llmblueprint
[ICLR 2024] Official code for the paper "LLM Blueprint: Enabling Text-to-Image Generation with Complex and Detailed Prompts"
Stars: 53
LLM Blueprint is an official implementation of a paper that enables text-to-image generation with complex and detailed prompts. It leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to extract critical components from text prompts, including bounding box coordinates for foreground objects, detailed textual descriptions for individual objects, and a succinct background context. The tool operates in two phases: Global Scene Generation creates an initial scene using object layouts and background context, and an Iterative Refinement Scheme refines box-level content to align with textual descriptions, ensuring consistency and improving recall compared to baseline diffusion models.
README:
Visit our project page
Hanan Gani1, Shariq Farooq Bhat2, Muzammal Naseer1, Salman Khan1,3, Peter Wonka2
1MBZUAI 2KAUST 3Australian National University
Official implementation of the paper "LLM Blueprint: Enabling Text-to-Image Generation with Complex and Detailed Prompts".
- Updates
- Highlights
- Main Contributions
- Installation
- Run LLMBlueprint
- Results
- Citation
- Contact
- Acknowledgements
- Code is released. [Feb 12, 2024]
- Our paper is accepted at ICLR 2024 [Jan 15, 2024]
Abstract: Diffusion-based generative models have significantly advanced text-to-image generation but encounter challenges when processing lengthy and intricate text prompts describing complex scenes with multiple objects. While excelling in generating images from short, single-object descriptions, these models often struggle to faithfully capture all the nuanced details within longer and more elaborate textual inputs. In response, we present a novel approach leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) to extract critical components from text prompts, including bounding box coordinates for foreground objects, detailed textual descriptions for individual objects, and a succinct background context. These components form the foundation of our layout-to-image generation model, which operates in two phases. The initial Global Scene Generation utilizes object layouts and background context to create an initial scene but often falls short in faithfully representing object characteristics as specified in the prompts. To address this limitation, we introduce an Iterative Refinement Scheme that iteratively evaluates and refines box-level content to align them with their textual descriptions, recomposing objects as needed to ensure consistency. Our evaluation on complex prompts featuring multiple objects demonstrates a substantial improvement in recall compared to baseline diffusion models. This is further validated by a user study, underscoring the efficacy of our approach in generating coherent and detailed scenes from intricate textual inputs.
- Scene Blueprints: we present a novel approach leveraging Large Language Models (LLMs) to extract critical components from text prompts, including bounding box coordinates for foreground objects, detailed textual descriptions for individual objects, and a succinct background context. Utilizing bounding
- Global Scene Generation: Utilzing the bounding box layout and genralized background prompt, we generate an initial image using Layout-to-Image generator.
- Iterative Refinement Scheme : Given the initial image, our proposed refinement mechanism iteratively evaluates and refines the box-level content of each object to align them with their textual descriptions, recomposing objects as needed to ensure consistency.
This codebase is tested on Ubuntu 20.04.2 LTS with python 3.8. Follow the below steps to create environment and install dependencies.
# Create a conda environment
conda create -n llmblueprint python==3.8
# Activate the environment
conda activate llmblueprint
#Install torch
conda install pytorch==2.0.0 torchvision==0.15.0 torchaudio==2.0.0 pytorch-cuda=11.7 -c pytorch -c nvidia
# Install requirements
pip install -r requirements.txt
# Additionally do this step at the end
python -m spacy download en_core_web_mdDownload the pretrained weights of composition model from here and provide its path in yaml files placed inside configs folder.
python main.py --config configs/livingroom_1.yamlThe hyperparameters and input arguments can be modified inside yaml files. The generated results will be saved in ./outputs folder.
Should you have any questions, please contact at [email protected]
If you use our work, please consider citing:
@inproceedings{gani2024llm,
title={{LLM} Blueprint: Enabling Text-to-Image Generation with Complex and Detailed Prompts},
author={Hanan Gani and Shariq Farooq Bhat and Muzammal Naseer and Salman Khan and Peter Wonka},
booktitle={The Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations},
year={2024},
url={https://openreview.net/forum?id=mNYF0IHbRy}
}Our code is built on the repositories of LLM Grounded Diffusion and Paint by Example. We thank them for their open-source implementation and instructions.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for llmblueprint
Similar Open Source Tools

llmblueprint
LLM Blueprint is an official implementation of a paper that enables text-to-image generation with complex and detailed prompts. It leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to extract critical components from text prompts, including bounding box coordinates for foreground objects, detailed textual descriptions for individual objects, and a succinct background context. The tool operates in two phases: Global Scene Generation creates an initial scene using object layouts and background context, and an Iterative Refinement Scheme refines box-level content to align with textual descriptions, ensuring consistency and improving recall compared to baseline diffusion models.
