
Pixel-Reasoner
Pixel-Level Reasoning Model trained with RL
Stars: 201
Pixel Reasoner is a framework that introduces reasoning in the pixel-space for Vision-Language Models (VLMs), enabling them to directly inspect, interrogate, and infer from visual evidences. This enhances reasoning fidelity for visual tasks by equipping VLMs with visual reasoning operations like zoom-in and select-frame. The framework addresses challenges like model's imbalanced competence and reluctance to adopt pixel-space operations through a two-phase training approach involving instruction tuning and curiosity-driven reinforcement learning. With these visual operations, VLMs can interact with complex visual inputs such as images or videos to gather necessary information, leading to improved performance across visual reasoning benchmarks.
README:






Authors: Alex Su* Haozhe Wang*†, Weiming Ren, Fangzhen Lin, Wenhu Chen‡
*Equal Contribution. †Project Lead. ‡Correspondence.
- [2025/5/25] We made really fun demos! You can now play with the online demo. Have fun!
- [2025/5/22] We released models-v1. Now actively working on data and code release.
- Supports Instruction Tuning with multi-turn trajectories
- Supports RL with multi-turn trajectories
- Supports RL with mixed video and image data
- Supports Inference/Evaluation with vLLM
Abstract
Chain-of-thought reasoning has significantly improved the performance of Large Language Models (LLMs) across various domains. However, this reasoning process has been confined exclusively to textual space, limiting its effectiveness in visually intensive tasks. To address this limitation, we introduce the concept of reasoning in the pixel-space. Within this novel framework, Vision-Language Models (VLMs) are equipped with a suite of visual reasoning operations, such as zoom-in and select-frame. These operations enable VLMs to directly inspect, interrogate, and infer from visual evidences, thereby enhancing reasoning fidelity for visual tasks. Cultivating such pixel-space reasoning capabilities in VLMs presents notable challenges, including the model's initially imbalanced competence and its reluctance to adopt the newly introduced pixel-space operations. We address these challenges through a two-phase training approach. The first phase employs instruction tuning on synthesized reasoning traces to familiarize the model with the novel visual operations. Following this, a reinforcement learning (RL) phase leverages a curiosity-driven reward scheme to balance exploration between pixel-space reasoning and textual reasoning. With these visual operations, VLMs can interact with complex visual inputs, such as information-rich images or videos to proactively gather necessary information. We demonstrate that this approach significantly improves VLM performance across diverse visual reasoning benchmarks. Our 7B model, \model, achieves 84\% on V* bench, 74\% on TallyQA-Complex, and 84\% on InfographicsVQA, marking the highest accuracy achieved by any open-source model to date. These results highlight the importance of pixel-space reasoning and the effectiveness of our framework.Please check the TIGER-Lab/PixelReasoner-RL-v1 and TIGER-Lab/PixelReasoner-WarmStart
We proposed two-staged post-training. The instruction tuning is adapted from Open-R1. The Curiosity-Driven RL is adapted from VL-Rethinker.
-
Instruction Tuning: TIGER-Lab/PixelReasoner-SFT-Data
-
RL Queries: TIGER-Lab/PixelReasoner-RL-Data
-
Evaluation: HF Collections
Follow these steps to start the instruction tuning process:
-
Installation
- Navigate to the
instruction_tuningfolder - Follow the detailed setup guide in installation instructions
- Navigate to the
-
Configuration -configure model and data path in sft.sh
-
Launch Training
bash sft.sh
First prepare data. Run the following will get the training data prepared under curiosity_driven_rl/data folder.
export dataname=PixelReasoner-RL-Data
export hf_user=TIGER-Lab
export newdataname=release
cd onestep_evaluation
bash prepare.sh ${dataname}
Then download model https://huggingface.co/TIGER-Lab/PixelReasoner-WarmStart. We use checkpoint-246.
Under curiosity_driven_rl folder, install the environment following the installation instructions.
