
Noema-Declarative-AI
A declarative way to control LLMs.
Stars: 66

Noema is a framework that enables developers to control a language model and choose the path it will follow. It integrates Python with llm's generations, allowing users to use LLM as a thought interpreter rather than a source of truth. Noema is built on llama.cpp and guidance's shoulders. It applies the declarative programming paradigm to a language model, providing a way to represent functions, descriptions, and transformations. Users can create subjects, think about tasks, and generate content through generators, selectors, and code generators. Noema supports ReAct prompting, visualization, and semantic Python functionalities, offering a versatile tool for automating tasks and guiding language models.
README:
With Noema, you can control the model and choose the path it will follow.
This framework aims to enable developpers to use **LLM as a though interpretor**, not as a source of truth.
pip install NoemaInstall llama-cpp-python using the correct backend.
from Noema import *
# Create a subject (LLM)
Subject("../Models/EXAONE-3.5-2.4B-Instruct-Q4_K_M.gguf", verbose=True) # Llama cpp model
@Noema
def think(task):
"""
You are a simple thinker. You have a task to perform.
Always looking for the best way to perform it.
"""
povs = []
task = Information(f"{task}") # inject information to the LLM
for i in range(4):
step_nb = i + 1
reflection = Sentence("Providing a reflection about the task.", step_nb)
consequence = Sentence("Providing the consequence of the reflection.", step_nb)
evaluate = Sentence("Evaluating the consequence.", step_nb)
point_of_view = Sentence(f"Providing a point of view about the task different than {povs}", step_nb)
point_of_view_qualification = Word(f"Qualifying the point of view, must choose a word different of: {povs}", step_nb)
povs.append(point_of_view_qualification.value)
creativitity_level = Float(f"How creative is this point of view: {povs[-1]}. (Between 0-10)", step_nb)
if creativitity_level.value < 8.0:
important = Information("I need to be more creative!")
conclusion = Paragraph("Providing a conclusion which is a synthesis of the previous steps.")
return conclusion.value # return the conclusion value
conclusion = think("How to write a good iOS application?")
print(conclusion)LLM output:
[INST]
You are a simple thinker. You have a task to perform.
Always looking for the best way to perform it.
#TASK : f'{self.task}'
#REFLEXION : Providing a reflection about the task. (Response format: a sentence)
#CONSEQUENCE : Providing the consequence of the reflection. (Response format: a sentence)
#EVALUATE : Evaluating the consequence. (Response format: a sentence)
#POINT_OF_VIEW : f'Providing a point of view about the task different than {povs}' (Response format: a sentence)
#IMPORTANT : I need to be more creative!
#CONCLUSION : Providing a conclusion which is a synthesis of the previous steps. (Response format: a paragraph)
[/INST]
#TASK: How to write a good iOS application?
#REFLEXION_1: Writing an iOS app requires balancing user experience with technical feasibility, which can be daunting without a structured approach.
#CONSEQUENCE_1: Without a clear roadmap, developers might overlook critical aspects like usability or performance optimization, leading to a subpar product.
#EVALUATE_1: The consequence highlights the necessity for meticulous planning and iterative testing to ensure both functionality and user satisfaction.
#POINT_OF_VIEW_1: Instead of focusing solely on coding, consider adopting a design-first approach where user stories guide the development process, ensuring alignment between vision and execution.
#POINT_OF_VIEW_QUALIFICATION_1: Designer
#CREATIVITITY_LEVEL_1: 7.5
#IMPORTANT: I need to be more creative!
#REFLEXION_2: The challenge lies in translating abstract design concepts into tangible iOS applications, necessitating a deep understanding of both user needs and platform capabilities.
#CONSEQUENCE_2: Ignoring user feedback during development phases could result in an application that fails to meet market expectations and user expectations, potentially causing significant financial losses and damage to brand reputation.
#EVALUATE_2: Ignoring user feedback during development phases could lead to a product that fails to resonate with its target audience, undermining both commercial success and user trust.
#POINT_OF_VIEW_2: From a developer's perspective, integrating innovative features while maintaining robustness requires a blend of creativity and technical expertise, ensuring seamless integration of cutting-edge functionalities without compromising stability.
#POINT_OF_VIEW_QUALIFICATION_2: Architect
#CREATIVITITY_LEVEL_2: 8.2
#CONCLUSION: Crafting a successful iOS application necessitates a multifaceted approach that harmonizes creativity with rigorous planning and iterative refinement. By adopting a design-first methodology and integrating user feedback throughout development, developers can navigate the complexities of balancing innovation with practicality, ultimately delivering applications that not only meet but exceed user expectations, thereby fostering both user satisfaction and commercial success. Emphasizing creativity alongside meticulous planning ensures that each aspect of the development process contributes meaningfully to the final product's success.
