ktransformers
A Flexible Framework for Experiencing Heterogeneous LLM Inference/Fine-tune Optimizations
Stars: 16508
KTransformers is a flexible Python-centric framework designed to enhance the user's experience with advanced kernel optimizations and placement/parallelism strategies for Transformers. It provides a Transformers-compatible interface, RESTful APIs compliant with OpenAI and Ollama, and a simplified ChatGPT-like web UI. The framework aims to serve as a platform for experimenting with innovative LLM inference optimizations, focusing on local deployments constrained by limited resources and supporting heterogeneous computing opportunities like GPU/CPU offloading of quantized models.
README:
KTransformers is a research project focused on efficient inference and fine-tuning of large language models through CPU-GPU heterogeneous computing. The project has evolved into two core modules: kt-kernel and kt-sft.
- Feb 13, 2026: MiniMax-M2.5 Day0 Support! (Tutorial)
- Jan 27, 2026: Kimi-K2.5 Day0 Support! (Tutorial) (SFT Tutorial)
- Jan 22, 2026: Support CPU-GPU Expert Scheduling, Native BF16 and FP8 per channel Precision and AutoDL unified fine-tuning and inference
- Dec 24, 2025: Support Native MiniMax-M2.1 inference. (Tutorial)
- Dec 22, 2025: Support RL-DPO fine-tuning with LLaMA-Factory. (Tutorial)
- Dec 5, 2025: Support Native Kimi-K2-Thinking inference (Tutorial)
- Nov 6, 2025: Support Kimi-K2-Thinking inference (Tutorial) and fine-tune (Tutorial)
- Nov 4, 2025: KTransformers Fine-Tuning × LLaMA-Factory Integration. (Tutorial)
- Oct 27, 2025: Support Ascend NPU. (Tutorial)
- Oct 10, 2025: Integrating into SGLang. (Roadmap, Blog)
- Sept 11, 2025: Support Qwen3-Next. (Tutorial)
- Sept 05, 2025: Support Kimi-K2-0905. (Tutorial)
- July 26, 2025: Support SmallThinker and GLM4-MoE. (Tutorial)
- July 11, 2025: Support Kimi-K2. (Tutorial)
- June 30, 2025: Support 3-layer (GPU-CPU-Disk) prefix cache reuse.
- May 14, 2025: Support Intel Arc GPU (Tutorial).
- Apr 29, 2025: Support AMX-Int8、 AMX-BF16 and Qwen3MoE (Tutorial)
- Apr 9, 2025: Experimental support for LLaMA 4 models (Tutorial).
- Apr 2, 2025: Support Multi-concurrency. (Tutorial).
- Mar 15, 2025: Support ROCm on AMD GPU (Tutorial).
- Mar 5, 2025: Support unsloth 1.58/2.51 bits weights and IQ1_S/FP8 hybrid weights. Support 139K Longer Context for DeepSeek-V3 and R1 in 24GB VRAM.
- Feb 25, 2025: Support FP8 GPU kernel for DeepSeek-V3 and R1; Longer Context.
- Feb 15, 2025: Longer Context (from 4K to 8K for 24GB VRAM) & Slightly Faster Speed (+15%, up to 16 Tokens/s), update docs and online books.
- Feb 10, 2025: Support Deepseek-R1 and V3 on single (24GB VRAM)/multi gpu and 382G DRAM, up to 3~28x speedup. For detailed show case and reproduction tutorial, see here.
- Aug 28, 2024: Decrease DeepseekV2's required VRAM from 21G to 11G.
- Aug 15, 2024: Update detailed tutorial for injection and multi-GPU.
- Aug 14, 2024: Support llamfile as linear backend.
- Aug 12, 2024: Support multiple GPU; Support new model: mixtral 8*7B and 8*22B; Support q2k, q3k, q5k dequant on gpu.
- Aug 9, 2024: Support windows native.
🚀 kt-kernel - High-Performance Inference Kernels
CPU-optimized kernel operations for heterogeneous LLM inference.
