
LLM-Finetuning-Toolkit
Toolkit for fine-tuning, ablating and unit-testing open-source LLMs.
Stars: 745
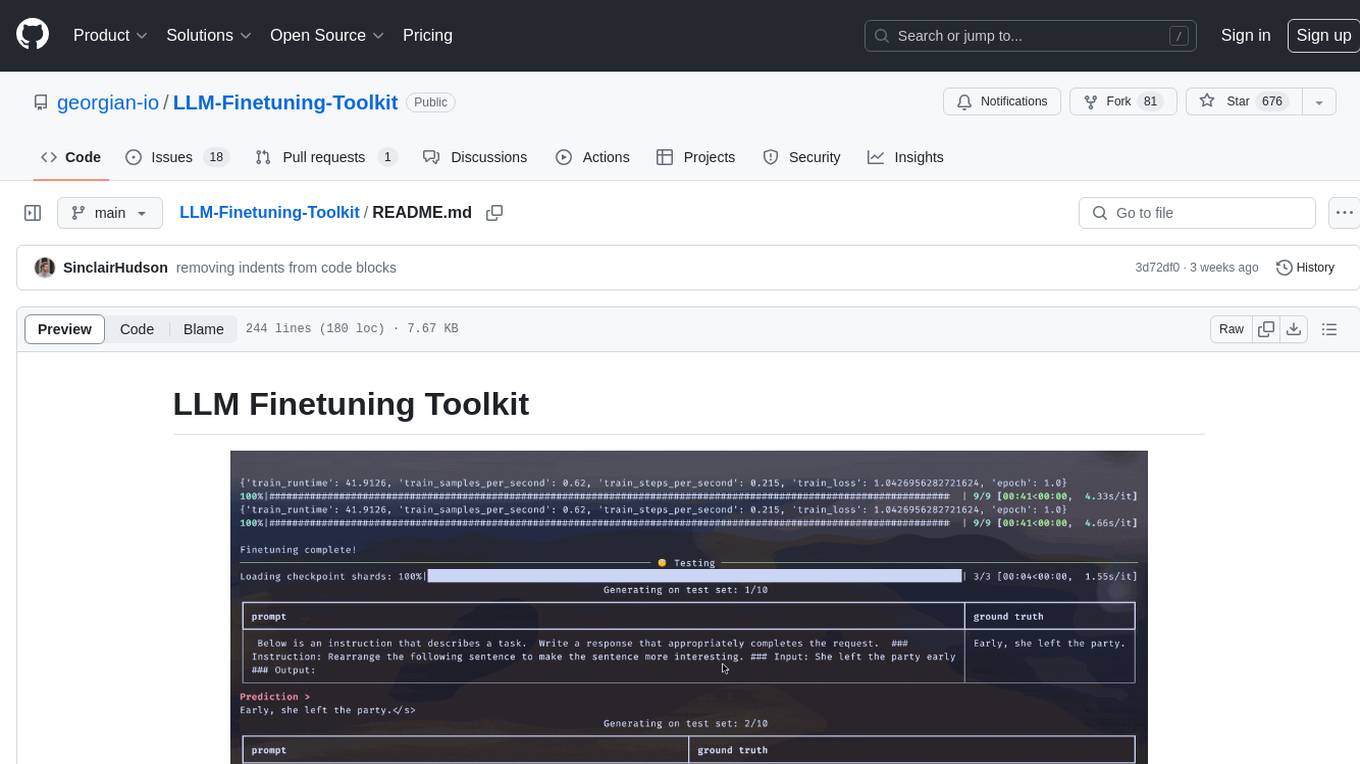
LLM Finetuning toolkit is a config-based CLI tool for launching a series of LLM fine-tuning experiments on your data and gathering their results. It allows users to control all elements of a typical experimentation pipeline - prompts, open-source LLMs, optimization strategy, and LLM testing - through a single YAML configuration file. The toolkit supports basic, intermediate, and advanced usage scenarios, enabling users to run custom experiments, conduct ablation studies, and automate fine-tuning workflows. It provides features for data ingestion, model definition, training, inference, quality assurance, and artifact outputs, making it a comprehensive tool for fine-tuning large language models.
README:
LLM Finetuning toolkit is a config-based CLI tool for launching a series of LLM fine-tuning experiments on your data and gathering their results. From one single yaml config file, control all elements of a typical experimentation pipeline - prompts, open-source LLMs, optimization strategy and LLM testing.
pipx (recommended)
pipx installs the package and dependencies in a separate virtual environment
pipx install llm-toolkitpip install llm-toolkitThis guide contains 3 stages that will enable you to get the most out of this toolkit!
