
MiniCheck
MiniCheck: Efficient Fact-Checking of LLMs on Grounding Documents [EMNLP 2024]
Stars: 80
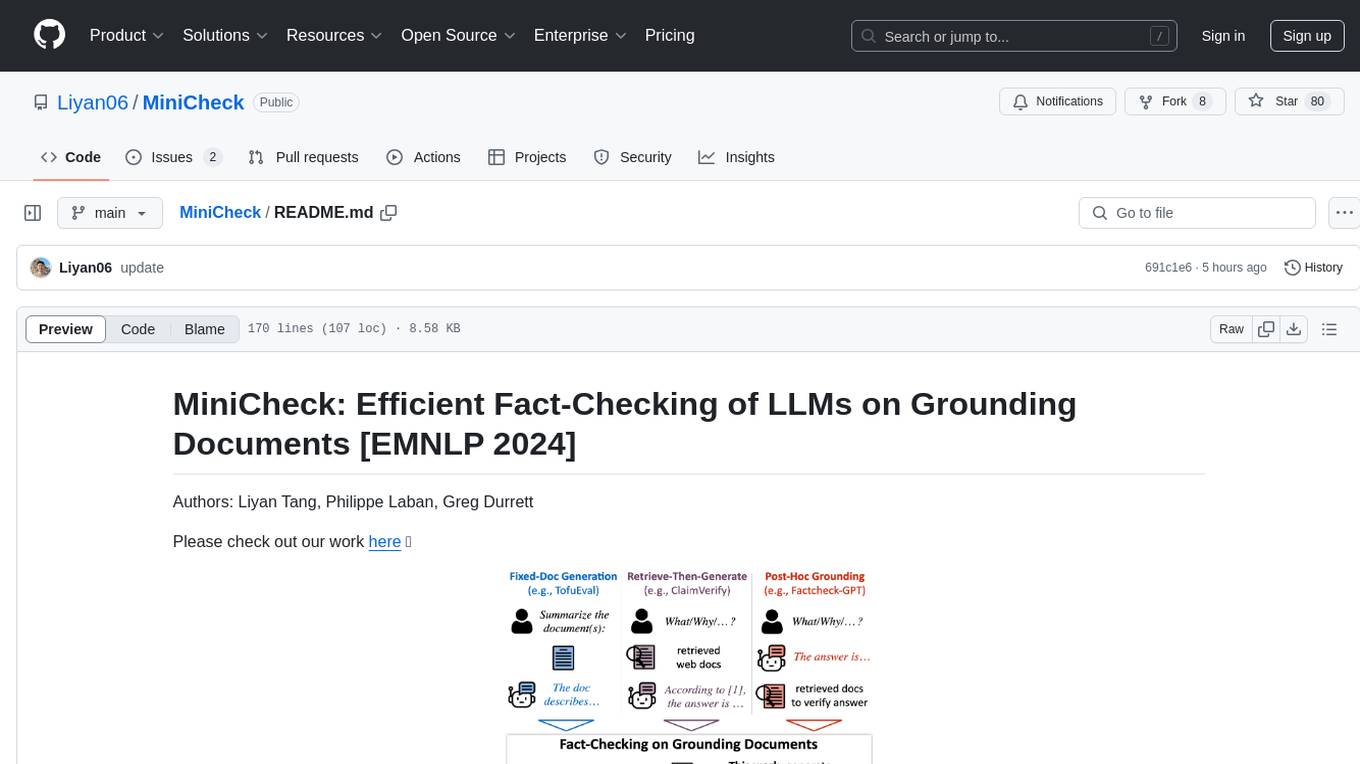
MiniCheck is an efficient fact-checking tool designed to verify claims against grounding documents using large language models. It provides a sentence-level fact-checking model that can be used to evaluate the consistency of claims with the provided documents. MiniCheck offers different models, including Bespoke-MiniCheck-7B, which is the state-of-the-art and commercially usable. The tool enables users to fact-check multi-sentence claims by breaking them down into individual sentences for optimal performance. It also supports automatic prefix caching for faster inference when repeatedly fact-checking the same document with different claims.
