llm-inference-solutions
A collection of all available inference solutions for the LLMs
Stars: 80
A collection of available inference solutions for Large Language Models (LLMs) including high-throughput engines, optimization libraries, deployment toolkits, and deep learning frameworks for production environments.
README:
A collection of all available inference solutions for the LLMs
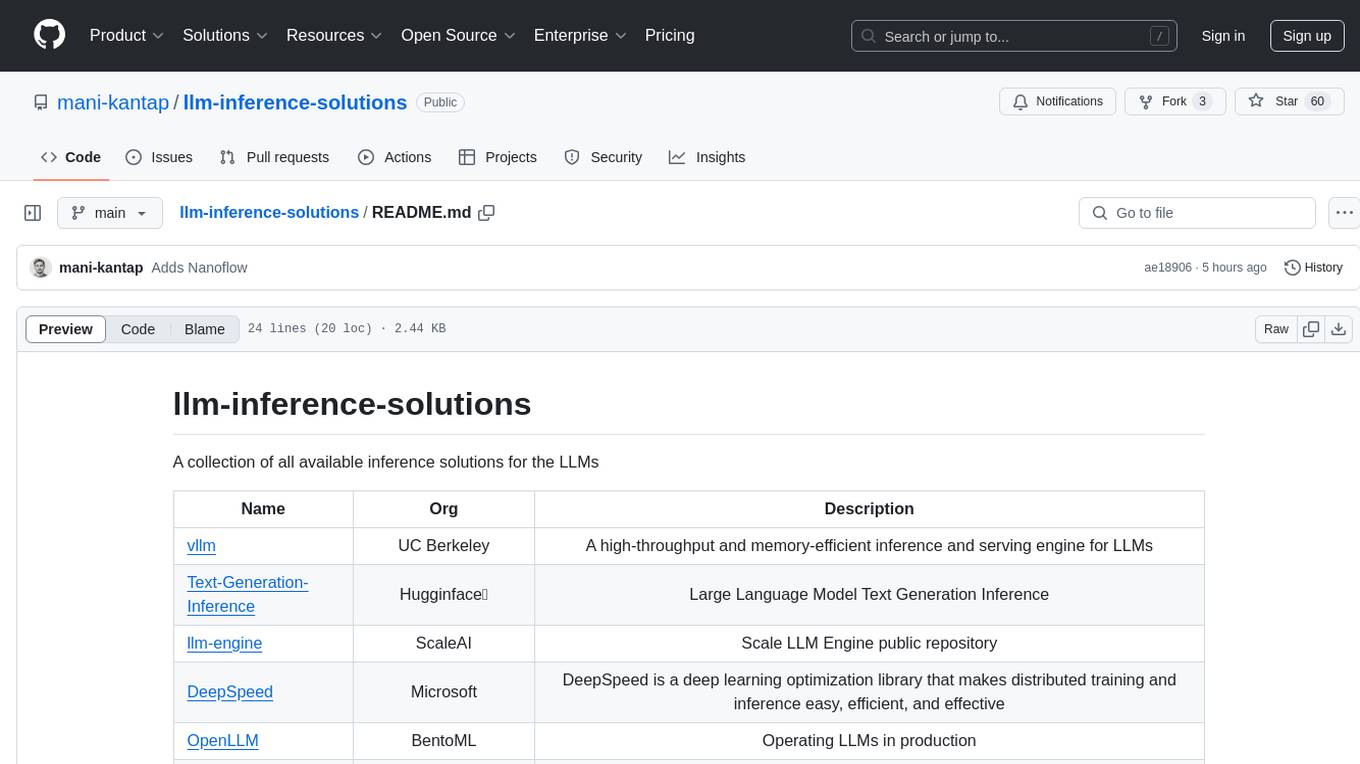
| Name | Organization | Description | Supported Hardware | Key Features | License |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| vLLM | UC Berkeley | High-throughput and memory-efficient inference and serving engine for LLMs. | CPU, GPU | PagedAttention for optimized memory management, high-throughput serving. | Apache 2.0 |
| Text-Generation-Inference | Hugging Face 🤗 | Efficient and scalable text generation inference for LLMs. | CPU, GPU | Multi-model serving, dynamic batching, optimized for transformers. | Apache 2.0 |
| llm-engine | Scale AI | Scale LLM Engine public repository for efficient inference. | CPU, GPU | Scalable deployment, monitoring tools, integration with Scale AI services. | Apache 2.0 |
| DeepSpeed | Microsoft | Deep learning optimization library for easy, efficient, and effective distributed training and inference. | CPU, GPU | ZeRO redundancy optimizer, mixed-precision training, model parallelism. | MIT |
| OpenLLM | BentoML | Operating LLMs in production with ease. | CPU, GPU | Model serving, deployment orchestration, integration with BentoML. | Apache 2.0 |
| LMDeploy | InternLM Team | Toolkit for compressing, deploying, and serving LLMs. | CPU, GPU | Model compression, deployment automation, serving optimization. | Apache 2.0 |
| FlexFlow | CMU, Stanford, UCSD | A distributed deep learning framework. | CPU, GPU, TPU | Automatic parallelization, support for complex models, scalability. | Apache 2.0 |
| CTranslate2 | OpenNMT | Fast inference engine for Transformer models. | CPU, GPU | Int8 quantization, multi-threaded execution, optimized for translation models. | MIT |
| FastChat | lm-sys | Open platform for training, serving, and evaluating large language models; release repo for Vicuna and Chatbot Arena. | CPU, GPU | Chatbot framework, multi-turn conversations, evaluation tools. | Apache 2.0 |
| Triton Inference Server | NVIDIA | Optimized cloud and edge inferencing solution. | CPU, GPU | Model ensemble, dynamic batching, support for multiple frameworks. | BSD-3-Clause |
| Lepton.AI | lepton.ai | Pythonic framework to simplify AI service building. | CPU, GPU | Service orchestration, API generation, scalability. | MIT |