Noema is an application of the declarative programming paradigm to a language model.
- Noesis: can be seen as the description of a function
- Noema: is the representation (step by step) of this description
- Constitution: is the process of transformation Noesis->Noema.
- Subject: the object producing the Noema via the constitution of the noesis. Here, the LLM.
Noema/Noesis, Subject, and Constitution are a pedantic and naive application of concept borrowed from Husserl's phenomenology.
We can use ReAct prompting with LLM.
ReAct prompting is a powerful way for guiding a LLM.
Question: Here is the question
Reflection: Thinking about the question
Observation: Providing observation about the Reflection
Analysis: Formulating an analysis about your current reflection
Conclusion: Conclude by a synthesis of the reflection.
Question: {user_input}
Reflection:
In that case, the LLM will follow the provided steps: Reflection,Observation,Analysis,Conclusion
Thinking about the quesion is the Noesis of Reflection
The content generated by the LLM corresponding to Reflection is the Noema.
- Build the ReAct prompt
- Let you intercepts (constrained) generations
- Use it in standard python code
from Noema import *
Subject("path/to/your/model.gguf", verbose=True) # Full Compatibiliy with LLamaCPP.from Noema import *
Subject("../Models/EXAONE-3.5-2.4B-Instruct-Q4_K_M.gguf", verbose=True) # Llama cpp model
@Noema
def comment_evaluation(comment):
passfrom Noema import *
@Noema
def comment_evaluation(comment):
"""
You are a specialist of comment analysis.
You always produce a deep analysis of the comment.
"""from Noema import *
@Noema
def comment_evaluation(comment):
"""
You are a specialist of comment analysis.
You always produce a deep analysis of the comment.
"""
comment_to_analyse = Information(f"{comment}")
specialists = ["Psychologist", "Product manager", "Satisfaction manager"]
analyse_by_specialists = {}
for specialist in specialists:
analysis = Sentence(f"Analysing the comment as a {specialist}")
analyse_by_specialists[specialist] = analysis.value
synthesis = Paragraph("Providing a synthesis of the analysis.")
return synthesis.value, analyse_by_specialists
Subject("../Models/EXAONE-3.5-2.4B-Instruct-Q4_K_M.gguf", verbose=True) # Llama cpp model
synthesis, abs = comment_evaluation("This llm is very good at following instructions!")
print(synthesis)LLM output:
[INST]You are a specialist of comment analysis. You always produce a deep analysis of the comment.
#COMMENT_TO_ANALYSE : f'{comment}'
#ANALYSIS : f'Analysing the comment as a {specialist}' (Response format: a sentence)
#SYNTHESIS : Providing a synthesis of the analysis. (Response format: a paragraph)
[/INST]
#COMMENT_TO_ANALYSE: This llm is very good!
#ANALYSIS: The comment expresses a positive sentiment towards the LLM's capabilities, suggesting satisfaction with its performance and possibly indicating a belief in its psychological sophistication or understanding of human interaction nuances.
#ANALYSIS: As a product manager, this feedback highlights the importance of user satisfaction and perceived intelligence in LLM evaluations, indicating a focus on enhancing user experience through advanced functionalities and addressing potential psychological aspects beyond mere functionality.
#ANALYSIS: The comment reflects high user satisfaction with the LLM's performance, emphasizing its perceived intelligence and nuanced understanding, which are critical factors for product managers aiming to meet user expectations and foster trust through advanced technological capabilities.
#SYNTHESIS: The comment underscores a significant positive reception of the LLM, highlighting its perceived intelligence and nuanced understanding beyond basic functionality. This feedback is crucial for product managers as it underscores the importance of aligning technological advancements with user expectations for psychological satisfaction and trust-building. Addressing these aspects could enhance user engagement and satisfaction, positioning the LLM as a valuable asset in meeting evolving technological and psychological needs within its applications. Future iterations should focus on maintaining and potentially elevating these perceived qualities to further solidify its role as a sophisticated tool in diverse user contexts.
Generators are used to generate content from the subject (LLM) through the noesis (the task description).
