
CodeFuse-ModelCache
A LLM semantic caching system aiming to enhance user experience by reducing response time via cached query-result pairs.
Stars: 626
Codefuse-ModelCache is a semantic cache for large language models (LLMs) that aims to optimize services by introducing a caching mechanism. It helps reduce the cost of inference deployment, improve model performance and efficiency, and provide scalable services for large models. The project caches pre-generated model results to reduce response time for similar requests and enhance user experience. It integrates various embedding frameworks and local storage options, offering functionalities like cache-writing, cache-querying, and cache-clearing through RESTful API. The tool supports multi-tenancy, system commands, and multi-turn dialogue, with features for data isolation, database management, and model loading schemes. Future developments include data isolation based on hyperparameters, enhanced system prompt partitioning storage, and more versatile embedding models and similarity evaluation algorithms.
README:
中文 | English
- news
- Introduction
- Quick-Deployment
- Service-Access
- Articles
- Modules
- Core-Features
- Acknowledgements
- Contributing
- 🔥🔥[2024.04.09] Add Redis Search to store and retrieve embeddings in multi-tenant scene, this can reduce the interaction time between Cache and vector databases to 10ms.
- 🔥🔥[2023.12.10] we integrate LLM embedding frameworks such as 'llmEmb', 'ONNX', 'PaddleNLP', 'FastText', alone with the image embedding framework 'timm', to bolster embedding functionality.
- 🔥🔥[2023.11.20] codefuse-ModelCache has integrated local storage, such as sqlite and faiss, providing users with the convenience of quickly initiating tests.
- [2023.08.26] codefuse-ModelCache...
Codefuse-ModelCache is a semantic cache for large language models (LLMs). By caching pre-generated model results, it reduces response time for similar requests and improves user experience.
This project aims to optimize services by introducing a caching mechanism. It helps businesses and research institutions reduce the cost of inference deployment, improve model performance and efficiency, and provide scalable services for large models. Through open-source, we aim to share and exchange technologies related to large model semantic cache.
The project's startup scripts are divided into flask4modelcache.py and flask4modelcache_demo.py.
- flask4modelcache_demo.py is a quick test service that embeds sqlite and faiss, and users do not need to be concerned about database-related matters.
- flask4modelcache.py is the normal service that requires configuration of mysql and milvus database services.
- Python version: 3.8 and above
- Package Installation
pip install -r requirements.txt - Download the embedding model bin file from the following address: https://huggingface.co/shibing624/text2vec-base-chinese/tree/main. Place the downloaded bin file in the model/text2vec-base-chinese folder.
- Start the backend service using the flask4modelcache_dome.py script.
cd CodeFuse-ModelCachepython flask4modelcache_demo.pyBefore starting the service, the following environment configurations should be performed:
- Install the relational database MySQL and import the SQL file to create the data tables. The SQL file can be found at:
reference_doc/create_table.sql - Install the vector database Milvus.
- Add the database access information to the configuration files:
modelcache/config/milvus_config.inimodelcache/config/mysql_config.ini
- Download the embedding model bin file from the following address: https://huggingface.co/shibing624/text2vec-base-chinese/tree/main. Place the downloaded bin file in the model/text2vec-base-chinese folder.
- Start the backend service using the flask4modelcache.py script.
