
EVE
EVE: Encoder-Free Vision-Language Models from BAAI
Stars: 155
EVE is an official PyTorch implementation of Unveiling Encoder-Free Vision-Language Models. The project aims to explore the removal of vision encoders from Vision-Language Models (VLMs) and transfer LLMs to encoder-free VLMs efficiently. It also focuses on bridging the performance gap between encoder-free and encoder-based VLMs. EVE offers a superior capability with arbitrary image aspect ratio, data efficiency by utilizing publicly available data for pre-training, and training efficiency with a transparent and practical strategy for developing a pure decoder-only architecture across modalities.
README:
Official pytorch implementation of Unveiling Encoder-Free Vision-Language Models.
[2024/07/01] We release training code and EVE-7B weights ! 🚀
[2024/06/23] We release evaluation code, EVE-7B-Pretrain, and EVE-7B-HD weights ! 🚀
[2024/06/18] The paper is released ! 💥
-
Can we remove vision encoder from VLMs?
-
How to transfer an LLM to an encoder-free VLM efficiently and stably?
-
How to bridge the performance gap between encoder-free and encoder-based VLMs?
-
Authors: Haiwen Diao*, Yufeng Cui*, Xiaotong Li, Yueze Wang, Huchuan Lu📧, Xinlong Wang📧
-
Institutes: Dalian University of Technology; Beijing Academy of Artificial Intelligence; Peking University
-
Model Zoo: [🤗EVE-7B-Pretrain] [🤗EVE-7B] [🤗EVE-7B-HD]
-
🔥 Superior Capability: An originated encoder-free LVLM with arbitrary image aspect ratio, outperforming the counterpart Fuyu-8B and approaching existing modular encoder-based LVLMs.
-
🔥 Data Efficiency: Filter solely 33M publicly avaliable data from OpenImages, SAM, LAION for pre-training; Utilizing 665K LLaVA SFT data for EVE-7B, and extra 1.2M SFT data for EVE-7B (HD).
-
🔥 Training Efficiency: Trained with two 8-A100 (40G) nodes in ~9 days or four 8-A100 nodes in ~5 days
-
🔥 Pioneering Route: We attempt to provide an efficient, transparent, and practical training strategy and procedure for developing a pure decoder-only architecture across modalities.
The usage of EVE checkpoints should comply with the base LLM's model license: Llama 2.
| Model | LLM | Weight | VQAv2 | GQA | VizWiz | SQA_I | TextVQA | POPE | MME_P | MMBench | SEED/SEED_I | MM_Vet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EVE_7B_Pretrain | Vicuna_7B | HF_link | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- / -- | -- |
| EVE_7B | Vicuna_7B | HF_link | 75.4 | 60.8 | 41.8 | 63.0 | 51.9 | 83.6 | 1217.3 | 49.5 | 54.3 / 61.3 | 25.6 |
| EVE_7B_HD | Vicuna-7B | HF_link | 78.6 | 62.6 | 51.1 | 64.9 | 56.8 | 85.0 | 1305.7 | 52.3 | 56.8 / 64.6 | 25.7 |
- [ ] Involve more modalities into the unified EVE network.
- [ ] Full EVE series trained with more data, varied sizes, and better base models.
git clone https://github.com/baaivision/EVE.git
cd EVE
conda create -n eve_envs python=3.10 -y
conda activate eve_envs
pip install --upgrade pip
pip install -e .
pip install -e ".[train]"
pip install flash-attn --no-build-isolationDownload vicuna_model and extract them into lmsys/ path:
Download preprocessor and extract them into openai/ path:
lmsys
├── vicuna-7b-v1.5
│ │── config.json
│ │── ...
openai
├── clip-vit-large-patch14-336
│ │── config.json
│ │── ...
├── eve-patch14-anypixel-672
│ │── preprocessor_config.json
│ │── ...
├── eve-patch14-anypixel-1344
│ │── preprocessor_config.json
│ │── ...
from eve.model.builder import load_pretrained_model
from eve.mm_utils import get_model_name_from_path
from eve.eval.run_eve import eval_model
model_path = "Absolute Path of BAAI/EVE-7B-HD-v1.0"
tokenizer, model, image_processor, context_len = load_pretrained_model(
model_path=model_path,
model_base=None,
model_name=get_model_name_from_path(model_path)
)Check out the details wth the load_pretrained_model function in eve/model/builder.py.