Generated value always have 3 properties:
- var_name.value -> The generated value
- var_name.noesis -> The instruction
- var_name.noema -> The generated value
They always produce the corresponding python type.
| Noema Type | Python Type | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Int | int | number = Int("Give me a number between 0 and 10") |
| Float | float | number = Float("Give me a number between 0.1 and 0.7") |
| Bool | bool | truth:Bool = Bool("Are local LLMs better than online LLMs?") |
| Word | str | better = Word("Which instruct LLM is the best?") |
| Sentence | str | explaination = Sentence("Explain why") |
| Paragraph | str | long_explaination = Paragraph("Give mode details") |
| Free | str | unlimited = Free("Speak a lot without control...") |
List of simple Generators can be built.
| Noema Type | Generator Type | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| ListOf | [Int] | number = ListOf(Int,"Give me a list of number between 0 and 10") |
| ListOf | [Float] | number = ListOf(Float,"Give me a list of number between 0.1 and 0.7") |
| ListOf | [Bool] | truth_list = ListOf(Bool,"Are local LLMs better than online LLMs, and Mistral better than LLama?") |
| ListOf | [Word] | better = ListOf(Word,"List the best instruct LLM") |
| ListOf | [Sentence] | explaination = ListOf(Sentence,"Explain step by step why") |
Select the appropriate value.
| Noema Type | Generator Type | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Select | str | qualify_synthesis = Select("Qualify the synthesis", options=["good", "bad", "neutral"]) |
| SelectOrNone | str | contains = SelectOrNone("Does contain the following ideas", options=["Need to update the code", "Is totally secured"]) |
The LanguageName type provide a way to generate LanguageName code
| Noema Type | Python Type | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Python | str | interface = Python("With pyqt5, genereate a window with a text field and a OK button.") |
Language List
- Python
- Java
- C
- Cpp
- CSharp
- JavaScript
- TypeScript
- HTML
- CSS
- SQL
- NoSQL
- GraphQL
- Rust
- Go
- Ruby
- PHP
- Shell
- Bash
- PowerShell
- Perl
- Lua
- R
- Scala
- Kotlin
- Dart
- Swift
- ObjectiveC
- Assembly
- VHDL
- Verilog
- SystemVerilog
- Julia
- MATLAB
- COBOL
- Fortran
- Ada
- Pascal
- Lisp
- Prolog
- Smalltalk
- APL
The type Information is useful to insert some context to the LLM at the right time in the reflection process.
| Noema Type | Python Type | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Information | str | tips = Information("Here you can inject some information in the LLM") |
Here we use a simple string, but we can also insert a string from a python function call, do some RAG or any other tasks.
The SemPy type is creating Python function dynamically and execute it with your parameters.
| Noema Type | Python Type | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| SemPy | depending | letter_place = SemPy("Find the place of a letter in a word.")("hello world","o") |
from Noema import *
@Noema
def simple_task(task, parameters):
"""You are an incredible Python developer.
Always looking for the best way to write code."""
task_to_code = Information(f"I want to {task}")
formulation = Sentence("Reformulate the task to be easily understood by a Python developer.")
decomposition = ListOf(Sentence,"Decompose the task into smaller sub-tasks.")
result = SemPy(formulation.value)(parameters)
# Generated code:
#
# def function_name(word):
# letter_counts = {}
# for char in word:
# if char.isalpha(): # Ensure only letters are counted
# char = char.lower() # Convert to lowercase for uniformity
# if char in letter_counts:
# letter_counts[char] += 1
# else:
# letter_counts[char] = 1
# return letter_counts
# def noema_func(word):
# return function_name(word)
return result.value
Subject("../Models/EXAONE-3.5-7.8B-Instruct-Q4_K_M.gguf",verbose=True)
nb_letter = simple_task("Count the occurence of letters in a word", "strawberry")
print(nb_letter)
# {'s': 1, 't': 1, 'r': 3, 'a': 1, 'w': 1, 'b': 1, 'e': 1, 'y': 1}Enabling reflection visualization with write_graph = True in the Subject init create a PlantUML and Mermaid diagram respectively in diagram.puml and diagram.mmd
from Noema import *
# Create a new Subject
Subject("../Models/granite-3.1-3b-a800m-instruct-Q4_K_M.gguf", verbose=True, write_graph=True)
@Noema
def analysis_evaluation(analysis):
"""
You are a specialist of analysis evaluation.
You produce a numerical evaluation of the analysis, 0 is bad, 10 is good.
Good means that the analysis is relevant and useful.
Bad means that the analysis is not relevant and not useful.