Set the data path, model path, wandb keys (if you want to use it) in curiosity_driven_rl/scripts/train_vlm_multi.sh.
Run the following for multinode training (e.g., 4x8 actor + 4x8 vllm).
cd curiosity_driven_rl
export temperature=1.0
export trainver="dataname"
export testver="testdataname"
export filter=True # filtering zero advantages
export algo=group # default for grpo
export lr=10
export MAX_PIXELS=4014080 # =[max_image_token]x28x28
export sys=vcot # system prompt version
export mode=train # [no_eval, eval_only, train]
export policy=/path/to/policy
export rbuffer=512 # replay buffer size
export bsz=256 # global train batch size
export evalsteps=4
export nactor=4 # 4x8 for actor if with multinode
export nvllm=32 # 4x8 for sampling if with multinode
export tp=1 # vllm tp, 1 for 7B
export repeat=1 # data repeat
export nepoch=3 # data epoch
export logp_bsz=1 # must be 1
export maxlen=10000 # generate_max_len
export tagname=Train
bash ./scripts/train_vlm_multi.shRun the following for single-node training.
cd curiosity_driven_rl
export temperature=1.0
export trainver="dataname"
export testver="testdataname"
export filter=True # filtering zero advantages
export algo=group # default for grpo
export lr=10
export MAX_PIXELS=4014080 # =[max_image_token]x28x28
export sys=vcot # system prompt version
export mode=train # [no_eval, eval_only, train]
export policy=/path/to/policy
export rbuffer=512 # replay buffer size
export bsz=256 # global train batch size
export evalsteps=1
export mbsz=2
export tp=1 # vllm tp, 1 for 7B
export repeat=1 # data repeat
export nepoch=3 # data epoch
export logp_bsz=1 # must be 1
export maxlen=10000 # generate_max_len
export tagname=Train
bash ./scripts/train_vlm_single.shNote: the number of prompts into vLLM inference is controlled by --eval_batch_size_pergpu during evaluation, and args.rollout_batch_size // strategy.world_size during training. Must set logp_bsz=1 or --micro_rollout_batch_size=1 for computing logprobs because model.generate() suffers from feature mismatch when batchsize > 1.
Evaluation data can be found in the HF Collection.
Note: For users in the mainload of China, please set the hf-endpoint as follows. Otherwise, the hf downloader won't work as expected.
export HF_ENDPOINT=https://hf-mirror.comLet's take the vstar evaluation as an example. The HF data path is JasperHaozhe/VStar-EvalData-PixelReasoner.
1. Prepare Data
export dataname=VStar-EvalData-PixelReasoner
export newdataname=mvbench
cd onestep_evaluation
bash prepare.sh ${dataname}
The bash script will download from HF, process the image paths, and move the data to curiosity_driven_rl/data.
Check the folder curiosity_driven_rl/data, you will know the downloaded parquet file is named as vstar.parquet.
2. Inference and Evaluation
Install the openrlhf according to curiosity_driven_rl/installation.md.
Under curiosity_driven_rl folder. Set benchmark=vstar, working_dir, policypath, and savefolder,tagname for saving evaluation results. Run the following.
benchmark=vstar
export working_dir="/path/to/curiosity_driven_rl"
export policy="/path/to/policy"
export savefolder=tooleval
export nvj_path="/path/to/nvidia/nvjitlink/lib" # in case the system cannot fiind the nvjit library
############
export sys=vcot # define the system prompt
export MIN_PIXELS=401408
export MAX_PIXELS=4014080 # define the image resolution
export eval_bsz=64 # vllm will processes this many queries
export tagname=eval_vstar_bestmodel
export testdata="${working_dir}/data/${benchmark}.parquet"
export num_vllm=8
export num_gpus=8
bash ${working_dir}/scripts/eval_vlm_new.sh
For the MVBench, we extracted the frames from videos and construct the eval data that fits into our evaluation. The data is available in JasperHaozhe/MVBench-EvalData-PixelReasoner
1. Prepare Data
export dataname=MVBench-EvalData-PixelReasoner
export newdataname=mvbench
cd onestep_evaluation
bash prepare.sh ${dataname}
2. Inference and Evaluation
Under curiosity_driven_rl folder. Set benchmark=mvbench, working_dir, policypath, and savefolder,tagname for saving evaluation results. Run the following.
