
glake
GLake: optimizing GPU memory management and IO transmission.
Stars: 330
GLake is an acceleration library and utilities designed to optimize GPU memory management and IO transmission for AI large model training and inference. It addresses challenges such as GPU memory bottleneck and IO transmission bottleneck by providing efficient memory pooling, sharing, and tiering, as well as multi-path acceleration for CPU-GPU transmission. GLake is easy to use, open for extension, and focuses on improving training throughput, saving inference memory, and accelerating IO transmission. It offers features like memory fragmentation reduction, memory deduplication, and built-in security mechanisms for troubleshooting GPU memory issues.
README:
- [2024.07] We release vTensor, our LLM serving and KV Cache management system using VMM technique.
- [2024.05] GLake overview and recent update is presented on AICon 2024 (in Beijing, China, 2024-05-17) here
- [2024.05] The presentation slides in ASPLOS'24 can be found here
- [2024.05] Preview: serverless with on-demand GPU memory shink (ckpt to CPU while), keeping process alive and auto backfill upon request coming
- [2024.04] Preview: optimizing LLM KV cache, different than PagedAttention, flexible and easy-to-adopt
- [2024.04] Preview: cross-stream GPU memory optimization dev done, will be released soon; integration with PyTorch expand segment is in-progress by AntGroup and Alibaba contributor
- [2024.03] compatible with PyTorch-1.13.1 at branch torch-1.13.1, also with a whl package
- [2023.11.10] Our paper: GMLake: Efficient and Transparent GPU Memory Defragmentation for Large-scale DNN Training with Virtual Memory Stitching, just accepted by ASPLOS24
- Blog
AI large model training and inference are increasingly confronted with the challenges of memory wall and IO transmission wall, that is, the growth of GPU memory capacity and IO bandwidth cannot keep up with the growth rate of AI model size.
To address these challenges, GLake is an acceleration library and relevant utilites that work at the bottom layer (GPU virtual and physical memory management) and system layer (multi-GPU, multi-path, and multi-tasking) to optimize GPU memory and IO.
GLake enables AI training, inference (including converting large models to TensorRT or ONNX Runtime on NVIDIA A10/3090) and DevOps (like Notebook) to fully utilize the underlying hardware resources, improving training throughput by up to 4 times, saving inference memory by up to 3 times, and accelerating IO transmission by 3~12 times.
To use GLake, the simplest way is to replace the underlying library (e.g., libcuda.so or PyTorch libc10_cuda.so), though more graceful way is to follow the detailed steps.
- GPU memory bottleneck GPUs are known for their high computing power and high concurrency. As a peripheral, however, its memory capacity (currently 80GB for mainstream training GPUs A100 and 24GB for mainstream inference GPUs A10) still restricts the use of its computing power. Especially recently, the growing demand for GPU memory capacity for large models has been much higher than the hardware development of GPU memory.
- IO transmission bottleneck Comparing the GPU computing power and CPU-GPU IO bandwidth of various GPU generations, it is not difficult to find that the limitations of transmission wall are intensifying and will be unlikely to be solved in the short term. It is worth noting that based on the customized interconnection NVLink, the GPU-to-GPU bandwidth is significantly faster than the PCIe bandwidth. In addition, GPU memory bandwidth (HBM, GDDR) is a performance bottleneck of large model inference.
GLake is designed with a layered architecture. Currently tests and verfications focus on PyTorch and NVIDIA GPUs, we're working on more devices support:
- Hardware interface includes GPUs and interconnection, currently mainly based on NV GPU (supporting NVLink, P2P, Unified Addressing, VMM, IPC, etc.). The interface is adapting to support domestic AI cards, and will consider supporting new interconnections (such as CXL) in the future.
- GPU memory pool provides global and heterogeneous GPU memory pools, built-in GPU memory fragmentation optimization, multi-stream and multi-process memory reuse, and memory security.
- Core optimization layer provides value-added optimization functions, including global allocation, multi-channel concurrency, tiering, memory deduplication, KV-cache optimization, etc.
- Extension layer combines the DL framework and the team's self-developed VGPU, which provides integration solutions or extensions, such as PyTorch.
- Application and ecology currently focuses on AI training and inference. In the future, different application scenarios can be supported, such as graph computing and graphic rendering.
- Efficient: With internal two-layer GPU memory management and global (multi-GPU, multi-task) optimization, GPU memory pooling, sharing and tiering are realized to provide larger GPU memory for training and inference. Multi-path can accelerate CPU-GPU transmission by 3~12X.
- Easy to use: The core functions are transparent to the model and do not require code modification for training and inference, as GLake can be easily plugged into existing engines (such as PyTorch). Meanwhile GPU memory internal stats. (e.g., fragmentation) can be queried online with RPC interface
- Open and easy to extend: Configurable strategies (e.g., compression, data verification, different levels of security check) will be provided.
- Security: For troubleshooting problems such as GPU memory out-of-bounds, a built-in GPU memory out-of-bounds detection mechanism will assist in diagnose.
- GLake reduces the memory fragmentation by up to 27%, save 25G of GPU memory, and increase the training throughput of a 10B model by up to nearly 4 times.
- For inference, GLake supports cross-process and cross-model elimination of duplicate memory, saving 3 times memory.
- GLake accelerates CPU-GPU IO transmission by 3 times.
GMLake tutorial
Multi-path tutorial
- GMLake When there is no contineous free buffer to satisfy allocation requests, GMLake will return a complete buffer to users by combining multiple memory fragementation.
- Multi-path CPU-GPU IO throughput is improved by exploiting multiple transfer paths concurrently.
- Data deduplication For AI inference, GLake is able to automatically find out duplicate memory use and share them between processes in fine-grained memory.
We are working on a few interesting featues. Any questions, suggestions and participations are welcomed.
- LLM KV cache : tackle LLM inference KV cache fragmentation in a unifed and efficient way (a little different from vLLM)
- cache-prefetch: optimize offloading & prefetching in fine-tuning and inference (i.e., atop DeepSpeed, may deep into L2 cache)
- tiering: manage and optimize memory allocations and data moving across cards/nodes and various memory types
- data deduplication: keep single unique content copy in fine-grained block across model instances and processes in inference or serverless
- memory debugging: enable efficient and friendly GPU memory debugging in case of overflow, segmentfault etc
- more accelerators: okey, we'll (have to) need more choices
- more scenarios: such as GNN、GraphDB etc
WeChat-Group: in case of invalid, pls contact wx: 13051161982
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for glake
Similar Open Source Tools

