
distributed-llama
Distributed LLM inference. Connect home devices into a powerful cluster to accelerate LLM inference. More devices means faster inference.
Stars: 2651
Distributed Llama is a tool that allows you to run large language models (LLMs) on weak devices or make powerful devices even more powerful by distributing the workload and dividing the RAM usage. It uses TCP sockets to synchronize the state of the neural network, and you can easily configure your AI cluster by using a home router. Distributed Llama supports models such as Llama 2 (7B, 13B, 70B) chat and non-chat versions, Llama 3, and Grok-1 (314B).
README:
Connect home devices into a powerful cluster to accelerate LLM inference. More devices mean faster performance, leveraging tensor parallelism and high-speed synchronization over Ethernet.
Supports Linux, macOS, and Windows. Optimized for ARM and x86_64 AVX2 CPUs.
How to Run
News
- 16 Sep 2025 - Qwen 3 MoE models are now supported on Vulkan.
- 5 Sep 2025 - Qwen 3 MoE models are now supported on CPU.
- 3 Aug 2025 - Qwen 3 0.6B, 1.7B, 8B and 14B models are now supported.
- 23 Mar 2025 - 🌋 Experimental Vulkan support
- 12 Feb 2025 - 🚧 Merged the fundamental codebase refactor
- 9 Jan 2025 - 🍎 Llama 3.3 70B on 4 x Mac Mini M4 Pro 24GB RAM
Python 3 and C++ compiler required. The command will download the model and the tokenizer.
| Model | Size | Command |
|---|---|---|
| Llama 3.1 8B Instruct Q40 | 6.32 GB | python launch.py llama3_1_8b_instruct_q40 |
| Llama 3.1 405B Instruct Q40 | 238 GB |
python launch.py llama3_1_405b_instruct_q40. |
| Llama 3.2 1B Instruct Q40 | 1.7 GB | python launch.py llama3_2_1b_instruct_q40 |
| Llama 3.2 3B Instruct Q40 | 3.4 GB | python launch.py llama3_2_3b_instruct_q40 |
| Llama 3.3 70B Instruct Q40 | 40 GB | python launch.py llama3_3_70b_instruct_q40 |
| DeepSeek R1 Distill Llama 8B Q40 | 6.32 GB | python launch.py deepseek_r1_distill_llama_8b_q40 |
| Qwen 3 0.6B Q40 | 0.9 GB | python launch.py qwen3_0.6b_q40 |
| Qwen 3 1.7B Q40 | 2.2 GB | python launch.py qwen3_1.7b_q40 |
| Qwen 3 8B Q40 | 6.7 GB | python launch.py qwen3_8b_q40 |
| Qwen 3 14B Q40 | 10.9 GB | python launch.py qwen3_14b_q40 |
| Qwen 3 30B A3B Q40 | 17.0 GB | python launch.py qwen3_30b_a3b_q40 |
- You can run Distributed Llama only on 1, 2, 4... 2^n nodes.
- The maximum number of nodes is equal to the number of KV heads in the model #70.
- Only the following quantizations are supported #183:
-
q40model withq80buffer-float-type -
f32model withf32buffer-float-type
-
[🔀 SWITCH OR ROUTER]
| | | |
| | | |_______ 🔸 device1 (ROOT) 10.0.0.1
| | |_________ 🔹 device2 (WORKER 1) 10.0.0.2:9999
| |___________ 🔹 device3 (WORKER 2) 10.0.0.3:9999
|_____________ 🔹 device4 (WORKER 3) 10.0.0.4:9999
...
The project is split up into two parts:
- 🔸 Root node - it's responsible for loading the model and weights and forward them to workers. Also, it synchronizes the state of the neural network. The root node is also a worker, it processes own slice of the neural network.
- 🔹 Worker node - it processes own slice of the neural network. It doesn't require any configuration related to the model.
You always need the root node and you can add 2^n - 1 worker nodes to speed up the inference. The RAM usage of the neural network is split up across all nodes. The root node requires a bit more RAM than worker nodes.
-
dllama inference- run the inference with a simple benchmark, -
dllama chat- run the CLI chat, -
dllama worker- run the worker node, -
dllama-api- run the API server.