| ScaleLLM | Vectorch | High-performance inference system for LLMs, designed for production environments. | CPU, GPU | Low-latency serving, high throughput, production-ready. | Apache 2.0 |
| Lorax | Predibase | Serve hundreds of fine-tuned LLMs in production for the cost of one. | CPU, GPU | Model multiplexing, cost-efficient serving, scalability. | Apache 2.0 |
| TensorRT-LLM | NVIDIA | Provides users with an easy-to-use Python API to define LLMs and build TensorRT engines. | GPU | TensorRT optimization, high-performance inference, integration with NVIDIA GPUs. | Apache 2.0 |
| mistral.rs | mistral.rs | Blazingly fast LLM inference. | CPU, GPU | Rust-based implementation, performance optimization, lightweight. | MIT |
| NanoFlow | NanoFlow | Throughput-oriented high-performance serving framework for LLMs. | CPU, GPU | High throughput, low latency, optimized for large-scale deployments. | Apache 2.0 |
| LMCache | LMCache | Fast and cost-efficient inference. | CPU, GPU | Caching mechanisms, cost optimization, scalable serving. | Apache 2.0 |
| Litserve | Lightning.AI | Lightning-fast serving engine for AI models; flexible, easy, enterprise-scale. | CPU, GPU | Rapid deployment, flexible architecture, enterprise integration. | Apache 2.0 |
| DeepSeek Inference System Overview | DeepSeek | Higher throughput and lower latency inference system. | CPU, GPU | Optimized performance, low latency, high throughput. | Proprietary |
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for llm-inference-solutions
Similar Open Source Tools

llm-inference-solutions
A collection of available inference solutions for Large Language Models (LLMs) including high-throughput engines, optimization libraries, deployment toolkits, and deep learning frameworks for production environments.
llm-engineer-toolkit
The LLM Engineer Toolkit is a curated repository containing over 120 LLM libraries categorized for various tasks such as training, application development, inference, serving, data extraction, data generation, agents, evaluation, monitoring, prompts, structured outputs, safety, security, embedding models, and other miscellaneous tools. It includes libraries for fine-tuning LLMs, building applications powered by LLMs, serving LLM models, extracting data, generating synthetic data, creating AI agents, evaluating LLM applications, monitoring LLM performance, optimizing prompts, handling structured outputs, ensuring safety and security, embedding models, and more. The toolkit covers a wide range of tools and frameworks to streamline the development, deployment, and optimization of large language models.