- Basic: Run your first LLM fine-tuning experiment
- Intermediate: Run a custom experiment by changing the components of the YAML configuration file
- Advanced: Launch series of fine-tuning experiments across different prompt templates, LLMs, optimization techniques -- all through one YAML configuration file
llmtune generate config
llmtune run ./config.ymlThe first command generates a helpful starter config.yml file and saves in the current working directory. This is provided to users to quickly get started and as a base for further modification.
Then the second command initiates the fine-tuning process using the settings specified in the default YAML configuration file config.yaml.
The configuration file is the central piece that defines the behavior of the toolkit. It is written in YAML format and consists of several sections that control different aspects of the process, such as data ingestion, model definition, training, inference, and quality assurance. We highlight some of the critical sections.
To enable Flash-attention for supported models. First install flash-attn:
pipx
pipx inject llm-toolkit flash-attn --pip-args=--no-build-isolationpip
pip install flash-attn --no-build-isolation
Then, add to config file.
model:
torch_dtype: "bfloat16" # or "float16" if using older GPU
attn_implementation: "flash_attention_2"An example of what the data ingestion may look like:
data:
file_type: "huggingface"
path: "yahma/alpaca-cleaned"
prompt:
### Instruction: {instruction}
### Input: {input}
### Output:
prompt_stub: { output }
test_size: 0.1 # Proportion of test as % of total; if integer then # of samples
train_size: 0.9 # Proportion of train as % of total; if integer then # of samples
train_test_split_seed: 42- While the above example illustrates using a public dataset from Hugging Face, the config file can also ingest your own data.
file_type: "json"
path: "<path to your data file> file_type: "csv"
path: "<path to your data file>-
The prompt fields help create instructions to fine-tune the LLM on. It reads data from specific columns, mentioned in {} brackets, that are present in your dataset. In the example provided, it is expected for the data file to have column names:
instruction,inputandoutput. -
The prompt fields use both
promptandprompt_stubduring fine-tuning. However, during testing, only thepromptsection is used as input to the fine-tuned LLM.
model:
hf_model_ckpt: "NousResearch/Llama-2-7b-hf"
quantize: true
bitsandbytes:
load_in_4bit: true
bnb_4bit_compute_dtype: "bf16"
bnb_4bit_quant_type: "nf4"
# LoRA Params -------------------
lora:
task_type: "CAUSAL_LM"
r: 32
lora_dropout: 0.1
target_modules:
- q_proj
- v_proj
- k_proj
- o_proj
- up_proj
- down_proj
- gate_proj- While the above example showcases using Llama2 7B, in theory, any open-source LLM supported by Hugging Face can be used in this toolkit.
hf_model_ckpt: "mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1"hf_model_ckpt: "tiiuae/falcon-7b"- The parameters for LoRA, such as the rank
rand dropout, can be altered.
lora:
r: 64
lora_dropout: 0.25qa:
llm_metrics:
- length_test
- word_overlap_test- To ensure that the fine-tuned LLM behaves as expected, you can add tests that check if the desired behaviour is being attained. Example: for an LLM fine-tuned for a summarization task, we may want to check if the generated summary is indeed smaller in length than the input text. We would also like to learn the overlap between words in the original text and generated summary.
This config will run fine-tuning and save the results under directory ./experiment/[unique_hash]. Each unique configuration will generate a unique hash, so that our tool can automatically pick up where it left off. For example, if you need to exit in the middle of the training, by relaunching the script, the program will automatically load the existing dataset that has been generated under the directory, instead of doing it all over again.
After the script finishes running you will see these distinct artifacts:
/dataset # generated pkl file in hf datasets format
/model # peft model weights in hf format
/results # csv of prompt, ground truth, and predicted values
/qa # csv of test results: e.g. vector similarity between ground truth and predictionOnce all the changes have been incorporated in the YAML file, you can simply use it to run a custom fine-tuning experiment!
python toolkit.py --config-path <path to custom YAML file>Fine-tuning workflows typically involve running ablation studies across various LLMs, prompt designs and optimization techniques. The configuration file can be altered to support running ablation studies.