🎹 Supported Arguments
Inference, Chat, API
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
--model <path> |
Path to model. | dllama_model_meta-llama-3-8b_q40.m |
--tokenizer <path> |
Tokenizer to model. | dllama_tokenizer_llama3.t |
--buffer-float-type <type> |
Float precision of synchronization. | q80 |
--workers <workers> |
Addresses of workers (ip:port), separated by space. | 10.0.0.1:9999 10.0.0.2:9999 |
--max-seq-len <n> |
The maximum sequence length, it helps to reduce the RAM usage. | 4096 |
Inference, Chat, Worker, API
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
--nthreads <n> |
Amount of threads. Don't set a higher value than number of CPU cores. | 4 |
Worker, API
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
--port <port> |
Binding port. | 9999 |
Inference
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
--prompt <prompt> |
Initial prompt. | "Hello World" |
--steps <steps> |
Number of tokens to generate. | 256 |
Please check the discussions section, where many measurements were published on different configurations.
Feel free to contribute to this project. For small changes, simply create a new merge request. For larger changes, please create an issue to discuss your plans. Please follow these guidelines when contributing:
- Make only minimal changes and avoid modifying files that are not necessary.
- Ensure the code is compatible across all supported systems and CPUs.
- This repository is maintained in English.
This project is released under the MIT license.
@misc{dllama,
author = {Bartłomiej Tadych},
title = {Distributed Llama},
year = {2024},
publisher = {GitHub},
journal = {GitHub repository},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/b4rtaz/distributed-llama}},
commit = {7eb77ca93ec0d502e28d36b6fb20039b449cbea4}
}
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for distributed-llama
Similar Open Source Tools

distributed-llama
Distributed Llama is a tool that allows you to run large language models (LLMs) on weak devices or make powerful devices even more powerful by distributing the workload and dividing the RAM usage. It uses TCP sockets to synchronize the state of the neural network, and you can easily configure your AI cluster by using a home router. Distributed Llama supports models such as Llama 2 (7B, 13B, 70B) chat and non-chat versions, Llama 3, and Grok-1 (314B).

deeppowers
Deeppowers is a powerful Python library for deep learning applications. It provides a wide range of tools and utilities to simplify the process of building and training deep neural networks. With Deeppowers, users can easily create complex neural network architectures, perform efficient training and optimization, and deploy models for various tasks. The library is designed to be user-friendly and flexible, making it suitable for both beginners and experienced deep learning practitioners.
open-ai
Open AI is a powerful tool for artificial intelligence research and development. It provides a wide range of machine learning models and algorithms, making it easier for developers to create innovative AI applications. With Open AI, users can explore cutting-edge technologies such as natural language processing, computer vision, and reinforcement learning. The platform offers a user-friendly interface and comprehensive documentation to support users in building and deploying AI solutions. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced AI practitioner, Open AI offers the tools and resources you need to accelerate your AI projects and stay ahead in the rapidly evolving field of artificial intelligence.
lemonai
LemonAI is a versatile machine learning library designed to simplify the process of building and deploying AI models. It provides a wide range of tools and algorithms for data preprocessing, model training, and evaluation. With LemonAI, users can easily experiment with different machine learning techniques and optimize their models for various tasks. The library is well-documented and beginner-friendly, making it suitable for both novice and experienced data scientists. LemonAI aims to streamline the development of AI applications and empower users to create innovative solutions using state-of-the-art machine learning methods.
ai
This repository contains a collection of AI algorithms and models for various machine learning tasks. It provides implementations of popular algorithms such as neural networks, decision trees, and support vector machines. The code is well-documented and easy to understand, making it suitable for both beginners and experienced developers. The repository also includes example datasets and tutorials to help users get started with building and training AI models. Whether you are a student learning about AI or a professional working on machine learning projects, this repository can be a valuable resource for your development journey.
simple-ai
Simple AI is a lightweight Python library for implementing basic artificial intelligence algorithms. It provides easy-to-use functions and classes for tasks such as machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision. With Simple AI, users can quickly prototype and deploy AI solutions without the complexity of larger frameworks.
