
chitu
High-performance inference framework for large language models, focusing on efficiency, flexibility, and availability.
Stars: 1289
Chitu is a high-performance inference framework for large language models, focusing on efficiency, flexibility, and availability. It supports various mainstream large language models, including DeepSeek, LLaMA series, Mixtral, and more. Chitu integrates latest optimizations for large language models, provides efficient operators with online FP8 to BF16 conversion, and is deployed for real-world production. The framework is versatile, supporting various hardware environments beyond NVIDIA GPUs. Chitu aims to enhance output speed per unit computing power, especially in decoding processes dependent on memory bandwidth.
README:
中文 | English
Chitu「赤兔」是一个专注于效率、灵活性和可用性的高性能大模型推理框架。
- [2025/08/01] 发布 v0.4.0,大幅提升了一体机推理部署场景的性能和稳定性,适配昇腾、英伟达、沐曦、海光,支持 DeepSeek、Qwen、GLM、Kimi 等模型。
- [2025/07/28] 发布 v0.3.9,首发支持华为昇腾 910B 推理部署智谱 GLM-4.5 MoE 模型。
- [2025/06/12] 发布 v0.3.5,提供昇腾 910B 完整原生支持,提供 Qwen3 系列模型高性能推理方案。
- [2025/04/29] 发布 v0.3.0,新增 FP4 在线转 FP8、BF16 的高效算子实现,支持 DeepSeek-R1 671B 的 FP4 量化版。
- [2025/04/18] 发布 v0.2.2,新增 CPU+GPU 异构混合推理支持,实现单卡推理 DeepSeek-R1 671B。
- [2025/03/14] 发布 v0.1.0,支持 DeepSeek-R1 671B,提供 FP8 在线转 BF16 的高效算子实现。
赤兔定位于「生产级大模型推理引擎」,充分考虑企业 AI 落地从小规模试验到大规模部署的渐进式需求,专注于提供以下重要特性:
- 多元算力适配:不仅支持 NVIDIA 最新旗舰到旧款的多系列产品,也为国产芯片提供优化支持。
- 全场景可伸缩:从纯 CPU 部署、单 GPU 部署到大规模集群部署,赤兔引擎提供可扩展的解决方案。
- 长期稳定运行:可应用于实际生产环境,稳定性足以承载并发业务流量。
项目团队感谢广大用户及开源社区提出的宝贵意见和建议,并将持续改进赤兔推理引擎。 然而,受制于团队成员的精力,无法保证及时解决所有用户在使用中遇到问题。 如需专业技术服务,欢迎致信 [email protected]
性能数据与您的硬件配置、软件版本、测试负载相关,多次测试结果可能存在波动。
请参阅开发手册获取完整的安装使用说明。
对于在单机环境上快速验证的场景,建议使用官方镜像进行部署。目前提供适用于以下平台的镜像:
- 昇腾:qingcheng-ai-cn-beijing.cr.volces.com/public/chitu-ascend:latest
- 英伟达:qingcheng-ai-cn-beijing.cr.volces.com/public/chitu-nvidia:latest
- 沐曦:qingcheng-ai-cn-beijing.cr.volces.com/public/chitu-muxi:latest
更多模型请参见 支持的模型。
赤兔项目欢迎开源社区的朋友们参与项目共建,请参阅贡献指南。
如果您有任何问题或疑虑,欢迎提交issue。
您也可以扫码加入赤兔交流微信群:
本项目采用 Apache License v2.0 许可证 - 详见 LICENSE 文件。
本代码仓库还引用了一些来自其他开源项目的代码片段,相关版权信息已在代码中以 SPDX 格式标注。这些代码片段的许可证信息可以在 LICENSES/ 目录下找到。
本代码仓库还包含遵循其他开源许可证的第三方子模块。您可以在 third_party/ 目录下找到这些子模块,该目录中包含了它们各自的许可证文件。
非常感谢来自华为、沐曦、海光、燧原、智谱、中国电信、并行科技等各方的帮助。
在构建 Chitu 的过程中,我们从以下项目(按字母排序)中学到了很多,并复用了一些函数:
我们将持续为开源社区贡献更高效、更灵活、更兼容、更稳定的大模型推理部署解决方案。
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for chitu
Similar Open Source Tools

chitu
Chitu is a high-performance inference framework for large language models, focusing on efficiency, flexibility, and availability. It supports various mainstream large language models, including DeepSeek, LLaMA series, Mixtral, and more. Chitu integrates latest optimizations for large language models, provides efficient operators with online FP8 to BF16 conversion, and is deployed for real-world production. The framework is versatile, supporting various hardware environments beyond NVIDIA GPUs. Chitu aims to enhance output speed per unit computing power, especially in decoding processes dependent on memory bandwidth.