Telco-AIX
Telco-AIX is a collaborative experimental workspace focusing on data-driven decision-making through open-source AI capabilities and open datasets. It covers various domains such as revenue management, service quality, network operations, sustainability, security, smart infrastructure, IoT security, advanced AI, customer experience, anomaly detection, connectivity, network operations, IT management, and agentic Telco-AI. The repository provides models, datasets, and published works related to telecommunications AI applications.
HighPerfLLMs2024
High Performance LLMs 2024 is a comprehensive course focused on building a high-performance Large Language Model (LLM) from scratch using Jax. The course covers various aspects such as training, inference, roofline analysis, compilation, sharding, profiling, and optimization techniques. Participants will gain a deep understanding of Jax and learn how to design high-performance computing systems that operate close to their physical limits.
redis-ai-resources
A curated repository of code recipes, demos, and resources for basic and advanced Redis use cases in the AI ecosystem. It includes demos for ArxivChatGuru, Redis VSS, Vertex AI & Redis, Agentic RAG, ArXiv Search, and Product Search. Recipes cover topics like Getting started with RAG, Semantic Cache, Advanced RAG, and Recommendation systems. The repository also provides integrations/tools like RedisVL, AWS Bedrock, LangChain Python, LangChain JS, LlamaIndex, Semantic Kernel, RelevanceAI, and DocArray. Additional content includes blog posts, talks, reviews, and documentation related to Vector Similarity Search, AI-Powered Document Search, Vector Databases, Real-Time Product Recommendations, and more. Benchmarks compare Redis against other Vector Databases and ANN benchmarks. Documentation includes QuickStart guides, official literature for Vector Similarity Search, Redis-py client library docs, Redis Stack documentation, and Redis client list.
willow-inference-server
Willow Inference Server (WIS) is a highly optimized language inference server implementation focused on enabling performant, cost-effective self-hosting of state-of-the-art models for speech and language tasks. It supports ASR and TTS tasks, runs on CUDA with low-end device support, and offers various transport options like REST, WebRTC, and Web Sockets. WIS is memory optimized, leverages CTranslate2 for Whisper support, and enables custom TTS voices. The server automatically detects available CUDA VRAM and optimizes functionality accordingly. Users can programmatically select Whisper models and parameters for each request to balance speed and quality.
awesome-generative-ai-data-scientist
A curated list of 50+ resources to help you become a Generative AI Data Scientist. This repository includes resources on building GenAI applications with Large Language Models (LLMs), and deploying LLMs and GenAI with Cloud-based solutions.
llm-compression-intelligence
This repository presents the findings of the paper "Compression Represents Intelligence Linearly". The study reveals a strong linear correlation between the intelligence of LLMs, as measured by benchmark scores, and their ability to compress external text corpora. Compression efficiency, derived from raw text corpora, serves as a reliable evaluation metric that is linearly associated with model capabilities. The repository includes the compression corpora used in the paper, code for computing compression efficiency, and data collection and processing pipelines.
recommenders
Recommenders is a project under the Linux Foundation of AI and Data that assists researchers, developers, and enthusiasts in prototyping, experimenting with, and bringing to production a range of classic and state-of-the-art recommendation systems. The repository contains examples and best practices for building recommendation systems, provided as Jupyter notebooks. It covers tasks such as preparing data, building models using various recommendation algorithms, evaluating algorithms, tuning hyperparameters, and operationalizing models in a production environment on Azure. The project provides utilities to support common tasks like loading datasets, evaluating model outputs, and splitting training/test data. It includes implementations of state-of-the-art algorithms for self-study and customization in applications.
GenAIComps
GenAIComps is an initiative aimed at building enterprise-grade Generative AI applications using a microservice architecture. It simplifies the scaling and deployment process for production, abstracting away infrastructure complexities. GenAIComps provides a suite of containerized microservices that can be assembled into a mega-service tailored for real-world Enterprise AI applications. The modular approach of microservices allows for independent development, deployment, and scaling of individual components, promoting modularity, flexibility, and scalability. The mega-service orchestrates multiple microservices to deliver comprehensive solutions, encapsulating complex business logic and workflow orchestration. The gateway serves as the interface for users to access the mega-service, providing customized access based on user requirements.