CoLLM
CoLLM is a novel method that integrates collaborative information into Large Language Models (LLMs) for recommendation. It converts recommendation data into language prompts, encodes them with both textual and collaborative information, and uses a two-step tuning method to train the model. The method incorporates user/item ID fields in prompts and employs a conventional collaborative model to generate user/item representations. CoLLM is built upon MiniGPT-4 and utilizes pretrained Vicuna weights for training.
Woodpecker
Woodpecker is a tool designed to correct hallucinations in Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) by introducing a training-free method that picks out and corrects inconsistencies between generated text and image content. It consists of five stages: key concept extraction, question formulation, visual knowledge validation, visual claim generation, and hallucination correction. Woodpecker can be easily integrated with different MLLMs and provides interpretable results by accessing intermediate outputs of the stages. The tool has shown significant improvements in accuracy over baseline models like MiniGPT-4 and mPLUG-Owl.
MemoryBear
MemoryBear is a next-generation AI memory system developed by RedBear AI, focusing on overcoming limitations in knowledge storage and multi-agent collaboration. It empowers AI with human-like memory capabilities, enabling deep knowledge understanding and cognitive collaboration. The system addresses challenges such as knowledge forgetting, memory gaps in multi-agent collaboration, and semantic ambiguity during reasoning. MemoryBear's core features include memory extraction engine, graph storage, hybrid search, memory forgetting engine, self-reflection engine, and FastAPI services. It offers a standardized service architecture for efficient integration and invocation across applications.
aligner
Aligner is a model-agnostic alignment tool designed to efficiently correct responses from large language models. It redistributes initial answers to align with human intentions, improving performance across various LLMs. The tool can be applied with minimal training, enhancing upstream models and reducing hallucination. Aligner's 'copy and correct' method preserves the base structure while enhancing responses. It achieves significant performance improvements in helpfulness, harmlessness, and honesty dimensions, with notable success in boosting Win Rates on evaluation leaderboards.
aligner
Aligner is a model-agnostic alignment tool that learns correctional residuals between preferred and dispreferred answers using a small model. It can be directly applied to various open-source and API-based models with only one-off training, suitable for rapid iteration and improving model performance. Aligner has shown significant improvements in helpfulness, harmlessness, and honesty dimensions across different large language models.
LongRoPE
LongRoPE is a method to extend the context window of large language models (LLMs) beyond 2 million tokens. It identifies and exploits non-uniformities in positional embeddings to enable 8x context extension without fine-tuning. The method utilizes a progressive extension strategy with 256k fine-tuning to reach a 2048k context. It adjusts embeddings for shorter contexts to maintain performance within the original window size. LongRoPE has been shown to be effective in maintaining performance across various tasks from 4k to 2048k context lengths.
Instruct2Act
Instruct2Act is a framework that utilizes Large Language Models to map multi-modal instructions to sequential actions for robotic manipulation tasks. It generates Python programs using the LLM model for perception, planning, and action. The framework leverages foundation models like SAM and CLIP to convert high-level instructions into policy codes, accommodating various instruction modalities and task demands. Instruct2Act has been validated on robotic tasks in tabletop manipulation domains, outperforming learning-based policies in several tasks.
awesome-synthetic-datasets
This repository focuses on organizing resources for building synthetic datasets using large language models. It covers important datasets, libraries, tools, tutorials, and papers related to synthetic data generation. The goal is to provide pragmatic and practical resources for individuals interested in creating synthetic datasets for machine learning applications.
ManipVQA
ManipVQA is a framework that enhances Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) with manipulation-centric knowledge through a Visual Question-Answering (VQA) format. It addresses the deficiency of conventional MLLMs in understanding affordances and physical concepts crucial for manipulation tasks. By infusing robotics-specific knowledge, including tool detection, affordance recognition, and physical concept comprehension, ManipVQA improves the performance of robots in manipulation tasks. The framework involves fine-tuning MLLMs with a curated dataset of interactive objects, enabling robots to understand and execute natural language instructions more effectively.
