
aira-dojo
AIRA-dojo: a framework for developing and evaluating AI research agents
Stars: 94
aira-dojo is a scalable and customizable framework for AI research agents, designed to accelerate hill-climbing on research capabilities toward a fully automated AI research scientist. The framework provides a general abstraction for tasks and agents, implements the MLE-bench task, and includes state-of-the-art agents. It features an isolated code execution environment that integrates smoothly with job schedulers like Slurm, enabling large-scale experiments and rapid iteration across a portfolio of tasks and solvers.
README:
aira-dojo is a scalable and customizable framework for AI research agents, designed to accelerate hill-climbing on research capabilities toward a fully automated AI research scientist.
The framework provides a general abstraction for tasks and agents, implements the MLE-bench task, and includes the state-of-the-art agents introduced in our paper, “AI Research Agents for Machine Learning: Search, Exploration, and Generalization in MLE-bench.” Additionally, it features an isolated code execution environment that integrates smoothly with job schedulers like Slurm.
The framework enabled 1,000 agents to run in parallel for up to 120 hours, uncovering valuable insights and results detailed in the paper.
The following documentation is available to help you get started with aira-dojo:
- Installation Guide - Detailed setup instructions
- Project Structure - Overview of the codebase organization
- Task Development Guide - How to create new tasks
- Solver Development Guide - How to implement new solvers
-
Running Experiments - How to run experiments with
aira-dojo - Building Superimage - Instructions for building the superimage container
Task: A specific problem or challenge that the AI agent (solver) is designed to solve. Each task has a defined execution environment, solver action space, and evaluation function.
Solver: An AI agent that attempts to solve a given task. A solver is composed of:
- Operators: Functions that are used to generate new solutions (e.g., a call to an LLM with a specific prompt and some context).
- Search Policy: The method used to explore the solution space and orchestrate the execution of operators (e.g., greedy search, evolutionary search, Monte Carlo Tree Search)
Run: A single execution in which a solver (an AI agent) attempts to solve a given task.
Runner: A component used to parallelize runs. It manages and orchestrates multiple solver-task pairs concurrently, allowing large-scale experiments and rapid iteration across a portfolio of tasks and solvers.
The diagram below gives a high-level overview of the key components of the framework and how they interact.
git clone https://github.com/facebookresearch/aira-dojo
cd aira-dojoconda env create -f environment.yaml
conda activate aira-dojopip install -e .cp .env_default .env
# Edit .env with your specific configurationNote that the .env file is ignored by git to avoid accidentally pushing tokens to github.
If you are using different endpoints, you should change them accordingly in dojo/configs/run/solver/client
Examples:
-
Changing Azure endpoint for 4o:
Go to
src/dojo/configs/run/solver/client/litellm_4o.yamland change thebase_urlto your Azure endpoint:... base_url: https://azure-services-endpoint-here.azure-api.net #<---- Set to your Azure endpoint ...
-
Changing to openai endpoint for 4o:
Go to
src/dojo/configs/run/solver/client/litellm_4o.yamland change thebase_urlanduse_azure_clientto the following:... base_url: null # litellm will use the openai endpoint by default use_azure_client: False ...
Finally, in
.env, set your primary key to your openai key:PRIMARY_KEY="sk-..." # <---- Set to your OpenAI key>
Note: To run the examples in the "Example Usage" section of this read me, you must setup the following models:
-
o3: Set thebase_urlinsrc//dojo/configs/solver/client/litellm_o3.yamland set thePRIMARY_KEY_O3in.env. -
gpt-4o: Set thebase_urlinsrc//dojo/configs/solver/client/litellm_4o.yamland set thePRIMARY_KEYin.env.
Follow the steps in docs/BUILD_SUPERIMAGE.md to build your superimage. This is necessary to run tasks that use jupyter as the interpreter.
Follow the steps in src/dojo/tasks/mlebench/README.md to install mle-bench and run your first task.
Log in with the following command:
wandb loginIt will ask you your API key, which you can get by going into "User settings" (click top right of screen) and scrolling down.
# Runs AIRA_GREEDY on a single MLE-bench task
python -m dojo.main_run +_exp=run_example logger.use_wandb=FalseSee the config run_example.yaml for details.
# Runs AIRA_GREEDY on our quick-dev set of MLE-bench tasks
python -m dojo.main_runner_job_array +_exp=runner_example logger.use_wandb=False launcher.debug=TrueSee the config runner_example.yaml for details.
# Runs AIRA_GREEDY on our quick-dev set of MLE-bench tasks
python -m dojo.main_runner_job_array +_exp=runner_multi_example logger.use_wandb=False launcher.debug=TrueSee the config runner_multi_example.yaml for details.