You can also use eve/eval/eval_one_sample.py to get the output easily. By doing so, you can use this code on Colab directly after downloading this repository.
# run script
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 python eve/eval/eval_one_sample.pyYou can also build up your local demo using the following script:
# run script
python tools/app.pyYou should follow this instruction Data.md to manage the datasets. Currently, we provide direct download access to the web data. However, to avoid potential disputes, we plan to release URLs for these datasets rather than the raw data in the near future.
(1) LLM-guided Pre-aligning Stage: we only adopt 16M of 33M image-text data (EVE-cap16/33M) to train patch embedding and aligning layers. It really does count for efficient training, as it prevents collapse and accelerates convergence throughout the entire process.
| Model | Epoch | Batch_Size | Learning_Rate | LR_Schedule | Warmup_Ratio | Max_Length | Weight_decay | Optimizer | DeepSpeed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EVE_Prealign | 1 | 512 | 4e-4 | cosine decay | 0.03 | 2048 | 0 | AdamW | zero3 |
Training script for EVE_Prealign as follows:
bash scripts/eve/eve7b_prealign.sh ${node_rank} ${master_addr}(2) Generative Pre-training Stage: we use all 33M image-text pairs (EVE-cap33M) to train patch embedding and aligning layers, and the full LLM modules.
| Model | Epoch | Batch_Size | Learning_Rate | LR_Schedule | Warmup_Ratio | Max_Length | Weight_decay | Optimizer | DeepSpeed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EVE_Pretrain | 1 | 512 | 4e-5 | cosine decay | 0.01 | 2048 | 0 | AdamW | zero3 |
Training script for EVE_Pretrain as follows:
bash scripts/eve/eve7b_pretrain.sh ${node_rank} ${master_addr}(3) Supervised Fine-tuning Stage: We finetune the entire architecture with LLaVA-mix-665K for EVE-7B and extra 1.2M SFT conversation data for EVE-7B (HD).
| Model | Epoch | Batch_Size | Learning_Rate | LR_Schedule | Warmup_Ratio | Max_Length | Weight_decay | Optimizer | DeepSpeed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EVE_Finetune | 1 | 128 | 2e-5 | cosine decay | 0.01 | 2048/4096 | 0 | AdamW | zero3 |
Training scripts for EVE_7B and EVE_7B_HD as follows:
bash scripts/eve/eve7b_finetune.sh ${node_rank} ${master_addr}
bash scripts/eve/eve7b_finetune_hd.sh ${node_rank} ${master_addr}[NOTE]:
To train on fewer GPUs, you can reduce the per_device_train_batch_size and increase the gradient_accumulation_steps accordingly. Always keep the global batch size the same: per_device_train_batch_size x gradient_accumulation_steps x num_gpus.
To ensure the reproducibility, we evaluate the models with greedy decoding. We do not evaluate using beam search to make the inference process consistent with the chat demo of real-time outputs.
See Evaluation.md.
- LLaVA, ShareGPT: Thanks for their wonderful works and code!
- Vicuna: The amazing open-sourced large language model series!
If EVE is helpful for your research, please consider star ⭐ and citation 📝 :
@article{diao2024EVE,
title={Unveiling Encoder-Free Vision-Language Models},
author={Diao, Haiwen and Cui, Yufeng and Li, Xiaotong and Wang, Yueze and Lu, Huchuan and Wang, Xinlong},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.11832},
year={2024}
}The content of this project itself is licensed under LICENSE.
For Tasks:
Click tags to check more tools for each tasksFor Jobs:
Alternative AI tools for EVE
Similar Open Source Tools

EVE
EVE is an official PyTorch implementation of Unveiling Encoder-Free Vision-Language Models. The project aims to explore the removal of vision encoders from Vision-Language Models (VLMs) and transfer LLMs to encoder-free VLMs efficiently. It also focuses on bridging the performance gap between encoder-free and encoder-based VLMs. EVE offers a superior capability with arbitrary image aspect ratio, data efficiency by utilizing publicly available data for pre-training, and training efficiency with a transparent and practical strategy for developing a pure decoder-only architecture across modalities.