"""
analysis_to_evaluate = Information(f"{analysis}")
evaluation = Float("Evaluation of the analysis, between 0 and 10")
return evaluation.value
@Noema
def comment_note_evaluation(analysis):
"""
You are a specialist of evaluation commenting.
You always produce a deep analysis of the comment.
"""
analysis_to_evaluate = Information(f"{analysis}")
comment = Sentence("Commenting the analysis")
return comment.value
@Noema
def comment_evaluation(comment):
"""
You are a specialist of comment analysis.
You always produce a deep analysis of the comment.
"""
comment_to_analyse = Information(f"{comment}")
specialists = ["Psychologist", "Sociologist", "Linguist", "Philosopher"]
analyse_by_specialists = {}
for specialist in specialists:
analysis = Sentence(f"Analysing the comment as a {specialist}")
analyse_by_specialists[specialist] = analysis.value
evaluation = analysis_evaluation(analysis.value)
comment_note_evaluation_res = comment_note_evaluation(evaluation)
improvements = ListOf(Sentence, "List 4 improvements")
synthesis = Paragraph("Providing a synthesis of the analysis.")
sub = Substring(f"Extracting synthesis comment from {synthesis.value}")
print(sub.value)
return synthesis.value
synthesis = comment_evaluation("This llm is very good!")
print(synthesis)For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Noema-Declarative-AI
Similar Open Source Tools

Noema-Declarative-AI
Noema is a framework that enables developers to control a language model and choose the path it will follow. It integrates Python with llm's generations, allowing users to use LLM as a thought interpreter rather than a source of truth. Noema is built on llama.cpp and guidance's shoulders. It applies the declarative programming paradigm to a language model, providing a way to represent functions, descriptions, and transformations. Users can create subjects, think about tasks, and generate content through generators, selectors, and code generators. Noema supports ReAct prompting, visualization, and semantic Python functionalities, offering a versatile tool for automating tasks and guiding language models.

Trace
Trace is a new AutoDiff-like tool for training AI systems end-to-end with general feedback. It generalizes the back-propagation algorithm by capturing and propagating an AI system's execution trace. Implemented as a PyTorch-like Python library, users can write Python code directly and use Trace primitives to optimize certain parts, similar to training neural networks.

marqo
Marqo is more than a vector database, it's an end-to-end vector search engine for both text and images. Vector generation, storage and retrieval are handled out of the box through a single API. No need to bring your own embeddings.
allms
allms is a versatile and powerful library designed to streamline the process of querying Large Language Models (LLMs). Developed by Allegro engineers, it simplifies working with LLM applications by providing a user-friendly interface, asynchronous querying, automatic retrying mechanism, error handling, and output parsing. It supports various LLM families hosted on different platforms like OpenAI, Google, Azure, and GCP. The library offers features for configuring endpoint credentials, batch querying with symbolic variables, and forcing structured output format. It also provides documentation, quickstart guides, and instructions for local development, testing, updating documentation, and making new releases.
xFinder
xFinder is a model specifically designed for key answer extraction from large language models (LLMs). It addresses the challenges of unreliable evaluation methods by optimizing the key answer extraction module. The model achieves high accuracy and robustness compared to existing frameworks, enhancing the reliability of LLM evaluation. It includes a specialized dataset, the Key Answer Finder (KAF) dataset, for effective training and evaluation. xFinder is suitable for researchers and developers working with LLMs to improve answer extraction accuracy.
Phi-3-Vision-MLX
Phi-3-MLX is a versatile AI framework that leverages both the Phi-3-Vision multimodal model and the Phi-3-Mini-128K language model optimized for Apple Silicon using the MLX framework. It provides an easy-to-use interface for a wide range of AI tasks, from advanced text generation to visual question answering and code execution. The project features support for batched generation, flexible agent system, custom toolchains, model quantization, LoRA fine-tuning capabilities, and API integration for extended functionality.

ActionWeaver
ActionWeaver is an AI application framework designed for simplicity, relying on OpenAI and Pydantic. It supports both OpenAI API and Azure OpenAI service. The framework allows for function calling as a core feature, extensibility to integrate any Python code, function orchestration for building complex call hierarchies, and telemetry and observability integration. Users can easily install ActionWeaver using pip and leverage its capabilities to create, invoke, and orchestrate actions with the language model. The framework also provides structured extraction using Pydantic models and allows for exception handling customization. Contributions to the project are welcome, and users are encouraged to cite ActionWeaver if found useful.
