
KG_RAG
Empower Large Language Models (LLM) using Knowledge Graph based Retrieval-Augmented Generation (KG-RAG) for knowledge intensive tasks
Stars: 525

KG-RAG (Knowledge Graph-based Retrieval Augmented Generation) is a task agnostic framework that combines the explicit knowledge of a Knowledge Graph (KG) with the implicit knowledge of a Large Language Model (LLM). KG-RAG extracts "prompt-aware context" from a KG, which is defined as the minimal context sufficient enough to respond to the user prompt. This framework empowers a general-purpose LLM by incorporating an optimized domain-specific 'prompt-aware context' from a biomedical KG. KG-RAG is specifically designed for running prompts related to Diseases.
README:
- Step 1: Clone the repo
- Step 2: Create a virtual environment
- Step 3: Install dependencies
- Step 4: Update config.yaml
- Step 5: Run the setup script
- Step 6: Run KG-RAG from your terminal
- Command line arguments for KG-RAG
KG-RAG stands for Knowledge Graph-based Retrieval Augmented Generation.
It is a task agnostic framework that combines the explicit knowledge of a Knowledge Graph (KG) with the implicit knowledge of a Large Language Model (LLM). Here is the arXiv preprint of the work.
Here, we utilize a massive biomedical KG called SPOKE as the provider for the biomedical context. SPOKE has incorporated over 40 biomedical knowledge repositories from diverse domains, each focusing on biomedical concept like genes, proteins, drugs, compounds, diseases, and their established connections. SPOKE consists of more than 27 million nodes of 21 different types and 53 million edges of 55 types [Ref]
The main feature of KG-RAG is that it extracts "prompt-aware context" from SPOKE KG, which is defined as:
the minimal context sufficient enough to respond to the user prompt.
Hence, this framework empowers a general-purpose LLM by incorporating an optimized domain-specific 'prompt-aware context' from a biomedical KG.
Following snippet shows the news from FDA website about the drug "setmelanotide" approved by FDA for weight management in patients with Bardet-Biedl Syndrome
Note: This example was run using KG-RAG v0.3.0. We are prompting GPT from the terminal, NOT from the chatGPT browser. Temperature parameter is set to 0 for all the analysis. Refer this yaml file for parameter setting
Note: This example was run using KG-RAG v0.3.0. Temperature parameter is set to 0 for all the analysis. Refer this yaml file for parameter setting
You can see that, KG-RAG was able to give the correct information about the FDA approved drug.
Note: At the moment, KG-RAG is specifically designed for running prompts related to Diseases. We are actively working on improving its versatility.
Clone this repository. All Biomedical data used in the paper are uploaded to this repository, hence you don't have to download that separately.
Note: Scripts in this repository were run using python 3.10.9
conda create -n kg_rag python=3.10.9
conda activate kg_rag
cd KG_RAG
pip install -r requirements.txt
config.yaml holds all the necessary information required to run the scripts in your machine. Make sure to populate this yaml file accordingly.
Note: There is another yaml file called system_prompts.yaml. This is already populated and it holds all the system prompts used in the KG-RAG framework.
Note: Make sure you are in KG_RAG folder
Setup script runs in an interactive fashion.
Running the setup script will:
- create disease vector database for KG-RAG
- download Llama model in your machine (optional, you can skip this and that is totally fine)
python -m kg_rag.run_setup
Note: Make sure you are in KG_RAG folder
You can run KG-RAG using GPT and Llama model.
# GPT_API_TYPE='azure'
python -m kg_rag.rag_based_generation.GPT.text_generation -g <your favorite gpt model - "gpt-4" or "gpt-35-turbo">
# GPT_API_TYPE='openai'
python -m kg_rag.rag_based_generation.GPT.text_generation -g <your favorite gpt model - "gpt-4" or "gpt-3.5-turbo">
Example:
Note: The following example was run on AWS p3.8xlarge EC2 instance and using KG-RAG v0.3.0.
This allows the user to go over each step of the process in an interactive fashion
# GPT_API_TYPE='azure'
python -m kg_rag.rag_based_generation.GPT.text_generation -i True -g <your favorite gpt model - "gpt-4" or "gpt-35-turbo">
# GPT_API_TYPE='openai'
python -m kg_rag.rag_based_generation.GPT.text_generation -i True -g <your favorite gpt model - "gpt-4" or "gpt-3.5-turbo">
Note: If you haven't downloaded Llama during setup step, then when you run the following, it may take sometime since it will download the model first.
python -m kg_rag.rag_based_generation.Llama.text_generation -m <method-1 or method2, if nothing is mentioned it will take 'method-1'>
Example:
Note: The following example was run on AWS p3.8xlarge EC2 instance and using KG-RAG v0.3.0.
This allows the user to go over each step of the process in an interactive fashion
python -m kg_rag.rag_based_generation.Llama.text_generation -i True -m <method-1 or method2, if nothing is mentioned it will take 'method-1'>
| Argument | Default Value | Definition | Allowed Options | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| -g | gpt-35-turbo | GPT model selection | gpt models provided by OpenAI | Use only for GPT models |
| -i | False | Flag for interactive mode (shows step-by-step) | True or False | Can be used for both GPT and Llama models |
| -e | False | Flag for showing evidence of association from the graph | True or False | Can be used for both GPT and Llama models |
| -m | method-1 | Which tokenizer method to use | method-1 or method-2. method-1 uses 'AutoTokenizer' and method-2 uses 'LlamaTokenizer' and with an additional 'legacy' flag set to False while initiating the tokenizer | Use only for Llama models |
@article{soman2023biomedical,
title={Biomedical knowledge graph-enhanced prompt generation for large language models},
author={Soman, Karthik and Rose, Peter W and Morris, John H and Akbas, Rabia E and Smith, Brett and Peetoom, Braian and Villouta-Reyes, Catalina and Cerono, Gabriel and Shi, Yongmei and Rizk-Jackson, Angela and others},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.17330},
year={2023}
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for KG_RAG
Similar Open Source Tools