benchmark=mvbench
export working_dir="/path/to/curiosity_driven_rl"
export policy="/path/to/policy"
export savefolder=tooleval
export nvj_path="/path/to/nvidia/nvjitlink/lib" # in case the system cannot fiind the nvjit library
############
export sys=vcot # define the system prompt
export MIN_PIXELS=401408
export MAX_PIXELS=4014080 # define the image resolution
export eval_bsz=64 # vllm will processes this many queries
export tagname=eval_vstar_bestmodel
export testdata="${working_dir}/data/${benchmark}.parquet"
export num_vllm=8
export num_gpus=8
bash ${working_dir}/scripts/eval_vlm_new.sh
Set sys=notool for textual reasoning with Qwen2.5-VL-Instruct . sys=vcot can trigger zero-shot use of visual operations but may also induce unexpected behaviors.
1. Exceeding Model Context Length
If you do sampling (e.g., during training) and set a larger MAX_PIXELS, you could encounter the following:
ValueError: The prompt (total length 10819) is too long to fit into the model (context length 10240). Make sure that `max_model_len` is no smaller than the number of text tokens plus multimodal tokens. For image inputs, the number of image tokens depends on the number of images, and possibly their aspect ratios as well.
This stems from:
- max model length is too short, try adjust
generate_max_len + prompt_max_len - too many image tokens, which means there could be too many images or the image resolution is too large and takes up many image tokens.
To address this problem during training, you could set smaller
MAX_PIXELS, or you could set the max number images during training, viamax_imgnumincuriosity_driven_rl/openrlhf/trainer/ppo_utils/experience_maker.py.
2. transformers and vLLM version mismatch
Input and cos/sin must have the same dtype, got torch.float32 and torch.bfloat32.
Try reinstall transformers: pip install --force-reinstall git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@9985d06add07a4cc691dc54a7e34f54205c04d4 and update vLLM.
3. logp_bsz=1
Exception: dump-info key solutions: {} should be {}
Must set logp_bsz=1 or --micro_rollout_batch_size=1 for computing logprobs because model.generate() suffers from feature mismatch when batchsize > 1.
4. Reproduction Mismath
Correct values of MAX_PIXELS and MIN_PIXELS are crucial for reproducing the results.
- make sure the env variables are correctly set
- make sure the vLLM engines correctly read the env variables
When using ray parallelism, chances are that the env variables are only set on one machine but not all machines. To fix this, add ray env variables as follows:
RUNTIME_ENV_JSON="{\"env_vars\": {\"MAX_PIXELS\": \"$MAX_PIXELS\", \"MIN_PIXELS\": \"$MIN_PIXELS\"}}"
ray job submit --address="http://127.0.0.1:8265" \
--runtime-env-json="$RUNTIME_ENV_JSON" \
Thanks @LiqiangJing for feedback!
Contact Haozhe ([email protected]) for direct solution of any bugs in RL.
Contact Muze ([email protected]) for SFT and another version of RL: VLM-R1.