glake
GLake is an acceleration library and utilities designed to optimize GPU memory management and IO transmission for AI large model training and inference. It addresses challenges such as GPU memory bottleneck and IO transmission bottleneck by providing efficient memory pooling, sharing, and tiering, as well as multi-path acceleration for CPU-GPU transmission. GLake is easy to use, open for extension, and focuses on improving training throughput, saving inference memory, and accelerating IO transmission. It offers features like memory fragmentation reduction, memory deduplication, and built-in security mechanisms for troubleshooting GPU memory issues.
llumnix
Llumnix is a cross-instance request scheduling layer built on top of LLM inference engines such as vLLM, providing optimized multi-instance serving performance with low latency, reduced time-to-first-token (TTFT) and queuing delays, reduced time-between-tokens (TBT) and preemption stalls, and high throughput. It achieves this through dynamic, fine-grained, KV-cache-aware scheduling, continuous rescheduling across instances, KV cache migration mechanism, and seamless integration with existing multi-instance deployment platforms. Llumnix is easy to use, fault-tolerant, elastic, and extensible to more inference engines and scheduling policies.
siiRL
siiRL is a novel, fully distributed reinforcement learning (RL) framework designed to break the scaling barriers in Large Language Models (LLMs) post-training. Developed by researchers from Shanghai Innovation Institute, siiRL delivers near-linear scalability, dramatic throughput gains, and unprecedented flexibility for RL-based LLM development. It eliminates the centralized controller common in other frameworks, enabling scalability to thousands of GPUs, achieving state-of-the-art throughput, and supporting cross-hardware compatibility. siiRL is extensively benchmarked and excels in data-intensive workloads such as long-context and multi-modal training.
Nanoflow
NanoFlow is a throughput-oriented high-performance serving framework for Large Language Models (LLMs) that consistently delivers superior throughput compared to other frameworks by utilizing key techniques such as intra-device parallelism, asynchronous CPU scheduling, and SSD offloading. The framework proposes nano-batching to schedule compute-, memory-, and network-bound operations for simultaneous execution, leading to increased resource utilization. NanoFlow also adopts an asynchronous control flow to optimize CPU overhead and eagerly offloads KV-Cache to SSDs for multi-round conversations. The open-source codebase integrates state-of-the-art kernel libraries and provides necessary scripts for environment setup and experiment reproduction.