LLM-PowerHouse-A-Curated-Guide-for-Large-Language-Models-with-Custom-Training-and-Inferencing
LLM-PowerHouse is a comprehensive and curated guide designed to empower developers, researchers, and enthusiasts to harness the true capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) and build intelligent applications that push the boundaries of natural language understanding. This GitHub repository provides in-depth articles, codebase mastery, LLM PlayLab, and resources for cost analysis and network visualization. It covers various aspects of LLMs, including NLP, models, training, evaluation metrics, open LLMs, and more. The repository also includes a collection of code examples and tutorials to help users build and deploy LLM-based applications.
learnopencv
LearnOpenCV is a repository containing code for Computer Vision, Deep learning, and AI research articles shared on the blog LearnOpenCV.com. It serves as a resource for individuals looking to enhance their expertise in AI through various courses offered by OpenCV. The repository includes a wide range of topics such as image inpainting, instance segmentation, robotics, deep learning models, and more, providing practical implementations and code examples for readers to explore and learn from.
tiny-llm
tiny-llm is a course on LLM serving using MLX for system engineers. The codebase is focused on MLX array/matrix APIs to build model serving infrastructure from scratch and explore optimizations. The goal is to efficiently serve large language models like Qwen2 models. The course covers implementing components in Python, building an inference system similar to vLLM, and advanced topics on model interaction. The tool aims to provide hands-on experience in serving language models without high-level neural network APIs.
awesome-llm-planning-reasoning
The 'Awesome LLMs Planning Reasoning' repository is a curated collection focusing on exploring the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) in planning and reasoning tasks. It includes research papers, code repositories, and benchmarks that delve into innovative techniques, reasoning limitations, and standardized evaluations related to LLMs' performance in complex cognitive tasks. The repository serves as a comprehensive resource for researchers, developers, and enthusiasts interested in understanding the advancements and challenges in leveraging LLMs for planning and reasoning in real-world scenarios.
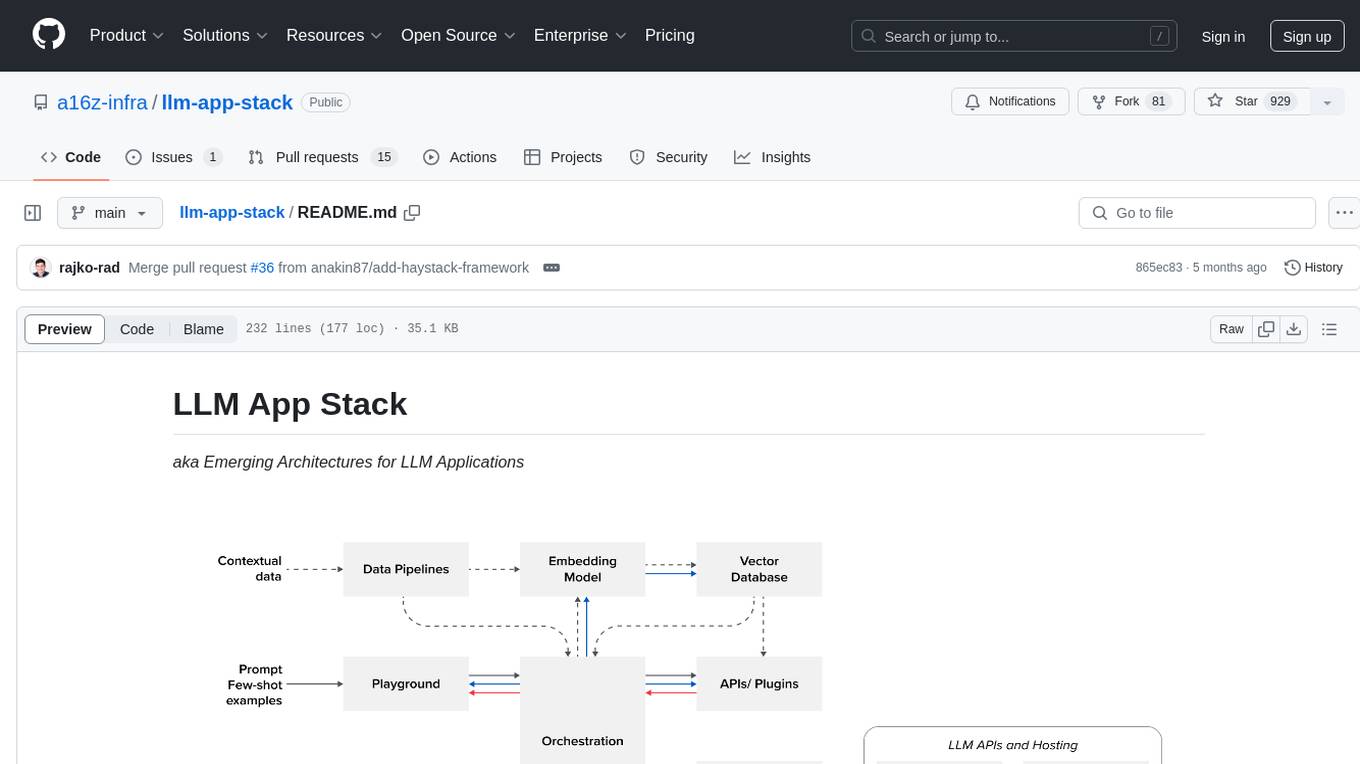
llm-app-stack
LLM App Stack, also known as Emerging Architectures for LLM Applications, is a comprehensive list of available tools, projects, and vendors at each layer of the LLM app stack. It covers various categories such as Data Pipelines, Embedding Models, Vector Databases, Playgrounds, Orchestrators, APIs/Plugins, LLM Caches, Logging/Monitoring/Eval, Validators, LLM APIs (proprietary and open source), App Hosting Platforms, Cloud Providers, and Opinionated Clouds. The repository aims to provide a detailed overview of tools and projects for building, deploying, and maintaining enterprise data solutions, AI models, and applications.
