superpipe
Superpipe - optimized LLM pipelines for structured data
Stars: 99
Superpipe is a lightweight framework designed for building, evaluating, and optimizing data transformation and data extraction pipelines using LLMs. It allows users to easily combine their favorite LLM libraries with Superpipe's building blocks to create pipelines tailored to their unique data and use cases. The tool facilitates rapid prototyping, evaluation, and optimization of end-to-end pipelines for tasks such as classification and evaluation of job departments based on work history. Superpipe also provides functionalities for evaluating pipeline performance, optimizing parameters for cost, accuracy, and speed, and conducting grid searches to experiment with different models and prompts.
README:
A lightweight framework for building, evaluating and optimizing data transformation and data extraction pipelines using LLMs. Designed for simplicity, rapid prototyping, evaluation and optimization.
Star us on Github! Read the docs


Make sure you have Python 3.10+ installed, then run
pip install superpipe-py
There are three stages of using Superpipe.
- Build — use your favorite LLM library (langchain, LlamaIndex) and combine with Superpipe's building blocks.
- Evaluate — your pipeline needs to be evaluated on your data. Your data and use case are unique, so benchmarks are insufficient.
- Optimize — build once, experiment many times. Easily try different models, prompts, and parameters to optimize end-to-end.
To see a toy example, keep reading. For more details go to Step 1: Build
In this toy example, we'll use Superpipe to classify someone's work history into job departments. A superpipe pipeline consists of one or more steps. Each step takes in an input dataframe or dictionary and returns a new dataframe or dictionary with the outputs of the step appended.
Below, we use a built-in Superpipe step: LLMStructuredStep which extracts structured data using an LLM call. The expected structure is specified by a Pydantic model.
from superpipe.steps import LLMStructuredStep
from superpipe.models import gpt35
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
work_history = "Software engineer at Tech Innovations, project manager at Creative Solutions, CTO at Startup Dreams."
input = {"work_history": work_history}
def current_job_prompt(row):
return f"""Given an employees work history, classify them into one of the following departments:
HR, Legal, Finance, Sales, Product, Founder, Engineering
{row['work_history']}"""
class Department(BaseModel):
job_department: str = Field(description="Job department")
job_department_step = LLMStructuredStep(
model=gpt35,
prompt=current_job_prompt,
out_schema=Department,
name="job_department")
job_department_step.run(input)Output
{
"work_history": "Software engineer at Tech Innovations, project manager at Creative Solutions, CTO at Startup Dreams.",
"__job_department__": {
"input_tokens": 97,
"output_tokens": 10,
"input_cost": 0.0000485,
"output_cost": 0.000015,
"success": true,
"error": null,
"latency": 0.9502187501639128,
"content": {
"job_department": "Engineering"
}
},
"job_department": "Engineering"
}
In addition to the input (work_history) and result (job_department), the output also contains some step metadata for the job_department step including token usage, cost, and latency.
Once you've built your pipeline it's time to see how well it works. Think of this as unit tests for your code. You wouldn't ship code to production without testing it, you shouldn't ship LLM pipelines to production without evaluating them.
This requires:
- A dataset with labels - the correct label for each row in your data. You can use an early version of your pipeline to generate candidate labels and manually inspect and correct to generate your ground truth.
- Evaluation function - a function that defines what "correct" is. In this example we use a simple string comparison evaluation function, but in general it could be any arbitrary function, including a call to an LLM to do more advanced evals.
from superpipe.pipeline import Pipeline
import pandas as pd
work_histories = [
"Software engineer at Tech Innovations, project manager at Creative Solutions, CTO at Startup Dreams.",
"Journalist for The Daily News, senior writer at Insight Magazine, currently Investor at VC Global.",
"Sales associate at Retail Giant, sales manager at Boutique Chain, now regional sales director at Luxury Brands Inc."