wiseflow
Wiseflow is an agile information mining tool that utilizes the thinking and analysis capabilities of large models to accurately extract specific information from various given sources, without the need for manual intervention. The tool focuses on filtering noise from a vast amount of information to reveal valuable insights. It is recommended to use normal language models for information extraction tasks to optimize speed and cost, rather than complex reasoning models. The tool is designed for continuous information gathering based on specified focus points from various sources.
hdu-cs-wiki
The HDU Computer Science Lecture Notes is a comprehensive guide designed to help students navigate through various challenges in the field of computer science. It covers topics such as programming languages, artificial intelligence, software development, and more. The notes provide insights on how to effectively utilize university time, balance grades with project experience, and make informed decisions regarding career paths. Created by a collaborative effort involving students, teachers, and industry experts, the lecture notes aim to serve as a guiding tool for individuals seeking guidance in the computer science domain.
jd_scripts
jd_scripts is a repository containing scripts for automating various tasks on the JD platform. The scripts provide instructions for setting up and using the tools to enhance user experience and efficiency in managing JD accounts and assets. Users can automate processes such as receiving notifications, redeeming rewards, participating in group purchases, and monitoring ticket availability. The repository also includes resources for optimizing performance and security measures to safeguard user accounts. With a focus on simplifying interactions with the JD platform, jd_scripts offers a comprehensive solution for maximizing benefits and convenience for JD users.
Embodied-AI-Guide
Embodied-AI-Guide is a comprehensive guide for beginners to understand Embodied AI, focusing on the path of entry and useful information in the field. It covers topics such as Reinforcement Learning, Imitation Learning, Large Language Model for Robotics, 3D Vision, Control, Benchmarks, and provides resources for building cognitive understanding. The repository aims to help newcomers quickly establish knowledge in the field of Embodied AI.
AiLearning-Theory-Applying
This repository provides a comprehensive guide to understanding and applying artificial intelligence (AI) theory, including basic knowledge, machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing (BERT). It features detailed explanations, annotated code, and datasets to help users grasp the concepts and implement them in practice. The repository is continuously updated to ensure the latest information and best practices are covered.
FastDeploy
FastDeploy is an inference and deployment toolkit for large language models and visual language models based on PaddlePaddle. It provides production-ready deployment solutions with core acceleration technologies such as load-balanced PD disaggregation, unified KV cache transmission, OpenAI API server compatibility, comprehensive quantization format support, advanced acceleration techniques, and multi-hardware support. The toolkit supports various hardware platforms like NVIDIA GPUs, Kunlunxin XPUs, Iluvatar GPUs, Enflame GCUs, and Hygon DCUs, with plans for expanding support to Ascend NPU and MetaX GPU. FastDeploy aims to optimize resource utilization, throughput, and performance for inference and deployment tasks.