Key Features:
- AMX/AVX Acceleration: Intel AMX and AVX512/AVX2 optimized kernels for INT4/INT8 quantized inference
- MoE Optimization: Efficient Mixture-of-Experts inference with NUMA-aware memory management
- Quantization Support: CPU-side INT4/INT8 quantized weights, GPU-side GPTQ support
- Easy Integration: Clean Python API for SGLang and other frameworks
Quick Start:
cd kt-kernel
pip install .Use Cases:
- CPU-GPU hybrid inference for large MoE models
- Integration with SGLang for production serving
- Heterogeneous expert placement (hot experts on GPU, cold experts on CPU)
Performance Examples:
| Model | Hardware Configuration | Total Throughput | Output Throughput |
|---|---|---|---|
| DeepSeek-R1-0528 (FP8) | 8×L20 GPU + Xeon Gold 6454S | 227.85 tokens/s | 87.58 tokens/s (8-way concurrency) |
🎓 kt-sft - Fine-Tuning Framework
KTransformers × LLaMA-Factory integration for ultra-large MoE model fine-tuning.
Key Features:
- Resource Efficient: Fine-tune 671B DeepSeek-V3 with just 70GB GPU memory + 1.3TB RAM
- LoRA Support: Full LoRA fine-tuning with heterogeneous acceleration
- LLaMA-Factory Integration: Seamless integration with popular fine-tuning framework
- Production Ready: Chat, batch inference, and metrics evaluation
Performance Examples:
| Model | Configuration | Throughput | GPU Memory |
|---|---|---|---|
| DeepSeek-V3 (671B) | LoRA + AMX | ~40 tokens/s | 70GB (multi-GPU) |
| DeepSeek-V2-Lite (14B) | LoRA + AMX | ~530 tokens/s | 6GB |
Quick Start:
cd kt-sft
# Install environment following kt-sft/README.md
USE_KT=1 llamafactory-cli train examples/train_lora/deepseek3_lora_sft_kt.yamlIf you use KTransformers in your research, please cite our paper:
@inproceedings{10.1145/3731569.3764843,
title = {KTransformers: Unleashing the Full Potential of CPU/GPU Hybrid Inference for MoE Models},
author = {Chen, Hongtao and Xie, Weiyu and Zhang, Boxin and Tang, Jingqi and Wang, Jiahao and Dong, Jianwei and Chen, Shaoyuan and Yuan, Ziwei and Lin, Chen and Qiu, Chengyu and Zhu, Yuening and Ou, Qingliang and Liao, Jiaqi and Chen, Xianglin and Ai, Zhiyuan and Wu, Yongwei and Zhang, Mingxing},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the ACM SIGOPS 31st Symposium on Operating Systems Principles},
year = {2025}
}Developed and maintained by:
- MADSys Lab @ Tsinghua University
- Approaching.AI
- 9#AISoft
- Community contributors
We welcome contributions! Please feel free to submit issues and pull requests.
- GitHub Issues: Report bugs or request features
- WeChat Group: See archive/WeChatGroup.png
The original integrated KTransformers framework has been archived to the archive/ directory for reference. The project now focuses on the two core modules above for better modularity and maintainability.
For the original documentation with full quick-start guides and examples, see:
- archive/README.md (English)
- archive/README_ZH.md (中文)
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for ktransformers
Similar Open Source Tools

ktransformers
KTransformers is a flexible Python-centric framework designed to enhance the user's experience with advanced kernel optimizations and placement/parallelism strategies for Transformers. It provides a Transformers-compatible interface, RESTful APIs compliant with OpenAI and Ollama, and a simplified ChatGPT-like web UI. The framework aims to serve as a platform for experimenting with innovative LLM inference optimizations, focusing on local deployments constrained by limited resources and supporting heterogeneous computing opportunities like GPU/CPU offloading of quantized models.
FLAME
FLAME is a lightweight and efficient deep learning framework designed for edge devices. It provides a simple and user-friendly interface for developing and deploying deep learning models on resource-constrained devices. With FLAME, users can easily build and optimize neural networks for tasks such as image classification, object detection, and natural language processing. The framework supports various neural network architectures and optimization techniques, making it suitable for a wide range of applications in the field of edge computing.