minions
Minions is a communication protocol that enables small on-device models to collaborate with frontier models in the cloud. By only reading long contexts locally, it reduces cloud costs with minimal or no quality degradation. The repository provides a demonstration of the protocol.
ai-algorithms
This repository is a work in progress that contains first-principle implementations of groundbreaking AI algorithms using various deep learning frameworks. Each implementation is accompanied by supporting research papers, aiming to provide comprehensive educational resources for understanding and implementing foundational AI algorithms from scratch.
airllm
AirLLM is a tool that optimizes inference memory usage, enabling large language models to run on low-end GPUs without quantization, distillation, or pruning. It supports models like Llama3.1 on 8GB VRAM. The tool offers model compression for up to 3x inference speedup with minimal accuracy loss. Users can specify compression levels, profiling modes, and other configurations when initializing models. AirLLM also supports prefetching and disk space management. It provides examples and notebooks for easy implementation and usage.
GEN-AI
GEN-AI is a versatile Python library for implementing various artificial intelligence algorithms and models. It provides a wide range of tools and functionalities to support machine learning, deep learning, natural language processing, computer vision, and reinforcement learning tasks. With GEN-AI, users can easily build, train, and deploy AI models for diverse applications such as image recognition, text classification, sentiment analysis, object detection, and game playing. The library is designed to be user-friendly, efficient, and scalable, making it suitable for both beginners and experienced AI practitioners.
FedML
FedML is a unified and scalable machine learning library for running training and deployment anywhere at any scale. It is highly integrated with FEDML Nexus AI, a next-gen cloud service for LLMs & Generative AI. FEDML Nexus AI provides holistic support of three interconnected AI infrastructure layers: user-friendly MLOps, a well-managed scheduler, and high-performance ML libraries for running any AI jobs across GPU Clouds.
Fast-dLLM
Fast-DLLM is a diffusion-based Large Language Model (LLM) inference acceleration framework that supports efficient inference for models like Dream and LLaDA. It offers fast inference support, multiple optimization strategies, code generation, evaluation capabilities, and an interactive chat interface. Key features include Key-Value Cache for Block-Wise Decoding, Confidence-Aware Parallel Decoding, and overall performance improvements. The project structure includes directories for Dream and LLaDA model-related code, with installation and usage instructions provided for using the LLaDA and Dream models.
cascadeflow
cascadeflow is an intelligent AI model cascading library that dynamically selects the optimal model for each query or tool call through speculative execution. It helps reduce API costs by 40-85% through intelligent model cascading and speculative execution with automatic per-query cost tracking. The tool is based on the research that shows 40-70% of queries don't require slow, expensive flagship models, and domain-specific smaller models often outperform large general-purpose models on specialized tasks. cascadeflow automatically escalates to flagship models for advanced reasoning when needed. It supports multiple providers, low latency, cost control, and transparency, and can be used for edge and local-hosted AI deployment.
public
This public repository contains API, tools, and packages for Datagrok, a web-based data analytics platform. It offers support for scientific domains, applications, connectors to web services, visualizations, file importing, scientific methods in R, Python, or Julia, file metadata extractors, custom predictive models, platform enhancements, and more. The open-source packages are free to use, with restrictions on server computational capacities for the public environment. Academic institutions can use Datagrok for research and education, benefiting from reproducible and scalable computations and data augmentation capabilities. Developers can contribute by creating visualizations, scientific methods, file editors, connectors to web services, and more.
Fast-LLM
Fast-LLM is an open-source library designed for training large language models with exceptional speed, scalability, and flexibility. Built on PyTorch and Triton, it offers optimized kernel efficiency, reduced overheads, and memory usage, making it suitable for training models of all sizes. The library supports distributed training across multiple GPUs and nodes, offers flexibility in model architectures, and is easy to use with pre-built Docker images and simple configuration. Fast-LLM is licensed under Apache 2.0, developed transparently on GitHub, and encourages contributions and collaboration from the community.