If you find this work useful, please give us a free cite:
@article{pixelreasoner,
title={Pixel Reasoner: Incentivizing Pixel-Space Reasoning with Curiosity-Driven Reinforcement Learning},
author = {Su, Alex and Wang, Haozhe and Ren, Weiming and Lin, Fangzhen and Chen, Wenhu},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2505.15966},
year={2025}
}For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for Pixel-Reasoner
Similar Open Source Tools
Pixel-Reasoner
Pixel Reasoner is a framework that introduces reasoning in the pixel-space for Vision-Language Models (VLMs), enabling them to directly inspect, interrogate, and infer from visual evidences. This enhances reasoning fidelity for visual tasks by equipping VLMs with visual reasoning operations like zoom-in and select-frame. The framework addresses challenges like model's imbalanced competence and reluctance to adopt pixel-space operations through a two-phase training approach involving instruction tuning and curiosity-driven reinforcement learning. With these visual operations, VLMs can interact with complex visual inputs such as images or videos to gather necessary information, leading to improved performance across visual reasoning benchmarks.
ProX
ProX is a lm-based data refinement framework that automates the process of cleaning and improving data used in pre-training large language models. It offers better performance, domain flexibility, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness compared to traditional methods. The framework has been shown to improve model performance by over 2% and boost accuracy by up to 20% in tasks like math. ProX is designed to refine data at scale without the need for manual adjustments, making it a valuable tool for data preprocessing in natural language processing tasks.

sieves
sieves is a library for zero- and few-shot NLP tasks with structured generation, enabling rapid prototyping of NLP applications without the need for training. It simplifies NLP prototyping by bundling capabilities into a single library, providing zero- and few-shot model support, a unified interface for structured generation, built-in tasks for common NLP operations, easy extendability, document-based pipeline architecture, caching to prevent redundant model calls, and more. The tool draws inspiration from spaCy and spacy-llm, offering features like immediate inference, observable pipelines, integrated tools for document parsing and text chunking, ready-to-use tasks such as classification, summarization, translation, and more, persistence for saving and loading pipelines, distillation for specialized model creation, and caching to optimize performance.
generative-models
Generative Models by Stability AI is a repository that provides various generative models for research purposes. It includes models like Stable Video 4D (SV4D) for video synthesis, Stable Video 3D (SV3D) for multi-view synthesis, SDXL-Turbo for text-to-image generation, and more. The repository focuses on modularity and implements a config-driven approach for building and combining submodules. It supports training with PyTorch Lightning and offers inference demos for different models. Users can access pre-trained models like SDXL-base-1.0 and SDXL-refiner-1.0 under a CreativeML Open RAIL++-M license. The codebase also includes tools for invisible watermark detection in generated images.

Biomni
Biomni is a general-purpose biomedical AI agent designed to autonomously execute a wide range of research tasks across diverse biomedical subfields. By integrating cutting-edge large language model (LLM) reasoning with retrieval-augmented planning and code-based execution, Biomni helps scientists dramatically enhance research productivity and generate testable hypotheses.
datadreamer
DataDreamer is an advanced toolkit designed to facilitate the development of edge AI models by enabling synthetic data generation, knowledge extraction from pre-trained models, and creation of efficient and potent models. It eliminates the need for extensive datasets by generating synthetic datasets, leverages latent knowledge from pre-trained models, and focuses on creating compact models suitable for integration into any device and performance for specialized tasks. The toolkit offers features like prompt generation, image generation, dataset annotation, and tools for training small-scale neural networks for edge deployment. It provides hardware requirements, usage instructions, available models, and limitations to consider while using the library.
probsem
ProbSem is a repository that provides a framework to leverage large language models (LLMs) for assigning context-conditional probability distributions over queried strings. It supports OpenAI engines and HuggingFace CausalLM models, and is flexible for research applications in linguistics, cognitive science, program synthesis, and NLP. Users can define prompts, contexts, and queries to derive probability distributions over possible completions, enabling tasks like cloze completion, multiple-choice QA, semantic parsing, and code completion. The repository offers CLI and API interfaces for evaluation, with options to customize models, normalize scores, and adjust temperature for probability distributions.