kdbai-samples
KDB.AI is a time-based vector database that allows developers to build scalable, reliable, and real-time applications by providing advanced search, recommendation, and personalization for Generative AI applications. It supports multiple index types, distance metrics, top-N and metadata filtered retrieval, as well as Python and REST interfaces. The repository contains samples demonstrating various use-cases such as temporal similarity search, document search, image search, recommendation systems, sentiment analysis, and more. KDB.AI integrates with platforms like ChatGPT, Langchain, and LlamaIndex. The setup steps require Unix terminal, Python 3.8+, and pip installed. Users can install necessary Python packages and run Jupyter notebooks to interact with the samples.
bocoel
BoCoEL is a tool that leverages Bayesian Optimization to efficiently evaluate large language models by selecting a subset of the corpus for evaluation. It encodes individual entries into embeddings, uses Bayesian optimization to select queries, retrieves from the corpus, and provides easily managed evaluations. The tool aims to reduce computation costs during evaluation with a dynamic budget, supporting models like GPT2, Pythia, and LLAMA through integration with Hugging Face transformers and datasets. BoCoEL offers a modular design and efficient representation of the corpus to enhance evaluation quality.
db-ally
db-ally is a library for creating natural language interfaces to data sources. It allows developers to outline specific use cases for a large language model (LLM) to handle, detailing the desired data format and the possible operations to fetch this data. db-ally effectively shields the complexity of the underlying data source from the model, presenting only the essential information needed for solving the specific use cases. Instead of generating arbitrary SQL, the model is asked to generate responses in a simplified query language.
Graph-CoT
This repository contains the source code and datasets for Graph Chain-of-Thought: Augmenting Large Language Models by Reasoning on Graphs accepted to ACL 2024. It proposes a framework called Graph Chain-of-thought (Graph-CoT) to enable Language Models to traverse graphs step-by-step for reasoning, interaction, and execution. The motivation is to alleviate hallucination issues in Language Models by augmenting them with structured knowledge sources represented as graphs.
gepa
GEPA (Genetic-Pareto) is a framework for optimizing arbitrary systems composed of text components like AI prompts, code snippets, or textual specs against any evaluation metric. It employs LLMs to reflect on system behavior, using feedback from execution and evaluation traces to drive targeted improvements. Through iterative mutation, reflection, and Pareto-aware candidate selection, GEPA evolves robust, high-performing variants with minimal evaluations, co-evolving multiple components in modular systems for domain-specific gains. The repository provides the official implementation of the GEPA algorithm as proposed in the paper titled 'GEPA: Reflective Prompt Evolution Can Outperform Reinforcement Learning'.
For similar tasks

llmblueprint
LLM Blueprint is an official implementation of a paper that enables text-to-image generation with complex and detailed prompts. It leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to extract critical components from text prompts, including bounding box coordinates for foreground objects, detailed textual descriptions for individual objects, and a succinct background context. The tool operates in two phases: Global Scene Generation creates an initial scene using object layouts and background context, and an Iterative Refinement Scheme refines box-level content to align with textual descriptions, ensuring consistency and improving recall compared to baseline diffusion models.