README:
Authors: Liyan Tang, Philippe Laban, Greg Durrett
Please check out our work here 📃
Updates 🔥
-
[2024/09] MiniCheck is now available at ollama. You can now run MiniCheck locally on your laptop 💻 with a simple command! More info in the ollama blog post and tweet.
-
[2024/09] MiniCheck is now available as a validator at Guardrails AI.
-
[2024/08] We release the LLM-AggreFact leaderboard, which currently contains the performance of 27 models on the LLM-AggreFact benchmark, including Llama-3.1, Mistral Large 2 and Claude-3.5.
-
[2024/08] We includ one additional dataset RAGTruth to our benchmark. We convert the dataset to the same format as in our benchmark and removed those non-checkworthy claims.
-
[2024/08] A stronger model,
Bespoke-MiniCheck-7B, is now available on HuggingFace for fact-checking. More details at this blog post. It's the current SOTA and is commercially useable! Please contact [email protected] for commercial use. -
[2024/08] We enable automic prefix caching for much faster inference when repeatedly using the same document for fact-checking.
-
[2024/08] Demo of
Bespoke-MiniCheck-7Bwith real-time inference!
LLM-AggreFact is a fact verification benchmark. It aggregates 11 of the most up-to-date publicly available datasets on factual consistency evaluation across both closed-book and grounded generation settings. In LLM-AggreFact:
- Documents come from diverse sources, including Wikipedia paragraphs, interviews, web text, covering domains such as news, dialogue, science, and healthcare.
- Claims to be verified are mostly generated from recent generative models (except for one dataset of human-written claims), without any human intervention in any format, such as injecting certain error types into model-generated claims.
Our Benchmark is available on HuggingFace 🤗 More benchmark details can be found here.
from datasets import load_dataset
dataset = load_dataset("lytang/LLM-AggreFact")The benchmark contains the following fields:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| dataset | One of the 11 datasets in the benchmark |
| doc | Document used to check the corresponding claim |
| claim | Claim to be checked by the corresponding document |
| label | 1 if the claim is supported, 0 otherwise |
| contamination_identifier | An identification string for contamination detection |
The following command will install the MiniCheck package and all necessary dependencies.
pip install "minicheck @ git+https://github.com/Liyan06/MiniCheck.git@main"or with optional vllm dependency for inference of LLM-based MiniCheck model Bespoke-MiniCheck-7B (Linux only)
pip install "minicheck[llm] @ git+https://github.com/Liyan06/MiniCheck.git@main"Our MiniCheck models are available on HuggingFace 🤗 More model details can be found from this collection.
[!IMPORTANT] MiniCheck(document, sentence) -> [0, 1] is a sentence-level fact-checking model. In order to fact-check a multi-sentence claim, the claim should first be broken up into sentences to achieve optimal performance.
Below is a simple use case of MiniCheck. MiniCheck models will be automatically downloaded from Huggingface for the first time and cached in the specified directory.
from minicheck.minicheck import MiniCheck
import os
os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "0"
doc = "A group of students gather in the school library to study for their upcoming final exams."
claim_1 = "The students are preparing for an examination."
claim_2 = "The students are on vacation."
# model_name can be one of the followings:
# ['roberta-large', 'deberta-v3-large', 'flan-t5-large', 'Bespoke-MiniCheck-7B']
# MiniCheck-Flan-T5-Large (770M) is the best fack-checking model
# with size < 1B and reaches GPT-4 performance.
scorer = MiniCheck(model_name='flan-t5-large', cache_dir='./ckpts')
pred_label, raw_prob, _, _ = scorer.score(docs=[doc, doc], claims=[claim_1, claim_2])
print(pred_label) # [1, 0]
print(raw_prob) # [0.9805923700332642, 0.007121330592781305]
# Alternatively, you can use our Bespoke-MiniCheck-7B model (7B) for evaluation.
# Bespoke-MiniCheck-7B is the most performant fact-checking model
# in the MiniCheck series AND is the current SOTA regardless of size.
# It's also commercially useable!
# For commercial licensing, please contact [email protected]
scorer = MiniCheck(model_name='Bespoke-MiniCheck-7B', enable_prefix_caching=False, cache_dir='./ckpts')
pred_label, raw_prob, _, _ = scorer.score(docs=[doc, doc], claims=[claim_1, claim_2])
print(pred_label) # [1, 0]
print(raw_prob) # [0.9840446675150499, 0.010986349594852094]A detailed walkthrough of the evaluation process on LLM-Aggrefact and replication of the results is available in this notebook: benchmark_evaluation_demo.ipynb.