call-center-ai
Call Center AI is an AI-powered call center solution leveraging Azure and OpenAI GPT. It allows for AI agent-initiated phone calls or direct calls to the bot from a configured phone number. The bot is customizable for various industries like insurance, IT support, and customer service, with features such as accessing claim information, conversation history, language change, SMS sending, and more. The project is a proof of concept showcasing the integration of Azure Communication Services, Azure Cognitive Services, and Azure OpenAI for an automated call center solution.
chatmemory
ChatMemory is a simple yet powerful long-term memory manager that facilitates communication between AI and users. It organizes conversation data into history, summary, and knowledge entities, enabling quick retrieval of context and generation of clear, concise answers. The tool leverages vector search on summaries/knowledge and detailed history to provide accurate responses. It balances speed and accuracy by using lightweight retrieval and fallback detailed search mechanisms, ensuring efficient memory management and response generation beyond mere data retrieval.
superpipe
Superpipe is a lightweight framework designed for building, evaluating, and optimizing data transformation and data extraction pipelines using LLMs. It allows users to easily combine their favorite LLM libraries with Superpipe's building blocks to create pipelines tailored to their unique data and use cases. The tool facilitates rapid prototyping, evaluation, and optimization of end-to-end pipelines for tasks such as classification and evaluation of job departments based on work history. Superpipe also provides functionalities for evaluating pipeline performance, optimizing parameters for cost, accuracy, and speed, and conducting grid searches to experiment with different models and prompts.
invariant
Invariant Analyzer is an open-source scanner designed for LLM-based AI agents to find bugs, vulnerabilities, and security threats. It scans agent execution traces to identify issues like looping behavior, data leaks, prompt injections, and unsafe code execution. The tool offers a library of built-in checkers, an expressive policy language, data flow analysis, real-time monitoring, and extensible architecture for custom checkers. It helps developers debug AI agents, scan for security violations, and prevent security issues and data breaches during runtime. The analyzer leverages deep contextual understanding and a purpose-built rule matching engine for security policy enforcement.
basiclingua-LLM-Based-NLP
BasicLingua is a Python library that provides functionalities for linguistic tasks such as tokenization, stemming, lemmatization, and many others. It is based on the Gemini Language Model, which has demonstrated promising results in dealing with text data. BasicLingua can be used as an API or through a web demo. It is available under the MIT license and can be used in various projects.

AirGym
AirGym is an open source Python quadrotor simulator based on IsaacGym, providing a high-fidelity dynamics and Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) framework for quadrotor robot learning research. It offers a lightweight and customizable platform with strict alignment with PX4 logic, multiple control modes, and Sim-to-Real toolkits. Users can perform tasks such as Hovering, Balloon, Tracking, Avoid, and Planning, with the ability to create customized environments and tasks. The tool also supports training from scratch, visual encoding approaches, playing and testing of trained models, and customization of new tasks and assets.
instructor-js
Instructor is a Typescript library for structured extraction in Typescript, powered by llms, designed for simplicity, transparency, and control. It stands out for its simplicity, transparency, and user-centric design. Whether you're a seasoned developer or just starting out, you'll find Instructor's approach intuitive and steerable.
probsem
ProbSem is a repository that provides a framework to leverage large language models (LLMs) for assigning context-conditional probability distributions over queried strings. It supports OpenAI engines and HuggingFace CausalLM models, and is flexible for research applications in linguistics, cognitive science, program synthesis, and NLP. Users can define prompts, contexts, and queries to derive probability distributions over possible completions, enabling tasks like cloze completion, multiple-choice QA, semantic parsing, and code completion. The repository offers CLI and API interfaces for evaluation, with options to customize models, normalize scores, and adjust temperature for probability distributions.
empower-functions
Empower Functions is a family of large language models (LLMs) that provide GPT-4 level capabilities for real-world 'tool using' use cases. These models offer compatibility support to be used as drop-in replacements, enabling interactions with external APIs by recognizing when a function needs to be called and generating JSON containing necessary arguments based on user inputs. This capability is crucial for building conversational agents and applications that convert natural language into API calls, facilitating tasks such as weather inquiries, data extraction, and interactions with knowledge bases. The models can handle multi-turn conversations, choose between tools or standard dialogue, ask for clarification on missing parameters, integrate responses with tool outputs in a streaming fashion, and efficiently execute multiple functions either in parallel or sequentially with dependencies.