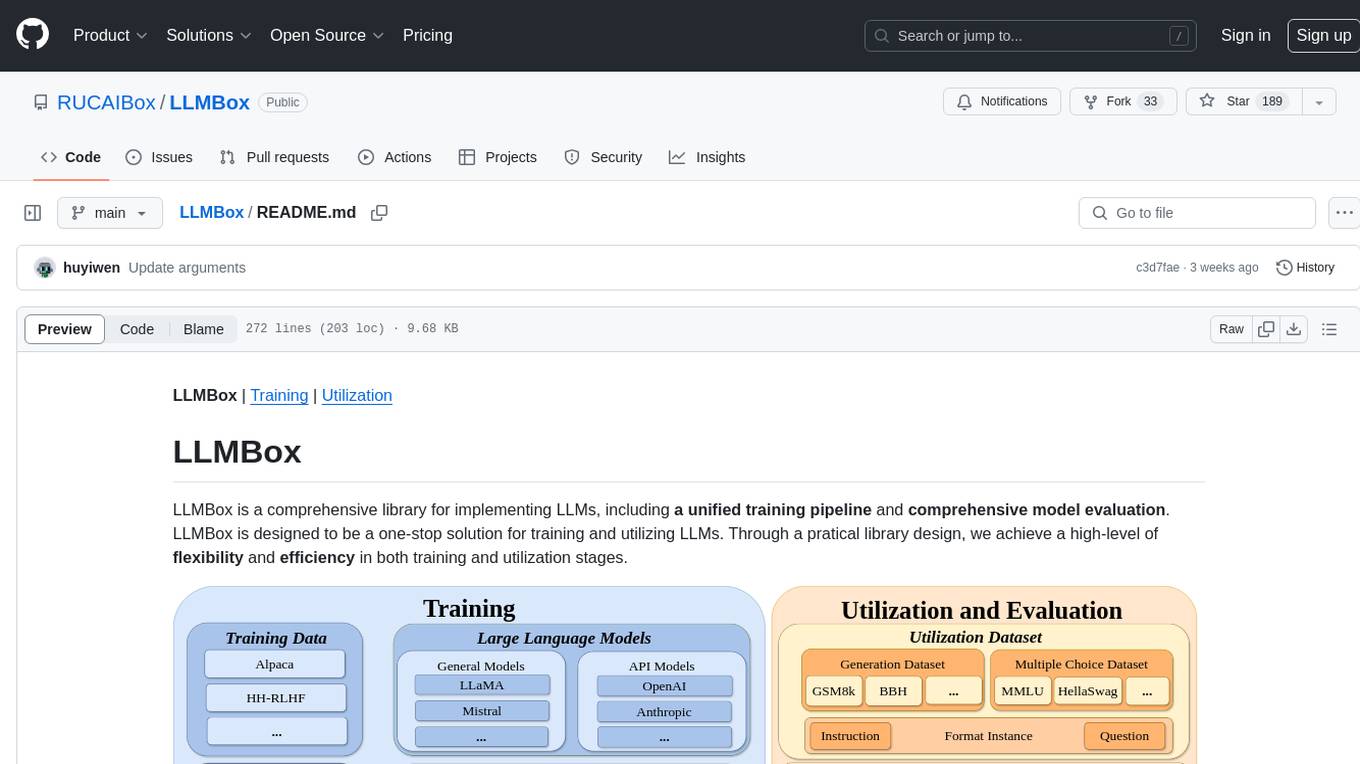
LLMBox
LLMBox is a comprehensive library designed for implementing Large Language Models (LLMs) with a focus on a unified training pipeline and comprehensive model evaluation. It serves as a one-stop solution for training and utilizing LLMs, offering flexibility and efficiency in both training and utilization stages. The library supports diverse training strategies, comprehensive datasets, tokenizer vocabulary merging, data construction strategies, parameter efficient fine-tuning, and efficient training methods. For utilization, LLMBox provides comprehensive evaluation on various datasets, in-context learning strategies, chain-of-thought evaluation, evaluation methods, prefix caching for faster inference, support for specific LLM models like vLLM and Flash Attention, and quantization options. The tool is suitable for researchers and developers working with LLMs for natural language processing tasks.