Note: Make you set <<<DEFAULT_SLURM_ACCOUNT>>>, <<<DEFAULT_SLURM_QOS>>>, and <<<DEFAULT_SLURM_PARTITION>>> with your actual Slurm account, QoS, and partition settings in your .env before running these commands
# Runs AIRA_GREEDY on MLE-bench lite tasks
python -m dojo.main_runner_job_array +_exp=mlebench/aide_greedy_o3 logger.use_wandb=False launcher.debug=False
# Runs AIDE_GREEDY on MLE-bench lite tasks
python -m dojo.main_runner_job_array +_exp=mlebench/aira_greedy_o3 logger.use_wandb=False launcher.debug=False
# Runs AIRA_MCTS on MLE-bench lite tasks
python -m dojo.main_runner_job_array +_exp=mlebench/aira_evo_o3 logger.use_wandb=False launcher.debug=False
# Runs AIRA_EVO on MLE-bench lite tasks
python -m dojo.main_runner_job_array +_exp=mlebench/aira_mcts_o3 logger.use_wandb=False launcher.debug=FalseTo visualize results checkout src/dojo/ui/README. To learn how to load and extract the best node of each experiment, checkout notebooks/analyze_results.ipynb.
If you found this work useful, please consider citing:
@article{toledo2025airesearchagentsmachine,
title={AI Research Agents for Machine Learning: Search, Exploration, and Generalization in MLE-bench},
author={Edan Toledo and Karen Hambardzumyan and Martin Josifoski and Rishi Hazra and Nicolas Baldwin and Alexis Audran-Reiss and Michael Kuchnik and Despoina Magka and Minqi Jiang and Alisia Maria Lupidi and Andrei Lupu and Roberta Raileanu and Kelvin Niu and Tatiana Shavrina and Jean-Christophe Gagnon-Audet and Michael Shvartsman and Shagun Sodhani and Alexander H. Miller and Abhishek Charnalia and Derek Dunfield and Carole-Jean Wu and Pontus Stenetorp and Nicola Cancedda and Jakob Nicolaus Foerster and Yoram Bachrach},
year={2025},
journal={arXiv},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2507.02554}
}
This code is made available under a CC BY-NC 4.0 license, as found in the LICENSE file. Some portions of the project are subject to separate license terms outlined in THIRD_PARTY_LICENSES.md.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for aira-dojo
Similar Open Source Tools

aira-dojo
aira-dojo is a scalable and customizable framework for AI research agents, designed to accelerate hill-climbing on research capabilities toward a fully automated AI research scientist. The framework provides a general abstraction for tasks and agents, implements the MLE-bench task, and includes state-of-the-art agents. It features an isolated code execution environment that integrates smoothly with job schedulers like Slurm, enabling large-scale experiments and rapid iteration across a portfolio of tasks and solvers.
pentagi
PentAGI is an innovative tool for automated security testing that leverages cutting-edge artificial intelligence technologies. It is designed for information security professionals, researchers, and enthusiasts who need a powerful and flexible solution for conducting penetration tests. The tool provides secure and isolated operations in a sandboxed Docker environment, fully autonomous AI-powered agent for penetration testing steps, a suite of 20+ professional security tools, smart memory system for storing research results, web intelligence for gathering information, integration with external search systems, team delegation system, comprehensive monitoring and reporting, modern interface, API integration, persistent storage, scalable architecture, self-hosted solution, flexible authentication, and quick deployment through Docker Compose.
holon
Holon is a tool that runs AI coding agents headlessly to automate the process of turning issues into PR-ready patches and summaries. It provides a sandboxed execution environment with standardized artifacts, allowing for deterministic and repeatable runs. Users can easily create or update PRs, manage state persistence, and customize agent bundles. Holon can be used locally or in CI environments, offering seamless integration with GitHub Actions.
llm-functions
LLM Functions is a project that enables the enhancement of large language models (LLMs) with custom tools and agents developed in bash, javascript, and python. Users can create tools for their LLM to execute system commands, access web APIs, or perform other complex tasks triggered by natural language prompts. The project provides a framework for building tools and agents, with tools being functions written in the user's preferred language and automatically generating JSON declarations based on comments. Agents combine prompts, function callings, and knowledge (RAG) to create conversational AI agents. The project is designed to be user-friendly and allows users to easily extend the capabilities of their language models.