openinference
OpenInference is a set of conventions and plugins that complement OpenTelemetry to enable tracing of AI applications. It provides a way to capture and analyze the performance and behavior of AI models, including their interactions with other components of the application. OpenInference is designed to be language-agnostic and can be used with any OpenTelemetry-compatible backend. It includes a set of instrumentations for popular machine learning SDKs and frameworks, making it easy to add tracing to your AI applications.
For similar tasks

distributed-llama
Distributed Llama is a tool that allows you to run large language models (LLMs) on weak devices or make powerful devices even more powerful by distributing the workload and dividing the RAM usage. It uses TCP sockets to synchronize the state of the neural network, and you can easily configure your AI cluster by using a home router. Distributed Llama supports models such as Llama 2 (7B, 13B, 70B) chat and non-chat versions, Llama 3, and Grok-1 (314B).
ml-engineering
This repository provides a comprehensive collection of methodologies, tools, and step-by-step instructions for successful training of large language models (LLMs) and multi-modal models. It is a technical resource suitable for LLM/VLM training engineers and operators, containing numerous scripts and copy-n-paste commands to facilitate quick problem-solving. The repository is an ongoing compilation of the author's experiences training BLOOM-176B and IDEFICS-80B models, and currently focuses on the development and training of Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) models at Contextual.AI. The content is organized into six parts: Insights, Hardware, Orchestration, Training, Development, and Miscellaneous. It includes key comparison tables for high-end accelerators and networks, as well as shortcuts to frequently needed tools and guides. The repository is open to contributions and discussions, and is licensed under Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International.
Awesome-LLMs-for-Video-Understanding
Awesome-LLMs-for-Video-Understanding is a repository dedicated to exploring Video Understanding with Large Language Models. It provides a comprehensive survey of the field, covering models, pretraining, instruction tuning, and hybrid methods. The repository also includes information on tasks, datasets, and benchmarks related to video understanding. Contributors are encouraged to add new papers, projects, and materials to enhance the repository.