- Specify different prompt templates to experiment with while fine-tuning.
data:
file_type: "huggingface"
path: "yahma/alpaca-cleaned"
prompt:
- >-
This is the first prompt template to iterate over
### Input: {input}
### Output:
- >-
This is the second prompt template
### Instruction: {instruction}
### Input: {input}
### Output:
prompt_stub: { output }
test_size: 0.1 # Proportion of test as % of total; if integer then # of samples
train_size: 0.9 # Proportion of train as % of total; if integer then # of samples
train_test_split_seed: 42- Specify various LLMs that you would like to experiment with.
model:
hf_model_ckpt:
[
"NousResearch/Llama-2-7b-hf",
mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1",
"tiiuae/falcon-7b",
]
quantize: true
bitsandbytes:
load_in_4bit: true
bnb_4bit_compute_dtype: "bf16"
bnb_4bit_quant_type: "nf4"- Specify different configurations of LoRA that you would like to ablate over.
lora:
r: [16, 32, 64]
lora_dropout: [0.25, 0.50]The toolkit provides a modular and extensible architecture that allows developers to customize and enhance its functionality to suit their specific needs. Each component of the toolkit, such as data ingestion, fine-tuning, inference, and quality assurance testing, is designed to be easily extendable.
Open-source contributions to this toolkit are welcome and encouraged. If you would like to contribute, please see CONTRIBUTING.md.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for LLM-Finetuning-Toolkit
Similar Open Source Tools

LLM-Finetuning-Toolkit
LLM Finetuning toolkit is a config-based CLI tool for launching a series of LLM fine-tuning experiments on your data and gathering their results. It allows users to control all elements of a typical experimentation pipeline - prompts, open-source LLMs, optimization strategy, and LLM testing - through a single YAML configuration file. The toolkit supports basic, intermediate, and advanced usage scenarios, enabling users to run custom experiments, conduct ablation studies, and automate fine-tuning workflows. It provides features for data ingestion, model definition, training, inference, quality assurance, and artifact outputs, making it a comprehensive tool for fine-tuning large language models.
Pixel-Reasoner