shellChatGPT
ShellChatGPT is a shell wrapper for OpenAI's ChatGPT, DALL-E, Whisper, and TTS, featuring integration with LocalAI, Ollama, Gemini, Mistral, Groq, and GitHub Models. It provides text and chat completions, vision, reasoning, and audio models, voice-in and voice-out chatting mode, text editor interface, markdown rendering support, session management, instruction prompt manager, integration with various service providers, command line completion, file picker dialogs, color scheme personalization, stdin and text file input support, and compatibility with Linux, FreeBSD, MacOS, and Termux for a responsive experience.
forge
Forge is a powerful open-source tool for building modern web applications. It provides a simple and intuitive interface for developers to quickly scaffold and deploy projects. With Forge, you can easily create custom components, manage dependencies, and streamline your development workflow. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced developer, Forge offers a flexible and efficient solution for your web development needs.
llm-vscode
llm-vscode is an extension designed for all things LLM, utilizing llm-ls as its backend. It offers features such as code completion with 'ghost-text' suggestions, the ability to choose models for code generation via HTTP requests, ensuring prompt size fits within the context window, and code attribution checks. Users can configure the backend, suggestion behavior, keybindings, llm-ls settings, and tokenization options. Additionally, the extension supports testing models like Code Llama 13B, Phind/Phind-CodeLlama-34B-v2, and WizardLM/WizardCoder-Python-34B-V1.0. Development involves cloning llm-ls, building it, and setting up the llm-vscode extension for use.
ChatSim
ChatSim is a tool designed for editable scene simulation for autonomous driving via LLM-Agent collaboration. It provides functionalities for setting up the environment, installing necessary dependencies like McNeRF and Inpainting tools, and preparing data for simulation. Users can train models, simulate scenes, and track trajectories for smoother and more realistic results. The tool integrates with Blender software and offers options for training McNeRF models and McLight's skydome estimation network. It also includes a trajectory tracking module for improved trajectory tracking. ChatSim aims to facilitate the simulation of autonomous driving scenarios with collaborative LLM-Agents.
BoxPwnr
BoxPwnr is a tool designed to test the performance of different agentic architectures using Large Language Models (LLMs) to autonomously solve HackTheBox machines. It provides a plug and play system with various strategies and platforms supported. BoxPwnr uses an iterative process where LLMs receive system prompts, suggest commands, execute them in a Docker container, analyze outputs, and repeat until the flag is found. The tool automates commands, saves conversations and commands for analysis, and tracks usage statistics. With recent advancements in LLM technology, BoxPwnr aims to evaluate AI systems' reasoning capabilities, creative thinking, security understanding, problem-solving skills, and code generation abilities.
k8sgpt
K8sGPT is a tool for scanning your Kubernetes clusters, diagnosing, and triaging issues in simple English. It has SRE experience codified into its analyzers and helps to pull out the most relevant information to enrich it with AI.
DeepPavlov
DeepPavlov is an open-source conversational AI library built on PyTorch. It is designed for the development of production-ready chatbots and complex conversational systems, as well as for research in the area of NLP and dialog systems. The library offers a wide range of models for tasks such as Named Entity Recognition, Intent/Sentence Classification, Question Answering, Sentence Similarity/Ranking, Syntactic Parsing, and more. DeepPavlov also provides embeddings like BERT, ELMo, and FastText for various languages, along with AutoML capabilities and integrations with REST API, Socket API, and Amazon AWS.
ProX
ProX is a lm-based data refinement framework that automates the process of cleaning and improving data used in pre-training large language models. It offers better performance, domain flexibility, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional methods. The framework has been shown to improve model performance by over 2% and boost accuracy by up to 20% in tasks like math. ProX is designed to refine data at scale without the need for manual adjustments, making it a valuable tool for data preprocessing in natural language processing tasks.
co-llm
Co-LLM (Collaborative Language Models) is a tool for learning to decode collaboratively with multiple language models. It provides a method for data processing, training, and inference using a collaborative approach. The tool involves steps such as formatting/tokenization, scoring logits, initializing Z vector, deferral training, and generating results using multiple models. Co-LLM supports training with different collaboration pairs and provides baseline training scripts for various models. In inference, it uses 'vllm' services to orchestrate models and generate results through API-like services. The tool is inspired by allenai/open-instruct and aims to improve decoding performance through collaborative learning.
ML-Bench
ML-Bench is a tool designed to evaluate large language models and agents for machine learning tasks on repository-level code. It provides functionalities for data preparation, environment setup, usage, API calling, open source model fine-tuning, and inference. Users can clone the repository, load datasets, run ML-LLM-Bench, prepare data, fine-tune models, and perform inference tasks. The tool aims to facilitate the evaluation of language models and agents in the context of machine learning tasks on code repositories.