Fast-dLLM
Fast-DLLM is a diffusion-based Large Language Model (LLM) inference acceleration framework that supports efficient inference for models like Dream and LLaDA. It offers fast inference support, multiple optimization strategies, code generation, evaluation capabilities, and an interactive chat interface. Key features include Key-Value Cache for Block-Wise Decoding, Confidence-Aware Parallel Decoding, and overall performance improvements. The project structure includes directories for Dream and LLaDA model-related code, with installation and usage instructions provided for using the LLaDA and Dream models.
verl
veRL is a flexible and efficient reinforcement learning training framework designed for large language models (LLMs). It allows easy extension of diverse RL algorithms, seamless integration with existing LLM infrastructures, and flexible device mapping. The framework achieves state-of-the-art throughput and efficient actor model resharding with 3D-HybridEngine. It supports popular HuggingFace models and is suitable for users working with PyTorch FSDP, Megatron-LM, and vLLM backends.
BentoVLLM
BentoVLLM is an example project demonstrating how to serve and deploy open-source Large Language Models using vLLM, a high-throughput and memory-efficient inference engine. It provides a basis for advanced code customization, such as custom models, inference logic, or vLLM options. The project allows for simple LLM hosting with OpenAI compatible endpoints without the need to write any code. Users can interact with the server using Swagger UI or other methods, and the service can be deployed to BentoCloud for better management and scalability. Additionally, the repository includes integration examples for different LLM models and tools.
deepteam
Deepteam is a powerful open-source tool designed for deep learning projects. It provides a user-friendly interface for training, testing, and deploying deep neural networks. With Deepteam, users can easily create and manage complex models, visualize training progress, and optimize hyperparameters. The tool supports various deep learning frameworks and allows seamless integration with popular libraries like TensorFlow and PyTorch. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced deep learning practitioner, Deepteam simplifies the development process and accelerates model deployment.

deeppowers
Deeppowers is a powerful Python library for deep learning applications. It provides a wide range of tools and utilities to simplify the process of building and training deep neural networks. With Deeppowers, users can easily create complex neural network architectures, perform efficient training and optimization, and deploy models for various tasks. The library is designed to be user-friendly and flexible, making it suitable for both beginners and experienced deep learning practitioners.
slime
Slime is an LLM post-training framework for RL scaling that provides high-performance training and flexible data generation capabilities. It connects Megatron with SGLang for efficient training and enables custom data generation workflows through server-based engines. The framework includes modules for training, rollout, and data buffer management, offering a comprehensive solution for RL scaling.
AimRT
AimRT is a basic runtime framework for modern robotics, developed in modern C++ with lightweight and easy deployment. It integrates research and development for robot applications in various deployment scenarios, providing debugging tools and observability support. AimRT offers a plug-in development interface compatible with ROS2, HTTP, Grpc, and other ecosystems for progressive system upgrades.
LocalLLMClient
LocalLLMClient is a Swift package designed to interact with local Large Language Models (LLMs) on Apple platforms. It supports GGUF, MLX models, and the FoundationModels framework, providing streaming API, multimodal capabilities, and tool calling functionalities. Users can easily integrate this tool to work with various models for text generation and processing. The package also includes advanced features for low-level API control and multimodal image processing. LocalLLMClient is experimental and subject to API changes, offering support for iOS, macOS, and Linux platforms.
arcade-ai
Arcade AI is a developer-focused tooling and API platform designed to enhance the capabilities of LLM applications and agents. It simplifies the process of connecting agentic applications with user data and services, allowing developers to concentrate on building their applications. The platform offers prebuilt toolkits for interacting with various services, supports multiple authentication providers, and provides access to different language models. Users can also create custom toolkits and evaluate their tools using Arcade AI. Contributions are welcome, and self-hosting is possible with the provided documentation.
lemonai
LemonAI is a versatile machine learning library designed to simplify the process of building and deploying AI models. It provides a wide range of tools and algorithms for data preprocessing, model training, and evaluation. With LemonAI, users can easily experiment with different machine learning techniques and optimize their models for various tasks. The library is well-documented and beginner-friendly, making it suitable for both novice and experienced data scientists. LemonAI aims to streamline the development of AI applications and empower users to create innovative solutions using state-of-the-art machine learning methods.