Pixel Reasoner is a framework that introduces reasoning in the pixel-space for Vision-Language Models (VLMs), enabling them to directly inspect, interrogate, and infer from visual evidences. This enhances reasoning fidelity for visual tasks by equipping VLMs with visual reasoning operations like zoom-in and select-frame. The framework addresses challenges like model's imbalanced competence and reluctance to adopt pixel-space operations through a two-phase training approach involving instruction tuning and curiosity-driven reinforcement learning. With these visual operations, VLMs can interact with complex visual inputs such as images or videos to gather necessary information, leading to improved performance across visual reasoning benchmarks.
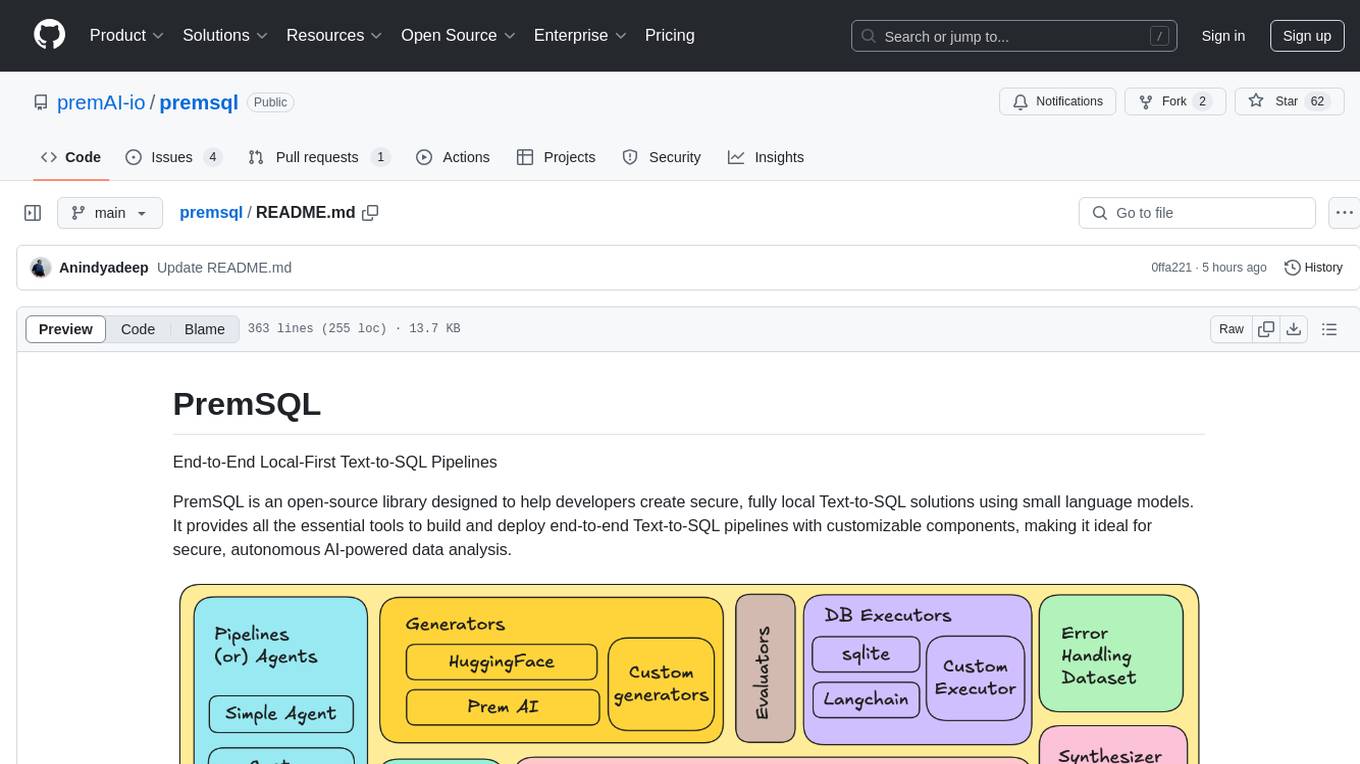
premsql
PremSQL is an open-source library designed to help developers create secure, fully local Text-to-SQL solutions using small language models. It provides essential tools for building and deploying end-to-end Text-to-SQL pipelines with customizable components, ideal for secure, autonomous AI-powered data analysis. The library offers features like Local-First approach, Customizable Datasets, Robust Executors and Evaluators, Advanced Generators, Error Handling and Self-Correction, Fine-Tuning Support, and End-to-End Pipelines. Users can fine-tune models, generate SQL queries from natural language inputs, handle errors, and evaluate model performance against predefined metrics. PremSQL is extendible for customization and private data usage.
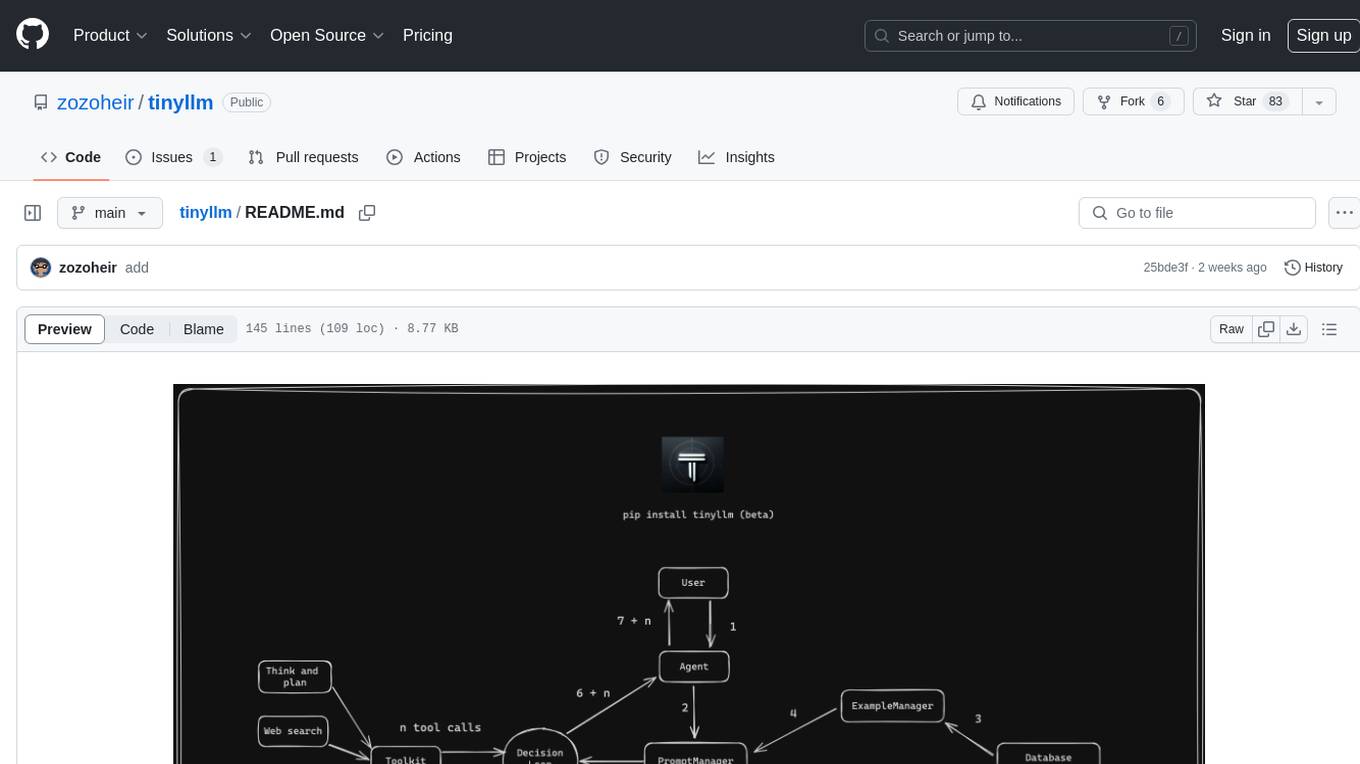
tinyllm
tinyllm is a lightweight framework designed for developing, debugging, and monitoring LLM and Agent powered applications at scale. It aims to simplify code while enabling users to create complex agents or LLM workflows in production. The core classes, Function and FunctionStream, standardize and control LLM, ToolStore, and relevant calls for scalable production use. It offers structured handling of function execution, including input/output validation, error handling, evaluation, and more, all while maintaining code readability. Users can create chains with prompts, LLM models, and evaluators in a single file without the need for extensive class definitions or spaghetti code. Additionally, tinyllm integrates with various libraries like Langfuse and provides tools for prompt engineering, observability, logging, and finite state machine design.
ControlLLM
ControlLLM is a framework that empowers large language models to leverage multi-modal tools for solving complex real-world tasks. It addresses challenges like ambiguous user prompts, inaccurate tool selection, and inefficient tool scheduling by utilizing a task decomposer, a Thoughts-on-Graph paradigm, and an execution engine with a rich toolbox. The framework excels in tasks involving image, audio, and video processing, showcasing superior accuracy, efficiency, and versatility compared to existing methods.