KG_RAG
KG-RAG (Knowledge Graph-based Retrieval Augmented Generation) is a task agnostic framework that combines the explicit knowledge of a Knowledge Graph (KG) with the implicit knowledge of a Large Language Model (LLM). KG-RAG extracts "prompt-aware context" from a KG, which is defined as the minimal context sufficient enough to respond to the user prompt. This framework empowers a general-purpose LLM by incorporating an optimized domain-specific 'prompt-aware context' from a biomedical KG. KG-RAG is specifically designed for running prompts related to Diseases.
kafka-ml
Kafka-ML is a framework designed to manage the pipeline of Tensorflow/Keras and PyTorch machine learning models on Kubernetes. It enables the design, training, and inference of ML models with datasets fed through Apache Kafka, connecting them directly to data streams like those from IoT devices. The Web UI allows easy definition of ML models without external libraries, catering to both experts and non-experts in ML/AI.
AI-Scientist
The AI Scientist is a comprehensive system for fully automatic scientific discovery, enabling Foundation Models to perform research independently. It aims to tackle the grand challenge of developing agents capable of conducting scientific research and discovering new knowledge. The tool generates papers on various topics using Large Language Models (LLMs) and provides a platform for exploring new research ideas. Users can create their own templates for specific areas of study and run experiments to generate papers. However, caution is advised as the codebase executes LLM-written code, which may pose risks such as the use of potentially dangerous packages and web access.
AIW
AIW is a code base for experiments and raw data related to Alice in Wonderland, showcasing complete reasoning breakdown in state-of-the-art large language models. Users can collect experiments data using LiteLLM and TogetherAI, and plot the data using provided scripts. The tool allows for executing experiments over LiteLLM and lmsys, with options for different prompt types and AIW variations. The project also includes acknowledgments and a citation for reference.
swt-bench
SWT-Bench is a benchmark tool for evaluating large language models on testing generation for real world software issues collected from GitHub. It tasks a language model with generating a reproducing test that fails in the original state of the code base and passes after a patch resolving the issue has been applied. The tool operates in unit test mode or reproduction script mode to assess model predictions and success rates. Users can run evaluations on SWT-Bench Lite using the evaluation harness with specific commands. The tool provides instructions for setting up and building SWT-Bench, as well as guidelines for contributing to the project. It also offers datasets and evaluation results for public access and provides a citation for referencing the work.