RustGPT
A complete Large Language Model implementation in pure Rust with no external ML frameworks. Demonstrates building a transformer-based language model from scratch, including pre-training, instruction tuning, interactive chat mode, full backpropagation, and modular architecture. Model learns basic world knowledge and conversational patterns. Features custom tokenization, greedy decoding, gradient clipping, modular layer system, and comprehensive test coverage. Ideal for understanding modern LLMs and key ML concepts. Dependencies include ndarray for matrix operations and rand for random number generation. Contributions welcome for model persistence, performance optimizations, better sampling, evaluation metrics, advanced architectures, training improvements, data handling, and model analysis. Follows standard Rust conventions and encourages contributions at beginner, intermediate, and advanced levels.
atomic-agents
The Atomic Agents framework is a modular and extensible tool designed for creating powerful applications. It leverages Pydantic for data validation and serialization. The framework follows the principles of Atomic Design, providing small and single-purpose components that can be combined. It integrates with Instructor for AI agent architecture and supports various APIs like Cohere, Anthropic, and Gemini. The tool includes documentation, examples, and testing features to ensure smooth development and usage.
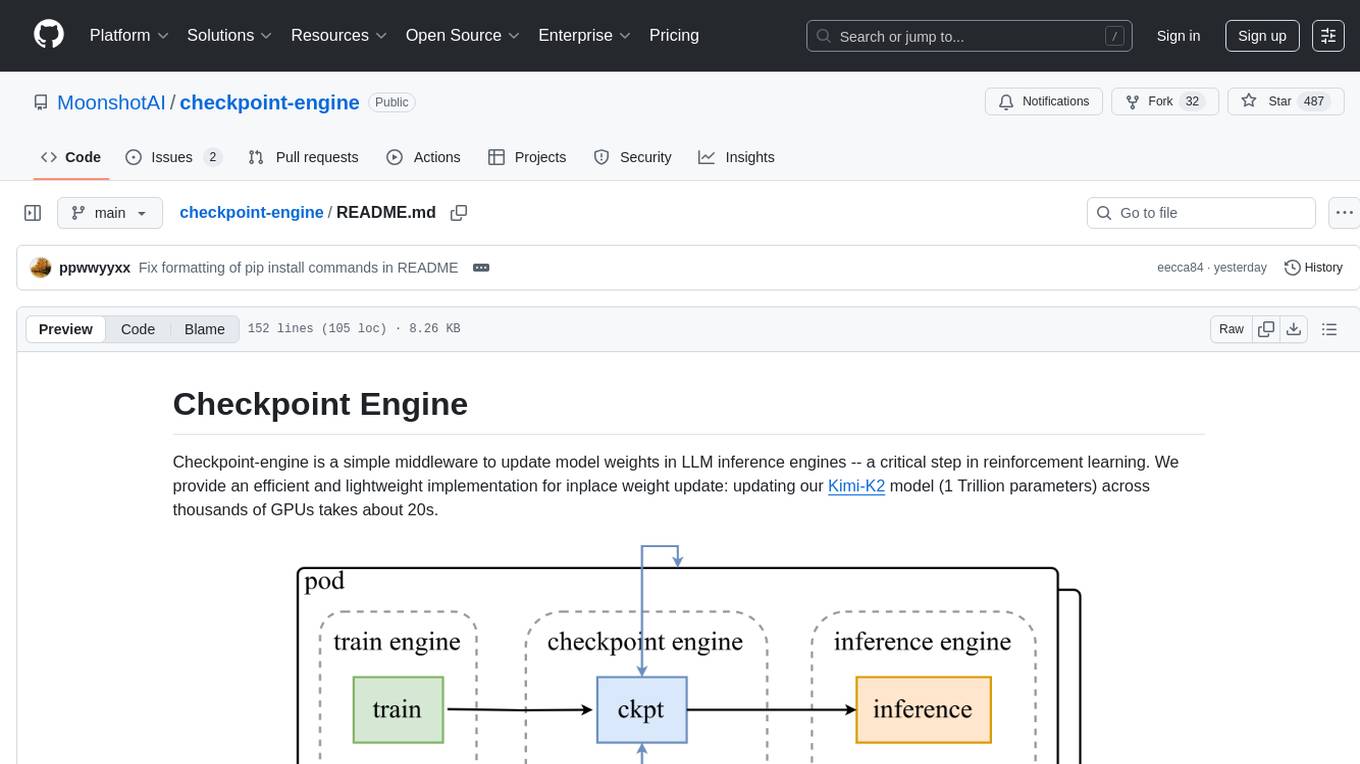
checkpoint-engine
Checkpoint-engine is a middleware tool designed for updating model weights in LLM inference engines efficiently. It provides implementations for both Broadcast and P2P weight update methods, orchestrating the transfer process and controlling the inference engine through ZeroMQ socket. The tool optimizes weight broadcast by arranging data transfer into stages and organizing transfers into a pipeline for performance. It supports flexible installation options and is tested with various models and device setups. Checkpoint-engine also allows reusing weights from existing instances and provides a patch for FP8 quantization in vLLM.