ControlLLM
ControlLLM is a framework that empowers large language models to leverage multi-modal tools for solving complex real-world tasks. It addresses challenges like ambiguous user prompts, inaccurate tool selection, and inefficient tool scheduling by utilizing a task decomposer, a Thoughts-on-Graph paradigm, and an execution engine with a rich toolbox. The framework excels in tasks involving image, audio, and video processing, showcasing superior accuracy, efficiency, and versatility compared to existing methods.

lhotse
Lhotse is a Python library designed to make speech and audio data preparation flexible and accessible. It aims to attract a wider community to speech processing tasks by providing a Python-centric design and an expressive command-line interface. Lhotse offers standard data preparation recipes, PyTorch Dataset classes for speech tasks, and efficient data preparation for model training with audio cuts. It supports data augmentation, feature extraction, and feature-space cut mixing. The tool extends Kaldi's data preparation recipes with seamless PyTorch integration, human-readable text manifests, and convenient Python classes.
llmgraph
llmgraph is a tool that enables users to create knowledge graphs in GraphML, GEXF, and HTML formats by extracting world knowledge from large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT. It supports various entity types and relationships, offers cache support for efficient graph growth, and provides insights into LLM costs. Users can customize the model used and interact with different LLM providers. The tool allows users to generate interactive graphs based on a specified entity type and Wikipedia link, making it a valuable resource for knowledge graph creation and exploration.
humanoid-gym
Humanoid-Gym is a reinforcement learning framework designed for training locomotion skills for humanoid robots, focusing on zero-shot transfer from simulation to real-world environments. It integrates a sim-to-sim framework from Isaac Gym to Mujoco for verifying trained policies in different physical simulations. The codebase is verified with RobotEra's XBot-S and XBot-L humanoid robots. It offers comprehensive training guidelines, step-by-step configuration instructions, and execution scripts for easy deployment. The sim2sim support allows transferring trained policies to accurate simulated environments. The upcoming features include Denoising World Model Learning and Dexterous Hand Manipulation. Installation and usage guides are provided along with examples for training PPO policies and sim-to-sim transformations. The code structure includes environment and configuration files, with instructions on adding new environments. Troubleshooting tips are provided for common issues, along with a citation and acknowledgment section.
labo
LABO is a time series forecasting and analysis framework that integrates pre-trained and fine-tuned LLMs with multi-domain agent-based systems. It allows users to create and tune agents easily for various scenarios, such as stock market trend prediction and web public opinion analysis. LABO requires a specific runtime environment setup, including system requirements, Python environment, dependency installations, and configurations. Users can fine-tune their own models using LABO's Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) for computational efficiency and continuous model updates. Additionally, LABO provides a Python library for building model training pipelines and customizing agents for specific tasks.
LayerSkip
LayerSkip is an implementation enabling early exit inference and self-speculative decoding. It provides a code base for running models trained using the LayerSkip recipe, offering speedup through self-speculative decoding. The tool integrates with Hugging Face transformers and provides checkpoints for various LLMs. Users can generate tokens, benchmark on datasets, evaluate tasks, and sweep over hyperparameters to optimize inference speed. The tool also includes correctness verification scripts and Docker setup instructions. Additionally, other implementations like gpt-fast and Native HuggingFace are available. Training implementation is a work-in-progress, and contributions are welcome under the CC BY-NC license.
rtdl-num-embeddings
This repository provides the official implementation of the paper 'On Embeddings for Numerical Features in Tabular Deep Learning'. It focuses on transforming scalar continuous features into vectors before integrating them into the main backbone of tabular neural networks, showcasing improved performance. The embeddings for continuous features are shown to enhance the performance of tabular DL models and are applicable to various conventional backbones, offering efficiency comparable to Transformer-based models. The repository includes Python packages for practical usage, exploration of metrics and hyperparameters, and reproducing reported results for different algorithms and datasets.
hound
Hound is a security audit automation pipeline for AI-assisted code review that mirrors how expert auditors think, learn, and collaborate. It features graph-driven analysis, sessionized audits, provider-agnostic models, belief system and hypotheses, precise code grounding, and adaptive planning. The system employs a senior/junior auditor pattern where the Scout actively navigates the codebase and annotates knowledge graphs while the Strategist handles high-level planning and vulnerability analysis. Hound is optimized for small-to-medium sized projects like smart contract applications and is language-agnostic.