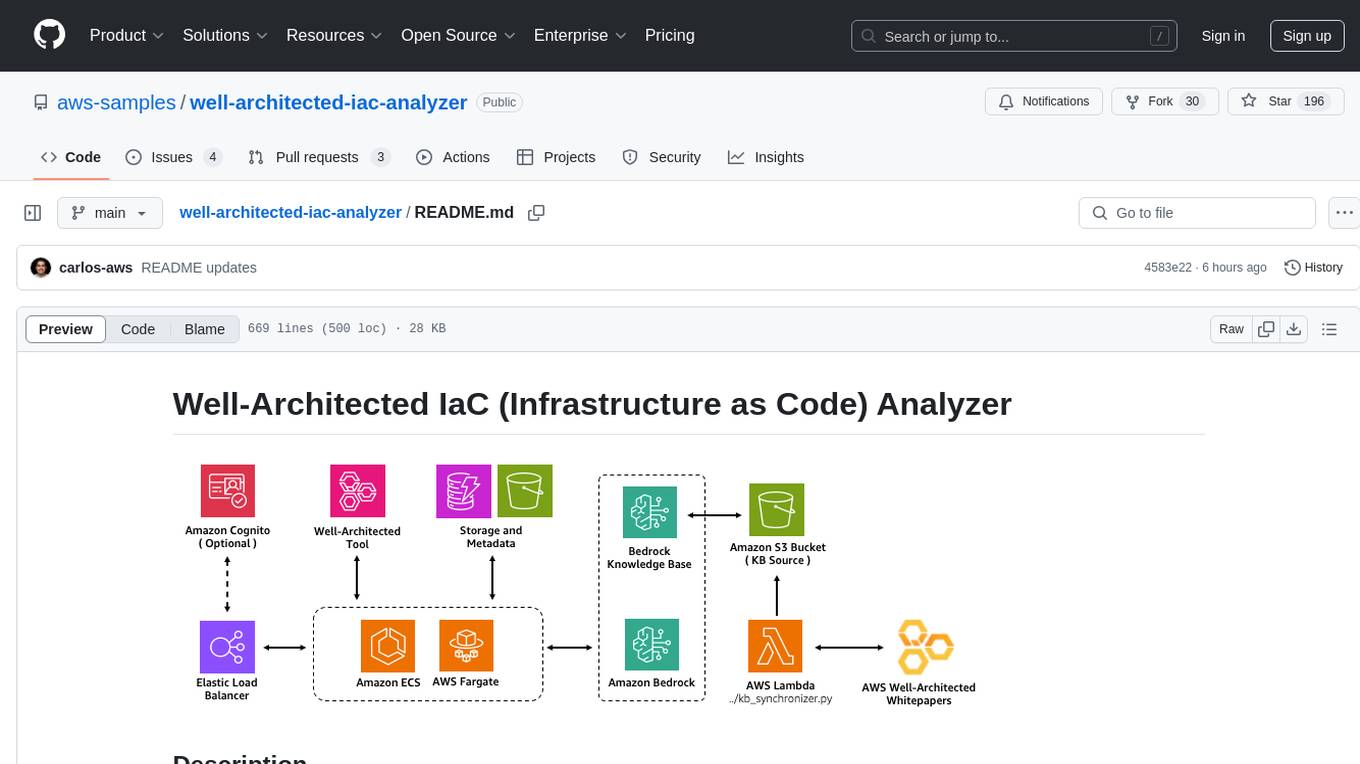
well-architected-iac-analyzer
Well-Architected Infrastructure as Code (IaC) Analyzer is a project demonstrating how generative AI can evaluate infrastructure code for alignment with best practices. It features a modern web application allowing users to upload IaC documents, complete IaC projects, or architecture diagrams for assessment. The tool provides insights into infrastructure code alignment with AWS best practices, offers suggestions for improving cloud architecture designs, and can generate IaC templates from architecture diagrams. Users can analyze CloudFormation, Terraform, or AWS CDK templates, architecture diagrams in PNG or JPEG format, and complete IaC projects with supporting documents. Real-time analysis against Well-Architected best practices, integration with AWS Well-Architected Tool, and export of analysis results and recommendations are included.
CosyVoice
CosyVoice is a tool designed for speech synthesis, offering pretrained models for zero-shot, sft, instruct inference. It provides a web demo for easy usage and supports advanced users with train and inference scripts. The tool can be deployed using grpc for service deployment. Users can download pretrained models and resources for immediate use or train their own models from scratch. CosyVoice is suitable for researchers, developers, linguists, AI engineers, and speech technology enthusiasts.