For similar tasks

Noema-Declarative-AI
Noema is a framework that enables developers to control a language model and choose the path it will follow. It integrates Python with llm's generations, allowing users to use LLM as a thought interpreter rather than a source of truth. Noema is built on llama.cpp and guidance's shoulders. It applies the declarative programming paradigm to a language model, providing a way to represent functions, descriptions, and transformations. Users can create subjects, think about tasks, and generate content through generators, selectors, and code generators. Noema supports ReAct prompting, visualization, and semantic Python functionalities, offering a versatile tool for automating tasks and guiding language models.
aise
The repository 'aise' is an open-source electronic book focusing on AI-assisted software engineering. It covers the latest AI-assisted software engineering practices, implementation details from AI models to IDE plugins, and practical experiences in coding intelligent agents. The book aims to provide insights on leveraging AI to enhance software development efficiency and effectiveness across the entire software development lifecycle.
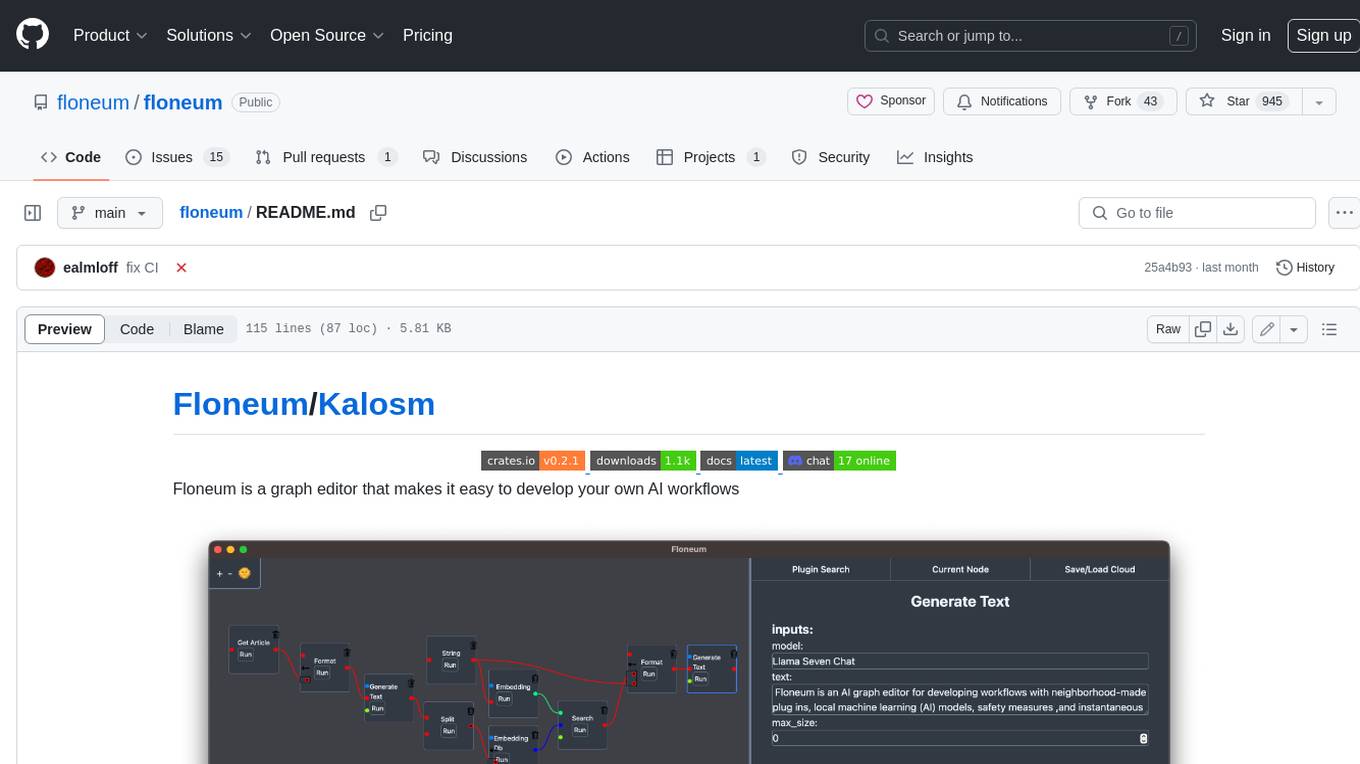
floneum
Floneum is a graph editor that makes it easy to develop your own AI workflows. It uses large language models (LLMs) to run AI models locally, without any external dependencies or even a GPU. This makes it easy to use LLMs with your own data, without worrying about privacy. Floneum also has a plugin system that allows you to improve the performance of LLMs and make them work better for your specific use case. Plugins can be used in any language that supports web assembly, and they can control the output of LLMs with a process similar to JSONformer or guidance.