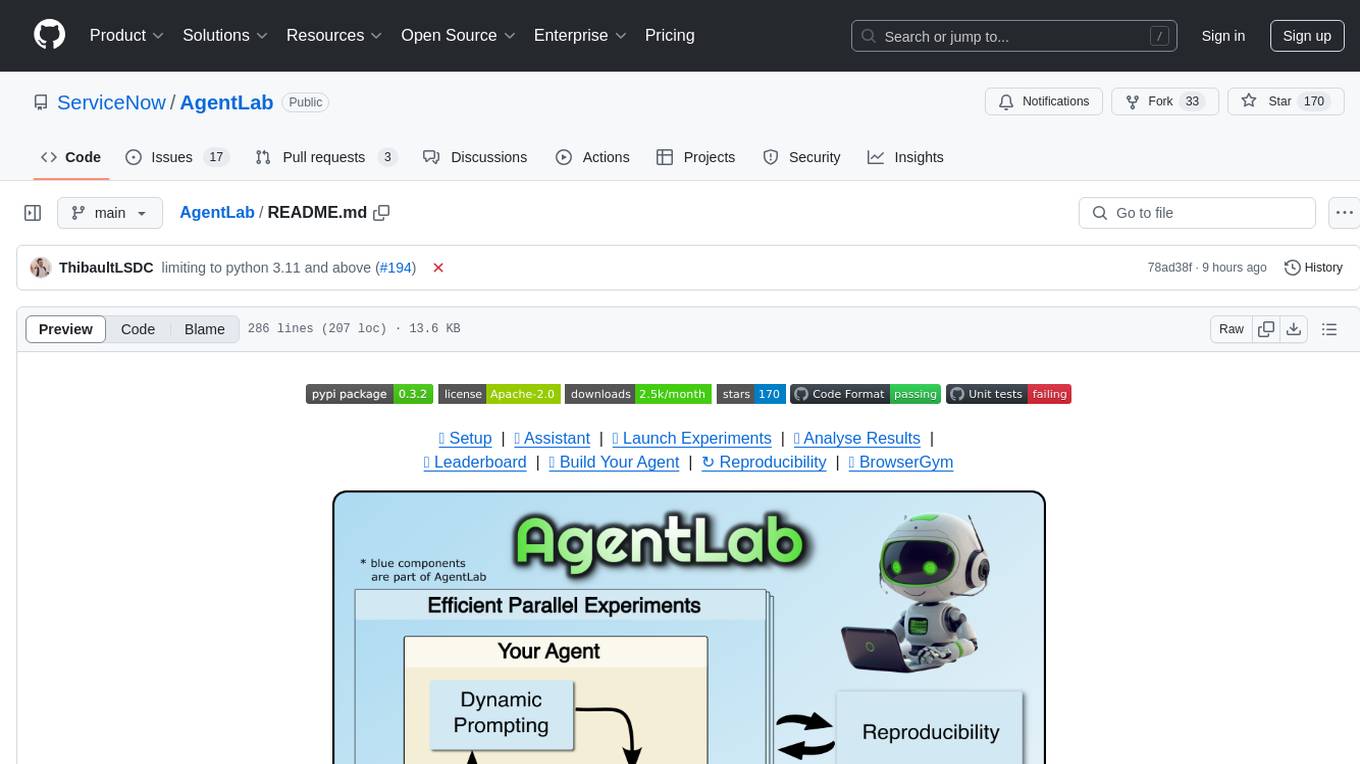
AgentLab
AgentLab is an open, easy-to-use, and extensible framework designed to accelerate web agent research. It provides features for developing and evaluating agents on various benchmarks supported by BrowserGym. The framework allows for large-scale parallel agent experiments using ray, building blocks for creating agents over BrowserGym, and a unified LLM API for OpenRouter, OpenAI, Azure, or self-hosted using TGI. AgentLab also offers reproducibility features, a unified LeaderBoard, and supports multiple benchmarks like WebArena, WorkArena, WebLinx, VisualWebArena, AssistantBench, GAIA, Mind2Web-live, and MiniWoB.
MiniCheck
MiniCheck is an efficient fact-checking tool designed to verify claims against grounding documents using large language models. It provides a sentence-level fact-checking model that can be used to evaluate the consistency of claims with the provided documents. MiniCheck offers different models, including Bespoke-MiniCheck-7B, which is the state-of-the-art and commercially usable. The tool enables users to fact-check multi-sentence claims by breaking them down into individual sentences for optimal performance. It also supports automatic prefix caching for faster inference when repeatedly fact-checking the same document with different claims.
LangBridge
LangBridge is a tool that bridges mT5 encoder and the target LM together using only English data. It enables models to effectively solve multilingual reasoning tasks without the need for multilingual supervision. The tool provides pretrained models like Orca 2, MetaMath, Code Llama, Llemma, and Llama 2 for various instruction-tuned and not instruction-tuned scenarios. Users can install the tool to replicate evaluations from the paper and utilize the models for multilingual reasoning tasks. LangBridge is particularly useful for low-resource languages and may lower performance in languages where the language model is already proficient.
TokenFormer
TokenFormer is a fully attention-based neural network architecture that leverages tokenized model parameters to enhance architectural flexibility. It aims to maximize the flexibility of neural networks by unifying token-token and token-parameter interactions through the attention mechanism. The architecture allows for incremental model scaling and has shown promising results in language modeling and visual modeling tasks. The codebase is clean, concise, easily readable, state-of-the-art, and relies on minimal dependencies.