The current service provides three core functionalities through RESTful API.: Cache-Writing, Cache-Querying, and Cache-Clearing. Demos:
import json
import requests
url = 'http://127.0.0.1:5000/modelcache'
type = 'insert'
scope = {"model": "CODEGPT-1008"}
chat_info = [{"query": [{"role": "system", "content": "You are an AI code assistant and you must provide neutral and harmless answers to help users solve code-related problems."}, {"role": "user", "content": "你是谁?"}],
"answer": "Hello, I am an intelligent assistant. How can I assist you?"}]
data = {'type': type, 'scope': scope, 'chat_info': chat_info}
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json"}
res = requests.post(url, headers=headers, json=json.dumps(data))import json
import requests
url = 'http://127.0.0.1:5000/modelcache'
type = 'query'
scope = {"model": "CODEGPT-1008"}
query = [{"role": "system", "content": "You are an AI code assistant and you must provide neutral and harmless answers to help users solve code-related problems."}, {"role": "user", "content": "Who are you?"}]
data = {'type': type, 'scope': scope, 'query': query}
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json"}
res = requests.post(url, headers=headers, json=json.dumps(data))import json
import requests
url = 'http://127.0.0.1:5000/modelcache'
type = 'remove'
scope = {"model": "CODEGPT-1008"}
remove_type = 'truncate_by_model'
data = {'type': type, 'scope': scope, 'remove_type': remove_type}
headers = {"Content-Type": "application/json"}
res = requests.post(url, headers=headers, json=json.dumps(data))https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/ExIRu2o7yvXa6nNLZcCfhQ
In terms of functionality, we have made several changes to the git repository. Firstly, we have addressed the network issues with huggingface and enhanced the inference speed by introducing local inference capabilities for embeddings. Additionally, considering the limitations of the SqlAlchemy framework, we have completely revamped the module responsible for interacting with relational databases, enabling more flexible database operations. In practical scenarios, LLM products often require integration with multiple users and multiple models. Hence, we have added support for multi-tenancy in the ModelCache, while also making preliminary compatibility adjustments for system commands and multi-turn dialogue.
| Module | Function | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ModelCache | GPTCache | ||
| Basic Interface | Data query interface | ☑ | ☑ |
| Data writing interface | ☑ | ☑ | |
| Embedding | Embedding model configuration | ☑ | ☑ |
| Large model embedding layer | ☑ | ||
| BERT model long text processing | ☑ | ||
| Large model invocation | Decoupling from large models | ☑ | |
| Local loading of embedding model | ☑ | ||
| Data isolation | Model data isolation | ☑ | ☑ |
| Hyperparameter isolation | |||
| Databases | MySQL | ☑ | ☑ |
| Milvus | ☑ | ☑ | |
| OceanBase | ☑ | ||
| Session management | Single-turn dialogue | ☑ | ☑ |
| System commands | ☑ | ||
| Multi-turn dialogue | ☑ | ||
| Data management | Data persistence | ☑ | ☑ |
| One-click cache clearance | ☑ | ||
| Tenant management | Support for multi-tenancy | ☑ | |
| Milvus multi-collection capability | ☑ | ||
| Other | Long-short dialogue distinction | ☑ |
In ModelCache, we adopted the main idea of GPTCache, includes core modules: adapter, embedding, similarity, and data_manager. The adapter module is responsible for handling the business logic of various tasks and can connect the embedding, similarity, and data_manager modules. The embedding module is mainly responsible for converting text into semantic vector representations, it transforms user queries into vector form.The rank module is used for sorting and evaluating the similarity of the recalled vectors. The data_manager module is primarily used for managing the database. In order to better facilitate industrial applications, we have made architectural and functional upgrades as follows:
- [x] We have modified it similar to Redis and embedded it into the LLMs product, providing semantic caching capabilities. This ensures that it does not interfere with LLM calls, security audits, and other functionalities, achieving compatibility with all large-scale model services.
- [x] Multiple Model Loading Schemes:
- Support loading local embedding models to address Hugging Face network connectivity issues.
- Support loading various pretrained model embedding layers.
- [x] Data Isolation Capability
- Environment Isolation: Can pull different database configurations based on the environment to achieve environment isolation (dev, prepub, prod).
- Multi-tenant Data Isolation: Dynamically create collections based on the model for data isolation, addressing data isolation issues in multi-model/services scenarios in LLMs products.
- [x] Support for System Commands: Adopting a concatenation approach to address the issue of system commands in the prompt format.
- [x] Differentiation of Long and Short Texts: Long texts pose more challenges for similarity evaluation. To address this, we have added differentiation between long and short texts, allowing for separate configuration of threshold values for determining similarity.
- [x] Milvus Performance Optimization: The consistency_level of Milvus has been adjusted to "Session" level, which can result in better performance.