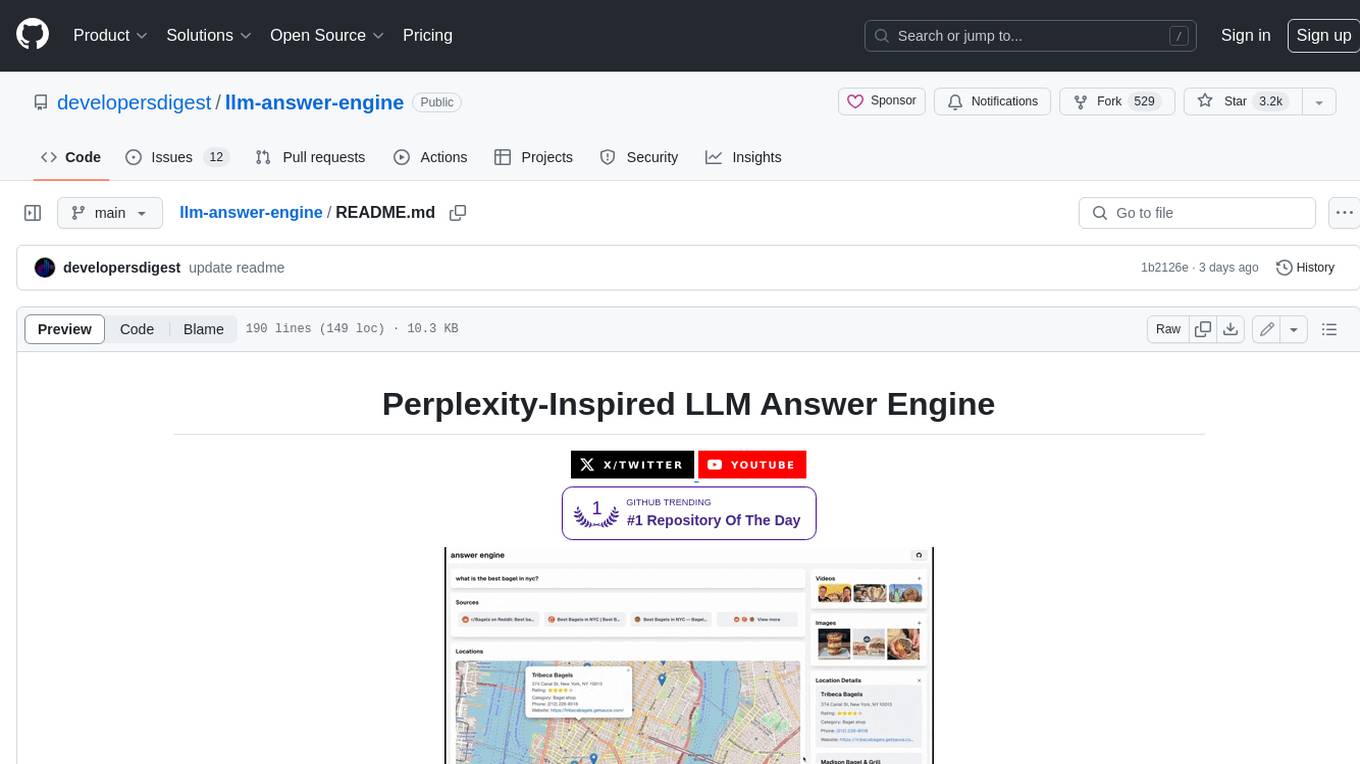
llm-answer-engine
This repository contains the code and instructions needed to build a sophisticated answer engine that leverages the capabilities of Groq, Mistral AI's Mixtral, Langchain.JS, Brave Search, Serper API, and OpenAI. Designed to efficiently return sources, answers, images, videos, and follow-up questions based on user queries, this project is an ideal starting point for developers interested in natural language processing and search technologies.
discourse-ai
Discourse AI is a plugin for the Discourse forum software that uses artificial intelligence to improve the user experience. It can automatically generate content, moderate posts, and answer questions. This can free up moderators and administrators to focus on other tasks, and it can help to create a more engaging and informative community.

Gemini-API
Gemini-API is a reverse-engineered asynchronous Python wrapper for Google Gemini web app (formerly Bard). It provides features like persistent cookies, ImageFx support, extension support, classified outputs, official flavor, and asynchronous operation. The tool allows users to generate contents from text or images, have conversations across multiple turns, retrieve images in response, generate images with ImageFx, save images to local files, use Gemini extensions, check and switch reply candidates, and control log level.