ReaLHF
ReaLHF is a distributed system designed for efficient RLHF training with Large Language Models (LLMs). It introduces a novel approach called parameter reallocation to dynamically redistribute LLM parameters across the cluster, optimizing allocations and parallelism for each computation workload. ReaL minimizes redundant communication while maximizing GPU utilization, achieving significantly higher Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) training throughput compared to other systems. It supports large-scale training with various parallelism strategies and enables memory-efficient training with parameter and optimizer offloading. The system seamlessly integrates with HuggingFace checkpoints and inference frameworks, allowing for easy launching of local or distributed experiments. ReaLHF offers flexibility through versatile configuration customization and supports various RLHF algorithms, including DPO, PPO, RAFT, and more, while allowing the addition of custom algorithms for high efficiency.

xllm
xLLM is an efficient LLM inference framework optimized for Chinese AI accelerators, enabling enterprise-grade deployment with enhanced efficiency and reduced cost. It adopts a service-engine decoupled inference architecture, achieving breakthrough efficiency through technologies like elastic scheduling, dynamic PD disaggregation, multi-stream parallel computing, graph fusion optimization, and global KV cache management. xLLM supports deployment of mainstream large models on Chinese AI accelerators, empowering enterprises in scenarios like intelligent customer service, risk control, supply chain optimization, ad recommendation, and more.

unified-cache-management
Unified Cache Manager (UCM) is a tool designed to persist the LLM KVCache and replace redundant computations through various retrieval mechanisms. It supports prefix caching and offers training-free sparse attention retrieval methods, enhancing performance for long sequence inference tasks. UCM also provides a PD disaggregation solution based on a storage-compute separation architecture, enabling easier management of heterogeneous computing resources. When integrated with vLLM, UCM significantly reduces inference latency in scenarios like multi-turn dialogue and long-context reasoning tasks.