Automatic Prefix Caching (More Info)
Automatic Prefix Caching (APC in short) caches the KV cache of existing queries, so that a new query can directly reuse the KV cache if it shares the same prefix with one of the existing queries, allowing the new query to skip the computation of the shared part.
If you use the same document to fact-check different claims, APC allows vLLM to process the document only once, and all future claims can avoid recomputing this document by reusing its KV cache. This allows vLLM to serve future grounded fact-checking with much higher throughput and much lower latency.
To enable automatic prefix caching for Bespoke-MiniCheck-7B, simply set enable_prefix_caching=True when initializing the MiniCheck model (no other changes are needed).:
scorer = MiniCheck(model_name='Bespoke-MiniCheck-7B', enable_prefix_caching=True, cache_dir='./ckpts')For some datasets in LLM-AggreFact, the grounded documents are repeatedly used, such as TofuEval-MediaS/MeetB, LFQA, and RAGTruth. Hence, we test the throughput of MiniCheck before and after APC is enabled. Results show that the inference time on the 29K test set is 30 mins and 55 mins with and without APC enabled, respectively, on a single NVIDIA A6000 (48 GB VRAM).
We compare the benchmark performance of Bespoke-MiniCheck-7B with APC enabled (top) and disabled (bottom). Performance varies slightly across different datasets, but the overall average is the same. Please decide whether to enable APC based on your specific use case.
Code for generating synthetic data (both C2D and D2C methods) is available in the synthetic_data_gen directory.
Our 14K synthetic data (7K C2D and 7K D2C) used for model training (MiniCheck-RoBERTa/DeBERTA/Flan-T5) is available on HuggingFace 🤗 and can be found here.
If you found our work useful, please consider citing our work.
@InProceedings{tang-etal-2024-minicheck,
title = {MiniCheck: Efficient Fact-Checking of LLMs on Grounding Documents},
author = {Liyan Tang and Philippe Laban and Greg Durrett},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 2024 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing},
year = {2024},
publisher = {Association for Computational Linguistics},
url = {https://arxiv.org/pdf/2404.10774}
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for MiniCheck
Similar Open Source Tools

MiniCheck
MiniCheck is an efficient fact-checking tool designed to verify claims against grounding documents using large language models. It provides a sentence-level fact-checking model that can be used to evaluate the consistency of claims with the provided documents. MiniCheck offers different models, including Bespoke-MiniCheck-7B, which is the state-of-the-art and commercially usable. The tool enables users to fact-check multi-sentence claims by breaking them down into individual sentences for optimal performance. It also supports automatic prefix caching for faster inference when repeatedly fact-checking the same document with different claims.
kafka-ml
Kafka-ML is a framework designed to manage the pipeline of Tensorflow/Keras and PyTorch machine learning models on Kubernetes. It enables the design, training, and inference of ML models with datasets fed through Apache Kafka, connecting them directly to data streams like those from IoT devices. The Web UI allows easy definition of ML models without external libraries, catering to both experts and non-experts in ML/AI.
NineRec
NineRec is a benchmark dataset suite for evaluating transferable recommendation models. It provides datasets for pre-training and transfer learning in recommender systems, focusing on multimodal and foundation model tasks. The dataset includes user-item interactions, item texts in multiple languages, item URLs, and raw images. Researchers can use NineRec to develop more effective and efficient methods for pre-training recommendation models beyond end-to-end training. The dataset is accompanied by code for dataset preparation, training, and testing in PyTorch environment.

Trace
Trace is a new AutoDiff-like tool for training AI systems end-to-end with general feedback. It generalizes the back-propagation algorithm by capturing and propagating an AI system's execution trace. Implemented as a PyTorch-like Python library, users can write Python code directly and use Trace primitives to optimize certain parts, similar to training neural networks.