]
labels = [
"Engineering",
"Finance",
"Sales"
]
input = pd.DataFrame([{"work_history": work_histories[i], "label": labels[i]} for i in range(3)])
evaluate = lambda row: row["job_department"] == row["label"]
categorizer = Pipeline(
steps=[job_department_step],
evaluation_fn=evaluate)
categorizer.run(input)
print(categorizer.statistics)Output
+---------------+------------------------------+
| score | 1.0 |
+---------------+------------------------------+
| input_tokens | {'gpt-3.5-turbo-0125': 1252} |
+---------------+------------------------------+
| output_tokens | {'gpt-3.5-turbo-0125': 130} |
+---------------+------------------------------+
| input_cost | $0.0006259999999999999 |
+---------------+------------------------------+
| output_cost | $0.00019500000000000005 |
+---------------+------------------------------+
| num_success | 3 |
+---------------+------------------------------+
| num_failure | 0 |
+---------------+------------------------------+
| total_latency | 9.609524499624968 |
+---------------+------------------------------+
The score field is calculated by applying the evaluate function on each row. In this case we were able to correctly classify each row so the score is 1 (i.e. 100%). We can also see the total cost and latency.
The last step in using Superpipe is trying out many combinations of parameters to optimize your pipeline along cost, accuracy, and speed. In this example, we'll try two different models and two prompts (4 combinations). Superpipe's grid search makes it easy to try all combinations - build once, experiment many times.
from superpipe.grid_search import GridSearch
from superpipe.models import gpt35, gpt4
def short_job_prompt(row):
return f"""Classify into: HR, Legal, Finance, Sales, Product, Founder, Engineering
{row['work_history']}"""
params_grid = {
job_department_step.name: {
"model": [gpt35, gpt4],
"prompt": [current_job_prompt, short_job_prompt]
},
}
grid_search = GridSearch(categorizer, params_grid)
grid_search.run(input)The results of the grid search show that:
- The longer prompt is more accurate even though it costs more and is slower
- There's no advantage in using gpt4 instead of gpt3.5
Our docs go much more in depth on how to use Superpipe including concepts, why Superpipe, and in depth examples.
This project is licensed under the terms of the MIT License.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for superpipe
Similar Open Source Tools

superpipe
Superpipe is a lightweight framework designed for building, evaluating, and optimizing data transformation and data extraction pipelines using LLMs. It allows users to easily combine their favorite LLM libraries with Superpipe's building blocks to create pipelines tailored to their unique data and use cases. The tool facilitates rapid prototyping, evaluation, and optimization of end-to-end pipelines for tasks such as classification and evaluation of job departments based on work history. Superpipe also provides functionalities for evaluating pipeline performance, optimizing parameters for cost, accuracy, and speed, and conducting grid searches to experiment with different models and prompts.
xFinder
xFinder is a model specifically designed for key answer extraction from large language models (LLMs). It addresses the challenges of unreliable evaluation methods by optimizing the key answer extraction module. The model achieves high accuracy and robustness compared to existing frameworks, enhancing the reliability of LLM evaluation. It includes a specialized dataset, the Key Answer Finder (KAF) dataset, for effective training and evaluation. xFinder is suitable for researchers and developers working with LLMs to improve answer extraction accuracy.
edsl
The Expected Parrot Domain-Specific Language (EDSL) package enables users to conduct computational social science and market research with AI. It facilitates designing surveys and experiments, simulating responses using large language models, and performing data labeling and other research tasks. EDSL includes built-in methods for analyzing, visualizing, and sharing research results. It is compatible with Python 3.9 - 3.11 and requires API keys for LLMs stored in a `.env` file.

Trace
Trace is a new AutoDiff-like tool for training AI systems end-to-end with general feedback. It generalizes the back-propagation algorithm by capturing and propagating an AI system's execution trace. Implemented as a PyTorch-like Python library, users can write Python code directly and use Trace primitives to optimize certain parts, similar to training neural networks.

swarms
Swarms provides simple, reliable, and agile tools to create your own Swarm tailored to your specific needs. Currently, Swarms is being used in production by RBC, John Deere, and many AI startups.
langevals
LangEvals is an all-in-one Python library for testing and evaluating LLM models. It can be used in notebooks for exploration, in pytest for writing unit tests, or as a server API for live evaluations and guardrails. The library is modular, with 20+ evaluators including Ragas for RAG quality, OpenAI Moderation, and Azure Jailbreak detection. LangEvals powers LangWatch evaluations and provides tools for batch evaluations on notebooks and unit test evaluations with PyTest. It also offers LangEvals evaluators for LLM-as-a-Judge scenarios and out-of-the-box evaluators for language detection and answer relevancy checks.