llm-consortium
LLM Consortium is a plugin for the `llm` package that implements a model consortium system with iterative refinement and response synthesis. It orchestrates multiple learned language models to collaboratively solve complex problems through structured dialogue, evaluation, and arbitration. The tool supports multi-model orchestration, iterative refinement, advanced arbitration, database logging, configurable parameters, hundreds of models, and the ability to save and load consortium configurations.
llm-d-inference-sim
The `llm-d-inference-sim` is a lightweight, configurable, and real-time simulator designed to mimic the behavior of vLLM without the need for GPUs or running heavy models. It operates as an OpenAI-compliant server, allowing developers to test clients, schedulers, and infrastructure using realistic request-response cycles, token streaming, and latency patterns. The simulator offers modes of operation, response generation from predefined text or real datasets, latency simulation, tokenization options, LoRA management, KV cache simulation, failure injection, and deployment options for standalone or Kubernetes testing. It supports a subset of standard vLLM Prometheus metrics for observability.
codellm-devkit
Codellm-devkit (CLDK) is a Python library that serves as a multilingual program analysis framework bridging traditional static analysis tools and Large Language Models (LLMs) specialized for code (CodeLLMs). It simplifies the process of analyzing codebases across multiple programming languages, enabling the extraction of meaningful insights and facilitating LLM-based code analysis. The library provides a unified interface for integrating outputs from various analysis tools and preparing them for effective use by CodeLLMs. Codellm-devkit aims to enable the development and experimentation of robust analysis pipelines that combine traditional program analysis tools and CodeLLMs, reducing friction in multi-language code analysis and ensuring compatibility across different tools and LLM platforms. It is designed to seamlessly integrate with popular analysis tools like WALA, Tree-sitter, LLVM, and CodeQL, acting as a crucial intermediary layer for efficient communication between these tools and CodeLLMs. The project is continuously evolving to include new tools and frameworks, maintaining its versatility for code analysis and LLM integration.