Fast-LLM
Fast-LLM is an open-source library designed for training large language models with exceptional speed, scalability, and flexibility. Built on PyTorch and Triton, it offers optimized kernel efficiency, reduced overheads, and memory usage, making it suitable for training models of all sizes. The library supports distributed training across multiple GPUs and nodes, offers flexibility in model architectures, and is easy to use with pre-built Docker images and simple configuration. Fast-LLM is licensed under Apache 2.0, developed transparently on GitHub, and encourages contributions and collaboration from the community.
For similar tasks

ktransformers
KTransformers is a flexible Python-centric framework designed to enhance the user's experience with advanced kernel optimizations and placement/parallelism strategies for Transformers. It provides a Transformers-compatible interface, RESTful APIs compliant with OpenAI and Ollama, and a simplified ChatGPT-like web UI. The framework aims to serve as a platform for experimenting with innovative LLM inference optimizations, focusing on local deployments constrained by limited resources and supporting heterogeneous computing opportunities like GPU/CPU offloading of quantized models.
handy-ollama
Handy-Ollama is a tutorial for deploying Ollama with hands-on practice, making the deployment of large language models accessible to everyone. The tutorial covers a wide range of content from basic to advanced usage, providing clear steps and practical tips for beginners and experienced developers to learn Ollama from scratch, deploy large models locally, and develop related applications. It aims to enable users to run large models on consumer-grade hardware, deploy models locally, and manage models securely and reliably.
BentoML
BentoML is an open-source model serving library for building performant and scalable AI applications with Python. It comes with everything you need for serving optimization, model packaging, and production deployment.
Qwen-TensorRT-LLM
Qwen-TensorRT-LLM is a project developed for the NVIDIA TensorRT Hackathon 2023, focusing on accelerating inference for the Qwen-7B-Chat model using TRT-LLM. The project offers various functionalities such as FP16/BF16 support, INT8 and INT4 quantization options, Tensor Parallel for multi-GPU parallelism, web demo setup with gradio, Triton API deployment for maximum throughput/concurrency, fastapi integration for openai requests, CLI interaction, and langchain support. It supports models like qwen2, qwen, and qwen-vl for both base and chat models. The project also provides tutorials on Bilibili and blogs for adapting Qwen models in NVIDIA TensorRT-LLM, along with hardware requirements and quick start guides for different model types and quantization methods.
CodeFuse-ModelCache
Codefuse-ModelCache is a semantic cache for large language models (LLMs) that aims to optimize services by introducing a caching mechanism. It helps reduce the cost of inference deployment, improve model performance and efficiency, and provide scalable services for large models. The project caches pre-generated model results to reduce response time for similar requests and enhance user experience. It integrates various embedding frameworks and local storage options, offering functionalities like cache-writing, cache-querying, and cache-clearing through RESTful API. The tool supports multi-tenancy, system commands, and multi-turn dialogue, with features for data isolation, database management, and model loading schemes. Future developments include data isolation based on hyperparameters, enhanced system prompt partitioning storage, and more versatile embedding models and similarity evaluation algorithms.