For similar tasks

HPT
Hyper-Pretrained Transformers (HPT) is a novel multimodal LLM framework from HyperGAI, trained for vision-language models capable of understanding both textual and visual inputs. The repository contains the open-source implementation of inference code to reproduce the evaluation results of HPT Air on different benchmarks. HPT has achieved competitive results with state-of-the-art models on various multimodal LLM benchmarks. It offers models like HPT 1.5 Air and HPT 1.0 Air, providing efficient solutions for vision-and-language tasks.
learnopencv
LearnOpenCV is a repository containing code for Computer Vision, Deep learning, and AI research articles shared on the blog LearnOpenCV.com. It serves as a resource for individuals looking to enhance their expertise in AI through various courses offered by OpenCV. The repository includes a wide range of topics such as image inpainting, instance segmentation, robotics, deep learning models, and more, providing practical implementations and code examples for readers to explore and learn from.
spark-free-api
Spark AI Free 服务 provides high-speed streaming output, multi-turn dialogue support, AI drawing support, long document interpretation, and image parsing. It offers zero-configuration deployment, multi-token support, and automatic session trace cleaning. It is fully compatible with the ChatGPT interface. The repository includes multiple free-api projects for various AI services. Users can access the API for tasks such as chat completions, AI drawing, document interpretation, image analysis, and ssoSessionId live checking. The project also provides guidelines for deployment using Docker, Docker-compose, Render, Vercel, and native deployment methods. It recommends using custom clients for faster and simpler access to the free-api series projects.
mlx-vlm
MLX-VLM is a package designed for running Vision LLMs on Mac systems using MLX. It provides a convenient way to install and utilize the package for processing large language models related to vision tasks. The tool simplifies the process of running LLMs on Mac computers, offering a seamless experience for users interested in leveraging MLX for vision-related projects.
clarifai-python-grpc
This is the official Clarifai gRPC Python client for interacting with their recognition API. Clarifai offers a platform for data scientists, developers, researchers, and enterprises to utilize artificial intelligence for image, video, and text analysis through computer vision and natural language processing. The client allows users to authenticate, predict concepts in images, and access various functionalities provided by the Clarifai API. It follows a versioning scheme that aligns with the backend API updates and includes specific instructions for installation and troubleshooting. Users can explore the Clarifai demo, sign up for an account, and refer to the documentation for detailed information.
horde-worker-reGen
This repository provides the latest implementation for the AI Horde Worker, allowing users to utilize their graphics card(s) to generate, post-process, or analyze images for others. It offers a platform where users can create images and earn 'kudos' in return, granting priority for their own image generations. The repository includes important details for setup, recommendations for system configurations, instructions for installation on Windows and Linux, basic usage guidelines, and information on updating the AI Horde Worker. Users can also run the worker with multiple GPUs and receive notifications for updates through Discord. Additionally, the repository contains models that are licensed under the CreativeML OpenRAIL License.