LightAgent
LightAgent is a lightweight, open-source Agentic AI development framework with memory, tools, and a tree of thought. It supports multi-agent collaboration, autonomous learning, tool integration, complex task handling, and multi-model support. It also features a streaming API, tool generator, agent self-learning, adaptive tool mechanism, and more. LightAgent is designed for intelligent customer service, data analysis, automated tools, and educational assistance.

zshot
Zshot is a highly customizable framework for performing Zero and Few shot named entity and relationships recognition. It can be used for mentions extraction, wikification, zero and few shot named entity recognition, zero and few shot named relationship recognition, and visualization of zero-shot NER and RE extraction. The framework consists of two main components: the mentions extractor and the linker. There are multiple mentions extractors and linkers available, each serving a specific purpose. Zshot also includes a relations extractor and a knowledge extractor for extracting relations among entities and performing entity classification. The tool requires Python 3.6+ and dependencies like spacy, torch, transformers, evaluate, and datasets for evaluation over datasets like OntoNotes. Optional dependencies include flair and blink for additional functionalities. Zshot provides examples, tutorials, and evaluation methods to assess the performance of the components.
LongBench
LongBench v2 is a benchmark designed to assess the ability of large language models (LLMs) to handle long-context problems requiring deep understanding and reasoning across various real-world multitasks. It consists of 503 challenging multiple-choice questions with contexts ranging from 8k to 2M words, covering six major task categories. The dataset is collected from nearly 100 highly educated individuals with diverse professional backgrounds and is designed to be challenging even for human experts. The evaluation results highlight the importance of enhanced reasoning ability and scaling inference-time compute to tackle the long-context challenges in LongBench v2.
raid
RAID is the largest and most comprehensive dataset for evaluating AI-generated text detectors. It contains over 10 million documents spanning 11 LLMs, 11 genres, 4 decoding strategies, and 12 adversarial attacks. RAID is designed to be the go-to location for trustworthy third-party evaluation of popular detectors. The dataset covers diverse models, domains, sampling strategies, and attacks, making it a valuable resource for training detectors, evaluating generalization, protecting against adversaries, and comparing to state-of-the-art models from academia and industry.
llm-strategy
The 'llm-strategy' repository implements the Strategy Pattern using Large Language Models (LLMs) like OpenAI’s GPT-3. It provides a decorator 'llm_strategy' that connects to an LLM to implement abstract methods in interface classes. The package uses doc strings, type annotations, and method/function names as prompts for the LLM and can convert the responses back to Python data. It aims to automate the parsing of structured data by using LLMs, potentially reducing the need for manual Python code in the future.
empower-functions
Empower Functions is a family of large language models (LLMs) that provide GPT-4 level capabilities for real-world 'tool using' use cases. These models offer compatibility support to be used as drop-in replacements, enabling interactions with external APIs by recognizing when a function needs to be called and generating JSON containing necessary arguments based on user inputs. This capability is crucial for building conversational agents and applications that convert natural language into API calls, facilitating tasks such as weather inquiries, data extraction, and interactions with knowledge bases. The models can handle multi-turn conversations, choose between tools or standard dialogue, ask for clarification on missing parameters, integrate responses with tool outputs in a streaming fashion, and efficiently execute multiple functions either in parallel or sequentially with dependencies.

marqo
Marqo is more than a vector database, it's an end-to-end vector search engine for both text and images. Vector generation, storage and retrieval are handled out of the box through a single API. No need to bring your own embeddings.

KaibanJS
KaibanJS is a JavaScript-native framework for building multi-agent AI systems. It enables users to create specialized AI agents with distinct roles and goals, manage tasks, and coordinate teams efficiently. The framework supports role-based agent design, tool integration, multiple LLMs support, robust state management, observability and monitoring features, and a real-time agentic Kanban board for visualizing AI workflows. KaibanJS aims to empower JavaScript developers with a user-friendly AI framework tailored for the JavaScript ecosystem, bridging the gap in the AI race for non-Python developers.
backtrack_sampler
Backtrack Sampler is a framework for experimenting with custom sampling algorithms that can backtrack the latest generated tokens. It provides a simple and easy-to-understand codebase for creating new sampling strategies. Users can implement their own strategies by creating new files in the `/strategy` directory. The repo includes examples for usage with llama.cpp and transformers, showcasing different strategies like Creative Writing, Anti-slop, Debug, Human Guidance, Adaptive Temperature, and Replace. The goal is to encourage experimentation and customization of backtracking algorithms for language models.