CogAgent
CogAgent is an advanced intelligent agent model designed for automating operations on graphical interfaces across various computing devices. It supports platforms like Windows, macOS, and Android, enabling users to issue commands, capture device screenshots, and perform automated operations. The model requires a minimum of 29GB of GPU memory for inference at BF16 precision and offers capabilities for executing tasks like sending Christmas greetings and sending emails. Users can interact with the model by providing task descriptions, platform specifications, and desired output formats.
llms
The 'llms' repository is a comprehensive guide on Large Language Models (LLMs), covering topics such as language modeling, applications of LLMs, statistical language modeling, neural language models, conditional language models, evaluation methods, transformer-based language models, practical LLMs like GPT and BERT, prompt engineering, fine-tuning LLMs, retrieval augmented generation, AI agents, and LLMs for computer vision. The repository provides detailed explanations, examples, and tools for working with LLMs.
MME-RealWorld
MME-RealWorld is a benchmark designed to address real-world applications with practical relevance, featuring 13,366 high-resolution images and 29,429 annotations across 43 tasks. It aims to provide substantial recognition challenges and overcome common barriers in existing Multimodal Large Language Model benchmarks, such as small data scale, restricted data quality, and insufficient task difficulty. The dataset offers advantages in data scale, data quality, task difficulty, and real-world utility compared to existing benchmarks. It also includes a Chinese version with additional images and QA pairs focused on Chinese scenarios.
storm
STORM is a LLM system that writes Wikipedia-like articles from scratch based on Internet search. While the system cannot produce publication-ready articles that often require a significant number of edits, experienced Wikipedia editors have found it helpful in their pre-writing stage. **Try out our [live research preview](https://storm.genie.stanford.edu/) to see how STORM can help your knowledge exploration journey and please provide feedback to help us improve the system 🙏!**
gepa
GEPA (Genetic-Pareto) is a framework for optimizing arbitrary systems composed of text components like AI prompts, code snippets, or textual specs against any evaluation metric. It employs LLMs to reflect on system behavior, using feedback from execution and evaluation traces to drive targeted improvements. Through iterative mutation, reflection, and Pareto-aware candidate selection, GEPA evolves robust, high-performing variants with minimal evaluations, co-evolving multiple components in modular systems for domain-specific gains. The repository provides the official implementation of the GEPA algorithm as proposed in the paper titled 'GEPA: Reflective Prompt Evolution Can Outperform Reinforcement Learning'.

zshot
Zshot is a highly customizable framework for performing Zero and Few shot named entity and relationships recognition. It can be used for mentions extraction, wikification, zero and few shot named entity recognition, zero and few shot named relationship recognition, and visualization of zero-shot NER and RE extraction. The framework consists of two main components: the mentions extractor and the linker. There are multiple mentions extractors and linkers available, each serving a specific purpose. Zshot also includes a relations extractor and a knowledge extractor for extracting relations among entities and performing entity classification. The tool requires Python 3.6+ and dependencies like spacy, torch, transformers, evaluate, and datasets for evaluation over datasets like OntoNotes. Optional dependencies include flair and blink for additional functionalities. Zshot provides examples, tutorials, and evaluation methods to assess the performance of the components.
LongBench
LongBench v2 is a benchmark designed to assess the ability of large language models (LLMs) to handle long-context problems requiring deep understanding and reasoning across various real-world multitasks. It consists of 503 challenging multiple-choice questions with contexts ranging from 8k to 2M words, covering six major task categories. The dataset is collected from nearly 100 highly educated individuals with diverse professional backgrounds and is designed to be challenging even for human experts. The evaluation results highlight the importance of enhanced reasoning ability and scaling inference-time compute to tackle the long-context challenges in LongBench v2.
oasis
OASIS is a scalable, open-source social media simulator that integrates large language models with rule-based agents to realistically mimic the behavior of up to one million users on platforms like Twitter and Reddit. It facilitates the study of complex social phenomena such as information spread, group polarization, and herd behavior, offering a versatile tool for exploring diverse social dynamics and user interactions in digital environments. With features like scalability, dynamic environments, diverse action spaces, and integrated recommendation systems, OASIS provides a comprehensive platform for simulating social media interactions at a large scale.