For similar tasks

aira-dojo
aira-dojo is a scalable and customizable framework for AI research agents, designed to accelerate hill-climbing on research capabilities toward a fully automated AI research scientist. The framework provides a general abstraction for tasks and agents, implements the MLE-bench task, and includes state-of-the-art agents. It features an isolated code execution environment that integrates smoothly with job schedulers like Slurm, enabling large-scale experiments and rapid iteration across a portfolio of tasks and solvers.
llm-random
This repository contains code for research conducted by the LLM-Random research group at IDEAS NCBR in Warsaw, Poland. The group focuses on developing and using this repository to conduct research. For more information about the group and its research, refer to their blog, llm-random.github.io.
AI4U
AI4U is a tool that provides a framework for modeling virtual reality and game environments. It offers an alternative approach to modeling Non-Player Characters (NPCs) in Godot Game Engine. AI4U defines an agent living in an environment and interacting with it through sensors and actuators. Sensors provide data to the agent's brain, while actuators send actions from the agent to the environment. The brain processes the sensor data and makes decisions (selects an action by time). AI4U can also be used in other situations, such as modeling environments for artificial intelligence experiments.
OSWorld
OSWorld is a benchmarking tool designed to evaluate multimodal agents for open-ended tasks in real computer environments. It provides a platform for running experiments, setting up virtual machines, and interacting with the environment using Python scripts. Users can install the tool on their desktop or server, manage dependencies with Conda, and run benchmark tasks. The tool supports actions like executing commands, checking for specific results, and evaluating agent performance. OSWorld aims to facilitate research in AI by providing a standardized environment for testing and comparing different agent baselines.
GPTSwarm
GPTSwarm is a graph-based framework for LLM-based agents that enables the creation of LLM-based agents from graphs and facilitates the customized and automatic self-organization of agent swarms with self-improvement capabilities. The library includes components for domain-specific operations, graph-related functions, LLM backend selection, memory management, and optimization algorithms to enhance agent performance and swarm efficiency. Users can quickly run predefined swarms or utilize tools like the file analyzer. GPTSwarm supports local LM inference via LM Studio, allowing users to run with a local LLM model. The framework has been accepted by ICML2024 and offers advanced features for experimentation and customization.