Awesome-LLM
Awesome-LLM is a curated list of resources related to large language models, focusing on papers, projects, frameworks, tools, tutorials, courses, opinions, and other useful resources in the field. It covers trending LLM projects, milestone papers, other papers, open LLM projects, LLM training frameworks, LLM evaluation frameworks, tools for deploying LLM, prompting libraries & tools, tutorials, courses, books, and opinions. The repository provides a comprehensive overview of the latest advancements and resources in the field of large language models.
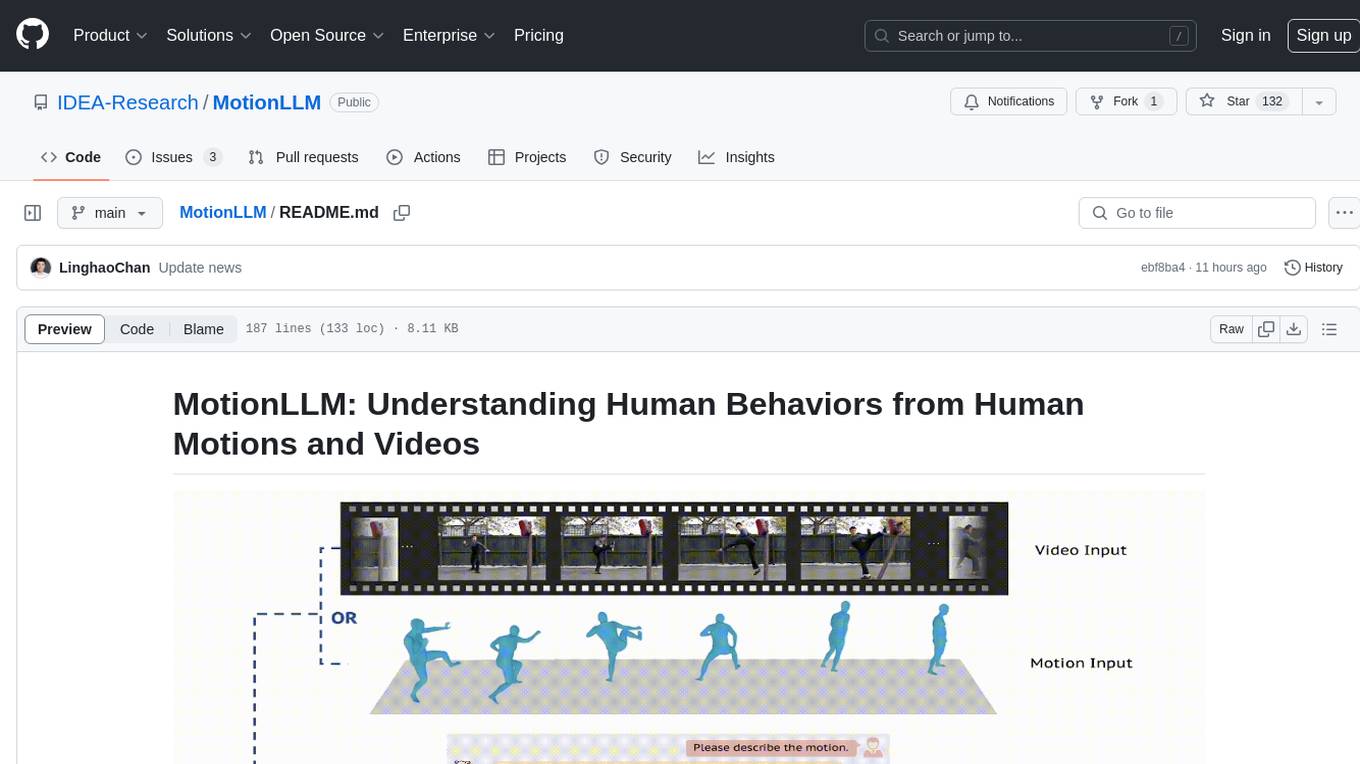
MotionLLM
MotionLLM is a framework for human behavior understanding that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to jointly model videos and motion sequences. It provides a unified training strategy, dataset MoVid, and MoVid-Bench for evaluating human behavior comprehension. The framework excels in captioning, spatial-temporal comprehension, and reasoning abilities.
LLMGA
LLMGA (Multimodal Large Language Model-based Generation Assistant) is a tool that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to assist users in image generation and editing. It provides detailed language generation prompts for precise control over Stable Diffusion (SD), resulting in more intricate and precise content in generated images. The tool curates a dataset for prompt refinement, similar image generation, inpainting & outpainting, and visual question answering. It offers a two-stage training scheme to optimize SD alignment and a reference-based restoration network to alleviate texture, brightness, and contrast disparities in image editing. LLMGA shows promising generative capabilities and enables wider applications in an interactive manner.
LLMs
LLMs is a Chinese large language model technology stack for practical use. It includes high-availability pre-training, SFT, and DPO preference alignment code framework. The repository covers pre-training data cleaning, high-concurrency framework, SFT dataset cleaning, data quality improvement, and security alignment work for Chinese large language models. It also provides open-source SFT dataset construction, pre-training from scratch, and various tools and frameworks for data cleaning, quality optimization, and task alignment.