EasyEdit
EasyEdit is a Python package for edit Large Language Models (LLM) like `GPT-J`, `Llama`, `GPT-NEO`, `GPT2`, `T5`(support models from **1B** to **65B**), the objective of which is to alter the behavior of LLMs efficiently within a specific domain without negatively impacting performance across other inputs. It is designed to be easy to use and easy to extend.
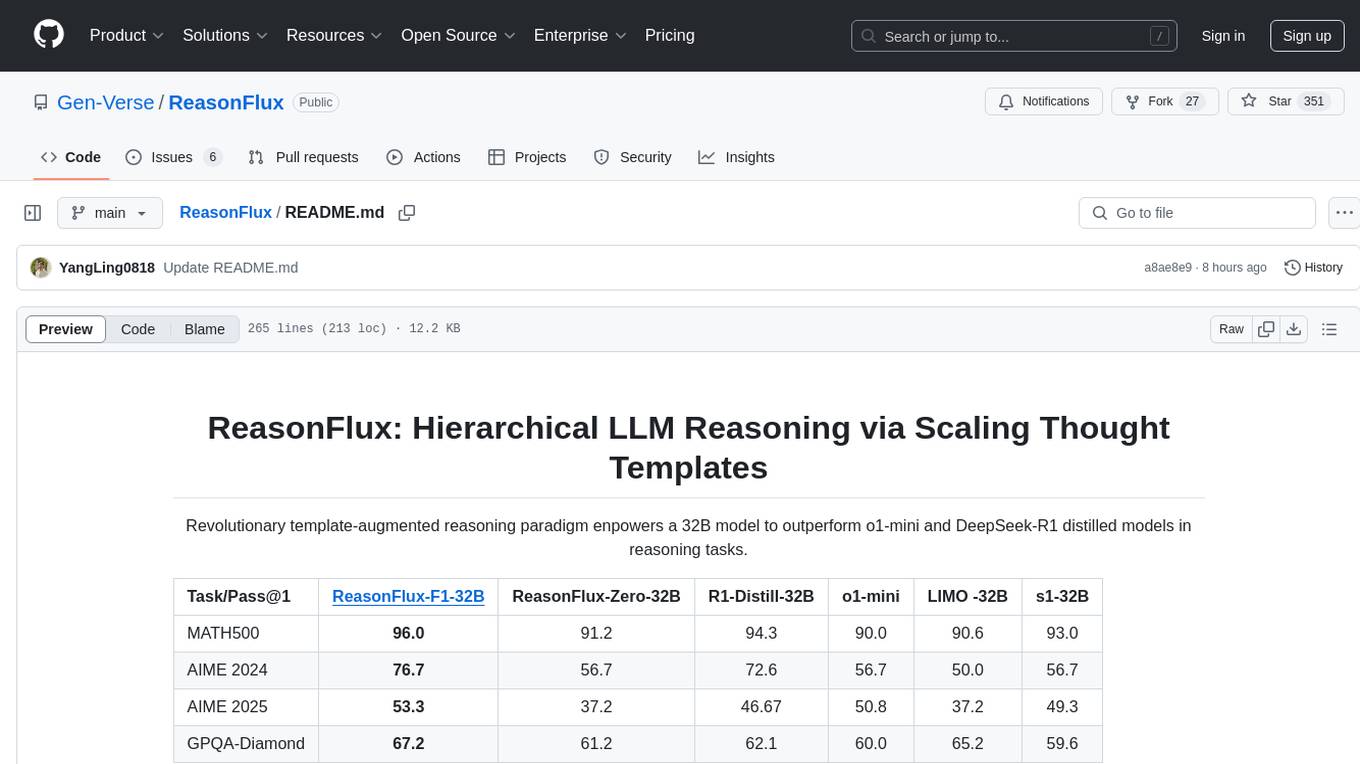
ReasonFlux
ReasonFlux is a revolutionary template-augmented reasoning paradigm that empowers a 32B model to outperform other models in reasoning tasks. The repository provides official resources for the paper 'ReasonFlux: Hierarchical LLM Reasoning via Scaling Thought Templates', including the latest released model ReasonFlux-F1-32B. It includes updates, dataset links, model zoo, getting started guide, training instructions, evaluation details, inference examples, performance comparisons, reasoning examples, preliminary work references, and citation information.