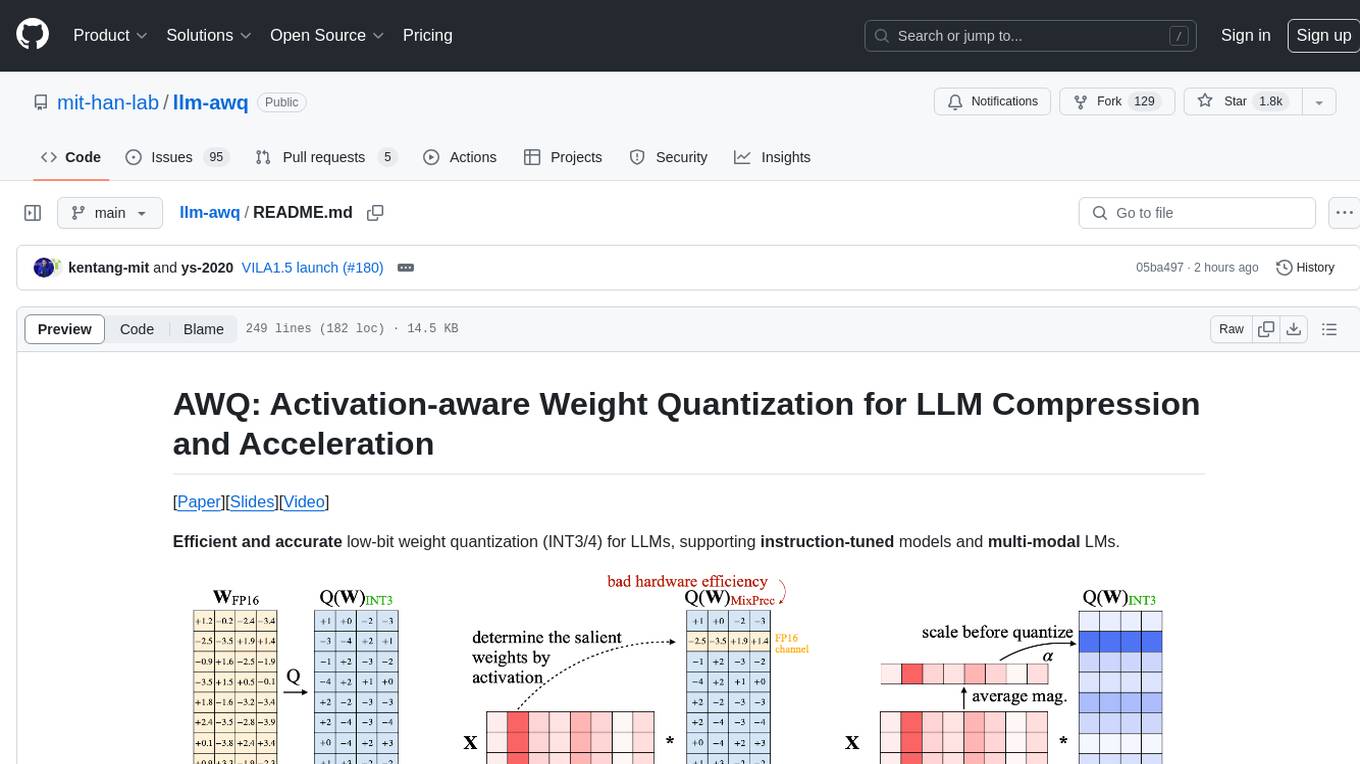
llm-awq
AWQ (Activation-aware Weight Quantization) is a tool designed for efficient and accurate low-bit weight quantization (INT3/4) for Large Language Models (LLMs). It supports instruction-tuned models and multi-modal LMs, providing features such as AWQ search for accurate quantization, pre-computed AWQ model zoo for various LLMs, memory-efficient 4-bit linear in PyTorch, and efficient CUDA kernel implementation for fast inference. The tool enables users to run large models on resource-constrained edge platforms, delivering more efficient responses with LLM/VLM chatbots through 4-bit inference.