- [x] Data Management Capability:
- Ability to clear the cache, used for data management after model upgrades.
- Hitquery recall for subsequent data analysis and model iteration reference.
- Asynchronous log write-back capability for data analysis and statistics.
- Added model field and data statistics field for feature expansion.
- [ ] Register adapter for Milvus:Based on the "model" parameter in the scope, initialize the corresponding Collection and perform the load operation.
- [ ] Inference Optimization: Optimizing the speed of embedding inference, compatible with inference engines such as FasterTransformer, TurboTransformers, and ByteTransformer.
- [ ] Compatibility with Hugging Face models and ModelScope models, offering more methods for model loading.
- [ ] Support MongoDB
- [ ] Support ElasticSearch
- [ ] Adapts Faiss storage in multimodal scenarios.
- [ ] Add ranking model to refine the order of data after embedding recall.
- [ ] Supports FastAPI.
- [ ] Add visual interface to offer a more direct user experience.
This project has referenced the following open-source projects. We would like to express our gratitude to the projects and their developers for their contributions and research.
GPTCache
ModelCache is a captivating and invaluable project, whether you are an experienced developer or a novice just starting out, your contributions to this project are warmly welcomed. Your involvement in this project, be it through raising issues, providing suggestions, writing code, or documenting and creating examples, will enhance the project's quality and make a significant contribution to the open-source community.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for CodeFuse-ModelCache
Similar Open Source Tools

CodeFuse-ModelCache
Codefuse-ModelCache is a semantic cache for large language models (LLMs) that aims to optimize services by introducing a caching mechanism. It helps reduce the cost of inference deployment, improve model performance and efficiency, and provide scalable services for large models. The project caches pre-generated model results to reduce response time for similar requests and enhance user experience. It integrates various embedding frameworks and local storage options, offering functionalities like cache-writing, cache-querying, and cache-clearing through RESTful API. The tool supports multi-tenancy, system commands, and multi-turn dialogue, with features for data isolation, database management, and model loading schemes. Future developments include data isolation based on hyperparameters, enhanced system prompt partitioning storage, and more versatile embedding models and similarity evaluation algorithms.
oasis
OASIS is a scalable, open-source social media simulator that integrates large language models with rule-based agents to realistically mimic the behavior of up to one million users on platforms like Twitter and Reddit. It facilitates the study of complex social phenomena such as information spread, group polarization, and herd behavior, offering a versatile tool for exploring diverse social dynamics and user interactions in digital environments. With features like scalability, dynamic environments, diverse action spaces, and integrated recommendation systems, OASIS provides a comprehensive platform for simulating social media interactions at a large scale.
superpipe
Superpipe is a lightweight framework designed for building, evaluating, and optimizing data transformation and data extraction pipelines using LLMs. It allows users to easily combine their favorite LLM libraries with Superpipe's building blocks to create pipelines tailored to their unique data and use cases. The tool facilitates rapid prototyping, evaluation, and optimization of end-to-end pipelines for tasks such as classification and evaluation of job departments based on work history. Superpipe also provides functionalities for evaluating pipeline performance, optimizing parameters for cost, accuracy, and speed, and conducting grid searches to experiment with different models and prompts.

DeepFabric
Deepfabric is an SDK and CLI tool that leverages large language models to generate high-quality synthetic datasets. It's designed for researchers and developers building teacher-student distillation pipelines, creating evaluation benchmarks for models and agents, or conducting research requiring diverse training data. The key innovation lies in Deepfabric's graph and tree-based architecture, which uses structured topic nodes as generation seeds. This approach ensures the creation of datasets that are both highly diverse and domain-specific, while minimizing redundancy and duplication across generated samples.
VMind
VMind is an open-source solution for intelligent visualization, providing an intelligent chart component based on LLM by VisActor. It allows users to create chart narrative works with natural language interaction, edit charts through dialogue, and export narratives as videos or GIFs. The tool is easy to use, scalable, supports various chart types, and offers one-click export functionality. Users can customize chart styles, specify themes, and aggregate data using LLM models. VMind aims to enhance efficiency in creating data visualization works through dialogue-based editing and natural language interaction.