Trace
Trace is a new AutoDiff-like tool for training AI systems end-to-end with general feedback. It generalizes the back-propagation algorithm by capturing and propagating an AI system's execution trace. Implemented as a PyTorch-like Python library, users can write Python code directly and use Trace primitives to optimize certain parts, similar to training neural networks.

onnxruntime-genai
ONNX Runtime Generative AI is a library that provides the generative AI loop for ONNX models, including inference with ONNX Runtime, logits processing, search and sampling, and KV cache management. Users can call a high level `generate()` method, or run each iteration of the model in a loop. It supports greedy/beam search and TopP, TopK sampling to generate token sequences, has built in logits processing like repetition penalties, and allows for easy custom scoring.
simple_GRPO
simple_GRPO is a very simple implementation of the GRPO algorithm for reproducing r1-like LLM thinking. It provides a codebase that supports saving GPU memory, understanding RL processes, trying various improvements like multi-answer generation, regrouping, penalty on KL, and parameter tuning. The project focuses on simplicity, performance, and core loss calculation based on Hugging Face's trl. It offers a straightforward setup with minimal dependencies and efficient training on multiple GPUs.
llms
The 'llms' repository is a comprehensive guide on Large Language Models (LLMs), covering topics such as language modeling, applications of LLMs, statistical language modeling, neural language models, conditional language models, evaluation methods, transformer-based language models, practical LLMs like GPT and BERT, prompt engineering, fine-tuning LLMs, retrieval augmented generation, AI agents, and LLMs for computer vision. The repository provides detailed explanations, examples, and tools for working with LLMs.
LLM-Pruner
LLM-Pruner is a tool for structural pruning of large language models, allowing task-agnostic compression while retaining multi-task solving ability. It supports automatic structural pruning of various LLMs with minimal human effort. The tool is efficient, requiring only 3 minutes for pruning and 3 hours for post-training. Supported LLMs include Llama-3.1, Llama-3, Llama-2, LLaMA, BLOOM, Vicuna, and Baichuan. Updates include support for new LLMs like GQA and BLOOM, as well as fine-tuning results achieving high accuracy. The tool provides step-by-step instructions for pruning, post-training, and evaluation, along with a Gradio interface for text generation. Limitations include issues with generating repetitive or nonsensical tokens in compressed models and manual operations for certain models.

aimo-progress-prize
This repository contains the training and inference code needed to replicate the winning solution to the AI Mathematical Olympiad - Progress Prize 1. It consists of fine-tuning DeepSeekMath-Base 7B, high-quality training datasets, a self-consistency decoding algorithm, and carefully chosen validation sets. The training methodology involves Chain of Thought (CoT) and Tool Integrated Reasoning (TIR) training stages. Two datasets, NuminaMath-CoT and NuminaMath-TIR, were used to fine-tune the models. The models were trained using open-source libraries like TRL, PyTorch, vLLM, and DeepSpeed. Post-training quantization to 8-bit precision was done to improve performance on Kaggle's T4 GPUs. The project structure includes scripts for training, quantization, and inference, along with necessary installation instructions and hardware/software specifications.
MARS5-TTS
MARS5 is a novel English speech model (TTS) developed by CAMB.AI, featuring a two-stage AR-NAR pipeline with a unique NAR component. The model can generate speech for various scenarios like sports commentary and anime with just 5 seconds of audio and a text snippet. It allows steering prosody using punctuation and capitalization in the transcript. Speaker identity is specified using an audio reference file, enabling 'deep clone' for improved quality. The model can be used via torch.hub or HuggingFace, supporting both shallow and deep cloning for inference. Checkpoints are provided for AR and NAR models, with hardware requirements of 750M+450M params on GPU. Contributions to improve model stability, performance, and reference audio selection are welcome.
For similar tasks