MooER
MooER (摩耳) is an LLM-based speech recognition and translation model developed by Moore Threads. It allows users to transcribe speech into text (ASR) and translate speech into other languages (AST) in an end-to-end manner. The model was trained using 5K hours of data and is now also available with an 80K hours version. MooER is the first LLM-based speech model trained and inferred using domestic GPUs. The repository includes pretrained models, inference code, and a Gradio demo for a better user experience.
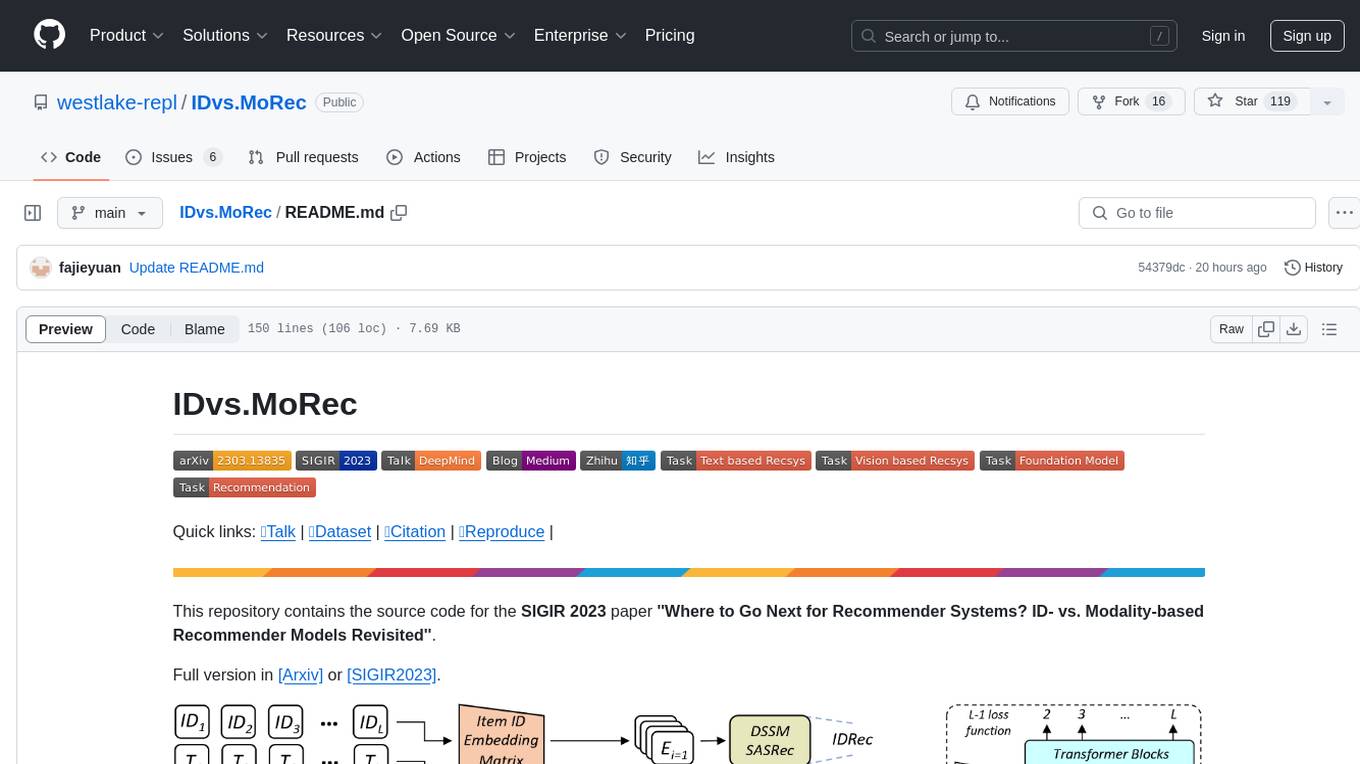
IDvs.MoRec
This repository contains the source code for the SIGIR 2023 paper 'Where to Go Next for Recommender Systems? ID- vs. Modality-based Recommender Models Revisited'. It provides resources for evaluating foundation, transferable, multi-modal, and LLM recommendation models, along with datasets, pre-trained models, and training strategies for IDRec and MoRec using in-batch debiased cross-entropy loss. The repository also offers large-scale datasets, code for SASRec with in-batch debias cross-entropy loss, and information on joining the lab for research opportunities.