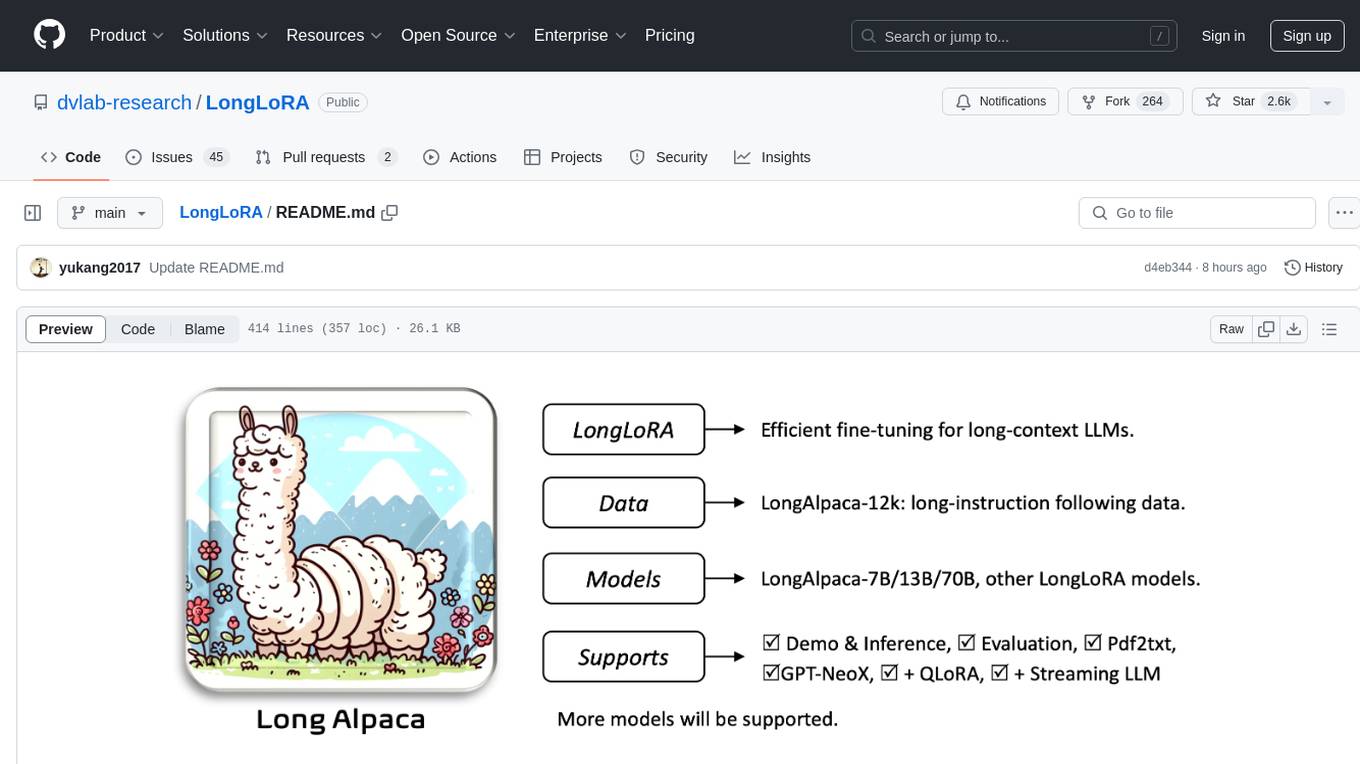
LongLoRA
LongLoRA is a tool for efficient fine-tuning of long-context large language models. It includes LongAlpaca data with long QA data collected and short QA sampled, models from 7B to 70B with context length from 8k to 100k, and support for GPTNeoX models. The tool supports supervised fine-tuning, context extension, and improved LoRA fine-tuning. It provides pre-trained weights, fine-tuning instructions, evaluation methods, local and online demos, streaming inference, and data generation via Pdf2text. LongLoRA is licensed under Apache License 2.0, while data and weights are under CC-BY-NC 4.0 License for research use only.
For similar jobs

promptflow
**Prompt flow** is a suite of development tools designed to streamline the end-to-end development cycle of LLM-based AI applications, from ideation, prototyping, testing, evaluation to production deployment and monitoring. It makes prompt engineering much easier and enables you to build LLM apps with production quality.

deepeval
DeepEval is a simple-to-use, open-source LLM evaluation framework specialized for unit testing LLM outputs. It incorporates various metrics such as G-Eval, hallucination, answer relevancy, RAGAS, etc., and runs locally on your machine for evaluation. It provides a wide range of ready-to-use evaluation metrics, allows for creating custom metrics, integrates with any CI/CD environment, and enables benchmarking LLMs on popular benchmarks. DeepEval is designed for evaluating RAG and fine-tuning applications, helping users optimize hyperparameters, prevent prompt drifting, and transition from OpenAI to hosting their own Llama2 with confidence.

MegaDetector
MegaDetector is an AI model that identifies animals, people, and vehicles in camera trap images (which also makes it useful for eliminating blank images). This model is trained on several million images from a variety of ecosystems. MegaDetector is just one of many tools that aims to make conservation biologists more efficient with AI. If you want to learn about other ways to use AI to accelerate camera trap workflows, check out our of the field, affectionately titled "Everything I know about machine learning and camera traps".