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

onnxruntime-genai
ONNX Runtime Generative AI is a library that provides the generative AI loop for ONNX models, including inference with ONNX Runtime, logits processing, search and sampling, and KV cache management. Users can call a high level `generate()` method, or run each iteration of the model in a loop. It supports greedy/beam search and TopP, TopK sampling to generate token sequences, has built in logits processing like repetition penalties, and allows for easy custom scoring.

jupyter-ai
Jupyter AI connects generative AI with Jupyter notebooks. It provides a user-friendly and powerful way to explore generative AI models in notebooks and improve your productivity in JupyterLab and the Jupyter Notebook. Specifically, Jupyter AI offers: * An `%%ai` magic that turns the Jupyter notebook into a reproducible generative AI playground. This works anywhere the IPython kernel runs (JupyterLab, Jupyter Notebook, Google Colab, Kaggle, VSCode, etc.). * A native chat UI in JupyterLab that enables you to work with generative AI as a conversational assistant. * Support for a wide range of generative model providers, including AI21, Anthropic, AWS, Cohere, Gemini, Hugging Face, NVIDIA, and OpenAI. * Local model support through GPT4All, enabling use of generative AI models on consumer grade machines with ease and privacy.

khoj
Khoj is an open-source, personal AI assistant that extends your capabilities by creating always-available AI agents. You can share your notes and documents to extend your digital brain, and your AI agents have access to the internet, allowing you to incorporate real-time information. Khoj is accessible on Desktop, Emacs, Obsidian, Web, and Whatsapp, and you can share PDF, markdown, org-mode, notion files, and GitHub repositories. You'll get fast, accurate semantic search on top of your docs, and your agents can create deeply personal images and understand your speech. Khoj is self-hostable and always will be.

langchain_dart
LangChain.dart is a Dart port of the popular LangChain Python framework created by Harrison Chase. LangChain provides a set of ready-to-use components for working with language models and a standard interface for chaining them together to formulate more advanced use cases (e.g. chatbots, Q&A with RAG, agents, summarization, extraction, etc.). The components can be grouped into a few core modules: * **Model I/O:** LangChain offers a unified API for interacting with various LLM providers (e.g. OpenAI, Google, Mistral, Ollama, etc.), allowing developers to switch between them with ease. Additionally, it provides tools for managing model inputs (prompt templates and example selectors) and parsing the resulting model outputs (output parsers). * **Retrieval:** assists in loading user data (via document loaders), transforming it (with text splitters), extracting its meaning (using embedding models), storing (in vector stores) and retrieving it (through retrievers) so that it can be used to ground the model's responses (i.e. Retrieval-Augmented Generation or RAG). * **Agents:** "bots" that leverage LLMs to make informed decisions about which available tools (such as web search, calculators, database lookup, etc.) to use to accomplish the designated task. The different components can be composed together using the LangChain Expression Language (LCEL).

danswer
Danswer is an open-source Gen-AI Chat and Unified Search tool that connects to your company's docs, apps, and people. It provides a Chat interface and plugs into any LLM of your choice. Danswer can be deployed anywhere and for any scale - on a laptop, on-premise, or to cloud. Since you own the deployment, your user data and chats are fully in your own control. Danswer is MIT licensed and designed to be modular and easily extensible. The system also comes fully ready for production usage with user authentication, role management (admin/basic users), chat persistence, and a UI for configuring Personas (AI Assistants) and their Prompts. Danswer also serves as a Unified Search across all common workplace tools such as Slack, Google Drive, Confluence, etc. By combining LLMs and team specific knowledge, Danswer becomes a subject matter expert for the team. Imagine ChatGPT if it had access to your team's unique knowledge! It enables questions such as "A customer wants feature X, is this already supported?" or "Where's the pull request for feature Y?"