DeepRetrieval
DeepRetrieval is a tool designed to enhance search engines and retrievers using Large Language Models (LLMs) and Reinforcement Learning (RL). It allows LLMs to learn how to search effectively by integrating with search engine APIs and customizing reward functions. The tool provides functionalities for data preparation, training, evaluation, and monitoring search performance. DeepRetrieval aims to improve information retrieval tasks by leveraging advanced AI techniques.
qserve
QServe is a serving system designed for efficient and accurate Large Language Models (LLM) on GPUs with W4A8KV4 quantization. It achieves higher throughput compared to leading industry solutions, allowing users to achieve A100-level throughput on cheaper L40S GPUs. The system introduces the QoQ quantization algorithm with 4-bit weight, 8-bit activation, and 4-bit KV cache, addressing runtime overhead challenges. QServe improves serving throughput for various LLM models by implementing compute-aware weight reordering, register-level parallelism, and fused attention memory-bound techniques.
YuLan-Mini
YuLan-Mini is a lightweight language model with 2.4 billion parameters that achieves performance comparable to industry-leading models despite being pre-trained on only 1.08T tokens. It excels in mathematics and code domains. The repository provides pre-training resources, including data pipeline, optimization methods, and annealing approaches. Users can pre-train their own language models, perform learning rate annealing, fine-tune the model, research training dynamics, and synthesize data. The team behind YuLan-Mini is AI Box at Renmin University of China. The code is released under the MIT License with future updates on model weights usage policies. Users are advised on potential safety concerns and ethical use of the model.
skpro
skpro is a library for supervised probabilistic prediction in python. It provides `scikit-learn`-like, `scikit-base` compatible interfaces to: * tabular **supervised regressors for probabilistic prediction** \- interval, quantile and distribution predictions * tabular **probabilistic time-to-event and survival prediction** \- instance-individual survival distributions * **metrics to evaluate probabilistic predictions** , e.g., pinball loss, empirical coverage, CRPS, survival losses * **reductions** to turn `scikit-learn` regressors into probabilistic `skpro` regressors, such as bootstrap or conformal * building **pipelines and composite models** , including tuning via probabilistic performance metrics * symbolic **probability distributions** with value domain of `pandas.DataFrame`-s and `pandas`-like interface

Athena-Public
Project Athena is a Linux OS designed for AI Agents, providing memory, persistence, scheduling, and governance for AI models. It offers a comprehensive memory layer that survives across sessions, models, and IDEs, allowing users to own their data and port it anywhere. The system is built bottom-up through 1,079+ sessions, focusing on depth and compounding knowledge. Athena features a trilateral feedback loop for cross-model validation, a Model Context Protocol server with 9 tools, and a robust security model with data residency options. The repository structure includes an SDK package, examples for quickstart, scripts, protocols, workflows, and deep documentation. Key concepts cover architecture, knowledge graph, semantic memory, and adaptive latency. Workflows include booting, reasoning modes, planning, research, and iteration. The project has seen significant content expansion, viral validation, and metrics improvements.
llumen
Llumen is a self-hosted interface optimized for modest hardware like Raspberry Pi, old laptops, and minimal VPS. It offers privacy without complexity, providing essential features with minimal resource demands. Users can enjoy sub-second cold starts, real-time token streaming, various chat modes, rich media support, and a universal API for OpenAI-compatible providers. The tool has a small footprint with a binary size of around 17MB and RAM usage under 128MB. Llumen aims to simplify the setup process and offer a user-friendly experience for individuals seeking a privacy-focused solution.

StableToolBench
StableToolBench is a new benchmark developed to address the instability of Tool Learning benchmarks. It aims to balance stability and reality by introducing features like Virtual API System, Solvable Queries, and Stable Evaluation System. The benchmark ensures consistency through a caching system and API simulators, filters queries based on solvability using LLMs, and evaluates model performance using GPT-4 with metrics like Solvable Pass Rate and Solvable Win Rate.
sktime
sktime is a Python library for time series analysis that provides a unified interface for various time series learning tasks such as classification, regression, clustering, annotation, and forecasting. It offers time series algorithms and tools compatible with scikit-learn for building, tuning, and validating time series models. sktime aims to enhance the interoperability and usability of the time series analysis ecosystem by empowering users to apply algorithms across different tasks and providing interfaces to related libraries like scikit-learn, statsmodels, tsfresh, PyOD, and fbprophet.