llm-d
LLM-D is a machine learning model for sentiment analysis. It is designed to classify text data into positive, negative, or neutral sentiment categories. The model is trained on a large dataset of labeled text samples and uses natural language processing techniques to analyze and predict sentiment in new text inputs. LLM-D is a powerful tool for businesses and researchers looking to understand customer feedback, social media sentiment, and other text data sources. It can be easily integrated into existing applications or used as a standalone tool for sentiment analysis tasks.
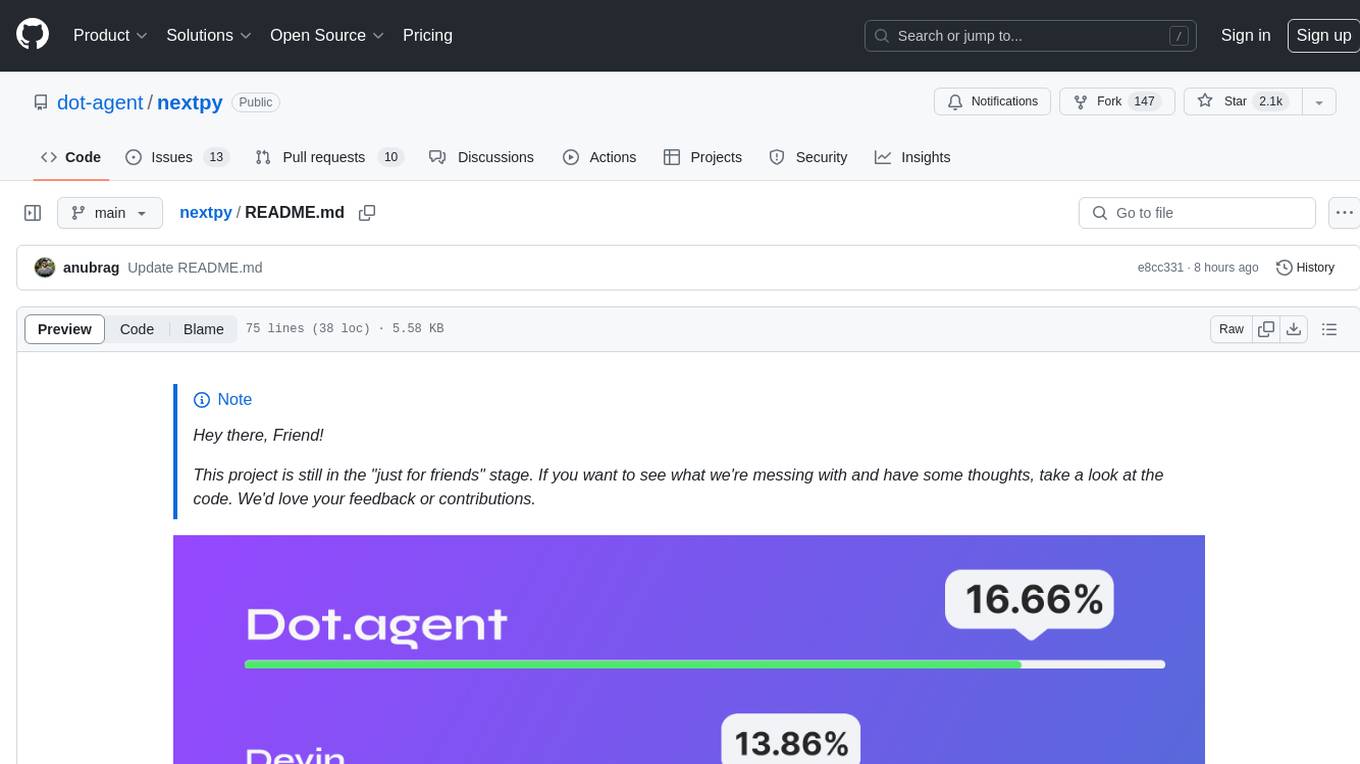
nextpy
Nextpy is a cutting-edge software development framework optimized for AI-based code generation. It provides guardrails for defining AI system boundaries, structured outputs for prompt engineering, a powerful prompt engine for efficient processing, better AI generations with precise output control, modularity for multiplatform and extensible usage, developer-first approach for transferable knowledge, and containerized & scalable deployment options. It offers 4-10x faster performance compared to Streamlit apps, with a focus on cooperation within the open-source community and integration of key components from various projects.