LLM-Finetuning-Toolkit
LLM Finetuning toolkit is a config-based CLI tool for launching a series of LLM fine-tuning experiments on your data and gathering their results. It allows users to control all elements of a typical experimentation pipeline - prompts, open-source LLMs, optimization strategy, and LLM testing - through a single YAML configuration file. The toolkit supports basic, intermediate, and advanced usage scenarios, enabling users to run custom experiments, conduct ablation studies, and automate fine-tuning workflows. It provides features for data ingestion, model definition, training, inference, quality assurance, and artifact outputs, making it a comprehensive tool for fine-tuning large language models.
athina-evals
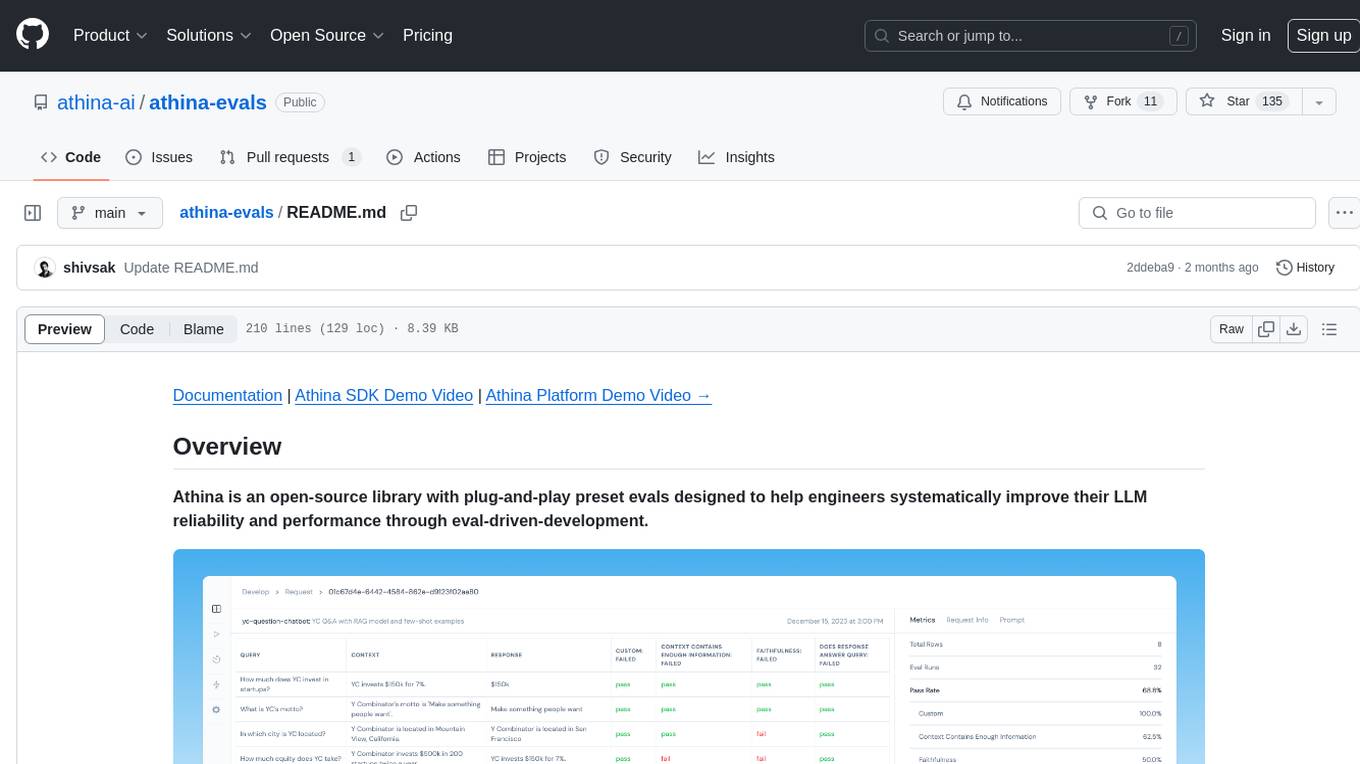
Athina is an open-source library designed to help engineers improve the reliability and performance of Large Language Models (LLMs) through eval-driven development. It offers plug-and-play preset evals for catching and preventing bad outputs, measuring model performance, running experiments, A/B testing models, detecting regressions, and monitoring production data. Athina provides a solution to the flaws in current LLM developer workflows by offering rapid experimentation, customizable evaluators, integrated dashboard, consistent metrics, historical record tracking, and easy setup. It includes preset evaluators for RAG applications and summarization accuracy, as well as the ability to write custom evals. Athina's evals can run on both development and production environments, providing consistent metrics and removing the need for manual infrastructure setup.
MachineSoM
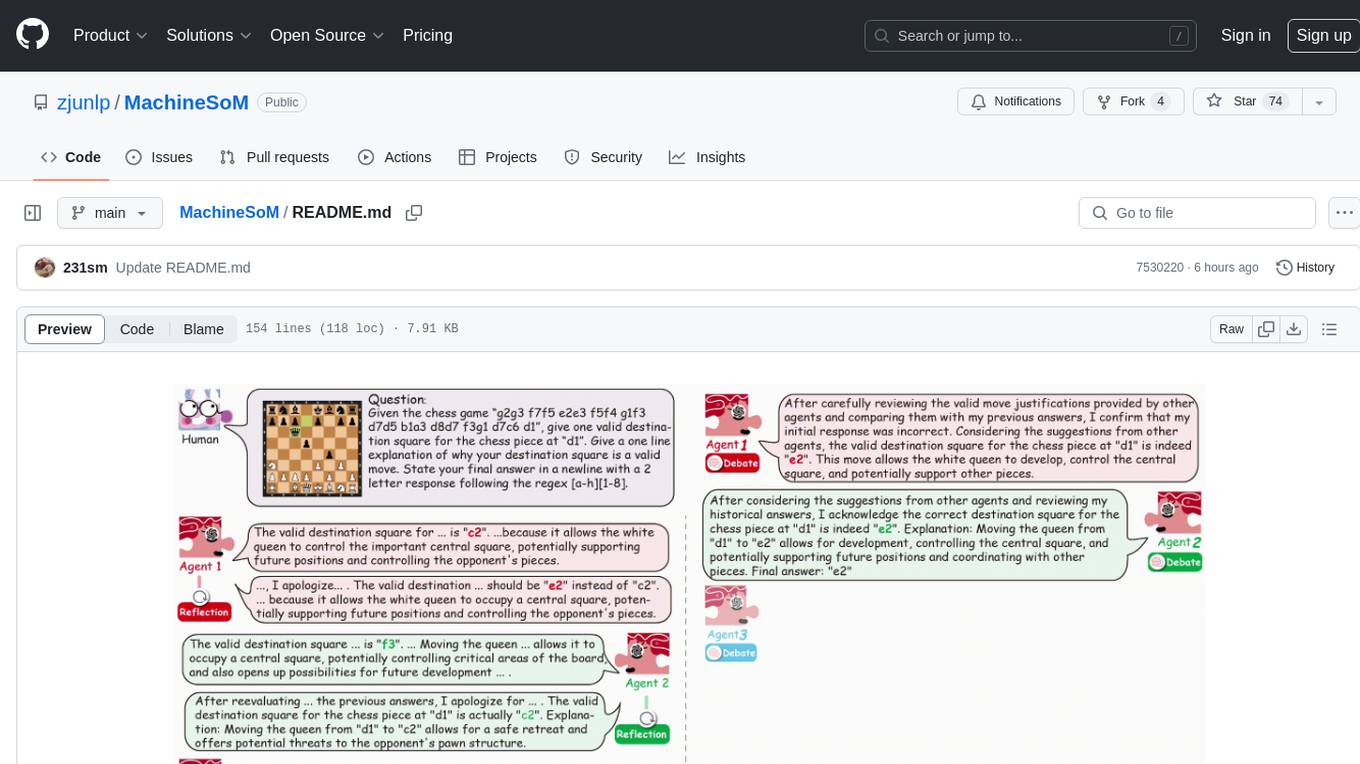
MachineSoM is a code repository for the paper 'Exploring Collaboration Mechanisms for LLM Agents: A Social Psychology View'. It focuses on the emergence of intelligence from collaborative and communicative computational modules, enabling effective completion of complex tasks. The repository includes code for societies of LLM agents with different traits, collaboration processes such as debate and self-reflection, and interaction strategies for determining when and with whom to interact. It provides a coding framework compatible with various inference services like Replicate, OpenAI, Dashscope, and Anyscale, supporting models like Qwen and GPT. Users can run experiments, evaluate results, and draw figures based on the paper's content, with available datasets for MMLU, Math, and Chess Move Validity.