infinity
Infinity is an AI-native database designed for LLM applications, providing incredibly fast full-text and vector search capabilities. It supports a wide range of data types, including vectors, full-text, and structured data, and offers a fused search feature that combines multiple embeddings and full text. Infinity is easy to use, with an intuitive Python API and a single-binary architecture that simplifies deployment. It achieves high performance, with 0.1 milliseconds query latency on million-scale vector datasets and up to 15K QPS.
For similar jobs

KG_RAG
KG-RAG (Knowledge Graph-based Retrieval Augmented Generation) is a task agnostic framework that combines the explicit knowledge of a Knowledge Graph (KG) with the implicit knowledge of a Large Language Model (LLM). KG-RAG extracts "prompt-aware context" from a KG, which is defined as the minimal context sufficient enough to respond to the user prompt. This framework empowers a general-purpose LLM by incorporating an optimized domain-specific 'prompt-aware context' from a biomedical KG. KG-RAG is specifically designed for running prompts related to Diseases.
Scientific-LLM-Survey
Scientific Large Language Models (Sci-LLMs) is a repository that collects papers on scientific large language models, focusing on biology and chemistry domains. It includes textual, molecular, protein, and genomic languages, as well as multimodal language. The repository covers various large language models for tasks such as molecule property prediction, interaction prediction, protein sequence representation, protein sequence generation/design, DNA-protein interaction prediction, and RNA prediction. It also provides datasets and benchmarks for evaluating these models. The repository aims to facilitate research and development in the field of scientific language modeling.
biochatter
Generative AI models have shown tremendous usefulness in increasing accessibility and automation of a wide range of tasks. This repository contains the `biochatter` Python package, a generic backend library for the connection of biomedical applications to conversational AI. It aims to provide a common framework for deploying, testing, and evaluating diverse models and auxiliary technologies in the biomedical domain. BioChatter is part of the BioCypher ecosystem, connecting natively to BioCypher knowledge graphs.
cellseg_models.pytorch
cellseg-models.pytorch is a Python library built upon PyTorch for 2D cell/nuclei instance segmentation models. It provides multi-task encoder-decoder architectures and post-processing methods for segmenting cell/nuclei instances. The library offers high-level API to define segmentation models, open-source datasets for training, flexibility to modify model components, sliding window inference, multi-GPU inference, benchmarking utilities, regularization techniques, and example notebooks for training and finetuning models with different backbones.
aicsimageio
AICSImageIO is a Python tool for Image Reading, Metadata Conversion, and Image Writing for Microscopy Images. It supports various file formats like OME-TIFF, TIFF, ND2, DV, CZI, LIF, PNG, GIF, and Bio-Formats. Users can read and write metadata and imaging data, work with different file systems like local paths, HTTP URLs, s3fs, and gcsfs. The tool provides functionalities for full image reading, delayed image reading, mosaic image reading, metadata reading, xarray coordinate plane attachment, cloud IO support, and saving to OME-TIFF. It also offers benchmarking and developer resources.
ceLLama
ceLLama is a streamlined automation pipeline for cell type annotations using large-language models (LLMs). It operates locally to ensure privacy, provides comprehensive analysis by considering negative genes, offers efficient processing speed, and generates customized reports. Ideal for quick and preliminary cell type checks.
PINNACLE
PINNACLE is a flexible geometric deep learning approach that trains on contextualized protein interaction networks to generate context-aware protein representations. It provides protein representations split across various cell-type contexts from different tissues and organs. The tool can be fine-tuned to study the genomic effects of drugs and nominate promising protein targets and cell-type contexts for further investigation. PINNACLE exemplifies the paradigm of incorporating context-specific effects for studying biological systems, especially the impact of disease and therapeutics.
Taiyi-LLM
Taiyi (太一) is a bilingual large language model fine-tuned for diverse biomedical tasks. It aims to facilitate communication between healthcare professionals and patients, provide medical information, and assist in diagnosis, biomedical knowledge discovery, drug development, and personalized healthcare solutions. The model is based on the Qwen-7B-base model and has been fine-tuned using rich bilingual instruction data. It covers tasks such as question answering, biomedical dialogue, medical report generation, biomedical information extraction, machine translation, title generation, text classification, and text semantic similarity. The project also provides standardized data formats, model training details, model inference guidelines, and overall performance metrics across various BioNLP tasks.