leapfrogai
LeapfrogAI is a self-hosted AI platform designed to be deployed in air-gapped resource-constrained environments. It brings sophisticated AI solutions to these environments by hosting all the necessary components of an AI stack, including vector databases, model backends, API, and UI. LeapfrogAI's API closely matches that of OpenAI, allowing tools built for OpenAI/ChatGPT to function seamlessly with a LeapfrogAI backend. It provides several backends for various use cases, including llama-cpp-python, whisper, text-embeddings, and vllm. LeapfrogAI leverages Chainguard's apko to harden base python images, ensuring the latest supported Python versions are used by the other components of the stack. The LeapfrogAI SDK provides a standard set of protobuffs and python utilities for implementing backends and gRPC. LeapfrogAI offers UI options for common use-cases like chat, summarization, and transcription. It can be deployed and run locally via UDS and Kubernetes, built out using Zarf packages. LeapfrogAI is supported by a community of users and contributors, including Defense Unicorns, Beast Code, Chainguard, Exovera, Hypergiant, Pulze, SOSi, United States Navy, United States Air Force, and United States Space Force.

llava-docker
This Docker image for LLaVA (Large Language and Vision Assistant) provides a convenient way to run LLaVA locally or on RunPod. LLaVA is a powerful AI tool that combines natural language processing and computer vision capabilities. With this Docker image, you can easily access LLaVA's functionalities for various tasks, including image captioning, visual question answering, text summarization, and more. The image comes pre-installed with LLaVA v1.2.0, Torch 2.1.2, xformers 0.0.23.post1, and other necessary dependencies. You can customize the model used by setting the MODEL environment variable. The image also includes a Jupyter Lab environment for interactive development and exploration. Overall, this Docker image offers a comprehensive and user-friendly platform for leveraging LLaVA's capabilities.

carrot
The 'carrot' repository on GitHub provides a list of free and user-friendly ChatGPT mirror sites for easy access. The repository includes sponsored sites offering various GPT models and services. Users can find and share sites, report errors, and access stable and recommended sites for ChatGPT usage. The repository also includes a detailed list of ChatGPT sites, their features, and accessibility options, making it a valuable resource for ChatGPT users seeking free and unlimited GPT services.

TrustLLM
TrustLLM is a comprehensive study of trustworthiness in LLMs, including principles for different dimensions of trustworthiness, established benchmark, evaluation, and analysis of trustworthiness for mainstream LLMs, and discussion of open challenges and future directions. Specifically, we first propose a set of principles for trustworthy LLMs that span eight different dimensions. Based on these principles, we further establish a benchmark across six dimensions including truthfulness, safety, fairness, robustness, privacy, and machine ethics. We then present a study evaluating 16 mainstream LLMs in TrustLLM, consisting of over 30 datasets. The document explains how to use the trustllm python package to help you assess the performance of your LLM in trustworthiness more quickly. For more details about TrustLLM, please refer to project website.

AI-YinMei
AI-YinMei is an AI virtual anchor Vtuber development tool (N card version). It supports fastgpt knowledge base chat dialogue, a complete set of solutions for LLM large language models: [fastgpt] + [one-api] + [Xinference], supports docking bilibili live broadcast barrage reply and entering live broadcast welcome speech, supports Microsoft edge-tts speech synthesis, supports Bert-VITS2 speech synthesis, supports GPT-SoVITS speech synthesis, supports expression control Vtuber Studio, supports painting stable-diffusion-webui output OBS live broadcast room, supports painting picture pornography public-NSFW-y-distinguish, supports search and image search service duckduckgo (requires magic Internet access), supports image search service Baidu image search (no magic Internet access), supports AI reply chat box [html plug-in], supports AI singing Auto-Convert-Music, supports playlist [html plug-in], supports dancing function, supports expression video playback, supports head touching action, supports gift smashing action, supports singing automatic start dancing function, chat and singing automatic cycle swing action, supports multi scene switching, background music switching, day and night automatic switching scene, supports open singing and painting, let AI automatically judge the content.