LazyLLM
LazyLLM is a low-code development tool for building complex AI applications with multiple agents. It assists developers in building AI applications at a low cost and continuously optimizing their performance. The tool provides a convenient workflow for application development and offers standard processes and tools for various stages of application development. Users can quickly prototype applications with LazyLLM, analyze bad cases with scenario task data, and iteratively optimize key components to enhance the overall application performance. LazyLLM aims to simplify the AI application development process and provide flexibility for both beginners and experts to create high-quality applications.
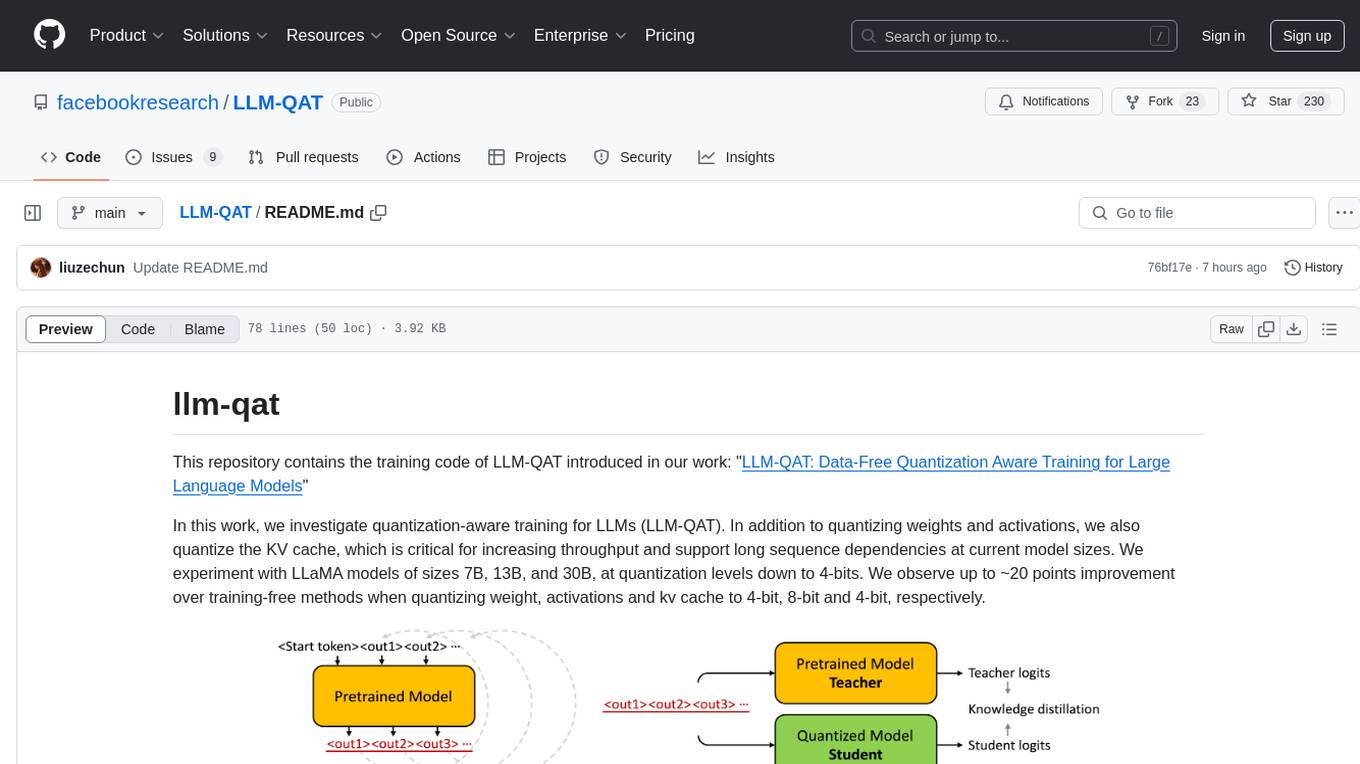
LLM-QAT
This repository contains the training code of LLM-QAT for large language models. The work investigates quantization-aware training for LLMs, including quantizing weights, activations, and the KV cache. Experiments were conducted on LLaMA models of sizes 7B, 13B, and 30B, at quantization levels down to 4-bits. Significant improvements were observed when quantizing weight, activations, and kv cache to 4-bit, 8-bit, and 4-bit, respectively.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.