learn-claude-code
Learn Claude Code is an educational project by shareAI Lab that aims to help users understand how modern AI agents work by building one from scratch. The repository provides original educational material on various topics such as the agent loop, tool design, explicit planning, context management, knowledge injection, task systems, parallel execution, team messaging, and autonomous teams. Users can follow a learning path through different versions of the project, each introducing new concepts and mechanisms. The repository also includes technical tutorials, articles, and example skills for users to explore and learn from. The project emphasizes the philosophy that the model is crucial in agent development, with code playing a supporting role.
Q-Bench
Q-Bench is a benchmark for general-purpose foundation models on low-level vision, focusing on multi-modality LLMs performance. It includes three realms for low-level vision: perception, description, and assessment. The benchmark datasets LLVisionQA and LLDescribe are collected for perception and description tasks, with open submission-based evaluation. An abstract evaluation code is provided for assessment using public datasets. The tool can be used with the datasets API for single images and image pairs, allowing for automatic download and usage. Various tasks and evaluations are available for testing MLLMs on low-level vision tasks.
KwaiAgents
KwaiAgents is a series of Agent-related works open-sourced by the [KwaiKEG](https://github.com/KwaiKEG) from [Kuaishou Technology](https://www.kuaishou.com/en). The open-sourced content includes: 1. **KAgentSys-Lite**: a lite version of the KAgentSys in the paper. While retaining some of the original system's functionality, KAgentSys-Lite has certain differences and limitations when compared to its full-featured counterpart, such as: (1) a more limited set of tools; (2) a lack of memory mechanisms; (3) slightly reduced performance capabilities; and (4) a different codebase, as it evolves from open-source projects like BabyAGI and Auto-GPT. Despite these modifications, KAgentSys-Lite still delivers comparable performance among numerous open-source Agent systems available. 2. **KAgentLMs**: a series of large language models with agent capabilities such as planning, reflection, and tool-use, acquired through the Meta-agent tuning proposed in the paper. 3. **KAgentInstruct**: over 200k Agent-related instructions finetuning data (partially human-edited) proposed in the paper. 4. **KAgentBench**: over 3,000 human-edited, automated evaluation data for testing Agent capabilities, with evaluation dimensions including planning, tool-use, reflection, concluding, and profiling.
For similar tasks
lighteval
LightEval is a lightweight LLM evaluation suite that Hugging Face has been using internally with the recently released LLM data processing library datatrove and LLM training library nanotron. We're releasing it with the community in the spirit of building in the open. Note that it is still very much early so don't expect 100% stability ^^' In case of problems or question, feel free to open an issue!
Firefly
Firefly is an open-source large model training project that supports pre-training, fine-tuning, and DPO of mainstream large models. It includes models like Llama3, Gemma, Qwen1.5, MiniCPM, Llama, InternLM, Baichuan, ChatGLM, Yi, Deepseek, Qwen, Orion, Ziya, Xverse, Mistral, Mixtral-8x7B, Zephyr, Vicuna, Bloom, etc. The project supports full-parameter training, LoRA, QLoRA efficient training, and various tasks such as pre-training, SFT, and DPO. Suitable for users with limited training resources, QLoRA is recommended for fine-tuning instructions. The project has achieved good results on the Open LLM Leaderboard with QLoRA training process validation. The latest version has significant updates and adaptations for different chat model templates.
Awesome-Text2SQL
Awesome Text2SQL is a curated repository containing tutorials and resources for Large Language Models, Text2SQL, Text2DSL, Text2API, Text2Vis, and more. It provides guidelines on converting natural language questions into structured SQL queries, with a focus on NL2SQL. The repository includes information on various models, datasets, evaluation metrics, fine-tuning methods, libraries, and practice projects related to Text2SQL. It serves as a comprehensive resource for individuals interested in working with Text2SQL and related technologies.
create-million-parameter-llm-from-scratch
The 'create-million-parameter-llm-from-scratch' repository provides a detailed guide on creating a Large Language Model (LLM) with 2.3 million parameters from scratch. The blog replicates the LLaMA approach, incorporating concepts like RMSNorm for pre-normalization, SwiGLU activation function, and Rotary Embeddings. The model is trained on a basic dataset to demonstrate the ease of creating a million-parameter LLM without the need for a high-end GPU.