paper-qa
PaperQA is a minimal package for question and answering from PDFs or text files, providing very good answers with in-text citations. It uses OpenAI Embeddings to embed and search documents, and includes a process of embedding docs, queries, searching for top passages, creating summaries, using an LLM to re-score and select relevant summaries, putting summaries into prompt, and generating answers. The tool can be used to answer specific questions related to scientific research by leveraging citations and relevant passages from documents.
llmware
LLMWare is a framework for quickly developing LLM-based applications including Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) and Multi-Step Orchestration of Agent Workflows. This project provides a comprehensive set of tools that anyone can use - from a beginner to the most sophisticated AI developer - to rapidly build industrial-grade, knowledge-based enterprise LLM applications. Our specific focus is on making it easy to integrate open source small specialized models and connecting enterprise knowledge safely and securely.

llm-reasoners
LLM Reasoners is a library that enables LLMs to conduct complex reasoning, with advanced reasoning algorithms. It approaches multi-step reasoning as planning and searches for the optimal reasoning chain, which achieves the best balance of exploration vs exploitation with the idea of "World Model" and "Reward". Given any reasoning problem, simply define the reward function and an optional world model (explained below), and let LLM reasoners take care of the rest, including Reasoning Algorithms, Visualization, LLM calling, and more!
AIW
AIW is a code base for experiments and raw data related to Alice in Wonderland, showcasing complete reasoning breakdown in state-of-the-art large language models. Users can collect experiments data using LiteLLM and TogetherAI, and plot the data using provided scripts. The tool allows for executing experiments over LiteLLM and lmsys, with options for different prompt types and AIW variations. The project also includes acknowledgments and a citation for reference.
For similar tasks

MiniCheck
MiniCheck is an efficient fact-checking tool designed to verify claims against grounding documents using large language models. It provides a sentence-level fact-checking model that can be used to evaluate the consistency of claims with the provided documents. MiniCheck offers different models, including Bespoke-MiniCheck-7B, which is the state-of-the-art and commercially usable. The tool enables users to fact-check multi-sentence claims by breaking them down into individual sentences for optimal performance. It also supports automatic prefix caching for faster inference when repeatedly fact-checking the same document with different claims.
OpenFactVerification
Loki is an open-source tool designed to automate the process of verifying the factuality of information. It provides a comprehensive pipeline for dissecting long texts into individual claims, assessing their worthiness for verification, generating queries for evidence search, crawling for evidence, and ultimately verifying the claims. This tool is especially useful for journalists, researchers, and anyone interested in the factuality of information.
awesome-llm-attributions
This repository focuses on unraveling the sources that large language models tap into for attribution or citation. It delves into the origins of facts, their utilization by the models, the efficacy of attribution methodologies, and challenges tied to ambiguous knowledge reservoirs, biases, and pitfalls of excessive attribution.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

agentcloud
AgentCloud is an open-source platform that enables companies to build and deploy private LLM chat apps, empowering teams to securely interact with their data. It comprises three main components: Agent Backend, Webapp, and Vector Proxy. To run this project locally, clone the repository, install Docker, and start the services. The project is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License, version 3 only. Contributions and feedback are welcome from the community.

oss-fuzz-gen
This framework generates fuzz targets for real-world `C`/`C++` projects with various Large Language Models (LLM) and benchmarks them via the `OSS-Fuzz` platform. It manages to successfully leverage LLMs to generate valid fuzz targets (which generate non-zero coverage increase) for 160 C/C++ projects. The maximum line coverage increase is 29% from the existing human-written targets.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement
The Azure-Analytics-and-AI-Engagement repository provides packaged Industry Scenario DREAM Demos with ARM templates (Containing a demo web application, Power BI reports, Synapse resources, AML Notebooks etc.) that can be deployed in a customer’s subscription using the CAPE tool within a matter of few hours. Partners can also deploy DREAM Demos in their own subscriptions using DPoC.


