration with Chat and Document Q/A, Agents for Search, Document Q/A, Python Code, CSV frames (Experimental, best with OpenAI currently), Evaluate performance using reward models, and Quality maintained with over 1000 unit and integration tests taking over 4 GPU-hours.

mistral.rs
Mistral.rs is a fast LLM inference platform written in Rust. We support inference on a variety of devices, quantization, and easy-to-use application with an Open-AI API compatible HTTP server and Python bindings.
ollama
Ollama is a lightweight, extensible framework for building and running language models on the local machine. It provides a simple API for creating, running, and managing models, as well as a library of pre-built models that can be easily used in a variety of applications. Ollama is designed to be easy to use and accessible to developers of all levels. It is open source and available for free on GitHub.
llama-cpp-agent
The llama-cpp-agent framework is a tool designed for easy interaction with Large Language Models (LLMs). Allowing users to chat with LLM models, execute structured function calls and get structured output (objects). It provides a simple yet robust interface and supports llama-cpp-python and OpenAI endpoints with GBNF grammar support (like the llama-cpp-python server) and the llama.cpp backend server. It works by generating a formal GGML-BNF grammar of the user defined structures and functions, which is then used by llama.cpp to generate text valid to that grammar. In contrast to most GBNF grammar generators it also supports nested objects, dictionaries, enums and lists of them.
llama_ros
This repository provides a set of ROS 2 packages to integrate llama.cpp into ROS 2. By using the llama_ros packages, you can easily incorporate the powerful optimization capabilities of llama.cpp into your ROS 2 projects by running GGUF-based LLMs and VLMs.
MITSUHA
OneReality is a virtual waifu/assistant that you can speak to through your mic and it'll speak back to you! It has many features such as: * You can speak to her with a mic * It can speak back to you * Has short-term memory and long-term memory * Can open apps * Smarter than you * Fluent in English, Japanese, Korean, and Chinese * Can control your smart home like Alexa if you set up Tuya (more info in Prerequisites) It is built with Python, Llama-cpp-python, Whisper, SpeechRecognition, PocketSphinx, VITS-fast-fine-tuning, VITS-simple-api, HyperDB, Sentence Transformers, and Tuya Cloud IoT.
wenxin-starter
WenXin-Starter is a spring-boot-starter for Baidu's "Wenxin Qianfan WENXINWORKSHOP" large model, which can help you quickly access Baidu's AI capabilities. It fully integrates the official API documentation of Wenxin Qianfan. Supports text-to-image generation, built-in dialogue memory, and supports streaming return of dialogue. Supports QPS control of a single model and supports queuing mechanism. Plugins will be added soon.
FlexFlow
FlexFlow Serve is an open-source compiler and distributed system for **low latency**, **high performance** LLM serving. FlexFlow Serve outperforms existing systems by 1.3-2.0x for single-node, multi-GPU inference and by 1.4-2.4x for multi-node, multi-GPU inference.