easyAi
EasyAi is a lightweight, beginner-friendly Java artificial intelligence algorithm framework. It can be seamlessly integrated into Java projects with Maven, requiring no additional environment configuration or dependencies. The framework provides pre-packaged modules for image object detection and AI customer service, as well as various low-level algorithm tools for deep learning, machine learning, reinforcement learning, heuristic learning, and matrix operations. Developers can easily develop custom micro-models tailored to their business needs.
eisonAI
EisonAI is an intelligent Safari browser plugin that uses advanced Large Language Models (LLM) technology to automatically summarize web content. It intelligently extracts the main content of web pages and generates accurate summaries to help users quickly understand the key points of the web page. The plugin features smart content extraction, AI-powered summarization, interactive dialogue with AI, elegant interface design, flexible display modes, and advanced functionalities like keyboard shortcuts, message deduplication, and intelligent text length limitation. The system architecture includes core modules for content extraction, UI elements injection, message handling, GPT integration, event listening, user control panel, API status management, mode switching interface, and cross-page communication. It utilizes Readability.js for web content parsing, modular event handling system, CSP security control, responsive design, and dark mode support. EisonAI requires macOS 12.0 or higher, iOS 15.0 or higher, and Safari 15.0 or higher for installation and usage.
llm-cookbook
LLM Cookbook is a developer-oriented comprehensive guide focusing on LLM for Chinese developers. It covers various aspects from Prompt Engineering to RAG development and model fine-tuning, providing guidance on how to learn and get started with LLM projects in a way suitable for Chinese learners. The project translates and reproduces 11 courses from Professor Andrew Ng's large model series, categorizing them for beginners to systematically learn essential skills and concepts before exploring specific interests. It encourages developers to contribute by replicating unreproduced courses following the format and submitting PRs for review and merging. The project aims to help developers grasp a wide range of skills and concepts related to LLM development, offering both online reading and PDF versions for easy access and learning.
PyTorch-Tutorial-2nd
The second edition of "PyTorch Practical Tutorial" was completed after 5 years, 4 years, and 2 years. On the basis of the essence of the first edition, rich and detailed deep learning application cases and reasoning deployment frameworks have been added, so that this book can more systematically cover the knowledge involved in deep learning engineers. As the development of artificial intelligence technology continues to emerge, the second edition of "PyTorch Practical Tutorial" is not the end, but the beginning, opening up new technologies, new fields, and new chapters. I hope to continue learning and making progress in artificial intelligence technology with you in the future.

PandaWiki
PandaWiki is a collaborative platform for creating and editing wiki pages. It allows users to easily collaborate on documentation, knowledge sharing, and information dissemination. With features like version control, user permissions, and rich text editing, PandaWiki simplifies the process of creating and managing wiki content. Whether you are working on a team project, organizing information for personal use, or building a knowledge base for your organization, PandaWiki provides a user-friendly and efficient solution for creating and maintaining wiki pages.
timeline-studio
Timeline Studio is a next-generation professional video editor with AI integration that automates content creation for social media. It combines the power of desktop applications with the convenience of web interfaces. With 257 AI tools, GPU acceleration, plugin system, multi-language interface, and local processing, Timeline Studio offers complete video production automation. Users can create videos for various social media platforms like TikTok, YouTube, Vimeo, Telegram, and Instagram with optimized versions. The tool saves time, understands trends, provides professional quality, and allows for easy feature extension through plugins. Timeline Studio is open source, transparent, and offers significant time savings and quality improvements for video editing tasks.
yu-picture
The 'yu-picture' project is an educational project that provides complete video tutorials, text tutorials, resume writing, interview question solutions, and Q&A services to help you improve your project skills and enhance your resume. It is an enterprise-level intelligent collaborative cloud image library platform based on Vue 3 + Spring Boot + COS + WebSocket. The platform has a wide range of applications, including public image uploading and retrieval, image analysis for administrators, private image management for individual users, and real-time collaborative image editing for enterprises. The project covers file management, content retrieval, permission control, and real-time collaboration, using various programming concepts, architectural design methods, and optimization strategies to ensure high-speed iteration and stable operation.