swarms
Swarms provides simple, reliable, and agile tools to create your own Swarm tailored to your specific needs. Currently, Swarms is being used in production by RBC, John Deere, and many AI startups.

Trace
Trace is a new AutoDiff-like tool for training AI systems end-to-end with general feedback. It generalizes the back-propagation algorithm by capturing and propagating an AI system's execution trace. Implemented as a PyTorch-like Python library, users can write Python code directly and use Trace primitives to optimize certain parts, similar to training neural networks.

marqo
Marqo is more than a vector database, it's an end-to-end vector search engine for both text and images. Vector generation, storage and retrieval are handled out of the box through a single API. No need to bring your own embeddings.
DemoGPT
DemoGPT is an all-in-one agent library that provides tools, prompts, frameworks, and LLM models for streamlined agent development. It leverages GPT-3.5-turbo to generate LangChain code, creating interactive Streamlit applications. The tool is designed for creating intelligent, interactive, and inclusive solutions in LLM-based application development. It offers model flexibility, iterative development, and a commitment to user engagement. Future enhancements include integrating Gorilla for autonomous API usage and adding a publicly available database for refining the generation process.
xFinder
xFinder is a model specifically designed for key answer extraction from large language models (LLMs). It addresses the challenges of unreliable evaluation methods by optimizing the key answer extraction module. The model achieves high accuracy and robustness compared to existing frameworks, enhancing the reliability of LLM evaluation. It includes a specialized dataset, the Key Answer Finder (KAF) dataset, for effective training and evaluation. xFinder is suitable for researchers and developers working with LLMs to improve answer extraction accuracy.
Figma-Context-MCP
Figma-Context-MCP is a plugin for Figma that allows users to easily manage and switch between multiple design contexts within a single Figma file. This tool simplifies the process of working on different design variations or versions by providing a seamless way to organize and switch between them. With Figma-Context-MCP, designers can streamline their workflow and improve collaboration by keeping all design contexts in one place and easily accessible. This plugin enhances productivity and efficiency for Figma users who frequently work on multiple design iterations or versions within a project.
instructor-js
Instructor is a Typescript library for structured extraction in Typescript, powered by llms, designed for simplicity, transparency, and control. It stands out for its simplicity, transparency, and user-centric design. Whether you're a seasoned developer or just starting out, you'll find Instructor's approach intuitive and steerable.
palimpzest
Palimpzest (PZ) is a tool for managing and optimizing workloads, particularly for data processing tasks. It provides a CLI tool and Python demos for users to register datasets, run workloads, and access results. Users can easily initialize their system, register datasets, and manage configurations using the CLI commands provided. Palimpzest also supports caching intermediate results and configuring for parallel execution with remote services like OpenAI and together.ai. The tool aims to streamline the workflow of working with datasets and optimizing performance for data extraction tasks.
llm-colosseum
llm-colosseum is a tool designed to evaluate Language Model Models (LLMs) in real-time by making them fight each other in Street Fighter III. The tool assesses LLMs based on speed, strategic thinking, adaptability, out-of-the-box thinking, and resilience. It provides a benchmark for LLMs to understand their environment and take context-based actions. Users can analyze the performance of different LLMs through ELO rankings and win rate matrices. The tool allows users to run experiments, test different LLM models, and customize prompts for LLM interactions. It offers installation instructions, test mode options, logging configurations, and the ability to run the tool with local models. Users can also contribute their own LLM models for evaluation and ranking.
SUPIR
SUPIR is an AI-based image processing and upscaling tool that leverages cutting-edge technology to enhance image quality and resolution. The tool provides users with the ability to upscale images with high generalization and quality, as well as specific settings for light degradation scenarios. It offers a range of models and checkpoints for different use cases, along with detailed instructions for installation and usage. SUPIR also includes features for color fixing, linear CFG adjustments, and various prompts for image enhancement. The tool is designed for non-commercial use only and comes with a contact email for inquiries and permission requests for commercial use.