For similar jobs
LitServe
LitServe is a high-throughput serving engine designed for deploying AI models at scale. It generates an API endpoint for models, handles batching, streaming, and autoscaling across CPU/GPUs. LitServe is built for enterprise scale with a focus on minimal, hackable code-base without bloat. It supports various model types like LLMs, vision, time-series, and works with frameworks like PyTorch, JAX, Tensorflow, and more. The tool allows users to focus on model performance rather than serving boilerplate, providing full control and flexibility.
Lidar_AI_Solution
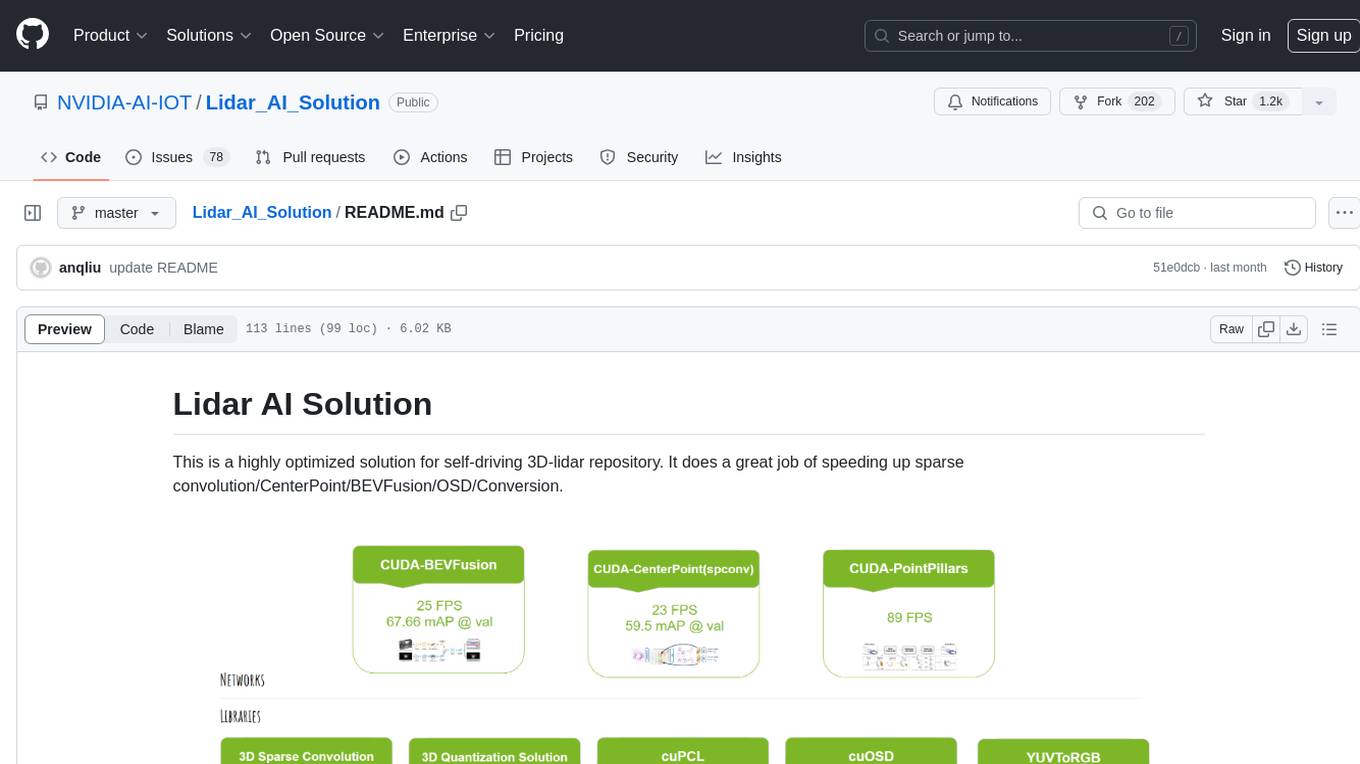
Lidar AI Solution is a highly optimized repository for self-driving 3D lidar, providing solutions for sparse convolution, BEVFusion, CenterPoint, OSD, and Conversion. It includes CUDA and TensorRT implementations for various tasks such as 3D sparse convolution, BEVFusion, CenterPoint, PointPillars, V2XFusion, cuOSD, cuPCL, and YUV to RGB conversion. The repository offers easy-to-use solutions, high accuracy, low memory usage, and quantization options for different tasks related to self-driving technology.
generative-ai-sagemaker-cdk-demo
This repository showcases how to deploy generative AI models from Amazon SageMaker JumpStart using the AWS CDK. Generative AI is a type of AI that can create new content and ideas, such as conversations, stories, images, videos, and music. The repository provides a detailed guide on deploying image and text generative AI models, utilizing pre-trained models from SageMaker JumpStart. The web application is built on Streamlit and hosted on Amazon ECS with Fargate. It interacts with the SageMaker model endpoints through Lambda functions and Amazon API Gateway. The repository also includes instructions on setting up the AWS CDK application, deploying the stacks, using the models, and viewing the deployed resources on the AWS Management Console.
cake
cake is a pure Rust implementation of the llama3 LLM distributed inference based on Candle. The project aims to enable running large models on consumer hardware clusters of iOS, macOS, Linux, and Windows devices by sharding transformer blocks. It allows running inferences on models that wouldn't fit in a single device's GPU memory by batching contiguous transformer blocks on the same worker to minimize latency. The tool provides a way to optimize memory and disk space by splitting the model into smaller bundles for workers, ensuring they only have the necessary data. cake supports various OS, architectures, and accelerations, with different statuses for each configuration.