sieves
sieves is a library for zero- and few-shot NLP tasks with structured generation, enabling rapid prototyping of NLP applications without the need for training. It simplifies NLP prototyping by bundling capabilities into a single library, providing zero- and few-shot model support, a unified interface for structured generation, built-in tasks for common NLP operations, easy extendability, document-based pipeline architecture, caching to prevent redundant model calls, and more. The tool draws inspiration from spaCy and spacy-llm, offering features like immediate inference, observable pipelines, integrated tools for document parsing and text chunking, ready-to-use tasks such as classification, summarization, translation, and more, persistence for saving and loading pipelines, distillation for specialized model creation, and caching to optimize performance.
deep-research
Deep Research is a lightning-fast tool that uses powerful AI models to generate comprehensive research reports in just a few minutes. It leverages advanced 'Thinking' and 'Task' models, combined with an internet connection, to provide fast and insightful analysis on various topics. The tool ensures privacy by processing and storing all data locally. It supports multi-platform deployment, offers support for various large language models, web search functionality, knowledge graph generation, research history preservation, local and server API support, PWA technology, multi-key payload support, multi-language support, and is built with modern technologies like Next.js and Shadcn UI. Deep Research is open-source under the MIT License.

fuse-med-ml
FuseMedML is a Python framework designed to accelerate machine learning-based discovery in the medical field by promoting code reuse. It provides a flexible design concept where data is stored in a nested dictionary, allowing easy handling of multi-modality information. The framework includes components for creating custom models, loss functions, metrics, and data processing operators. Additionally, FuseMedML offers 'batteries included' key components such as fuse.data for data processing, fuse.eval for model evaluation, and fuse.dl for reusable deep learning components. It supports PyTorch and PyTorch Lightning libraries and encourages the creation of domain extensions for specific medical domains.
generative-models
Generative Models by Stability AI is a repository that provides various generative models for research purposes. It includes models like Stable Video 4D (SV4D) for video synthesis, Stable Video 3D (SV3D) for multi-view synthesis, SDXL-Turbo for text-to-image generation, and more. The repository focuses on modularity and implements a config-driven approach for building and combining submodules. It supports training with PyTorch Lightning and offers inference demos for different models. Users can access pre-trained models like SDXL-base-1.0 and SDXL-refiner-1.0 under a CreativeML Open RAIL++-M license. The codebase also includes tools for invisible watermark detection in generated images.
labo
LABO is a time series forecasting and analysis framework that integrates pre-trained and fine-tuned LLMs with multi-domain agent-based systems. It allows users to create and tune agents easily for various scenarios, such as stock market trend prediction and web public opinion analysis. LABO requires a specific runtime environment setup, including system requirements, Python environment, dependency installations, and configurations. Users can fine-tune their own models using LABO's Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) for computational efficiency and continuous model updates. Additionally, LABO provides a Python library for building model training pipelines and customizing agents for specific tasks.
llama-cpp-agent
The llama-cpp-agent framework is a tool designed for easy interaction with Large Language Models (LLMs). Allowing users to chat with LLM models, execute structured function calls and get structured output (objects). It provides a simple yet robust interface and supports llama-cpp-python and OpenAI endpoints with GBNF grammar support (like the llama-cpp-python server) and the llama.cpp backend server. It works by generating a formal GGML-BNF grammar of the user defined structures and functions, which is then used by llama.cpp to generate text valid to that grammar. In contrast to most GBNF grammar generators it also supports nested objects, dictionaries, enums and lists of them.
LLM-Drop
LLM-Drop is an official implementation of the paper 'What Matters in Transformers? Not All Attention is Needed'. The tool investigates redundancy in transformer-based Large Language Models (LLMs) by analyzing the architecture of Blocks, Attention layers, and MLP layers. It reveals that dropping certain Attention layers can enhance computational and memory efficiency without compromising performance. The tool provides a pipeline for Block Drop and Layer Drop based on LLaMA-Factory, and implements quantization using AutoAWQ and AutoGPTQ.
hound
Hound is a security audit automation pipeline for AI-assisted code review that mirrors how expert auditors think, learn, and collaborate. It features graph-driven analysis, sessionized audits, provider-agnostic models, belief system and hypotheses, precise code grounding, and adaptive planning. The system employs a senior/junior auditor pattern where the Scout actively navigates the codebase and annotates knowledge graphs while the Strategist handles high-level planning and vulnerability analysis. Hound is optimized for small-to-medium sized projects like smart contract applications and is language-agnostic.