StableToolBench
StableToolBench is a new benchmark developed to address the instability of Tool Learning benchmarks. It aims to balance stability and reality by introducing features such as a Virtual API System with caching and API simulators, a new set of solvable queries determined by LLMs, and a Stable Evaluation System using GPT-4. The Virtual API Server can be set up either by building from source or using a prebuilt Docker image. Users can test the server using provided scripts and evaluate models with Solvable Pass Rate and Solvable Win Rate metrics. The tool also includes model experiments results comparing different models' performance.
BetaML.jl
The Beta Machine Learning Toolkit is a package containing various algorithms and utilities for implementing machine learning workflows in multiple languages, including Julia, Python, and R. It offers a range of supervised and unsupervised models, data transformers, and assessment tools. The models are implemented entirely in Julia and are not wrappers for third-party models. Users can easily contribute new models or request implementations. The focus is on user-friendliness rather than computational efficiency, making it suitable for educational and research purposes.
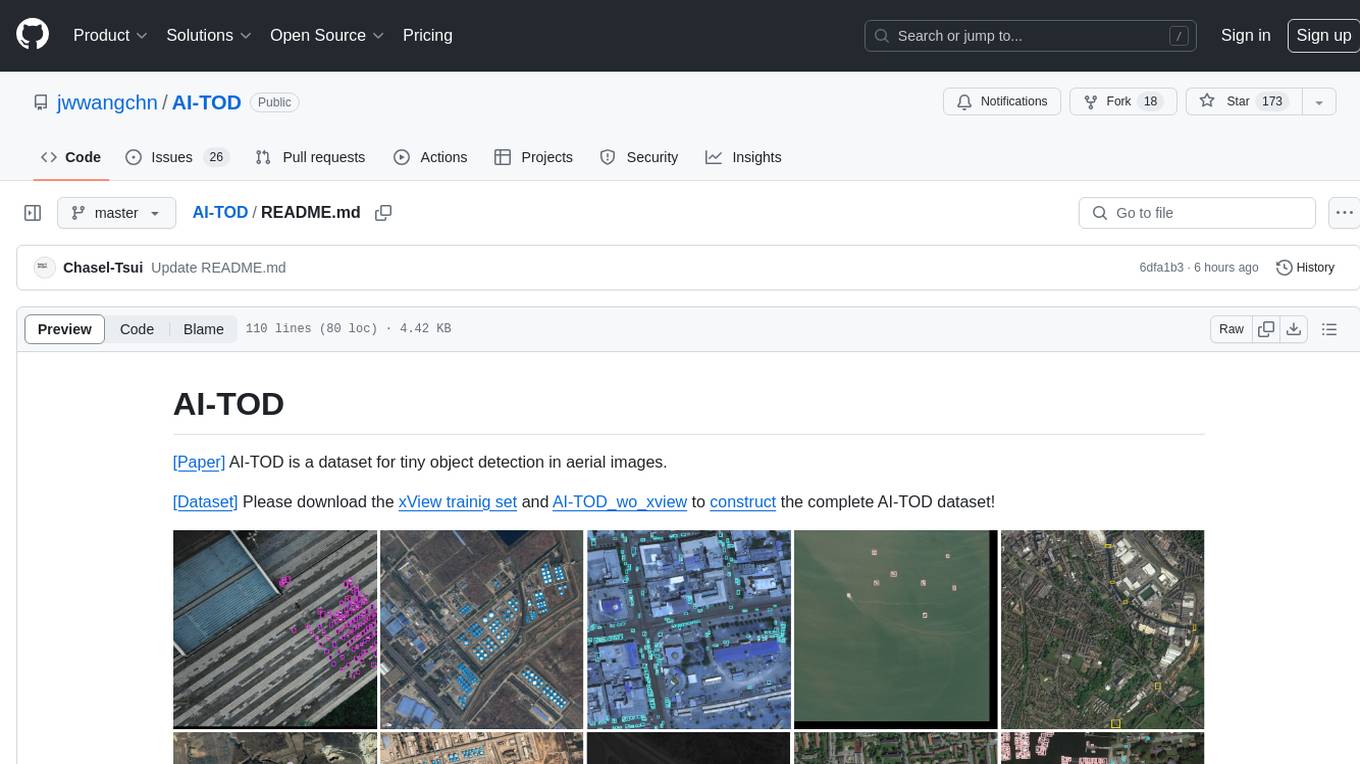
AI-TOD
AI-TOD is a dataset for tiny object detection in aerial images, containing 700,621 object instances across 28,036 images. Objects in AI-TOD are smaller with a mean size of 12.8 pixels compared to other aerial image datasets. To use AI-TOD, download xView training set and AI-TOD_wo_xview, then generate the complete dataset using the provided synthesis tool. The dataset is publicly available for academic and research purposes under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license.