For similar tasks
aimet
AIMET is a library that provides advanced model quantization and compression techniques for trained neural network models. It provides features that have been proven to improve run-time performance of deep learning neural network models with lower compute and memory requirements and minimal impact to task accuracy. AIMET is designed to work with PyTorch, TensorFlow and ONNX models. We also host the AIMET Model Zoo - a collection of popular neural network models optimized for 8-bit inference. We also provide recipes for users to quantize floating point models using AIMET.
hqq
HQQ is a fast and accurate model quantizer that skips the need for calibration data. It's super simple to implement (just a few lines of code for the optimizer). It can crunch through quantizing the Llama2-70B model in only 4 minutes! 🚀
llm-resource
llm-resource is a comprehensive collection of high-quality resources for Large Language Models (LLM). It covers various aspects of LLM including algorithms, training, fine-tuning, alignment, inference, data engineering, compression, evaluation, prompt engineering, AI frameworks, AI basics, AI infrastructure, AI compilers, LLM application development, LLM operations, AI systems, and practical implementations. The repository aims to gather and share valuable resources related to LLM for the community to benefit from.
llmc
llmc is an off-the-shell tool designed for compressing LLM, leveraging state-of-the-art compression algorithms to enhance efficiency and reduce model size without compromising performance. It provides users with the ability to quantize LLMs, choose from various compression algorithms, export transformed models for further optimization, and directly infer compressed models with a shallow memory footprint. The tool supports a range of model types and quantization algorithms, with ongoing development to include pruning techniques. Users can design their configurations for quantization and evaluation, with documentation and examples planned for future updates. llmc is a valuable resource for researchers working on post-training quantization of large language models.
Awesome-Efficient-LLM
Awesome-Efficient-LLM is a curated list focusing on efficient large language models. It includes topics such as knowledge distillation, network pruning, quantization, inference acceleration, efficient MOE, efficient architecture of LLM, KV cache compression, text compression, low-rank decomposition, hardware/system, tuning, and survey. The repository provides a collection of papers and projects related to improving the efficiency of large language models through various techniques like sparsity, quantization, and compression.