LLM-Drop
LLM-Drop is an official implementation of the paper 'What Matters in Transformers? Not All Attention is Needed'. The tool investigates redundancy in transformer-based Large Language Models (LLMs) by analyzing the architecture of Blocks, Attention layers, and MLP layers. It reveals that dropping certain Attention layers can enhance computational and memory efficiency without compromising performance. The tool provides a pipeline for Block Drop and Layer Drop based on LLaMA-Factory, and implements quantization using AutoAWQ and AutoGPTQ.
For similar tasks

CodeFuse-ModelCache
Codefuse-ModelCache is a semantic cache for large language models (LLMs) that aims to optimize services by introducing a caching mechanism. It helps reduce the cost of inference deployment, improve model performance and efficiency, and provide scalable services for large models. The project caches pre-generated model results to reduce response time for similar requests and enhance user experience. It integrates various embedding frameworks and local storage options, offering functionalities like cache-writing, cache-querying, and cache-clearing through RESTful API. The tool supports multi-tenancy, system commands, and multi-turn dialogue, with features for data isolation, database management, and model loading schemes. Future developments include data isolation based on hyperparameters, enhanced system prompt partitioning storage, and more versatile embedding models and similarity evaluation algorithms.
ModelCache
Codefuse-ModelCache is a semantic cache for large language models (LLMs) that aims to optimize services by introducing a caching mechanism. It helps reduce the cost of inference deployment, improve model performance and efficiency, and provide scalable services for large models. The project facilitates sharing and exchanging technologies related to large model semantic cache through open-source collaboration.
BentoML
BentoML is an open-source model serving library for building performant and scalable AI applications with Python. It comes with everything you need for serving optimization, model packaging, and production deployment.
Qwen-TensorRT-LLM
Qwen-TensorRT-LLM is a project developed for the NVIDIA TensorRT Hackathon 2023, focusing on accelerating inference for the Qwen-7B-Chat model using TRT-LLM. The project offers various functionalities such as FP16/BF16 support, INT8 and INT4 quantization options, Tensor Parallel for multi-GPU parallelism, web demo setup with gradio, Triton API deployment for maximum throughput/concurrency, fastapi integration for openai requests, CLI interaction, and langchain support. It supports models like qwen2, qwen, and qwen-vl for both base and chat models. The project also provides tutorials on Bilibili and blogs for adapting Qwen models in NVIDIA TensorRT-LLM, along with hardware requirements and quick start guides for different model types and quantization methods.