knowledge
This repository serves as a personal knowledge base for the owner's reference and use. It covers a wide range of topics including cloud-native operations, Kubernetes ecosystem, networking, cloud services, telemetry, CI/CD, electronic engineering, hardware projects, operating systems, homelab setups, high-performance computing applications, openwrt router usage, programming languages, music theory, blockchain, distributed systems principles, and various other knowledge domains. The content is periodically refined and published on the owner's blog for maintenance purposes.
writing-helper
A Next.js-based AI writing assistant that helps users organize writing style prompts and sends them to large language models (LLMs) to generate content. The tool aims to help writers, content creators, and copywriters improve writing efficiency and quality through AI technology. It features rich writing style customization, support for multiple LLM APIs, flexible API settings, user-friendly interface, real-time content editing, export function, detailed debugging information, dark/light mode support, and more.
For similar tasks
arena-hard-auto
Arena-Hard-Auto-v0.1 is an automatic evaluation tool for instruction-tuned LLMs. It contains 500 challenging user queries. The tool prompts GPT-4-Turbo as a judge to compare models' responses against a baseline model (default: GPT-4-0314). Arena-Hard-Auto employs an automatic judge as a cheaper and faster approximator to human preference. It has the highest correlation and separability to Chatbot Arena among popular open-ended LLM benchmarks. Users can evaluate their models' performance on Chatbot Arena by using Arena-Hard-Auto.

max
The Modular Accelerated Xecution (MAX) platform is an integrated suite of AI libraries, tools, and technologies that unifies commonly fragmented AI deployment workflows. MAX accelerates time to market for the latest innovations by giving AI developers a single toolchain that unlocks full programmability, unparalleled performance, and seamless hardware portability.
ai-hub
AI Hub Project aims to continuously test and evaluate mainstream large language models, while accumulating and managing various effective model invocation prompts. It has integrated all mainstream large language models in China, including OpenAI GPT-4 Turbo, Baidu ERNIE-Bot-4, Tencent ChatPro, MiniMax abab5.5-chat, and more. The project plans to continuously track, integrate, and evaluate new models. Users can access the models through REST services or Java code integration. The project also provides a testing suite for translation, coding, and benchmark testing.
long-context-attention
Long-Context-Attention (YunChang) is a unified sequence parallel approach that combines the strengths of DeepSpeed-Ulysses-Attention and Ring-Attention to provide a versatile and high-performance solution for long context LLM model training and inference. It addresses the limitations of both methods by offering no limitation on the number of heads, compatibility with advanced parallel strategies, and enhanced performance benchmarks. The tool is verified in Megatron-LM and offers best practices for 4D parallelism, making it suitable for various attention mechanisms and parallel computing advancements.

marlin
Marlin is a highly optimized FP16xINT4 matmul kernel designed for large language model (LLM) inference, offering close to ideal speedups up to batchsizes of 16-32 tokens. It is suitable for larger-scale serving, speculative decoding, and advanced multi-inference schemes like CoT-Majority. Marlin achieves optimal performance by utilizing various techniques and optimizations to fully leverage GPU resources, ensuring efficient computation and memory management.
MMC
This repository, MMC, focuses on advancing multimodal chart understanding through large-scale instruction tuning. It introduces a dataset supporting various tasks and chart types, a benchmark for evaluating reasoning capabilities over charts, and an assistant achieving state-of-the-art performance on chart QA benchmarks. The repository provides data for chart-text alignment, benchmarking, and instruction tuning, along with existing datasets used in experiments. Additionally, it offers a Gradio demo for the MMCA model.
Tiktoken
Tiktoken is a high-performance implementation focused on token count operations. It provides various encodings like o200k_base, cl100k_base, r50k_base, p50k_base, and p50k_edit. Users can easily encode and decode text using the provided API. The repository also includes a benchmark console app for performance tracking. Contributions in the form of PRs are welcome.