UMOE-Scaling-Unified-Multimodal-LLMs
Uni-MoE is a MoE-based unified multimodal model that can handle diverse modalities including audio, speech, image, text, and video. The project focuses on scaling Unified Multimodal LLMs with a Mixture of Experts framework. It offers enhanced functionality for training across multiple nodes and GPUs, as well as parallel processing at both the expert and modality levels. The model architecture involves three training stages: building connectors for multimodal understanding, developing modality-specific experts, and incorporating multiple trained experts into LLMs using the LoRA technique on mixed multimodal data. The tool provides instructions for installation, weights organization, inference, training, and evaluation on various datasets.
For similar jobs

sweep
Sweep is an AI junior developer that turns bugs and feature requests into code changes. It automatically handles developer experience improvements like adding type hints and improving test coverage.

teams-ai
The Teams AI Library is a software development kit (SDK) that helps developers create bots that can interact with Teams and Microsoft 365 applications. It is built on top of the Bot Framework SDK and simplifies the process of developing bots that interact with Teams' artificial intelligence capabilities. The SDK is available for JavaScript/TypeScript, .NET, and Python.

ai-guide
This guide is dedicated to Large Language Models (LLMs) that you can run on your home computer. It assumes your PC is a lower-end, non-gaming setup.

classifai
Supercharge WordPress Content Workflows and Engagement with Artificial Intelligence. Tap into leading cloud-based services like OpenAI, Microsoft Azure AI, Google Gemini and IBM Watson to augment your WordPress-powered websites. Publish content faster while improving SEO performance and increasing audience engagement. ClassifAI integrates Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning technologies to lighten your workload and eliminate tedious tasks, giving you more time to create original content that matters.

chatbot-ui
Chatbot UI is an open-source AI chat app that allows users to create and deploy their own AI chatbots. It is easy to use and can be customized to fit any need. Chatbot UI is perfect for businesses, developers, and anyone who wants to create a chatbot.

BricksLLM
BricksLLM is a cloud native AI gateway written in Go. Currently, it provides native support for OpenAI, Anthropic, Azure OpenAI and vLLM. BricksLLM aims to provide enterprise level infrastructure that can power any LLM production use cases. Here are some use cases for BricksLLM: * Set LLM usage limits for users on different pricing tiers * Track LLM usage on a per user and per organization basis * Block or redact requests containing PIIs * Improve LLM reliability with failovers, retries and caching * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for internal development/production use cases * Distribute API keys with rate limits and cost limits for students

uAgents
uAgents is a Python library developed by Fetch.ai that allows for the creation of autonomous AI agents. These agents can perform various tasks on a schedule or take action on various events. uAgents are easy to create and manage, and they are connected to a fast-growing network of other uAgents. They are also secure, with cryptographically secured messages and wallets.

griptape
Griptape is a modular Python framework for building AI-powered applications that securely connect to your enterprise data and APIs. It offers developers the ability to maintain control and flexibility at every step. Griptape's core components include Structures (Agents, Pipelines, and Workflows), Tasks, Tools, Memory (Conversation Memory, Task Memory, and Meta Memory), Drivers (Prompt and Embedding Drivers, Vector Store Drivers, Image Generation Drivers, Image Query Drivers, SQL Drivers, Web Scraper Drivers, and Conversation Memory Drivers), Engines (Query Engines, Extraction Engines, Summary Engines, Image Generation Engines, and Image Query Engines), and additional components (Rulesets, Loaders, Artifacts, Chunkers, and Tokenizers). Griptape enables developers to create AI-powered applications with ease and efficiency.