ServerlessLLM
ServerlessLLM is a fast, affordable, and easy-to-use library designed for multi-LLM serving, optimized for environments with limited GPU resources. It supports loading various leading LLM inference libraries, achieving fast load times, and reducing model switching overhead. The library facilitates easy deployment via Ray Cluster and Kubernetes, integrates with the OpenAI Query API, and is actively maintained by contributors.
learn-agentic-ai
Learn Agentic AI is a repository that is part of the Panaversity Certified Agentic and Robotic AI Engineer program. It covers AI-201 and AI-202 courses, providing fundamentals and advanced knowledge in Agentic AI. The repository includes video playlists, projects, and project submission guidelines for students to enhance their understanding and skills in the field of AI engineering.

vllm
vLLM is a fast and easy-to-use library for LLM inference and serving. It is designed to be efficient, flexible, and easy to use. vLLM can be used to serve a variety of LLM models, including Hugging Face models. It supports a variety of decoding algorithms, including parallel sampling, beam search, and more. vLLM also supports tensor parallelism for distributed inference and streaming outputs. It is open-source and available on GitHub.
reductstore
ReductStore is a high-performance time series database designed for storing and managing large amounts of unstructured blob data. It offers features such as real-time querying, batching data, and HTTP(S) API for edge computing, computer vision, and IoT applications. The database ensures data integrity, implements retention policies, and provides efficient data access, making it a cost-effective solution for applications requiring unstructured data storage and access at specific time intervals.

deepflow
DeepFlow is an open-source project that provides deep observability for complex cloud-native and AI applications. It offers Zero Code data collection with eBPF for metrics, distributed tracing, request logs, and function profiling. DeepFlow is integrated with SmartEncoding to achieve Full Stack correlation and efficient access to all observability data. With DeepFlow, cloud-native and AI applications automatically gain deep observability, removing the burden of developers continually instrumenting code and providing monitoring and diagnostic capabilities covering everything from code to infrastructure for DevOps/SRE teams.
AITemplate
AITemplate (AIT) is a Python framework that transforms deep neural networks into CUDA (NVIDIA GPU) / HIP (AMD GPU) C++ code for lightning-fast inference serving. It offers high performance close to roofline fp16 TensorCore (NVIDIA GPU) / MatrixCore (AMD GPU) performance on major models. AITemplate is unified, open, and flexible, supporting a comprehensive range of fusions for both GPU platforms. It provides excellent backward capability, horizontal fusion, vertical fusion, memory fusion, and works with or without PyTorch. FX2AIT is a tool that converts PyTorch models into AIT for fast inference serving, offering easy conversion and expanded support for models with unsupported operators.

Bodo
Bodo is a high-performance Python compute engine designed for large-scale data processing and AI workloads. It utilizes an auto-parallelizing just-in-time compiler to optimize Python programs, making them 20x to 240x faster compared to alternatives. Bodo seamlessly integrates with native Python APIs like Pandas and NumPy, eliminates runtime overheads using MPI for distributed execution, and provides exceptional performance and scalability for data workloads. It is easy to use, interoperable with the Python ecosystem, and integrates with modern data platforms like Apache Iceberg and Snowflake. Bodo focuses on data-intensive and computationally heavy workloads in data engineering, data science, and AI/ML, offering automatic optimization and parallelization, linear scalability, advanced I/O support, and a high-performance SQL engine.
For similar tasks

glake
GLake is an acceleration library and utilities designed to optimize GPU memory management and IO transmission for AI large model training and inference. It addresses challenges such as GPU memory bottleneck and IO transmission bottleneck by providing efficient memory pooling, sharing, and tiering, as well as multi-path acceleration for CPU-GPU transmission. GLake is easy to use, open for extension, and focuses on improving training throughput, saving inference memory, and accelerating IO transmission. It offers features like memory fragmentation reduction, memory deduplication, and built-in security mechanisms for troubleshooting GPU memory issues.
bee-agent-framework
The Bee Agent Framework is an open-source tool for building, deploying, and serving powerful agentic workflows at scale. It provides AI agents, tools for creating workflows in Javascript/Python, a code interpreter, memory optimization strategies, serialization for pausing/resuming workflows, traceability features, production-level control, and upcoming features like model-agnostic support and a chat UI. The framework offers various modules for agents, llms, memory, tools, caching, errors, adapters, logging, serialization, and more, with a roadmap including MLFlow integration, JSON support, structured outputs, chat client, base agent improvements, guardrails, and evaluation.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.