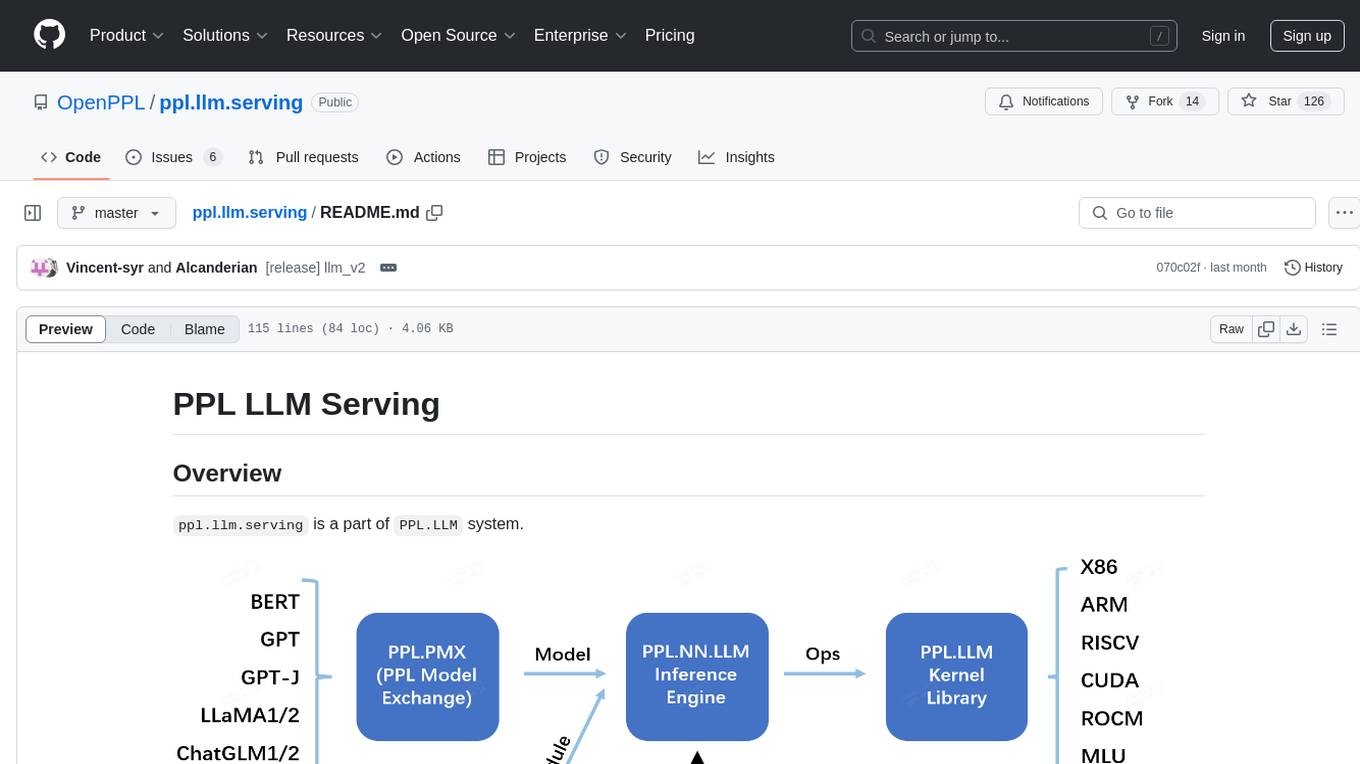
ppl.llm.serving
ppl.llm.serving is a serving component for Large Language Models (LLMs) within the PPL.LLM system. It provides a server based on gRPC and supports inference for LLaMA. The repository includes instructions for prerequisites, quick start guide, model exporting, server setup, client usage, benchmarking, and offline inference. Users can refer to the LLaMA Guide for more details on using this serving component.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.