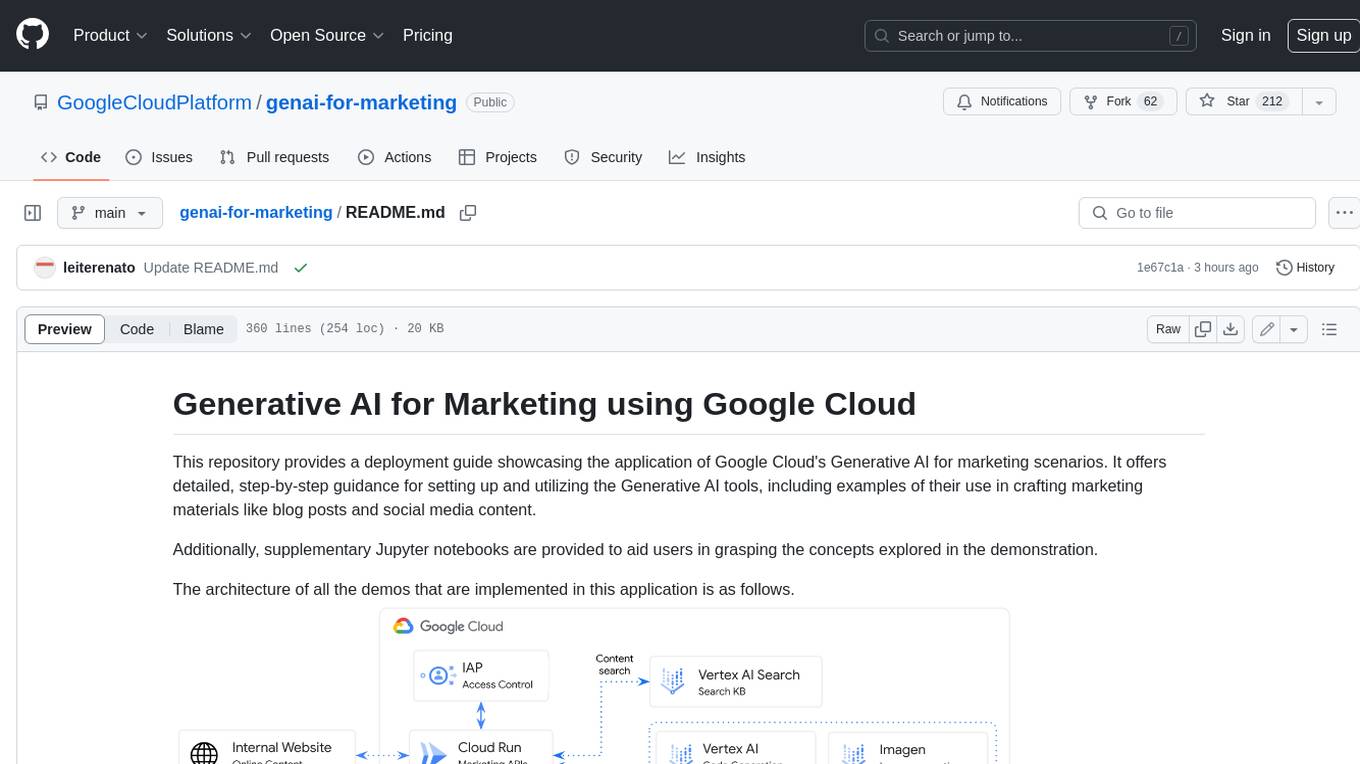
genai-for-marketing
This repository provides a deployment guide for utilizing Google Cloud's Generative AI tools in marketing scenarios. It includes step-by-step instructions, examples of crafting marketing materials, and supplementary Jupyter notebooks. The demos cover marketing insights, audience analysis, trendspotting, content search, content generation, and workspace integration. Users can access and visualize marketing data, analyze trends, improve search experience, and generate compelling content. The repository structure includes backend APIs, frontend code, sample notebooks, templates, and installation scripts.
generative-ai-dart
The Google Generative AI SDK for Dart enables developers to utilize cutting-edge Large Language Models (LLMs) for creating language applications. It provides access to the Gemini API for generating content using state-of-the-art models. Developers can integrate the SDK into their Dart or Flutter applications to leverage powerful AI capabilities. It is recommended to use the SDK for server-side API calls to ensure the security of API keys and protect against potential key exposure in mobile or web apps.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.