RTL-Coder
RTL-Coder is a tool designed to outperform GPT-3.5 in RTL code generation by providing a fully open-source dataset and a lightweight solution. It targets Verilog code generation and offers an automated flow to generate a large labeled dataset with over 27,000 diverse Verilog design problems and answers. The tool addresses the data availability challenge in IC design-related tasks and can be used for various applications beyond LLMs. The tool includes four RTL code generation models available on the HuggingFace platform, each with specific features and performance characteristics. Additionally, RTL-Coder introduces a new LLM training scheme based on code quality feedback to further enhance model performance and reduce GPU memory consumption.
For similar tasks

superpipe
Superpipe is a lightweight framework designed for building, evaluating, and optimizing data transformation and data extraction pipelines using LLMs. It allows users to easily combine their favorite LLM libraries with Superpipe's building blocks to create pipelines tailored to their unique data and use cases. The tool facilitates rapid prototyping, evaluation, and optimization of end-to-end pipelines for tasks such as classification and evaluation of job departments based on work history. Superpipe also provides functionalities for evaluating pipeline performance, optimizing parameters for cost, accuracy, and speed, and conducting grid searches to experiment with different models and prompts.
premsql
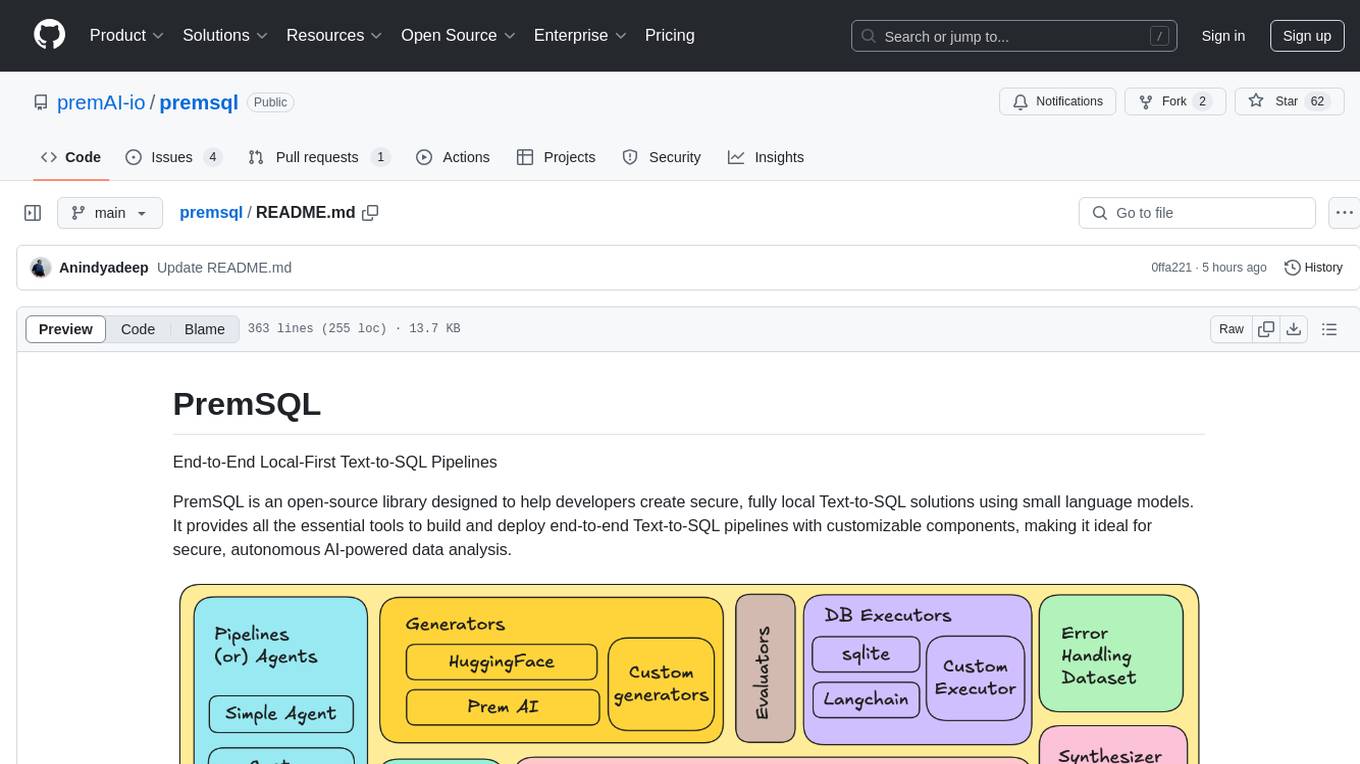
PremSQL is an open-source library designed to help developers create secure, fully local Text-to-SQL solutions using small language models. It provides essential tools for building and deploying end-to-end Text-to-SQL pipelines with customizable components, ideal for secure, autonomous AI-powered data analysis. The library offers features like Local-First approach, Customizable Datasets, Robust Executors and Evaluators, Advanced Generators, Error Handling and Self-Correction, Fine-Tuning Support, and End-to-End Pipelines. Users can fine-tune models, generate SQL queries from natural language inputs, handle errors, and evaluate model performance against predefined metrics. PremSQL is extendible for customization and private data usage.