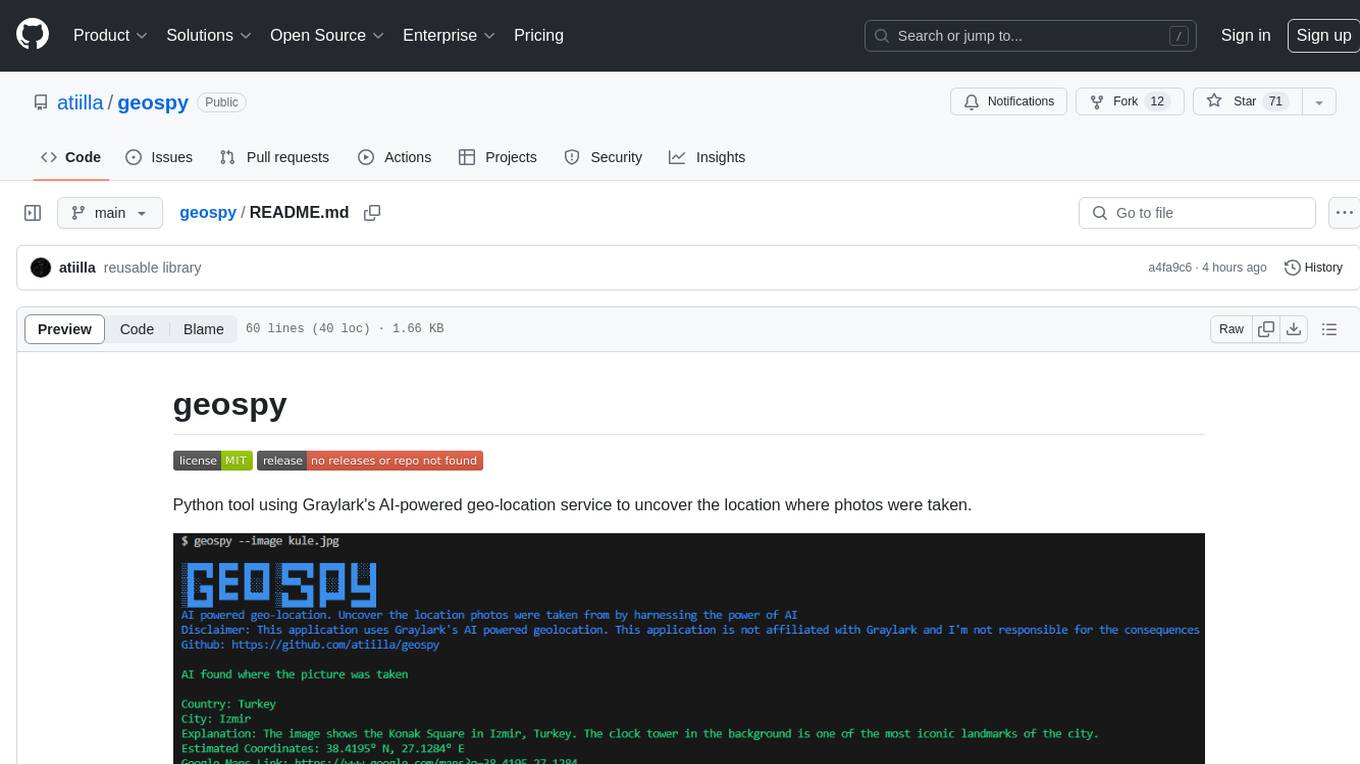
geospy
Geospy is a Python tool that utilizes Graylark's AI-powered geolocation service to determine the location where photos were taken. It allows users to analyze images and retrieve information such as country, city, explanation, coordinates, and Google Maps links. The tool provides a seamless way to integrate geolocation services into various projects and applications.
Awesome-Colorful-LLM
Awesome-Colorful-LLM is a meticulously assembled anthology of vibrant multimodal research focusing on advancements propelled by large language models (LLMs) in domains such as Vision, Audio, Agent, Robotics, and Fundamental Sciences like Mathematics. The repository contains curated collections of works, datasets, benchmarks, projects, and tools related to LLMs and multimodal learning. It serves as a comprehensive resource for researchers and practitioners interested in exploring the intersection of language models and various modalities for tasks like image understanding, video pretraining, 3D modeling, document understanding, audio analysis, agent learning, robotic applications, and mathematical research.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.