For similar tasks

LLM-Finetuning-Toolkit
LLM Finetuning toolkit is a config-based CLI tool for launching a series of LLM fine-tuning experiments on your data and gathering their results. It allows users to control all elements of a typical experimentation pipeline - prompts, open-source LLMs, optimization strategy, and LLM testing - through a single YAML configuration file. The toolkit supports basic, intermediate, and advanced usage scenarios, enabling users to run custom experiments, conduct ablation studies, and automate fine-tuning workflows. It provides features for data ingestion, model definition, training, inference, quality assurance, and artifact outputs, making it a comprehensive tool for fine-tuning large language models.

interpreto
Interpreto is an interpretability toolkit for large language models (LLMs) that provides a modular framework encompassing attribution methods, concept-based methods, and evaluation metrics. It includes various inference-based and gradient-based attribution methods for both classification and generation tasks. The toolkit also offers concept-based explanations to provide high-level interpretations of latent model representations through steps like concept discovery, interpretation, and concept-to-output attribution. Interpreto aims to enhance model interpretability and facilitate understanding of model decisions and outputs.
autogen
AutoGen is a framework that enables the development of LLM applications using multiple agents that can converse with each other to solve tasks. AutoGen agents are customizable, conversable, and seamlessly allow human participation. They can operate in various modes that employ combinations of LLMs, human inputs, and tools.

tracecat
Tracecat is an open-source automation platform for security teams. It's designed to be simple but powerful, with a focus on AI features and a practitioner-obsessed UI/UX. Tracecat can be used to automate a variety of tasks, including phishing email investigation, evidence collection, and remediation plan generation.
ciso-assistant-community
CISO Assistant is a tool that helps organizations manage their cybersecurity posture and compliance. It provides a centralized platform for managing security controls, threats, and risks. CISO Assistant also includes a library of pre-built frameworks and tools to help organizations quickly and easily implement best practices.
ck
Collective Mind (CM) is a collection of portable, extensible, technology-agnostic and ready-to-use automation recipes with a human-friendly interface (aka CM scripts) to unify and automate all the manual steps required to compose, run, benchmark and optimize complex ML/AI applications on any platform with any software and hardware: see online catalog and source code. CM scripts require Python 3.7+ with minimal dependencies and are continuously extended by the community and MLCommons members to run natively on Ubuntu, MacOS, Windows, RHEL, Debian, Amazon Linux and any other operating system, in a cloud or inside automatically generated containers while keeping backward compatibility - please don't hesitate to report encountered issues here and contact us via public Discord Server to help this collaborative engineering effort! CM scripts were originally developed based on the following requirements from the MLCommons members to help them automatically compose and optimize complex MLPerf benchmarks, applications and systems across diverse and continuously changing models, data sets, software and hardware from Nvidia, Intel, AMD, Google, Qualcomm, Amazon and other vendors: * must work out of the box with the default options and without the need to edit some paths, environment variables and configuration files; * must be non-intrusive, easy to debug and must reuse existing user scripts and automation tools (such as cmake, make, ML workflows, python poetry and containers) rather than substituting them; * must have a very simple and human-friendly command line with a Python API and minimal dependencies; * must require minimal or zero learning curve by using plain Python, native scripts, environment variables and simple JSON/YAML descriptions instead of inventing new workflow languages; * must have the same interface to run all automations natively, in a cloud or inside containers. CM scripts were successfully validated by MLCommons to modularize MLPerf inference benchmarks and help the community automate more than 95% of all performance and power submissions in the v3.1 round across more than 120 system configurations (models, frameworks, hardware) while reducing development and maintenance costs.

zenml
ZenML is an extensible, open-source MLOps framework for creating portable, production-ready machine learning pipelines. By decoupling infrastructure from code, ZenML enables developers across your organization to collaborate more effectively as they develop to production.

clearml
ClearML is a suite of tools designed to streamline the machine learning workflow. It includes an experiment manager, MLOps/LLMOps, data management, and model serving capabilities. ClearML is open-source and offers a free tier hosting option. It supports various ML/DL frameworks and integrates with Jupyter Notebook and PyCharm. ClearML provides extensive logging capabilities, including source control info, execution environment, hyper-parameters, and experiment outputs. It also offers automation features, such as remote job execution and pipeline creation. ClearML is designed to be easy to integrate, requiring only two lines of code to add to existing scripts. It aims to improve collaboration, visibility, and data transparency within ML teams.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.