Awesome-Robotics-3D
Awesome-Robotics-3D is a curated list of 3D Vision papers related to Robotics domain, focusing on large models like LLMs/VLMs. It includes papers on Policy Learning, Pretraining, VLM and LLM, Representations, and Simulations, Datasets, and Benchmarks. The repository is maintained by Zubair Irshad and welcomes contributions and suggestions for adding papers. It serves as a valuable resource for researchers and practitioners in the field of Robotics and Computer Vision.
tensorzero
TensorZero is an open-source platform that helps LLM applications graduate from API wrappers into defensible AI products. It enables a data & learning flywheel for LLMs by unifying inference, observability, optimization, and experimentation. The platform includes a high-performance model gateway, structured schema-based inference, observability, experimentation, and data warehouse for analytics. TensorZero Recipes optimize prompts and models, and the platform supports experimentation features and GitOps orchestration for deployment.
vector-inference
This repository provides an easy-to-use solution for running inference servers on Slurm-managed computing clusters using vLLM. All scripts in this repository run natively on the Vector Institute cluster environment. Users can deploy models as Slurm jobs, check server status and performance metrics, and shut down models. The repository also supports launching custom models with specific configurations. Additionally, users can send inference requests and set up an SSH tunnel to run inference from a local device.
rhesis
Rhesis is a comprehensive test management platform designed for Gen AI teams, offering tools to create, manage, and execute test cases for generative AI applications. It ensures the robustness, reliability, and compliance of AI systems through features like test set management, automated test generation, edge case discovery, compliance validation, integration capabilities, and performance tracking. The platform is open source, emphasizing community-driven development, transparency, extensible architecture, and democratizing AI safety. It includes components such as backend services, frontend applications, SDK for developers, worker services, chatbot applications, and Polyphemus for uncensored LLM service. Rhesis enables users to address challenges unique to testing generative AI applications, such as non-deterministic outputs, hallucinations, edge cases, ethical concerns, and compliance requirements.