crossfire-yolo-TensorRT
This repository supports the YOLO series models and provides an AI auto-aiming tool based on YOLO-TensorRT for the game CrossFire. Users can refer to the provided link for compilation and running instructions. The tool includes functionalities for screenshot + inference, mouse movement, and smooth mouse movement. The next goal is to automatically set the optimal PID parameters on the local machine. Developers are welcome to contribute to the improvement of this tool.
Simplifine
Simplifine is an open-source library designed for easy LLM finetuning, enabling users to perform tasks such as supervised fine tuning, question-answer finetuning, contrastive loss for embedding tasks, multi-label classification finetuning, and more. It provides features like WandB logging, in-built evaluation tools, automated finetuning parameters, and state-of-the-art optimization techniques. The library offers bug fixes, new features, and documentation updates in its latest version. Users can install Simplifine via pip or directly from GitHub. The project welcomes contributors and provides comprehensive documentation and support for users.
mystic
The `mystic` framework provides a collection of optimization algorithms and tools that allow the user to robustly solve hard optimization problems. It offers fine-grained power to monitor and steer optimizations during the fit processes. Optimizers can advance one iteration or run to completion, with customizable stop conditions. `mystic` optimizers share a common interface for easy swapping without writing new code. The framework supports parameter constraints, including soft and hard constraints, and provides tools for scientific machine learning, uncertainty quantification, adaptive sampling, nonlinear interpolation, and artificial intelligence. `mystic` is actively developed and welcomes user feedback and contributions.
intelligence-layer-sdk
The Aleph Alpha Intelligence Layer️ offers a comprehensive suite of development tools for crafting solutions that harness the capabilities of large language models (LLMs). With a unified framework for LLM-based workflows, it facilitates seamless AI product development, from prototyping and prompt experimentation to result evaluation and deployment. The Intelligence Layer SDK provides features such as Composability, Evaluability, and Traceability, along with examples to get started. It supports local installation using poetry, integration with Docker, and access to LLM endpoints for tutorials and tasks like Summarization, Question Answering, Classification, Evaluation, and Parameter Optimization. The tool also offers pre-configured tasks for tasks like Classify, QA, Search, and Summarize, serving as a foundation for custom development.
zenu
ZeNu is a high-performance deep learning framework implemented in pure Rust, featuring a pure Rust implementation for safety and performance, GPU performance comparable to PyTorch with CUDA support, a simple and intuitive API, and a modular design for easy extension. It supports various layers like Linear, Convolution 2D, LSTM, and optimizers such as SGD and Adam. ZeNu also provides device support for CPU and CUDA (NVIDIA GPU) with CUDA 12.3 and cuDNN 9. The project structure includes main library, automatic differentiation engine, neural network layers, matrix operations, optimization algorithms, CUDA implementation, and other support crates. Users can find detailed implementations like MNIST classification, CIFAR10 classification, and ResNet implementation in the examples directory. Contributions to ZeNu are welcome under the MIT License.
simple_GRPO
simple_GRPO is a very simple implementation of the GRPO algorithm for reproducing r1-like LLM thinking. It provides a codebase that supports saving GPU memory, understanding RL processes, trying various improvements like multi-answer generation, regrouping, penalty on KL, and parameter tuning. The project focuses on simplicity, performance, and core loss calculation based on Hugging Face's trl. It offers a straightforward setup with minimal dependencies and efficient training on multiple GPUs.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.