TensorRT-Model-Optimizer
The NVIDIA TensorRT Model Optimizer is a library designed to quantize and compress deep learning models for optimized inference on GPUs. It offers state-of-the-art model optimization techniques including quantization and sparsity to reduce inference costs for generative AI models. Users can easily stack different optimization techniques to produce quantized checkpoints from torch or ONNX models. The quantized checkpoints are ready for deployment in inference frameworks like TensorRT-LLM or TensorRT, with planned integrations for NVIDIA NeMo and Megatron-LM. The tool also supports 8-bit quantization with Stable Diffusion for enterprise users on NVIDIA NIM. Model Optimizer is available for free on NVIDIA PyPI, and this repository serves as a platform for sharing examples, GPU-optimized recipes, and collecting community feedback.
Awesome_LLM_System-PaperList
Since the emergence of chatGPT in 2022, the acceleration of Large Language Model has become increasingly important. Here is a list of papers on LLMs inference and serving.
llm-compressor
llm-compressor is an easy-to-use library for optimizing models for deployment with vllm. It provides a comprehensive set of quantization algorithms, seamless integration with Hugging Face models and repositories, and supports mixed precision, activation quantization, and sparsity. Supported algorithms include PTQ, GPTQ, SmoothQuant, and SparseGPT. Installation can be done via git clone and local pip install. Compression can be easily applied by selecting an algorithm and calling the oneshot API. The library also offers end-to-end examples for model compression. Contributions to the code, examples, integrations, and documentation are appreciated.
For similar jobs

weave
Weave is a toolkit for developing Generative AI applications, built by Weights & Biases. With Weave, you can log and debug language model inputs, outputs, and traces; build rigorous, apples-to-apples evaluations for language model use cases; and organize all the information generated across the LLM workflow, from experimentation to evaluations to production. Weave aims to bring rigor, best-practices, and composability to the inherently experimental process of developing Generative AI software, without introducing cognitive overhead.

LLMStack
LLMStack is a no-code platform for building generative AI agents, workflows, and chatbots. It allows users to connect their own data, internal tools, and GPT-powered models without any coding experience. LLMStack can be deployed to the cloud or on-premise and can be accessed via HTTP API or triggered from Slack or Discord.

VisionCraft
The VisionCraft API is a free API for using over 100 different AI models. From images to sound.

kaito
Kaito is an operator that automates the AI/ML inference model deployment in a Kubernetes cluster. It manages large model files using container images, avoids tuning deployment parameters to fit GPU hardware by providing preset configurations, auto-provisions GPU nodes based on model requirements, and hosts large model images in the public Microsoft Container Registry (MCR) if the license allows. Using Kaito, the workflow of onboarding large AI inference models in Kubernetes is largely simplified.

PyRIT
PyRIT is an open access automation framework designed to empower security professionals and ML engineers to red team foundation models and their applications. It automates AI Red Teaming tasks to allow operators to focus on more complicated and time-consuming tasks and can also identify security harms such as misuse (e.g., malware generation, jailbreaking), and privacy harms (e.g., identity theft). The goal is to allow researchers to have a baseline of how well their model and entire inference pipeline is doing against different harm categories and to be able to compare that baseline to future iterations of their model. This allows them to have empirical data on how well their model is doing today, and detect any degradation of performance based on future improvements.

tabby
Tabby is a self-hosted AI coding assistant, offering an open-source and on-premises alternative to GitHub Copilot. It boasts several key features: * Self-contained, with no need for a DBMS or cloud service. * OpenAPI interface, easy to integrate with existing infrastructure (e.g Cloud IDE). * Supports consumer-grade GPUs.

spear
SPEAR (Simulator for Photorealistic Embodied AI Research) is a powerful tool for training embodied agents. It features 300 unique virtual indoor environments with 2,566 unique rooms and 17,234 unique objects that can be manipulated individually. Each environment is designed by a professional artist and features detailed geometry, photorealistic materials, and a unique floor plan and object layout. SPEAR is implemented as Unreal Engine assets and provides an OpenAI Gym interface for interacting with the environments via Python.

Magick
Magick is a groundbreaking visual AIDE (Artificial Intelligence Development Environment) for no-code data pipelines and multimodal agents. Magick can connect to other services and comes with nodes and templates well-suited for intelligent agents, chatbots, complex reasoning systems and realistic characters.