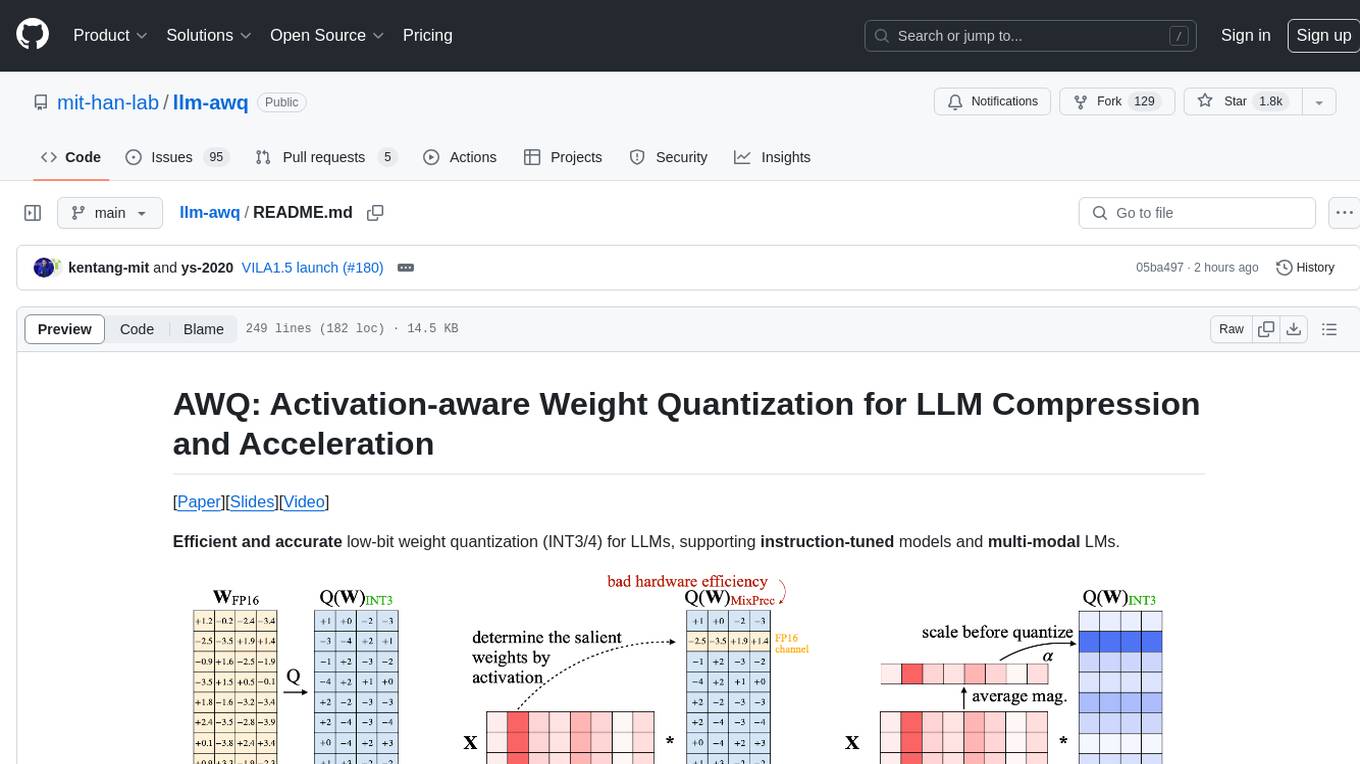
llm-awq
AWQ (Activation-aware Weight Quantization) is a tool designed for efficient and accurate low-bit weight quantization (INT3/4) for Large Language Models (LLMs). It supports instruction-tuned models and multi-modal LMs, providing features such as AWQ search for accurate quantization, pre-computed AWQ model zoo for various LLMs, memory-efficient 4-bit linear in PyTorch, and efficient CUDA kernel implementation for fast inference. The tool enables users to run large models on resource-constrained edge platforms, delivering more efficient responses with LLM/VLM chatbots through 4-bit inference.
LazyLLM
LazyLLM is a low-code development tool for building complex AI applications with multiple agents. It assists developers in building AI applications at a low cost and continuously optimizing their performance. The tool provides a convenient workflow for application development and offers standard processes and tools for various stages of application development. Users can quickly prototype applications with LazyLLM, analyze bad cases with scenario task data, and iteratively optimize key components to enhance the overall application performance. LazyLLM aims to simplify the AI application development process and provide flexibility for both beginners and experts to create high-quality applications.
ktransformers
KTransformers is a flexible Python-centric framework designed to enhance the user's experience with advanced kernel optimizations and placement/parallelism strategies for Transformers. It provides a Transformers-compatible interface, RESTful APIs compliant with OpenAI and Ollama, and a simplified ChatGPT-like web UI. The framework aims to serve as a platform for experimenting with innovative LLM inference optimizations, focusing on local deployments constrained by limited resources and supporting heterogeneous computing opportunities like GPU/CPU offloading of quantized models.
LLM-QAT
This repository contains the training code of LLM-QAT for large language models. The work investigates quantization-aware training for LLMs, including quantizing weights, activations, and the KV cache. Experiments were conducted on LLaMA models of sizes 7B, 13B, and 30B, at quantization levels down to 4-bits. Significant improvements were observed when quantizing weight, activations, and kv cache to 4-bit, 8-bit, and 4-bit, respectively.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.