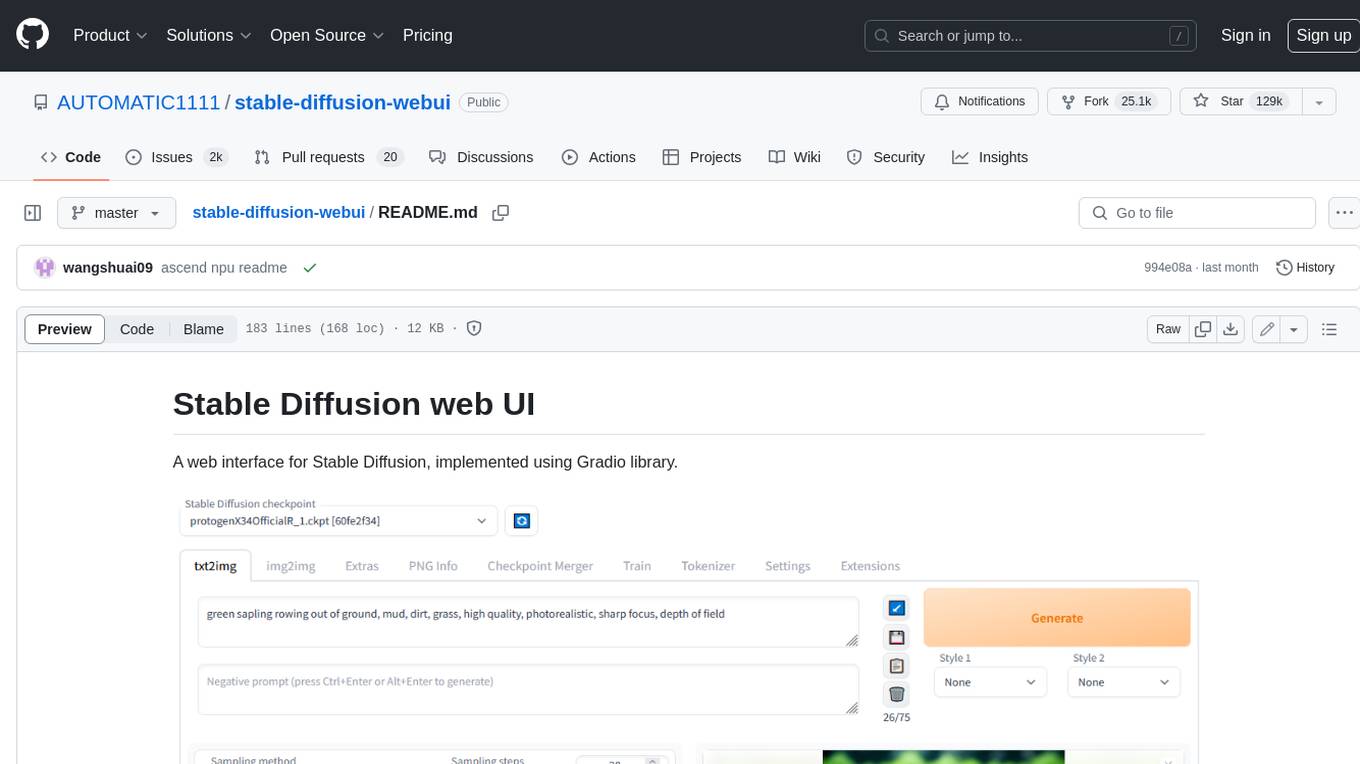
stable-diffusion-webui
Stable Diffusion web UI is a web interface for Stable Diffusion, implemented using Gradio library. It provides a user-friendly interface to access the powerful image generation capabilities of Stable Diffusion. With Stable Diffusion web UI, users can easily generate images from text prompts, edit and refine images using inpainting and outpainting, and explore different artistic styles and techniques. The web UI also includes a range of advanced features such as textual inversion, hypernetworks, and embeddings, allowing users to customize and fine-tune the image generation process. Whether you're an artist, designer, or simply curious about the possibilities of AI-generated art, Stable Diffusion web UI is a valuable tool that empowers you to create stunning and unique images.

GIMP-ML
A.I. for GNU Image Manipulation Program (GIMP-ML) is a repository that provides Python plugins for using computer vision models in GIMP. The code base and models are continuously updated to support newer and more stable functionality. Users can edit images with text, outpaint images, and generate images from text using models like Dalle 2 and Dalle 3. The repository encourages citations using a specific bibtex entry and follows the MIT license for GIMP-ML and the original models.

ClaraVerse
ClaraVerse is a privacy-first AI assistant and agent builder that allows users to chat with AI, create intelligent agents, and turn them into fully functional apps. It operates entirely on open-source models running on the user's device, ensuring data privacy and security. With features like AI assistant, image generation, intelligent agent builder, and image gallery, ClaraVerse offers a versatile platform for AI interaction and app development. Users can install ClaraVerse through Docker, native desktop apps, or the web version, with detailed instructions provided for each option. The tool is designed to empower users with control over their AI stack and leverage community-driven innovations for AI development.
sora-prompt
Sora Prompt Collection is a repository dedicated to inspiring AI-driven video creation with Sora, an AI model that can create realistic and imaginative scenes from text instructions. The repository provides prompt words and video generation tips to help users quickly start using Sora for text-to-video, animation, video editing, image generation, and more. It offers a variety of examples ranging from stylish urban scenes to fantastical creatures in vibrant settings. Users can find prompt examples based on different video styles and modify them as needed.
LLM-Discrete-Tokenization-Survey
The repository contains a comprehensive survey paper on Discrete Tokenization for Multimodal Large Language Models (LLMs). It covers various techniques, applications, and challenges related to discrete tokenization in the context of LLMs. The survey explores the use of vector quantization, product quantization, and other methods for tokenizing different modalities like text, image, audio, video, graph, and more. It also discusses the integration of discrete tokenization with LLMs for tasks such as image generation, speech recognition, recommendation systems, and multimodal understanding and generation.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.